CoLight: Learning Network-level
Cooperation for Traffic Signal Control
ABSTRACT
Cooperation among the traffic signals enables vehicles to move through intersections more quickly. Conventional transportation approaches implement cooperation by pre-calculating the offsets between two intersections. Such pre-calculated offsets are not suitable for dynamic traffic environments.
To enable cooperation of traffic signals, in this paper, we propose a model, CoLight, which uses graph attentional networks to facilitate communication. Specifically, for a target intersection in a network, CoLight can not only incorporate the temporal and spatial influences of neighboring intersections to the target intersection, but also build up index-free modeling of neighboring intersections. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to use graph attentional networks in the setting of reinforcement learning for traffic signal control and to conduct experiments on the large-scale road network with hundreds of traffic signals. In experiments, we demonstrate that by learning the communication, the proposed model can achieve superior performance against the state-of-the-art methods.
key contributions
Cooperation through dynamic communication
Index-free model learning with parameter sharing
Experiment on the large-scale road network
key contributions
Cooperation through dynamic communication
Index-free model learning with parameter sharing
Experiment on the large-scale road network
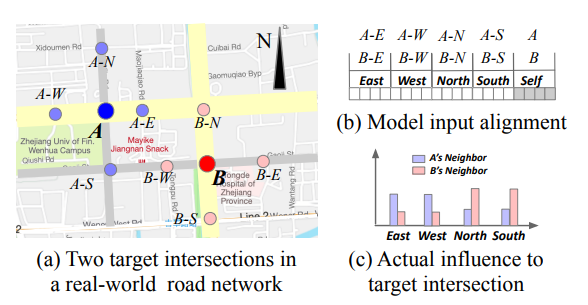
key contributions
Cooperation through dynamic communication
Index-free model learning with parameter sharing
Experiment on the large-scale road network

key contributions
Cooperation through dynamic communication
Index-free model learning with parameter sharing
Experiment on the large-scale road network
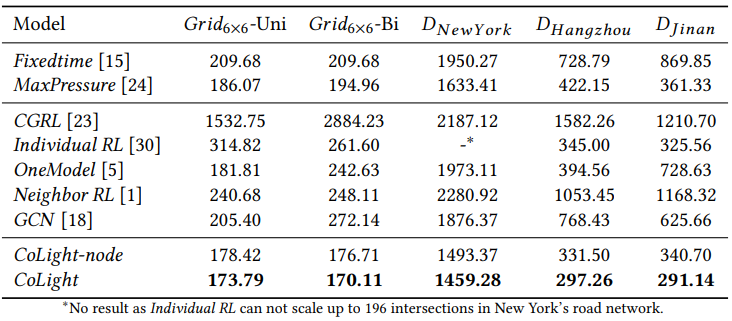
METHOD
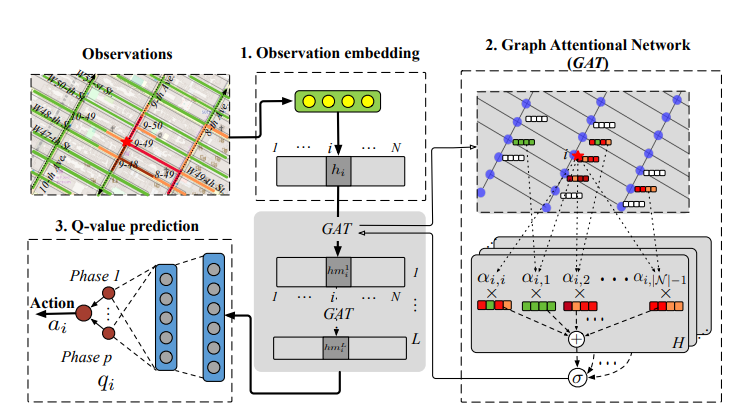
METHOD

METHOD

METHOD
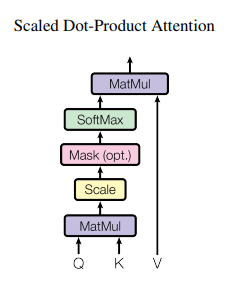
Get Q, K, V
METHOD
METHOD

METHOD

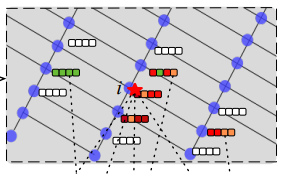
METHOD


METHOD


METHOD

METHOD

METHOD

METHOD

CLF
CLF
CLF
CLF
0
2
3
1
Action
Performance
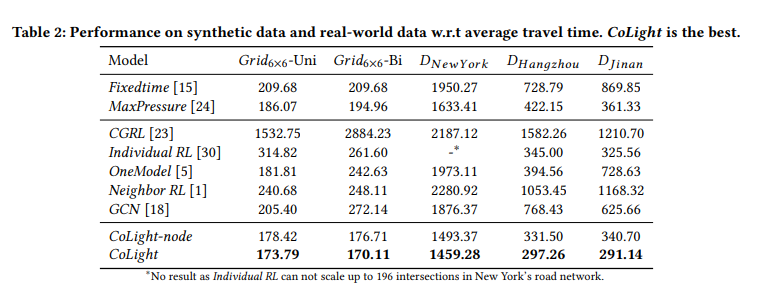
c0light
By r oger
c0light
- 3



