Extreme Weather
125班29號賴昱錡
ck1100801@gl.ck.tp.edu.tw
OUTLINE




COP26
Glasgow Climate Pact
Definition & Origin
What is "Extreme Weather"?
How does it form?

definition
Refering to weather phenomena that are at the extremes of the historical distribution and are rare for a particular place and/or time, especially severe or unseasonal weather.

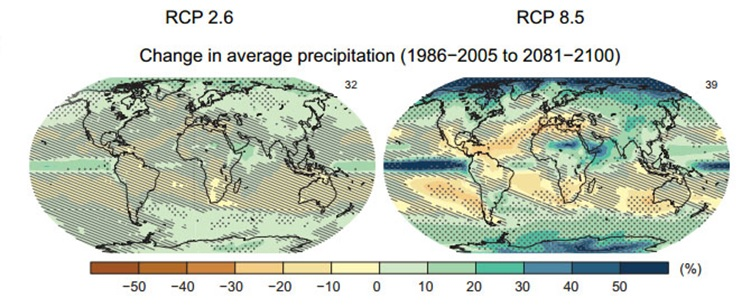
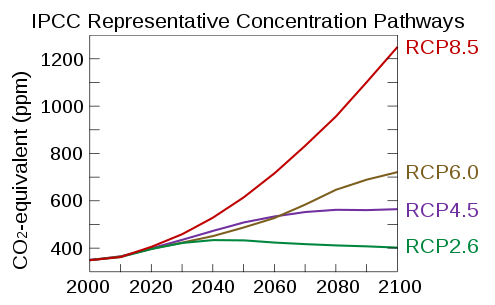
RCP
RCP stands for "Representative Concentration Pathway". It is also known as a greenhouse gas concentration (not emissions) trajectory adopted by the IPCC.
Definition
Simply put, it is the "scenario assumption" of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions for different degrees of warming paths
| RCP | Radiant Force (W/m^2) |
CO2 concentration(ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.6 | 3.0 | 490 |
| 4.5 | 4.5 | 650 |
| 6.0 | 6.0 | 850 |
| 8.5 | 8.5 | 1370 |

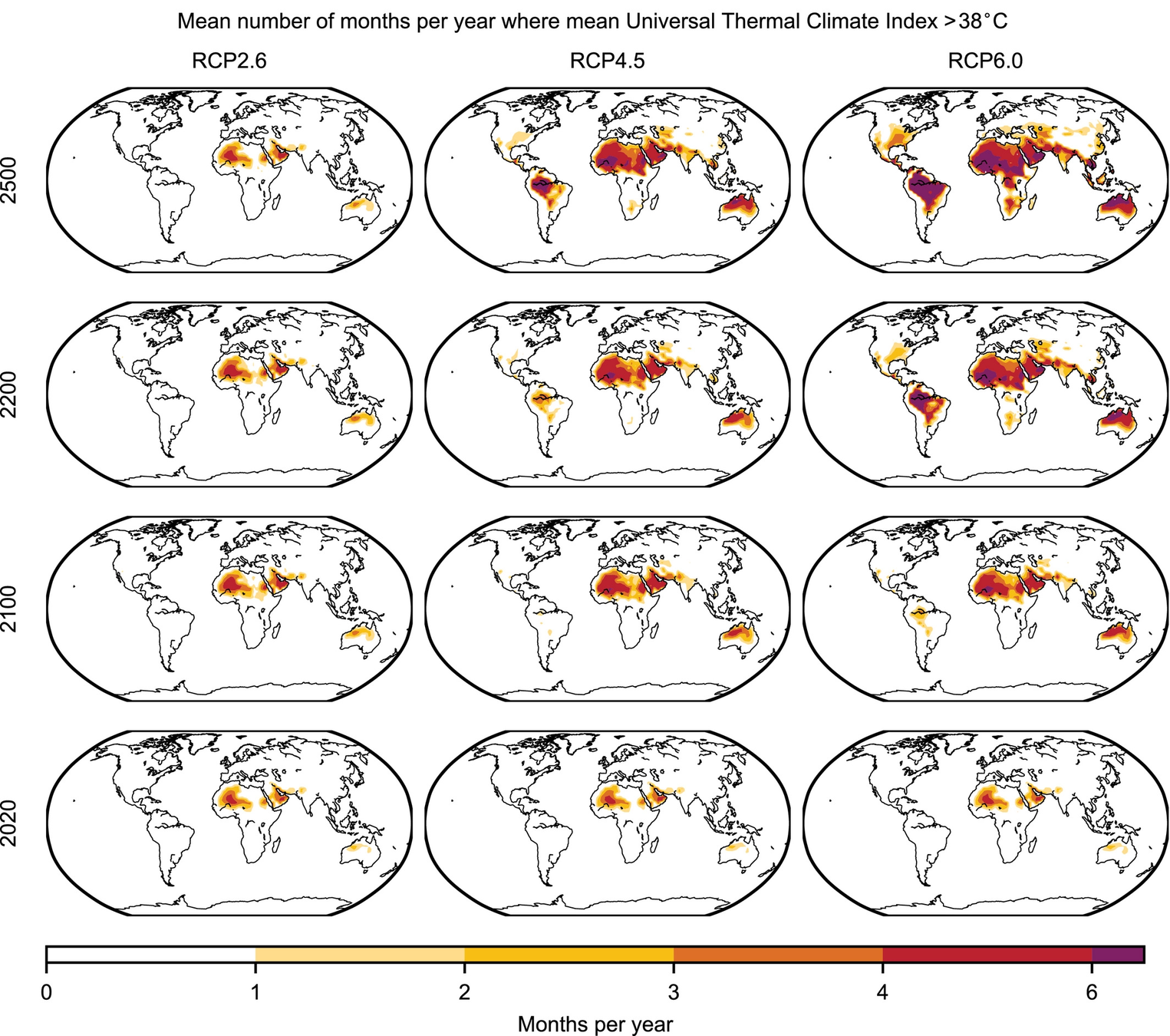
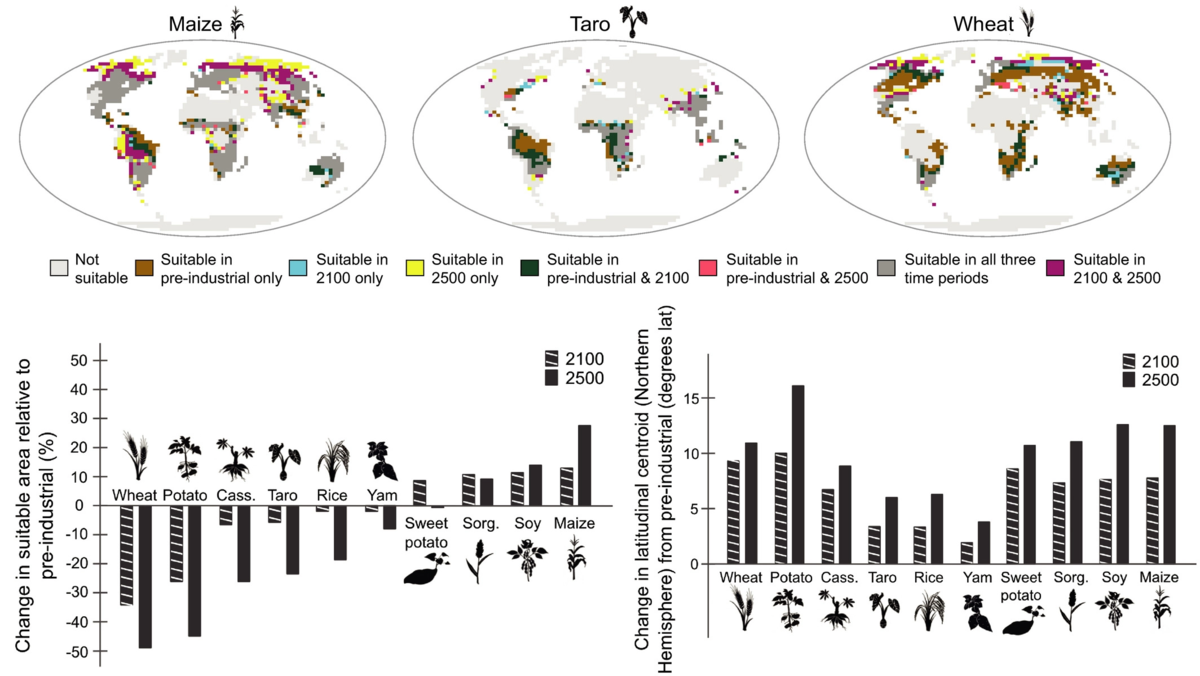
prediction
Projections for crop suitability to 2100 and 2500 under the moderate–high RCP6.0 emission scenario. ->
<- Mean number of months per year where heat stress exceeds 38°C (UTCI scale) in present (2020) and future climates




origin
- Global warming
- Rotten luck
- Changes in ocean currents and air pressure

climate Shift
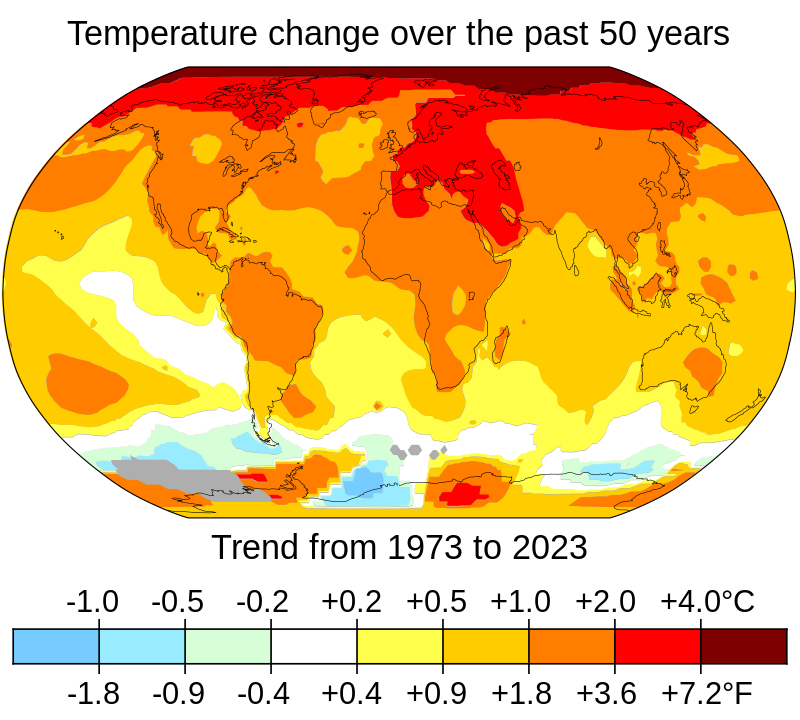
CLIMATE change
Temperature
average
change


Types & introduction
Different extreme weather types
and its effect on environment
- Climate change may affect the type, frequency and intensity of these extreme events.
- In terms of rainfall, seasonal rainfall is uneven, and the difference between wet and dry seasons becomes larger.
- Rainfall polarization(降雨兩極化) is usually more pronounced in areas with distinct wet and dry seasons
How climate change affect the extreme events?
HOT wave

-
More than five consecutive days with a maximum temperature of more than 5°C (9°F) above the average maximum temperature.
-
Related to the result of high pressure in the atmosphere.
-
It can cause heat stroke, heat exhaustion, and febrile convulsion in peopl
HOT wave

- Global warming increases the chance of heat wave.
- Heat Island Effect
- Geographical factors such as Foehn wind in Pingtung, Taiwan.
- Heat Dome Effect.



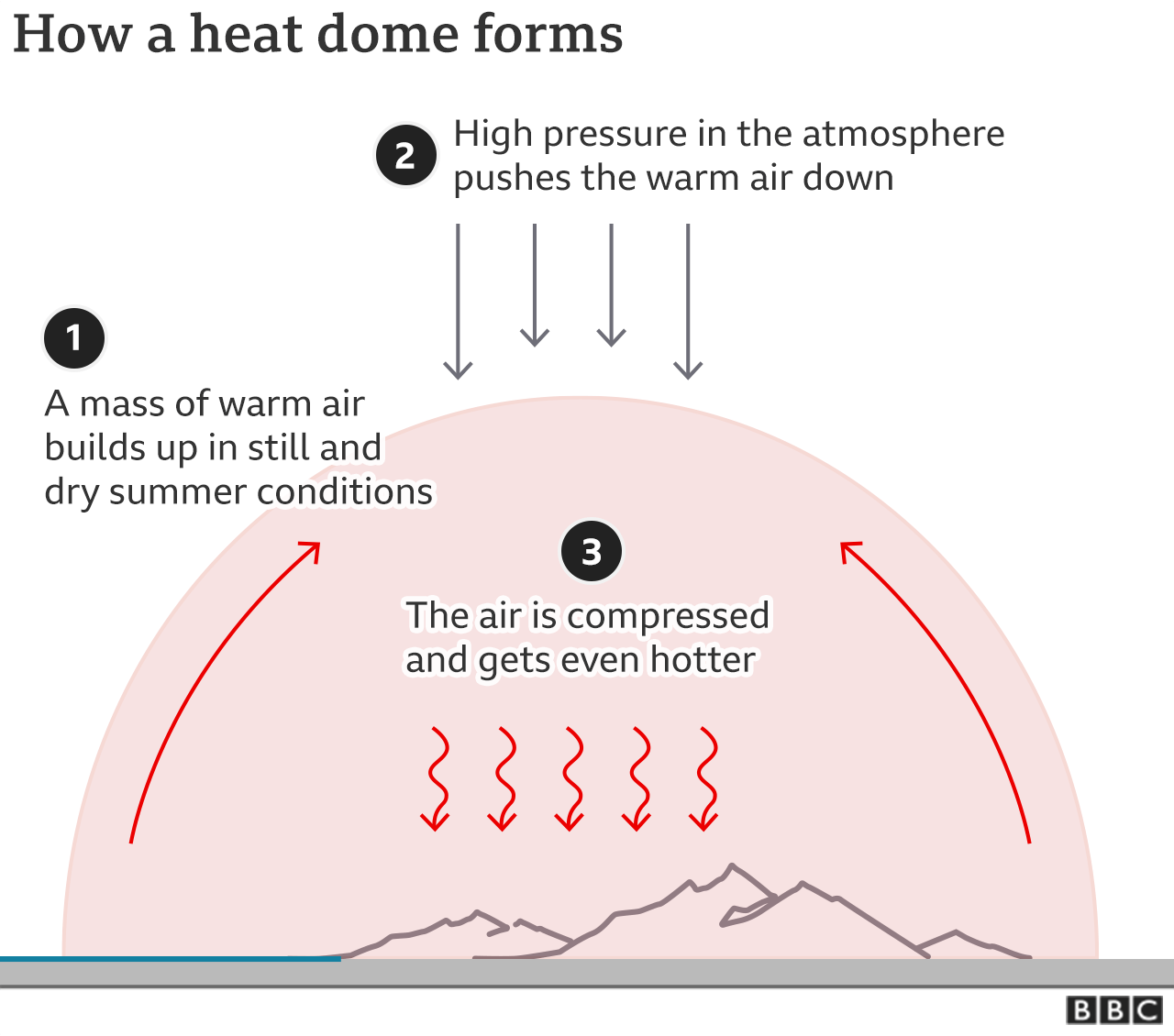
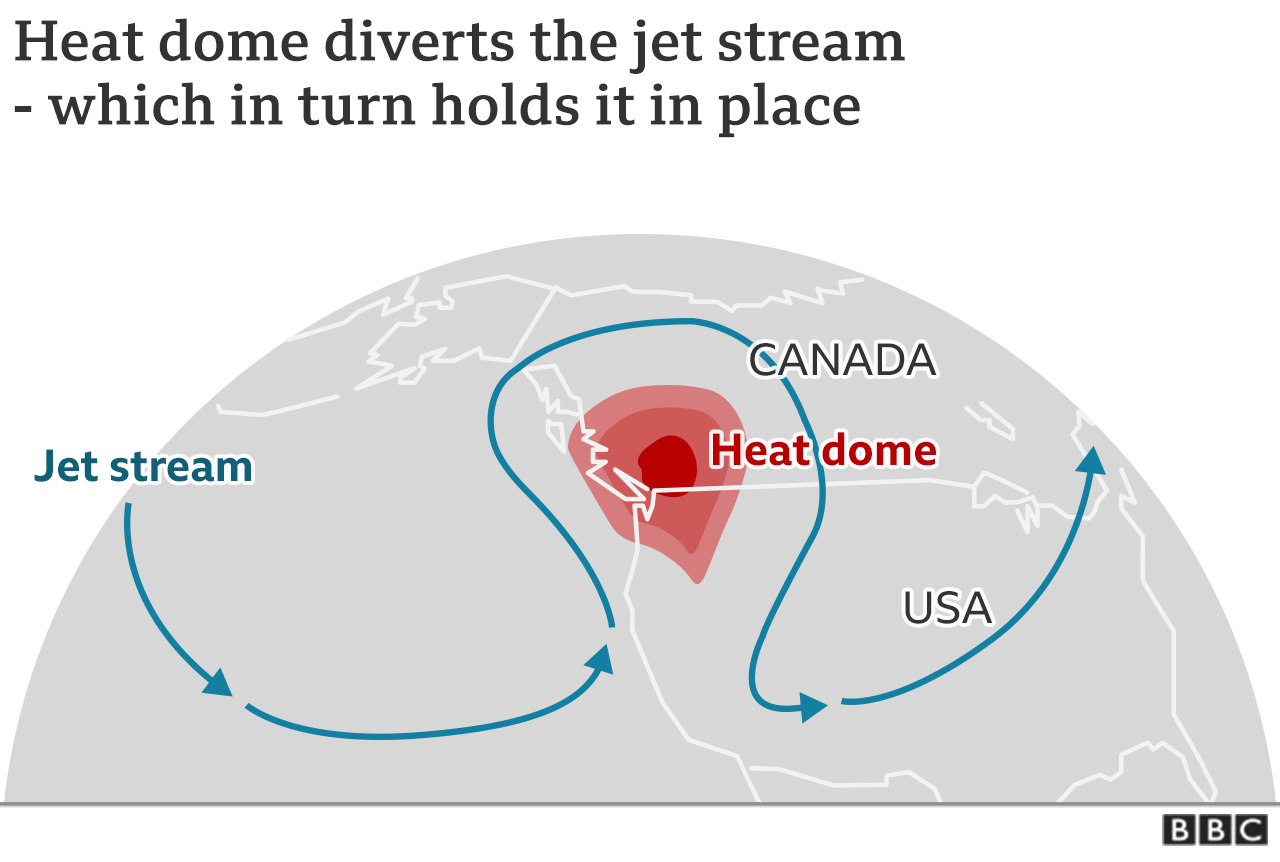
-
Heatwaves in some areas last so long because blocking high air pressure blocks fast airflow in the upper atmosphere, which can't get into the hot cap and cold air.
HEAT dome effect
-
Generally speaking, a cold current refers to a high pressure generated at high latitudes, a cold high pressure invading low latitudes, and finally going to sea to degenerate cold air
-
During a cold snap, the cold air causes a sudden drop in local temperature, a sudden increase in ground pressure, and sometimes strong winds and large waves.
COLD wave


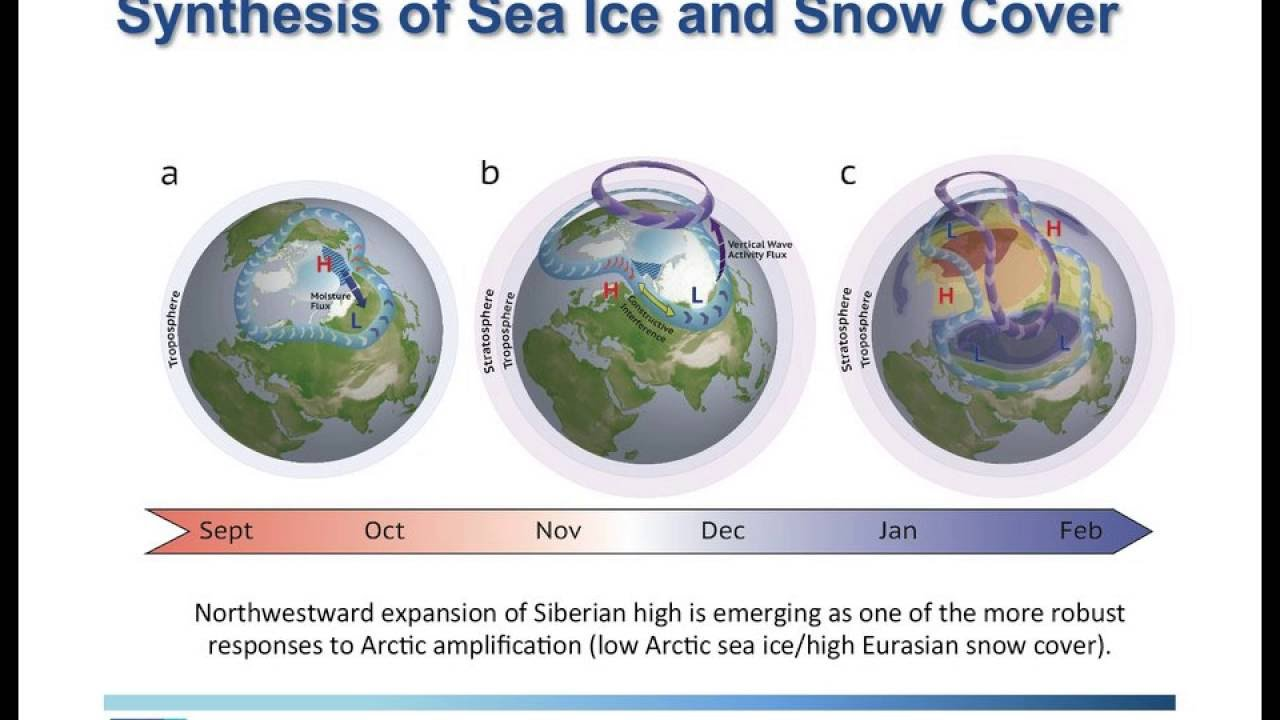
Arctic oscillation
It refers to the phenomenon that the air pressure in the North Pole and the air pressure in the middle latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere show an inverse relationship.
- Siberian high
- Polar vortex
- Westerly trough moving south.
- Harmful to health, ecology, environment and people's livelihood
Various causes

-
Heat islands are urbanized areas that experience higher temperatures than outlying areas.
-
From the heat storage of sunlight by buildings and asphalt, the hot air exhausted by the air conditioning equipment in the buildings in the city, the urban dome effect caused by the reduction of trees, etc.
HEAT island effect
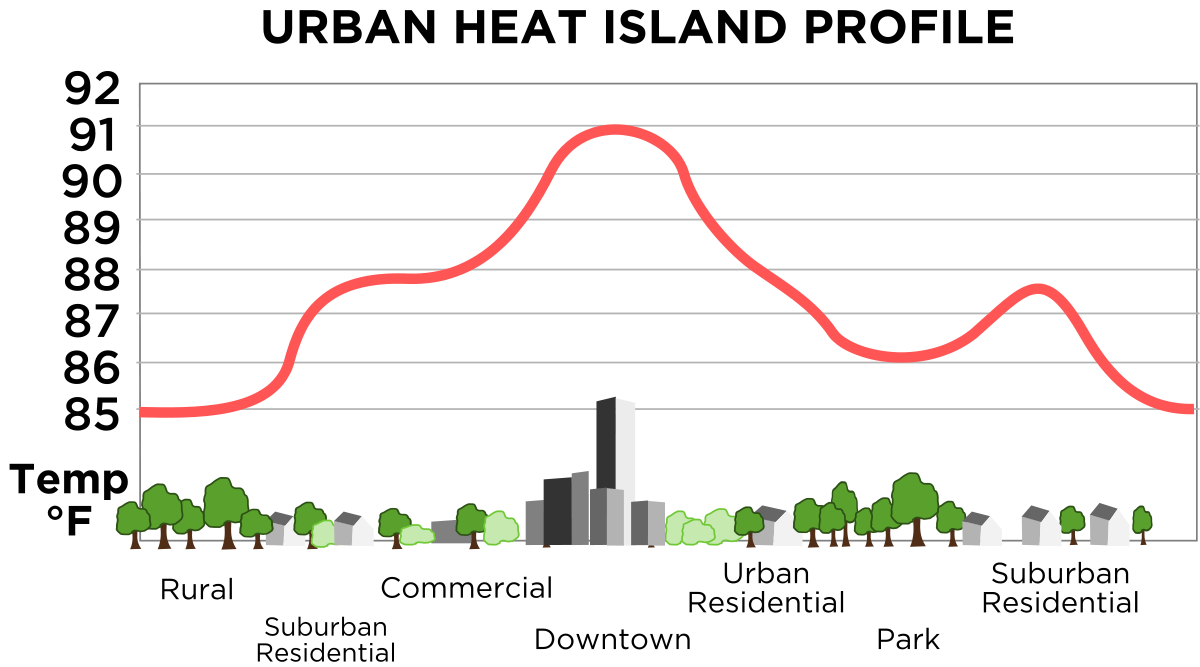
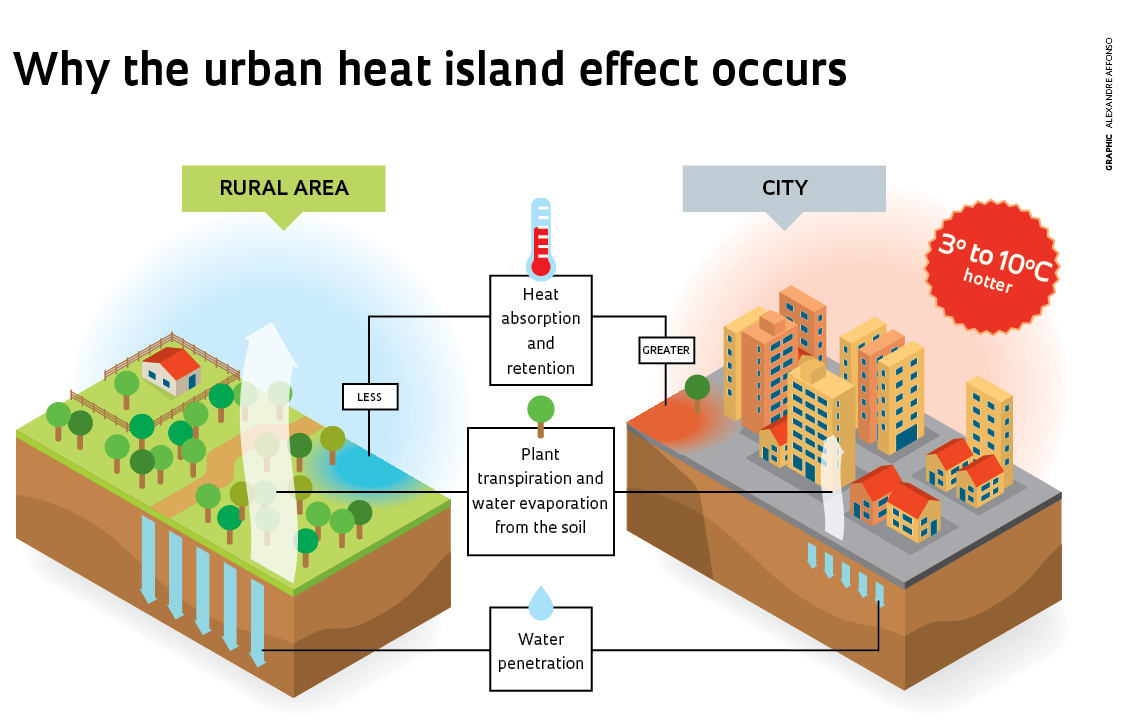
- Reduction of trees and bare ground
- Air pollution
- Low albedo asphalt and glass facades and concrete cladding
- Industrial activities and artificial waste heat from automobiles, air-conditioning equipment, etc.
- High-rise buildings obstruct the flow of wind
Causes

-
A mature tropycal cyclone.
-
Closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and/or squalls.
-
Sea-level rise resulting from climate change will also worsen the effects of these strong typhoons.
typhoon

-
A natural disaster, which refers to the phenomenon of water flow in which the water body contained in rivers, lakes and oceans rises and exceeds the normal water level.
-
Typhoon, snow water, rain.
-
Flash Flooding.
FLOODing

- A drought is a period of time when an area or region experiences below-normal precipitation.
- Warmer temperatures enhance evaporation, which reduces surface water and dries out soils and vegetation.
drought

- A type of winter storm characterized by freezing rain.
- The freezing rain from an ice storm covers everything with heavy, smooth glaze ice.
ICE storm

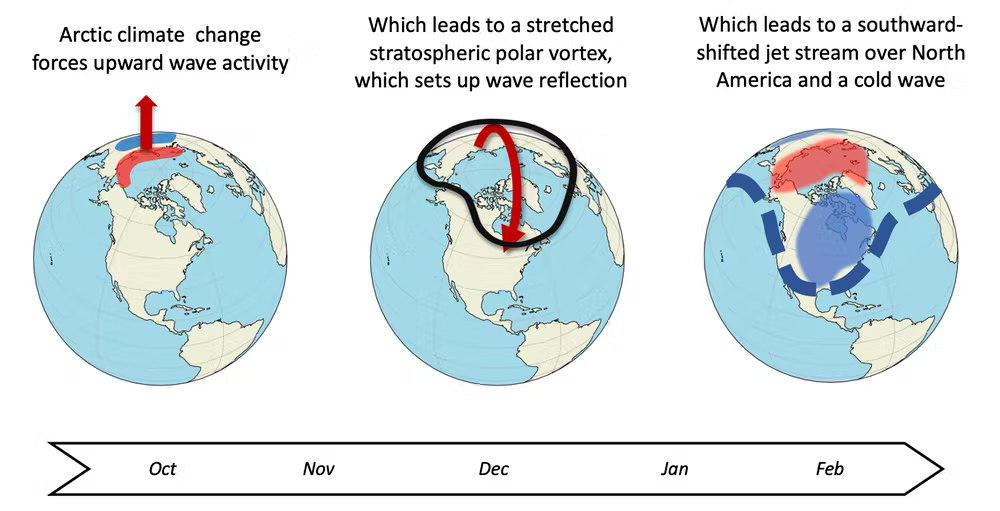
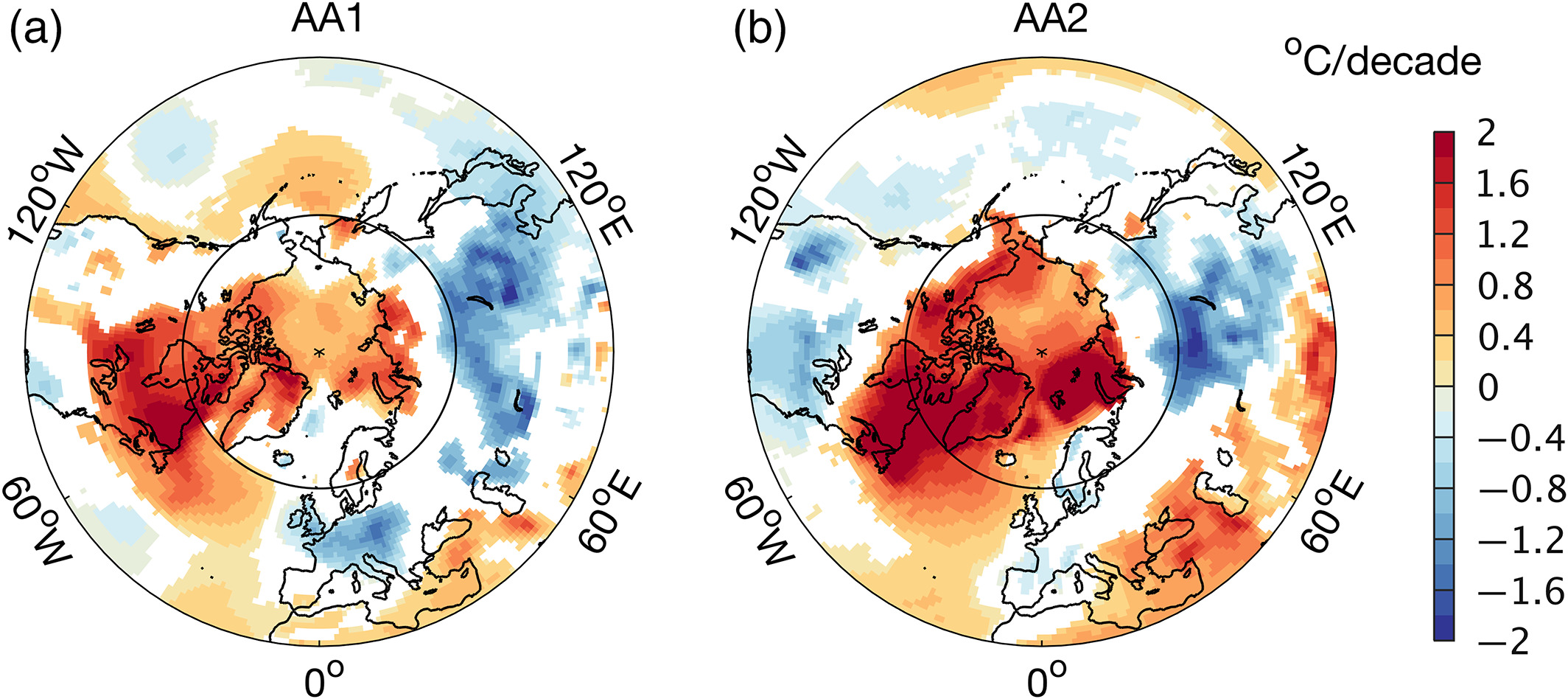
Warm arctic / Cold continents
Cause
- Rapid Arctic warming in recent decades coincided with unusually cold winters over Northern Hemisphere continents.
- It has been speculated that this “Warm Arctic, Cold Continents” trend pattern is due to sea ice loss.
Details
Conjecture has it that more cold extremes over the mid-latitude continents should occur due to global warming and the impacts of Arctic sea ice loss. A Northern Hemisphere temperature signal termed the "Warm Arctic, Cold Continent" pattern has thus been surmised.
Soloution & Adaption pathway
How to reduce the harm caused by extreme weather?
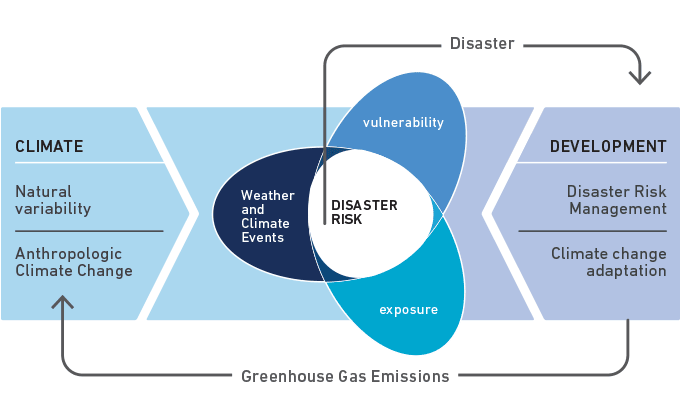
Disaster risk
The potential loss of life, injury, or destroyed or damaged assets which could occur to a system, society or a community in a specific period of time, determined probabilistically as a function of hazard, exposure, vulnerability and capacity.


Adaption pathway
An adaptation pathway is a decision-making strategy that is made up of a sequence of manageable steps or decision-points over time. Characteristics of the strategy are: Each decision-point is triggered by some change (environmental or social).
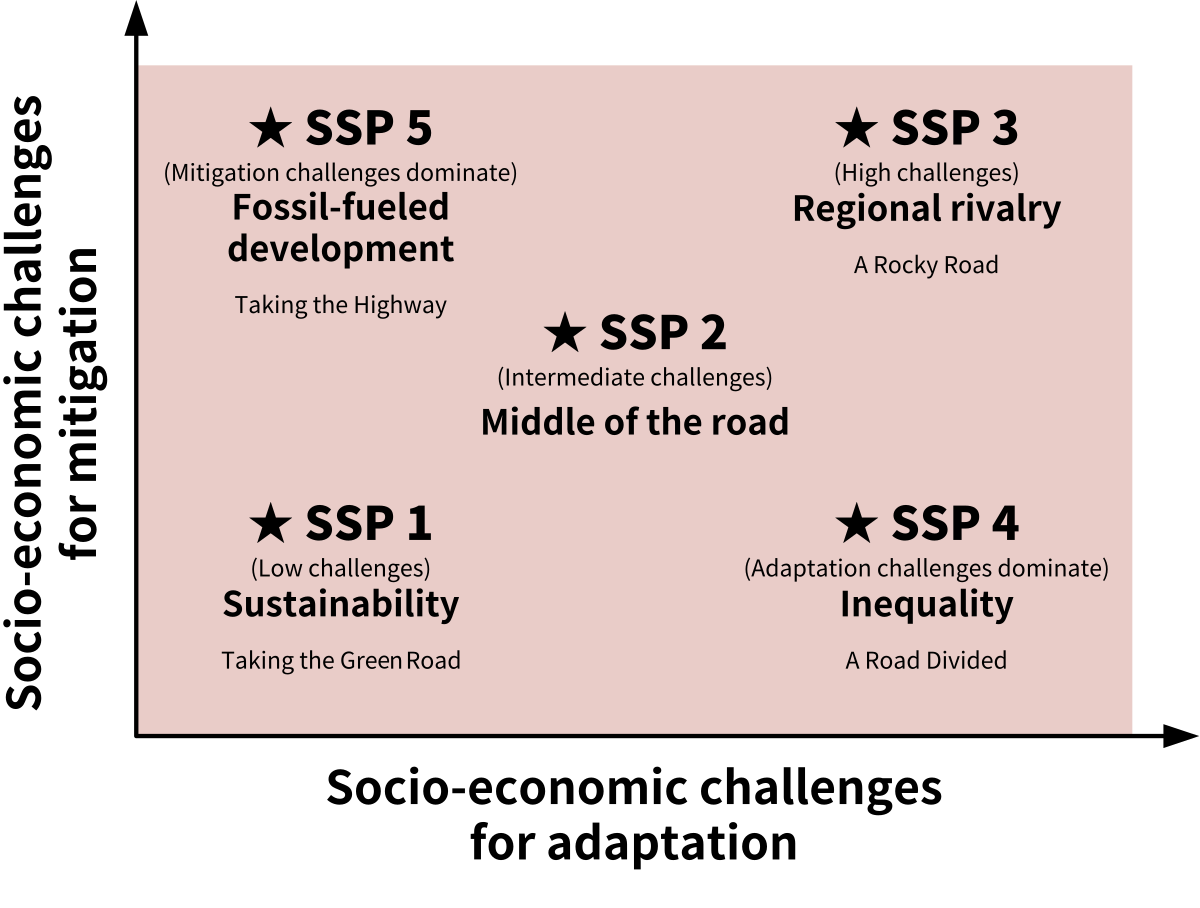
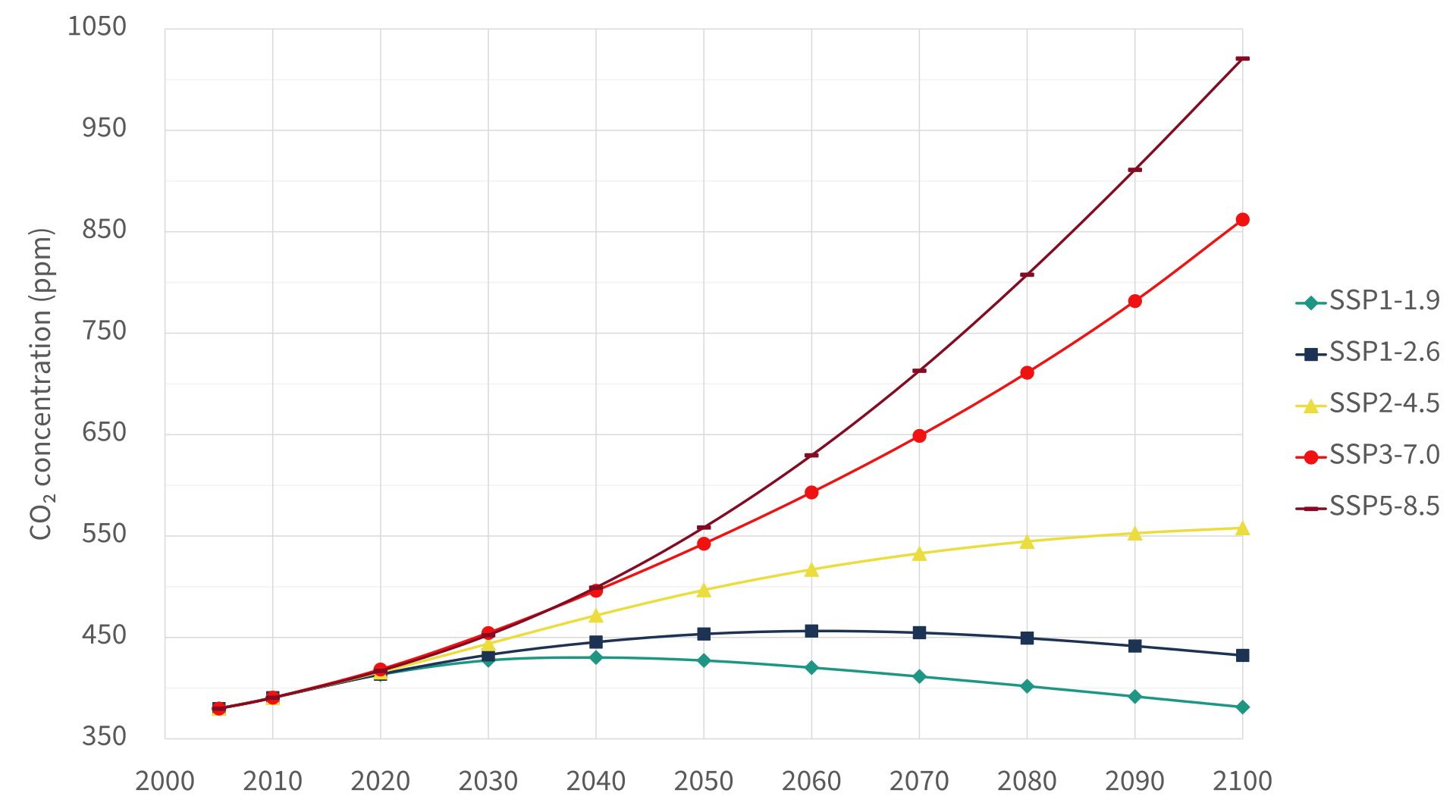
SSP(Shared Socioeconomic Pathways)
SSPs integrate different population, economic growth, and other socioeconomic assumptions into future emission scenarios. They also consider a broad potential no-policy baseline scenario and how different mitigation scenarios can be achieved under different socioeconomic pathways.
- develop renewable energy
- Promoting Friendly Buildings and Healthy Housing
Action
- phasing out fossil fuels
- Rational consumption, prolong the service life of goods
reduction

Solution
- Protect forests like the Amazon.
- Protect the oceans.
- Reduce how much people consume.
- Reduce plastic.
- Keep fossil fuels in the ground.
- Invest in renewable energy.
- Switch to sustainable transport.
- Help us keep our homes cosy.
- Improve farming and encourage vegan diets.
- Restore nature to absorb more carbon.

Taiccat
TCCIP
& Quiz
How is the TaiCCAT DSS(Decision Support System) implemented?

Urban resilience
Measurable ability of any urban system, with its inhabitants, to maintain continuity through all shocks and stresses, while positively adapting and transforming towards sustainability.
Engineering method -> Adaption
-
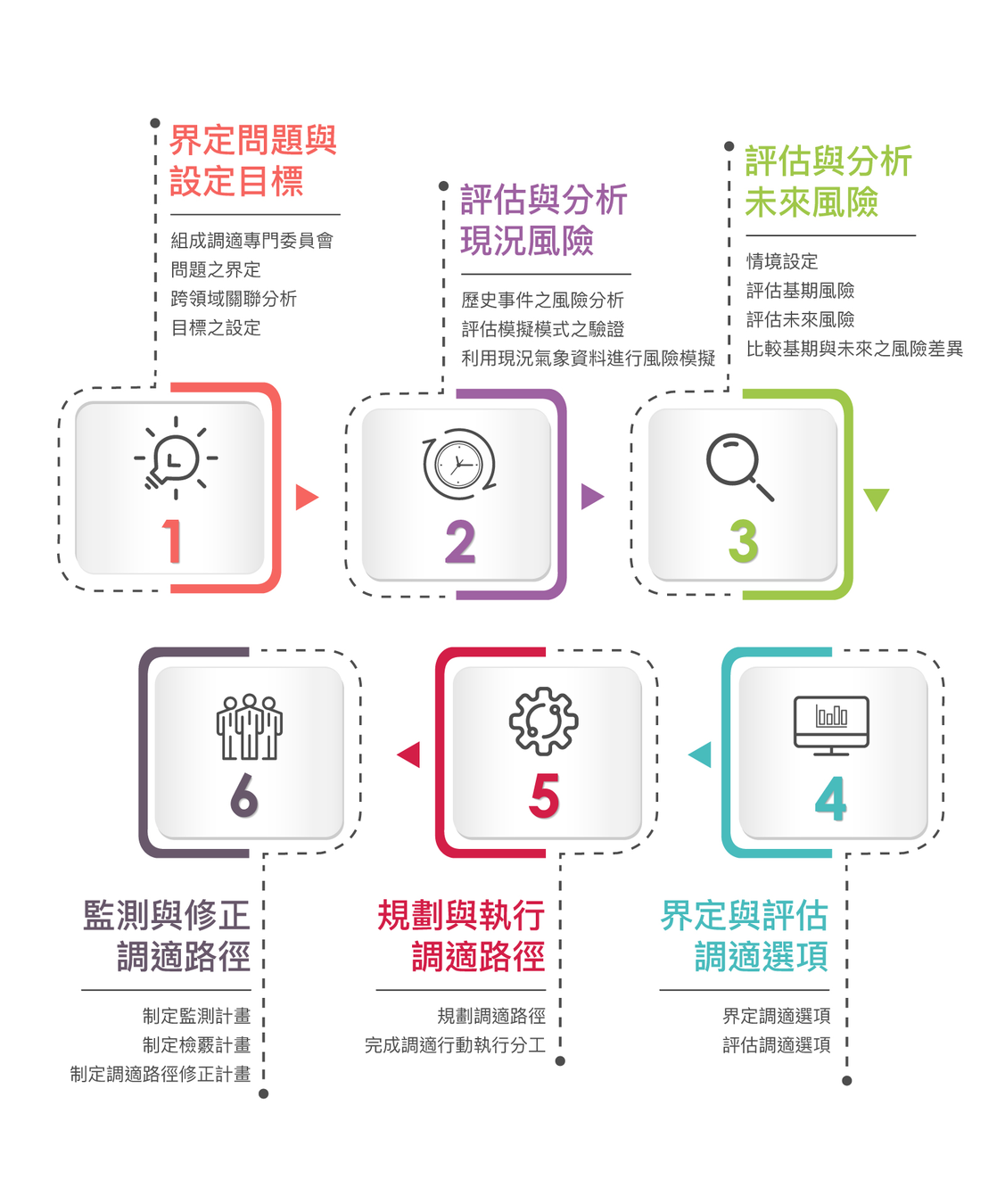
TaiCCAT is a systematic standard procedure developed by the Ministry of Science and Technology.
-
Reference to the relevant international adaptation assessment framework and considering the current domestic situation.
-
It clearly defines the sub-steps and work items of each step, etc. And provide complete construction guidelines.
TAICCAT

- TCCIP's main mission is to produce climate data that meets the needs of Taiwan's climate change research, and to provide value-added and services.
- Climate Change Integration Service established by the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology
TCCIP


Q1:
There may be more than one correct answer.
Choose the incorrect statements:
(A)TaiCCAT consists of six-step process.
(B)The hot/heat wave forms in low pressure environment.
(C)A RCP is a greenhouse gas concentration (equals to CO2 emissions).
(D)"Warm Arctic, Cold Continents” trend pattern is due to sea ice loss.
(E)In adaption pathway, each decision-point is triggered by some change (environmental or social).
Answer: (B)(C)
QUIZ
Q2:
Which of the following is NOT in the process of TaiCCAT?
(A)Defining the problem and goal
(B)Assessing and analyzing current risks
(C)Planning and executing adaption pathways
(D)Carrying out massive urban renewal
(E)Defining and avaluating adaption options
Answer: (D)
QUIZ
The end of presentation
Thank you for listening.
-
IPCC
-
TCCIP
-
BBC news
Reference

125-29-賴昱錡-極端氣候概論.PPT
By Richard Lai
125-29-賴昱錡-極端氣候概論.PPT
Earth Science Presentation made by Yu-Chi Lai(CKHS class125) in June, 2022.
- 143