Motivation and Autonomy:
Tv series as a way of learning English

What is Autonomy?
- Holec ( 1981), defines autonomous learning as a person having the ability to take full responsability of his or her own learning.
- This includes the ability to decide what, when, how and for how long learning should take place.
- This also involves defining goals and objectives, selecting the appropriate materials, techniques and approaches, AND finally evaluation outcomes.
History of learning autonomy
- The term "learner autonomy" was first coined in 1981 by Henri Holec, the "father" of learner autonomy. Many definitions have been given to the term depending on the writer, the context, and the level of debate educators have come to.
- Some of the most well known definitions in present literature are:
- "Autonomy is the ability to take charge of one's own learning". (Henri Holec)
- "Autonomy is essentially a matter of the learner's psychological relation to the process and content of learning". (David Little)
- "Autonomy is a situation in which the learner is totally responsible for all the decisions concerned with his [or her] learning and the implementation of those decisions". (Leslie Dickinson)
- "Autonomy is recognition of the rights of learners within educational systems". (Phil Benson)
- In a world where intelligence and cognition are distributed, the distribution of knowledge seems like a reasonable hypothesis. Autonomy itself, like cognition, intelligence and knowledge cease to be individualized in order to become collective and shared. (LEFFA, p.36)
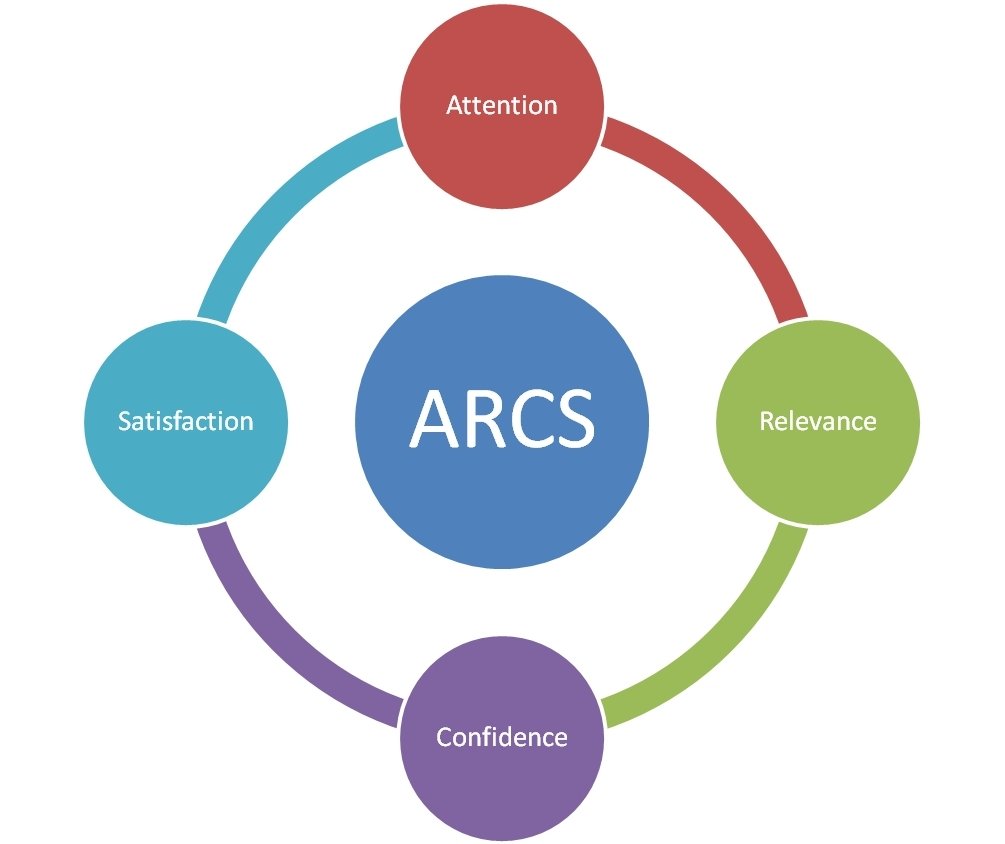
Model of Motivation: ARCS (J.Keller)
| Major Category |
Sub Category | Instructional Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Attention | Perceptual Arousal Inquiry Arousal Variability |
1. What can I do to capture their interest? 2. How can I stimulate an attitude of inquiry? 3. How can I maintain their attention? |
| Relevance | Goal Orientation Motive Matching Familiarity |
1. How can I best meet my leaner's needs? (Do I know their needs?) 2. How and when can I provide my leanerswith appropriate choices, responsabilities and influences? 3. How can I tie the instruction to the learner's experiences? |
| Confidence/ Challenge |
Learning Requirements Success Oportunities Personal Control |
1. How can I assist in building a positive expectation for success? 2. How will learning experience support or enhance the student's beliefs in their competence? 3. How will learners clearly know their success is based upon their efforts and abilities? |
| Satisfaction/ Success |
Natural Consequences Positive Consequences Equity |
1. How can I provide meaningful opportunities to leaners use their newly-acquired knowledge/skill? 2. What will provide reinforcements to the learner's successes? 3. How can I assist the students in anchoring a positive feeling about their accomplishments? |
References
- LEFFA, V.J. Como produzir materiais para o ensino de línguas. In: Produção de materiais de ensino : teoria e prática .1 ed. Pelotas : Educat, 2003, v.1
- BAFFI-BONVINO, CAVALARI e GARCIA. Rede São Paulo de Formação Docente, curso de especialização para o quadro do Magistério da SEESP (Ensino fundamental II e Ensino Médio). Pesquisas do ensino e aprendizagem de inglês como língua estrangeira: tendências e perspectivas. São Paulo: 2012.
Motivation and Autonomy
By Robson Cruz
Motivation and Autonomy
- 201



