

I am going to bore you with...
-
What is Open Source
-
What is GitHub
-
What is a Git Repository
-
What is Forking and Cloning
-
Setting up Git on your computer
-
git add, git commit, git push
-
git fetch, git merge, git branch
-
Git Workflow
-
Contribution guidelines
What is Open Source, Again?
Source Code is available(to mess with)
Generally, available to distribute
may(may not) be free
Why Open Source turned out to be an instant love of every programmer?

I can do what I want.
I am SUPERMAN.
An open source software(application) can be modified according to one's needs
Learn how others are creating that application
Easy to be a part of an ongoing development work
Re-usable code
Generally Free to use
No need to wait for the organization in charge to make changes
Free of any Piracy
Why was it a hassle to contribute into Open Source?

"I am done with all these guys messing up with my code."
Managing code by thousands of contributors was almost impossible.
Following a proper development schedule was not easy.
Hard to find projects of your choice.
...
Solution?
GitHub
GitHub makes it easier to...
make your code Open Source
manage literally any number of contributors
manage versions of your product
follow a well defined structure to complete the project
contribute into projects of your choice
find open source projects to work on
create an online portfolio of your skills
Why should I contribute?
To add the functionality you want
To get experience about any technology you have just learnt
To work with people from around the globe
To learn new things
To get a feeling of a significant work
To get known by people in a community
To showcase your skills by working on real-world projects
Getting Your Hands Dirty...
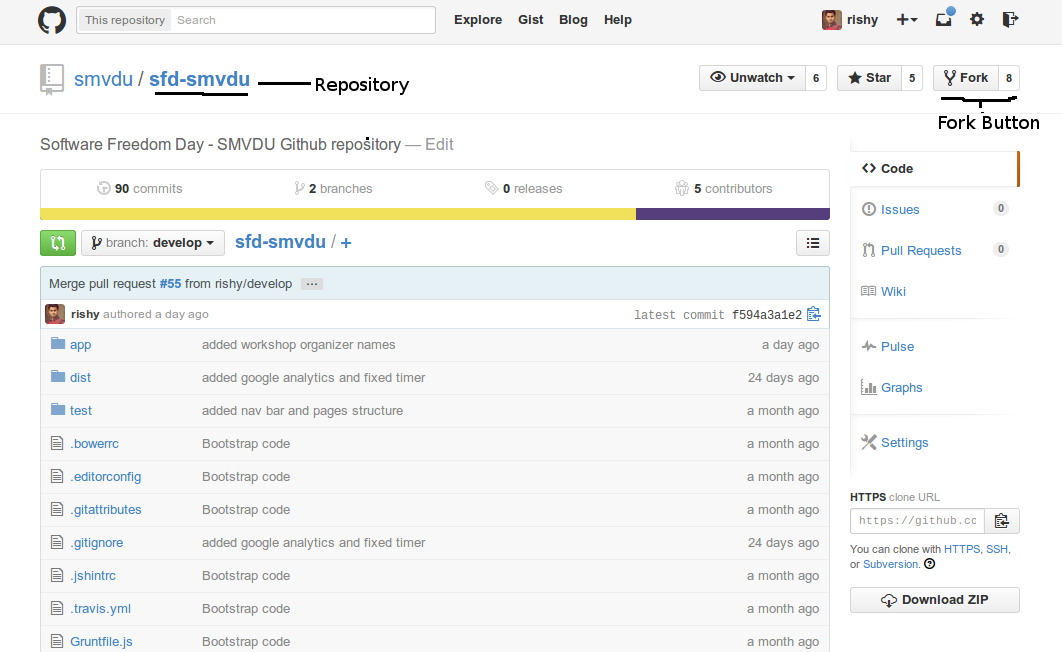
Repository
A GitHub Repository is an online Folder at Github, which contains all of the files within a project.
GitHub allows any contributor to get notified about any changes in any file within a Repository.
A Repository in one account can be copied in another account using "Fork" Button.
A new Repository can be created by clicking on the the "+" button in Github Menu bar.
A GitHub Repository
Some well-know Repositories
-
Vlc - https://github.com/videolan/vlc
-
Ruby on Rails - https://github.com/rails/rails
-
facebook-ios-sdk - https://github.com/facebook/facebook-ios-sdk
...
Git Structure
Remote Server(Github)
Local System (Your PC)
Github Profile
Online Repositories
Work Graph
Navigable code
Git bash(terminal)
Local copy of Git Repo
Edit files locally
Working branches
Git Bash
Provides a new "git" command within your Linux terminal or a separate command prompt kind of tool for windows and macs.
Git can be downloaded from: http://git-scm.com/downloads
Git Installation
Linux(Ubuntu): sudo apt-get install git
Windows: http://git-scm.com/download/win
Mac: http://git-scm.com/download/mac
Setting up for first use
Open up your terminal and set up your user name, as
$ git config --global user.name "YOUR NAME"Set up your e-mail address(the one you signed up with on github), as
$ git config --global user.email "YOUR EMAIL ADDRESS"For Further Reference: https://help.github.com/articles/set-up-git
git clone
Clones a repo from Remote Server(Github Website) to your local machine(PC).
$ git clone "REPOSITORY CLONE ADDRESS"For example,
$ git clone https://github.com/smvdu/sfd-smvdu.gitReview
What is Open Source
What is Github
What is a Repository
Forking a Repo
Cloning a Repo
How to edit cloned files?
How do you edit a text file?
By Using an Editor. No complicated stuff here.
eg. Sublime Text, gedit, vim, notepad, etc.
README File
Should
mustbe present in every github repoSummary of the project
Basic setup information about the repo
Contribution guidelines
Workflow for this repo
git status
"git status" shows the modified files in cloned copy of repo on the local machine.
$ cd "REPO NAME"
$ git status
on branch master
Files modified:
file1
file2
.
.
git add
"git add" command is used to add modified files for committing.
$ git add --all
This will add all the modified files in the next commit.
.gitignore
Used to ignore the changes in certain files/directories.
"." marks this file as a hidden file.
git commit
"git commit" will group together all the changes you have made with a meaningful message.
$ git commit -m "DESCRIPTION ABOUT MODIFICATIONS"-m stands for commit message
Review
-
cloned a repo using git clone
-
made some modifications using a text editor
-
checked for modified code using git status
-
finalized files to be committed using git add
-
committed added files using git commit
-
README and .gitignore file
git branch
Branches in a git repo allows, even further copies of the same code.
Changes done in one branch do not affect the code in another branch, until done explicitly
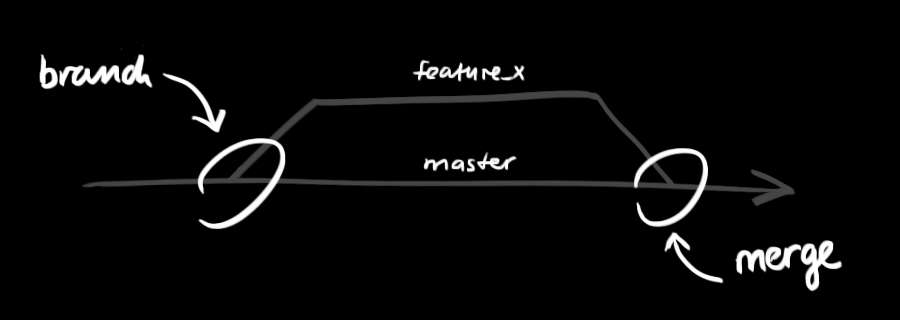
For any new task, create a new branch and later merge it with the parent branch. In this case new branch is "feature_x" and parent branch is "merge".
branching commands
To see all the branches in a repo
$ git branchTo create a new branch, from current branch
$ git branch "NEW_BRANCH NAME"To move to another branch
$ git checkout "BRANCH_NAME"git push
"git push" sends all the commits to the remote server(Github), from where you cloned your repo.
$ git push "REMOTE NAME" "BRANCH NAME" $ git push origin master
eg:
Pull Requests
Hey(Repo Owner), I have made some changes in this repo, can you add those up with the main repo?
Pull Requests Sequence Flow
Go to your forked repo on Github
Click on "pull requests" on right hand side of the repo page
Click on "new pull request"
Add the title of the pull request
Send the pull request
Your pull request will be merged by the "Repo Owner" with the parent repo(from where you forked it).
git fetch
"git fetch" gets the latest code from the parent repo and add it directly to your local repo.
$ git fetch "REMOTE NAME"
$ git merge "REMOTE NAME"/"BRANCH NAME"Github Remotes
Github Remotes are like variables which have the values as the link to a particular repo on Github remote server.
$ git remote add upstream "REPO LINK"$ git remote add upstream "https://github.com/smvdu/sfd-smvdu.git"Now anytime when you run "git fetch upstream" it will check your local files against this repo.
git pull
"git pull" is similar to "git fetch", but it also runs "git merge" command by itself.
git pull will update all the branches in local repo. Whereas while using git fetch only listed branches will be updated.
$ git pull upstream git merge
"git merge" merges two different copies of code.
Generally used for merging two different branches and code from upstream to local repo.
git merge usage
In branch context,
$ git merge "BRANCH_NAME"This will add the code from the "BRANCH_NAME" branch to the current branch. Code in any other branch will remain as it is.
If we are on master branch and wants to merge it with develop branch then run,
$ git merge developAfter running "git fetch" command. Fetched code is merged with one of the branches as,
$ git merge "REMOTE NAME"/"LOCAL BRANCH NAME"for example,
$ git fetch upstream develop
$ git merge upstream/developHere, fetch commands gets the code from develop branch of remote server and merges it with current branch.
merge-conflicts
Arise while using "git merge" command
When git can't decide by itself which code to be preserved
merge conflicts has to be removed by the programmer manually
There shouldn't be any merge conflicts before sending a Pull Request
<<<<<<<< HEAD
def func(a b):
=============
def func(x, y):
>>>>>>> refs/head/new_funcReview
- Git branching structure
- git push to push new changes on your forked repo
- Pull Requests to submit your changes to parent repo
- git fetch and git pull to update your local repo
- git merge to merge two different copies of code
- merge-conflicts and how to remove them
The Next LeveL
- git init
- git diff
- git log
- git rebase
- git reset
- git stash
Github Flow
https://guides.github.com/introduction/flow/index.html
Github Issues
-
Used to define and assign tasks to be completed
-
Used for any queries regarding the code
-
Used to report a bug or to give a suggestion
Git Network Graph
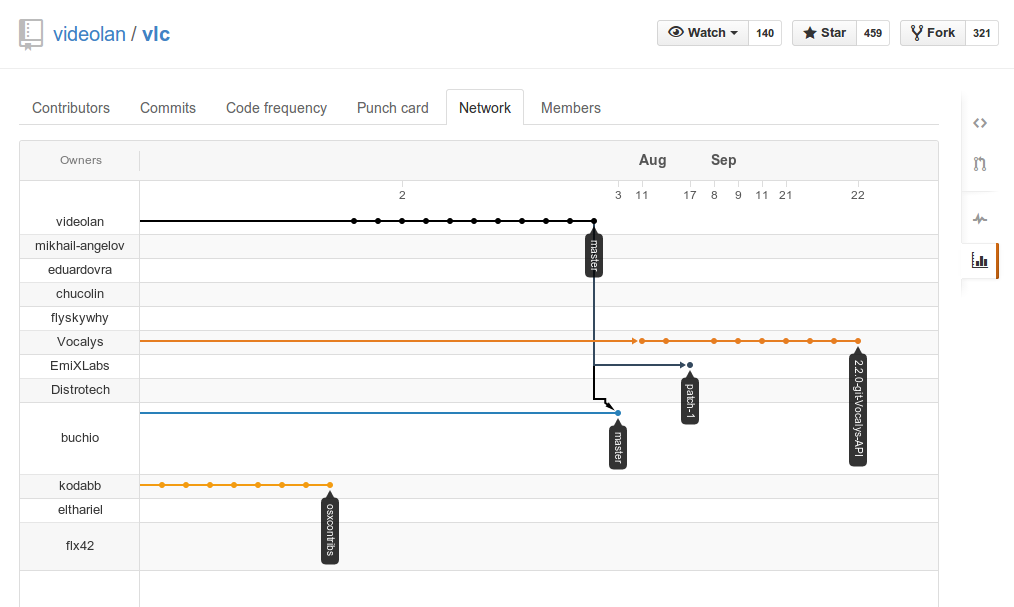
Contribution Workflow
First of all fork the the repo and clone it to your local machine
Run the code on your local machine
Check out the issue page on Github for the repo
Pick up one of the issue and start working on it
Comment below on the issue if there is any doubt
Every good repo on Github has a contribution guidelines link, go through it
Start working on the issue
Create a different branch for every new task
For every small change, create a commit
push the code to your forked repo
From there send a Pull Request to the parent repo
A word about Commit messages
Keep them meaningful, short and to the point.

Create a Repo of your own and run all listed operations on it.
References/Resources
- https://help.github.com/articles/set-up-git
- https://help.github.com/
- https://try.github.io/levels/1/challenges/1
- http://www.codecademy.com/blog/74-getting-started-with-git
- https://help.github.com/articles/setting-guidelines-for-repository-contributors
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/10240125/working-with-readme-md-on-github-com
- http://nvie.com/posts/a-successful-git-branching-model/
- https://training.github.com/kit/downloads/github-git-cheat-sheet.pdf
Create.Share.Collaborate
Thank you :)
SHOOT YOUR QUESTIONS...
Github Workshop - SFD'14
By Rishabh Shukla
Github Workshop - SFD'14
- 2,615



