Deploying Django in AWS

Andres Duque Hincapie
Software Developer
With Elastic Beanstalk, you can quickly deploy and manage applications in the AWS Cloud without worrying about the infrastructure that runs those applications.

Prerequisites
-
Python 2.7
-
pip
-
virtualenv
-
awsebcli
Set Up a Basic Venv with Django
(Create directory, Ie "djangoapp")
> mkdir djangoapp
(Open our new directory)
> cd djangoapp
(Create virtual environment, Ie "venv")
> virtualenv venv
(Activate our virtual environment)
> source venv/bin/activate
(Install Django)
> pip install djangoCreate a Django Project
(Activate our virtual environment)
> source venv/bin/activate
(Create new Django project called "ebdjango")
> django-admin startproject ebdjango
(Open Django project)
> cd ebdjango
(Run Django project)
> python manage.py runserver
If all is OK you can access to "http://127.0.0.1:8000/"
and see Django project.Configure Django Application for Elastic Beanstalk
(Activate our virtual environment)
> source venv/bin/activate
(Save pip freeze output to file called "requirements.txt")
> pip freeze > requirements.txt
(Create a directory called ".ebextensions")
> mkdir .ebextensions
(Add configuration file called django.config)
> nano .ebextensions/application.config
Write it in the file:
option_settings:
aws:elasticbeanstalk:container:python:
WSGIPath: ebdjango.wsgi:application
(Deactivate virtual environment)
> deactivate

Into Django APP
Configure Django Application for Elastic Beanstalk
> Set ALLOWED_HOST as ['*'] instead []
In settings.py

> eb init
Select an application to use
...
Enter Application Name
..
It appears you are using Python. Is this correct?
(y/n): y
Select a platform version.
1) Python 3.4
2) Python
3) Python 2.7
4) Python 3.4 (Preconfigured - Docker)
(default is 1): 3
Do you want to set up SSH for your instances?
...
Select a keypair.
...
EB init
Deploy With the EB CLI
(Your project looks like this)
├── .ebextensions
│ └── django.config
├── .elasticbeanstalk
│ └── config.yml
├── .gitignore
├── db.sqlite3
├── ebdjango
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── __init__.pyc
│ ├── settings.py
│ ├── settings.pyc
│ ├── urls.py
│ ├── urls.pyc
│ ├── wsgi.py
│ └── wsgi.pyc
├── manage.py
└── requirements.txt

Deploy With the EB CLI
Create an environment and deploy application
> eb create ebdjango-environmentDeploy With the EB CLI
Creating application version archive "app-1.1...6_1....1".
Uploading ebdjangoapp/app-1...26_1....1.zip to S3. This may take a while.
Upload Complete.
Environment details for: ebdjango-environment
Application name: ebdjangoapp
Region: us-west-2
...
...
Printing Status:
INFO: createEnvironment is starting.
...
You can close the process in your terminal
(safe to Ctrl+C)AWS EB Console
eb console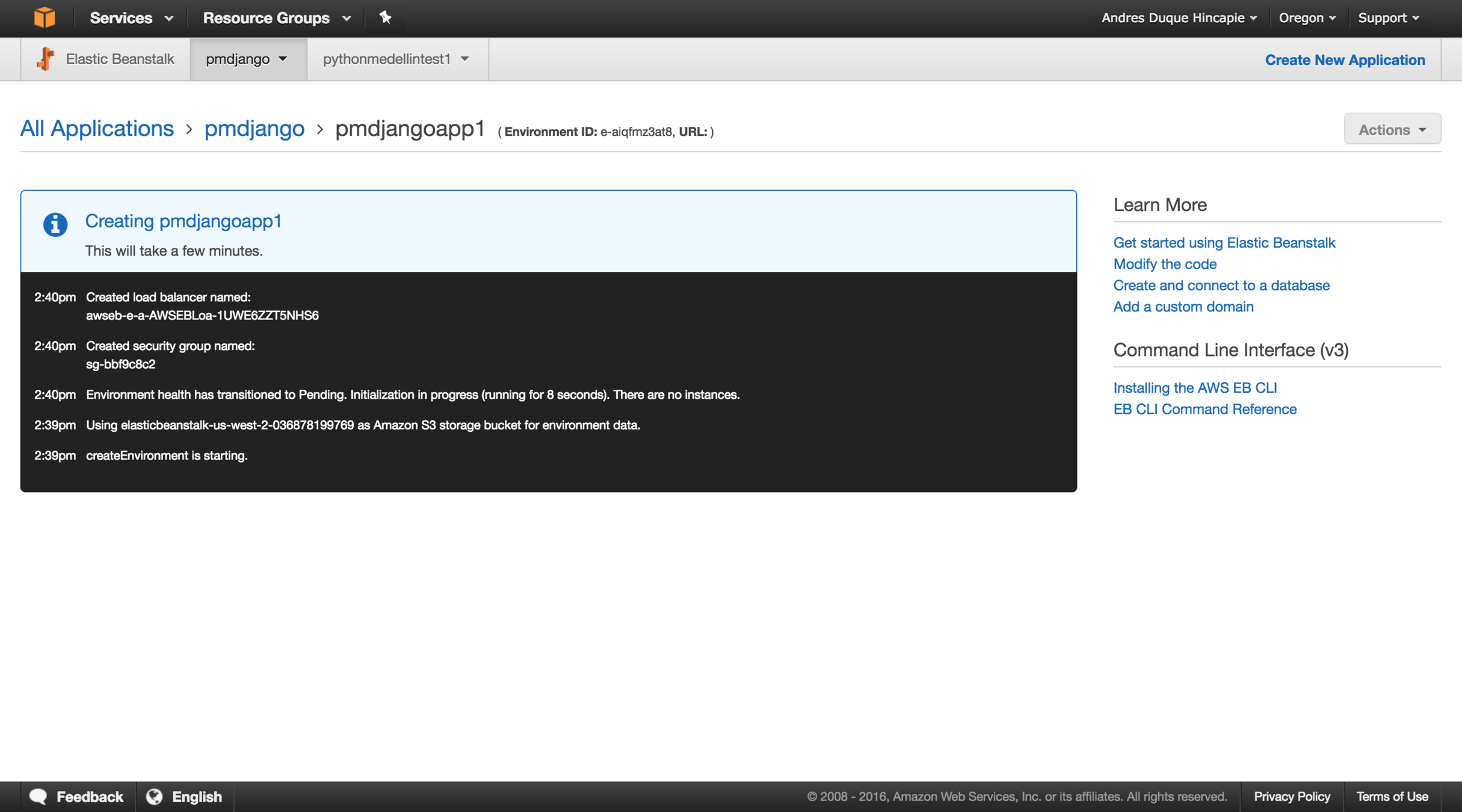
AWS EB Console
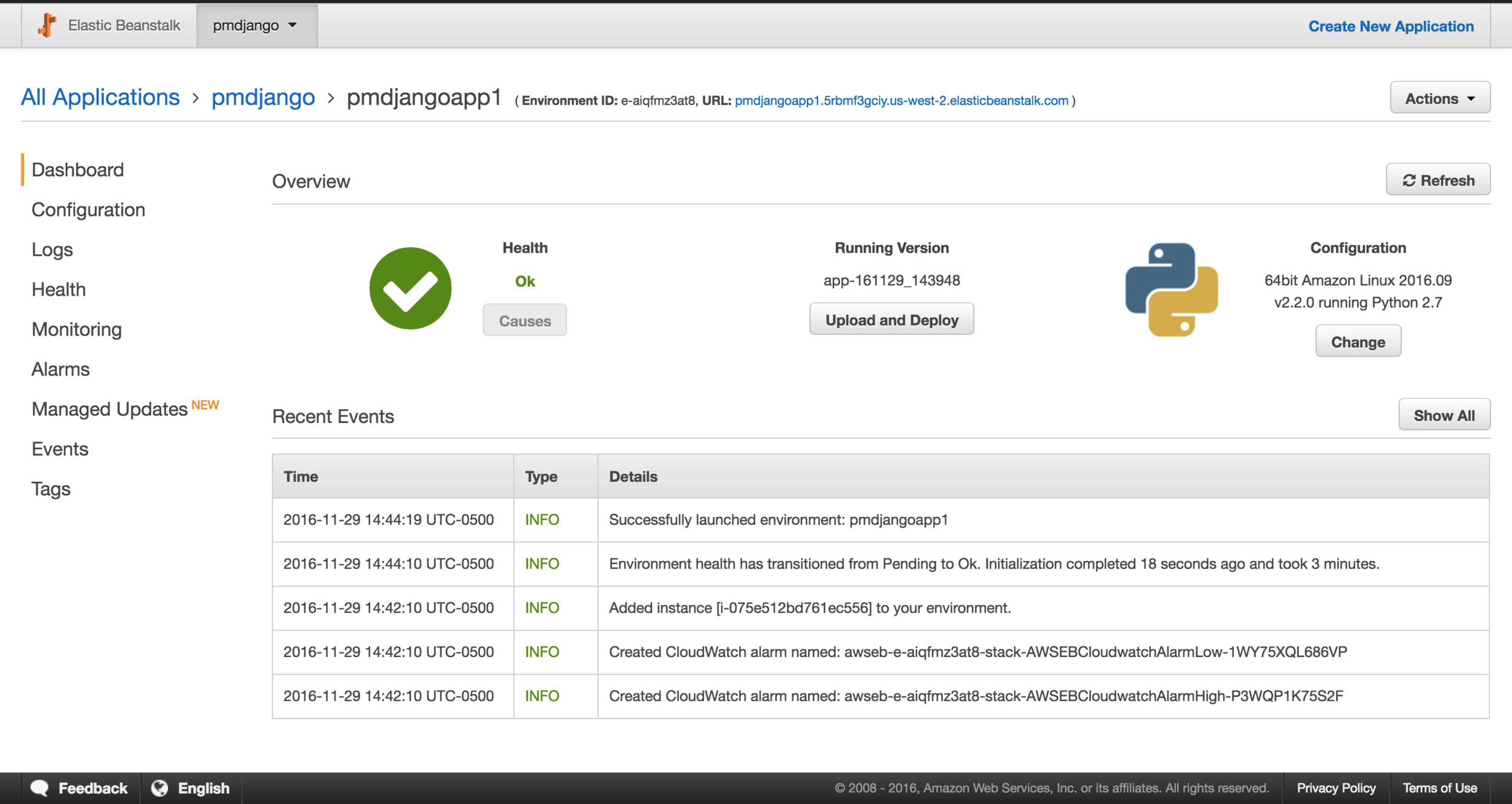
Application is OK
AWS EB Console
Application is OK
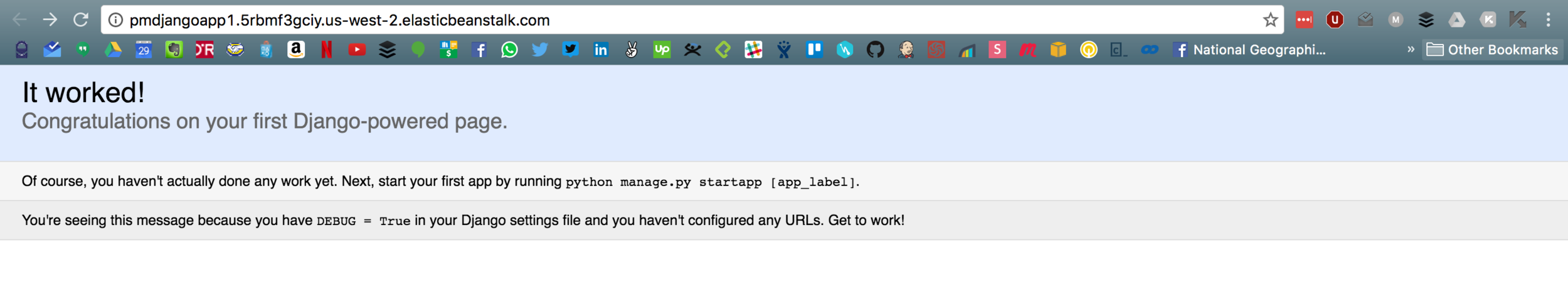
Django Application
- We can't log-in to our application
- Django admin haven't static files
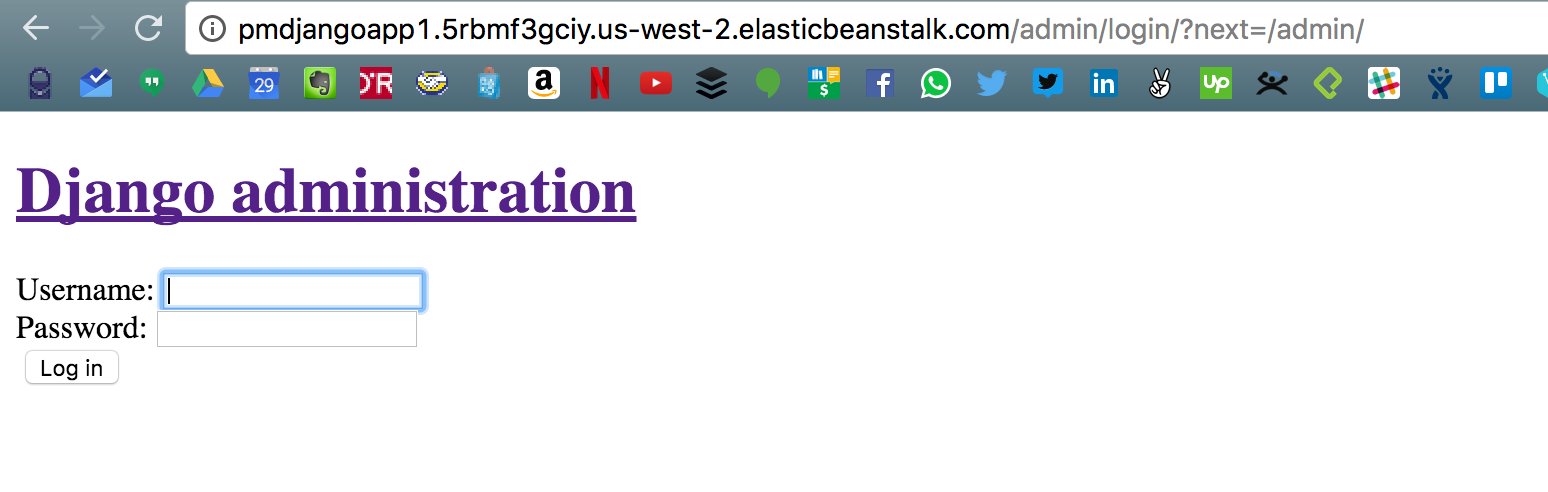
Django Application
Add STATIC_ROOT to settings.py
and
collect static files
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static")
Read about Django Static Files
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.10/howto/static-files/
python manage.py collectstaticDjango Application
Create migrations (Use sqlite for now)
(With virtualenv activated)
> python manage.py migrateRead about Django Migrations
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.10/topics/migrations/
Django Application
Create superuser, set username, password, email, etc.
(With virtualenv activated)
> python manage.py createsuperuserAWS EB Deploy Changes
eb deployIf we're using Git we should add the changes and create a commit. Deploy description will be commit message.
You'll see again the deploy status in the shell and you can open AWS EB Console to see the deploy status there.
Django Application
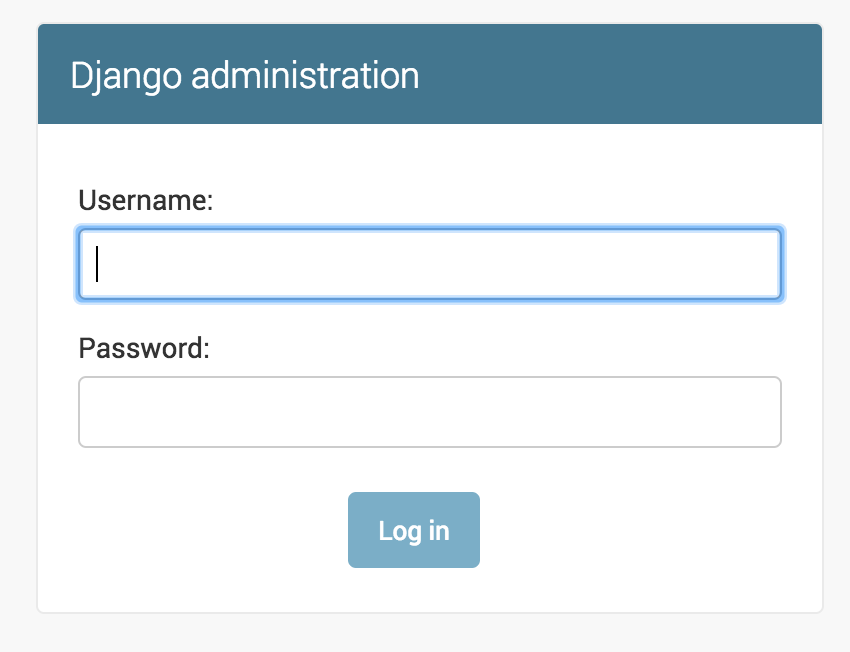
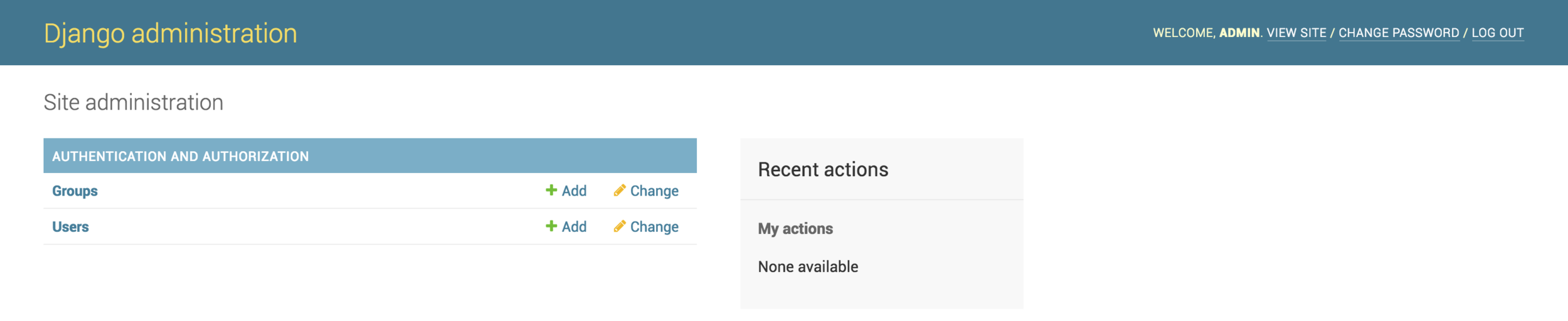
We can log-in with created user
AWS EB RDS
Configuring a Database
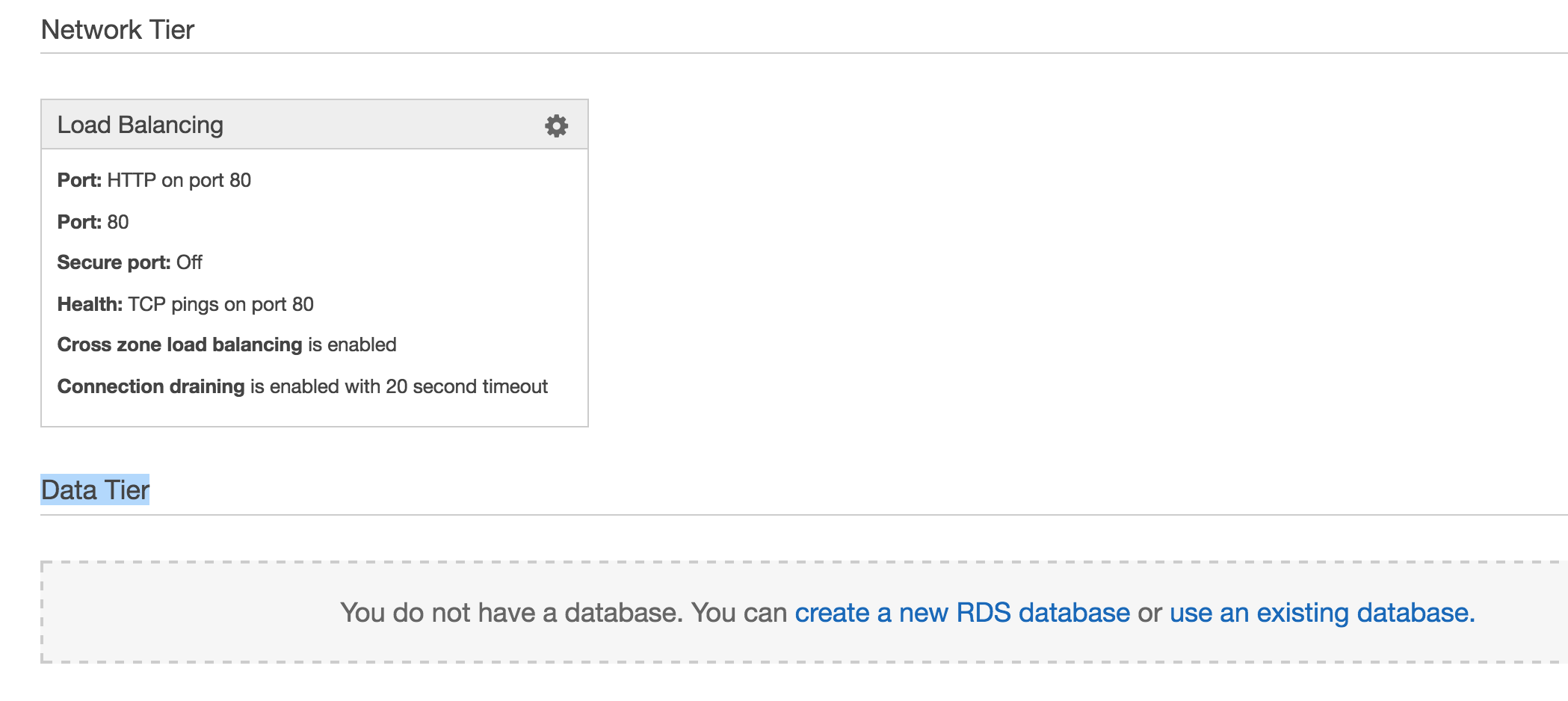
- Click the “Configuration” link (At the left).
- Scroll all the way to the bottom of the page, and click "create a new RDS " in “Data Tier” section.
- On the RDS setup page set "DB Engine" to “postgres”.
- Create a “Username” and “Password” to DataBase.
- Save.
AWS EB RDS
Configuring a Database
AWS EB RDS
Configuring a Database
AWS EB RDS
Configuring a Database
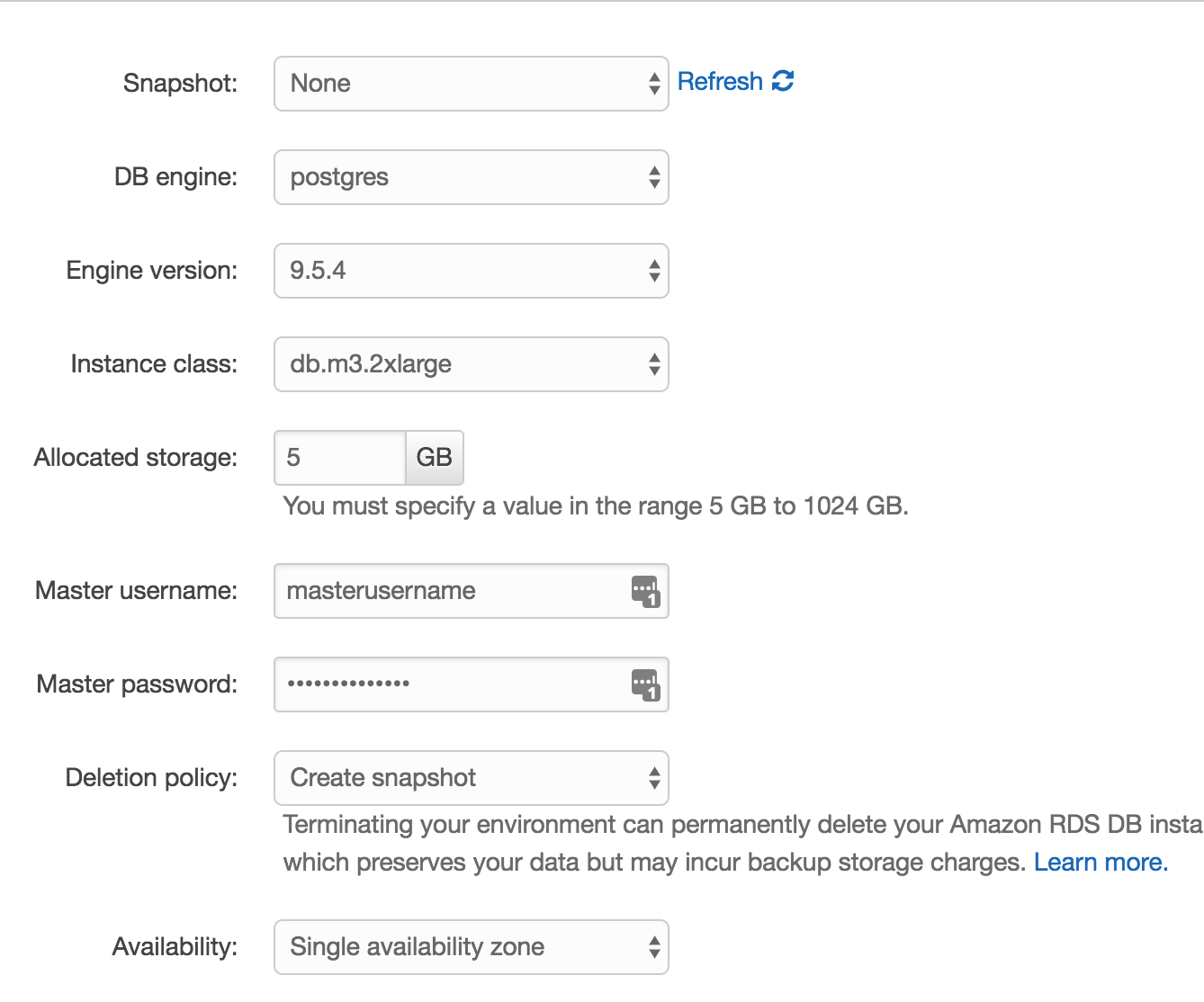
AWS EB RDS
Configuring a Database
How to connect Django Application to RDS DataBase?
When we created a new RDS DataBase, EB added 5 environment variables with DB.
AWS EB RDS
Configuring a Database
Update settings.py DATABASE configuration
if 'RDS_DB_NAME' in os.environ:
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql',
'NAME': os.environ['RDS_DB_NAME'],
'USER': os.environ['RDS_USERNAME'],
'PASSWORD': os.environ['RDS_PASSWORD'],
'HOST': os.environ['RDS_HOSTNAME'],
'PORT': os.environ['RDS_PORT'],
}
}
else:
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'),
}
}AWS EB RDS
Connecting with PostgreSQL
We need install psycopg2 to can connect to PostgreSQL
(You need to have PostgreSQL installed)
(With virtualenv activated)
> pip install psycopg2AWS EB RDS
Updating Requirements
Update requirements.txt with the psycopg2
(With virtualenv activated)
> pip freeze > requirements.txtAWS EB RDS
Configuring a Database
We need install PostgreSQL to can install psycopg2, how we can do it in EB?
Remember the file application.config into .ebextensions
We can say to EB that install some package that we need
AWS EB RDS
Update .ebextensions/application.config adding
"packages:"
packages:
yum:
git: []
postgresql93-devel: []
option_settings:
aws:elasticbeanstalk:container:python:
WSGIPath: ebdjango/wsgi.pyAWS EB Deploy
Update our changes
eb deployAWS EB Deploy
We can't log-in into our application. Now we're using new DataBase and we haven't executed the migrations there.
How we can execute commands in EB Application?
AWS EB Deploy
Update .ebextensions/application.config adding
"container_commands:" and updating "option_settings:"
container_commands:
01_migrate:
command: "django-admin.py migrate"
leader_only: true
packages:
yum:
git: []
postgresql93-devel: []
option_settings:
aws:elasticbeanstalk:container:python:
WSGIPath: ebdjango/wsgi.py
aws:elasticbeanstalk:application:environment:
DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE: ebdjango.settings
AWS EB Deploy
How we can create a superuser?
Unfortunately createsuperuser doesn’t allow you to specify a password when using the --noinput option, so we will have to write our own command. Fortunately, Django makes it very easy to create custom commands.
Read about Custom Commands
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.10/howto/custom-management-commands/
AWS EB Deploy
Create an application into Django project, IE "application_setup"
(With virtualenv activated)
> django-admin startapp application_setupCreate a file called "createsu.py"
into:
application_setup/management/commands/createsu.py
Note: Remember add the application to INSTALLED_APPS in settings.py
Note: Make sure you add __init__.py into management and commands folders
AWS EB Deploy
from django.core.management.base import BaseCommand
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class Command(BaseCommand):
def handle(self, *args, **options):
if not User.objects.filter(username="admin").exists():
User.objects.create_superuser("admin", "admin@admin.com", "admin")
Write into "createsu.py"
AWS EB Deploy
Update .ebextensions/application.config adding
"02_createsu" to "container_commands:"
container_commands:
01_migrate:
command: "django-admin.py migrate"
leader_only: true
02_createsu:
command: "django-admin.py createsu"
leader_only: true
packages:
yum:
git: []
postgresql93-devel: []
option_settings:
aws:elasticbeanstalk:container:python:
WSGIPath: ebdjango/wsgi.py
aws:elasticbeanstalk:application:environment:
DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE: ebdjango.settings
AWS EB Deploy
Now, you can log-in to /admin with user "admin" and password "1234"
You can more commands to container_commands, IE to execute collectstatic after each deploy
03_collectestatics:
command: "django-admin.py collectstatic --noinput"AWS EB Deploy
The final file should looks like this:
container_commands:
01_migrate:
command: "django-admin.py migrate"
leader_only: true
02_createsu:
command: "django-admin.py createsu"
leader_only: true
packages:
yum:
git: []
postgresql93-devel: []
option_settings:
aws:elasticbeanstalk:container:python:
WSGIPath: pmdjango/wsgi.py
aws:elasticbeanstalk:application:environment:
DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE: pmdjango.settings
AWS EB Deploy
Note: You can set container_commands, packages and option_settings in different files into .ebextensions
Ie, "db-migration.config" to scripts into DB, "django.config" for project settings and "packages.config" for packages.
Thank you so much !!!
Deploying Django in AWS Elastic Beanstalk
By saduqz
Deploying Django in AWS Elastic Beanstalk
With Elastic Beanstalk, you can quickly deploy and manage applications in the AWS Cloud without worrying about the infrastructure that runs those applications.
- 1,466

