Growth and Development
Saj Arora
Questions
- When do girls get their growth spurt? Boys?
- How quickly does the head grow in comparison to the body? What is the gradient called?
- How does the mandible get primarily displaced? Secondarily displaced?
- Where is the apposition and resorption of bone during the maxillary and mandibular development?
- What are the faults in Suture and Cartilage Theory?
Questions
- When harvesting Chondrocyte tissue which cephalic or caudal tissue has bone generation potential?
- Why is understanding growth theories important from a dental standpoint?
Growth
- Increase in Size and Capacity
- There is no such thing as Independent growth
- Well controlled growth = Functional and Structural equilibrium
- Development = Specialization and in turn, loss of differentiation potential
Bone Formation
- Bone Remodeling
- Bone Displacement
- Size Increase
- Surface Apposition (after mineralization)
Intramembranous Bone formation
-
Flat bones of the Cranial Vault
-
Mesenchymal Cells differentiate to Osteoblasts and lay down bone
Endochondral Ossification
-
Long bones base of skull
-
Base of skull
-
Cartilage first and then bone
Growth Mechanisms
- Endosteal/Periosteal (deposition/resorption)
- Thickness of bone remains constant
- Cortical Drift
- Unilateral deposition (increasing thickness)
- Over time resorption will have caused bone to shift
- Relocation/Remodeling
- Different position of the bone vs. physiologic changes to accommodate new functional loads
Displacement
- Primary Displacement
- Structure moves in opposite direction of appositional growth
- Secondary Displacement
- Structure grows in the direction of new bone formation
V-Principle
- New bone is formed on the lingual of the mandible
- Bone is resorbed from the anterior of the mandible
- Results in Horizontal Expansion
- V will enlarge and move away from the apex
Mandibular Growth
- V-Principle
- Primary Displacement
- Apposition at the condyles and at the posterior ramus
- Resorption at the angle of the mandible and the inside of the ramus
- Secondary Displacement
- Growth of temporal bone moves the condylar fossa shifting the mandible down and forward
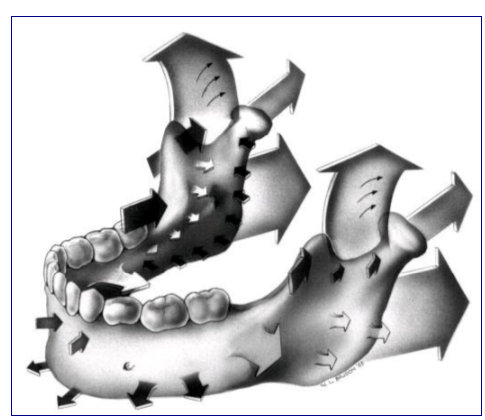
Maxillary Growth
- V-Principle
- resorption on the anterior
- Primary Displacement
- Apposition on the oral cavity side
- Resorption on the nasal side
- Overall there is drift down (imbalance in deposition/resorption)
- Secondary Displacement
- Nasomaxillary Complex grows pushing the maxilla down and forward
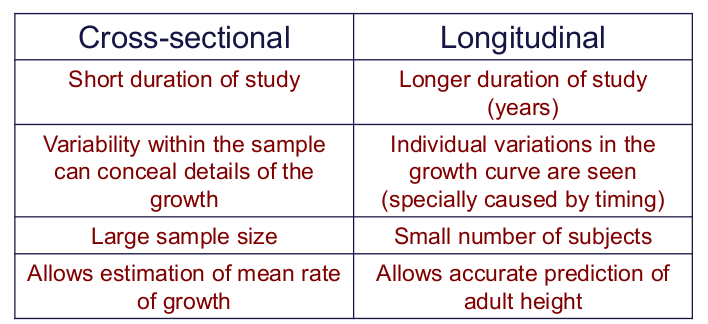
Studying Bone Formation
- Longitudinal Studies
- Cross-sectional Studies
- Mixed Longitudinal Studies
- Know disadvantages and advantages for each
How to study Growth
- Anthropometric Studies
- Cephalometric Studies
- Craniometry
Growth Curves
- Distance Curves
- Function of age
- Cross-sectional and Longitudinal Studies
- Velocity Curves
- Rate of change over time
- Only Longitudinal Studies
- How?
- Vital Staining
- Radioactive Tracers
- Implant Radiology
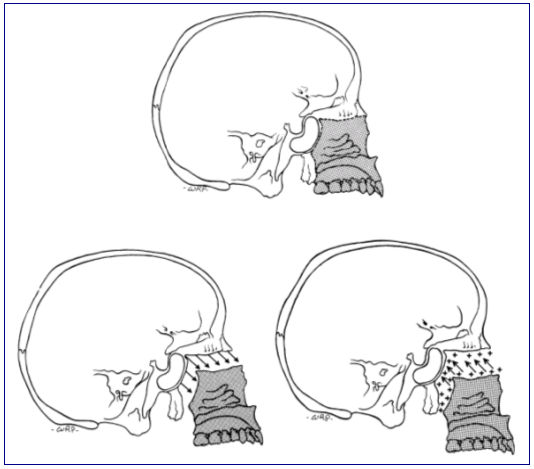
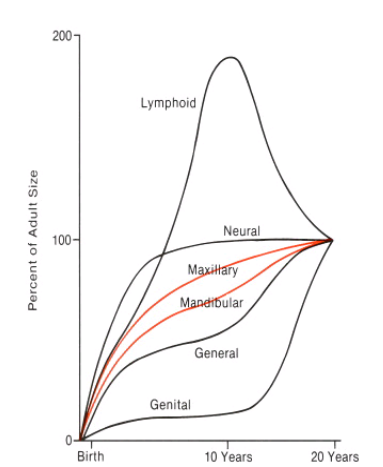
Patterns of Growth
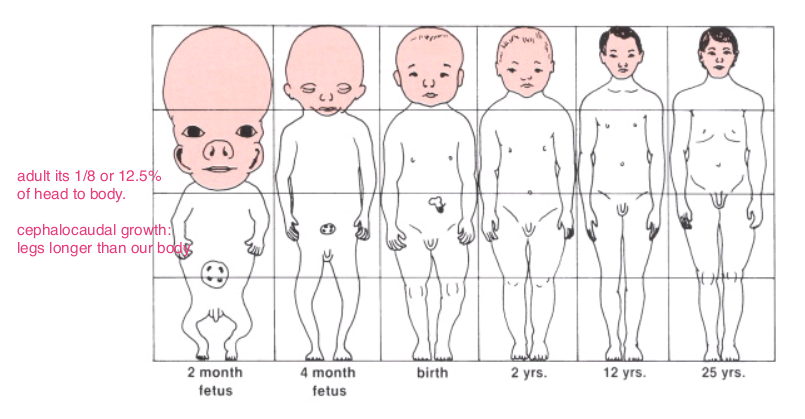
- Cephalocaudal gradient of Growth
- Scammon's Curves
Growth in Height
- Normal = 1 standard deviation around the mean
- between 16th and 84th percentile
- Girls spurt starts at the age of 12
- Boys spurt starts at 14
- Girls spurt begins 2-2.5 yrs before boys
- Girls menarche comes right after peak velocity of growth
Weight
More Variation in weight than height
Weight spurt lags by about 3 months
Timing
Most variations in growth are timing
Late bloomers grow slower but for a longer period
Maturity Indices
- Chronological Age -> Usually the worst
- Morphological Age
- Sexual Age
- Menarchy in girls
- Skeletal Age
- Cervical vertebrae and wrist bones
- Dental Age
- Eruption age
- Crown calcifications
Growth Theories
- Sutural Growth theory: False
- Sites of growth vs. Centers of Growth
- Suture transplanted do not form new bone
- Primary Cartilage Theory
- Cartilage contains growth information
- Everything else gets remodeled/displaced depending on the growth of cartilage
- Transplanting cartilage shows growth so it is a center of growth
- Removing it from the condyle doesn't affect other growth
- Removing it from the nasal septum affects growth
- Therefore, condyles are not centers of growth
Growth Theories
- Functional Matrix Theory: Best theory
- Growth occurs in response to functional needs
- Functional Matrix: includes teeth and muscles
- Skeletal Matrix: hard tissues
Bone Tissue Engineering
Sternal Chondrocytes
- Artificially created scaffold can generate new bone
- Harvest cartilage cells from bat place them in Chitosan
- Chitosan is the scaffold
- Bone is generated from Cephalic tissue and not from Caudal tissue
- Cephalic tissue can be induced by Vitamin A
- Caudal tissue is permanent cartilage
Early Treatment
- Remember Sutures react so if you apply force to separate them you will get bone formation
- Bases of distraction osteogenesis (Functional Matrix Theory)
- If the person is still pre-spurt you can get a lot of bone formation
- Palate Expanders and Head gear are amazing appliances to control growth
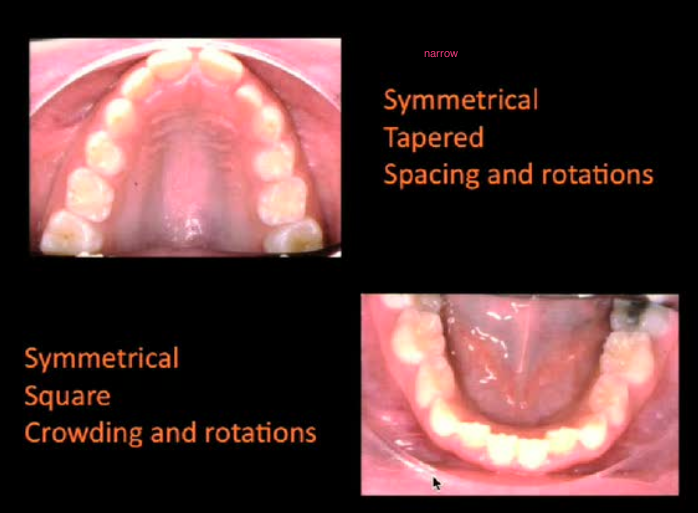
Narrow Arch
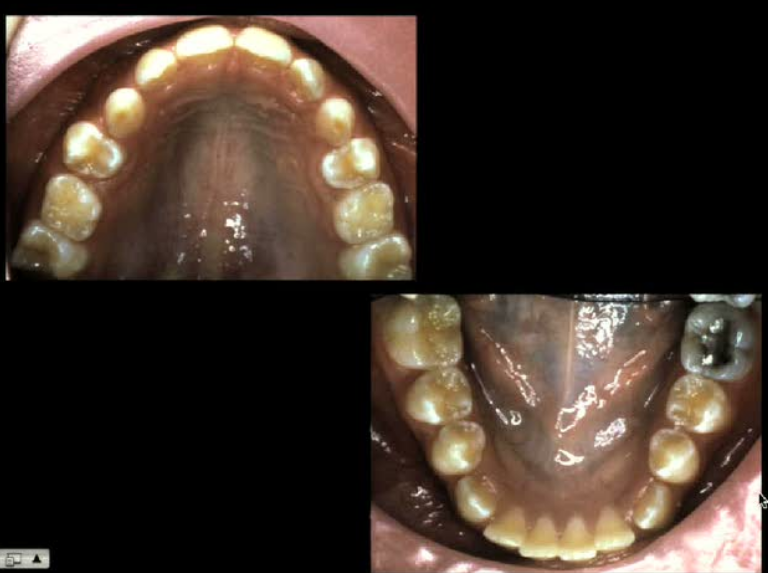
After Expander
Bite Modification
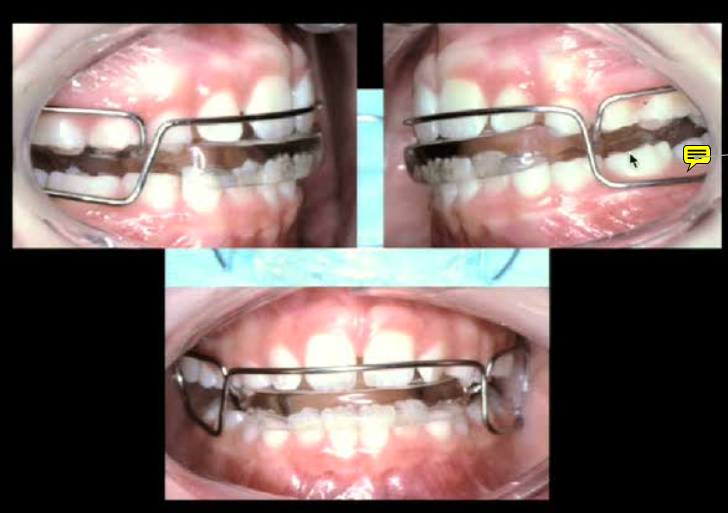
Bite Modification
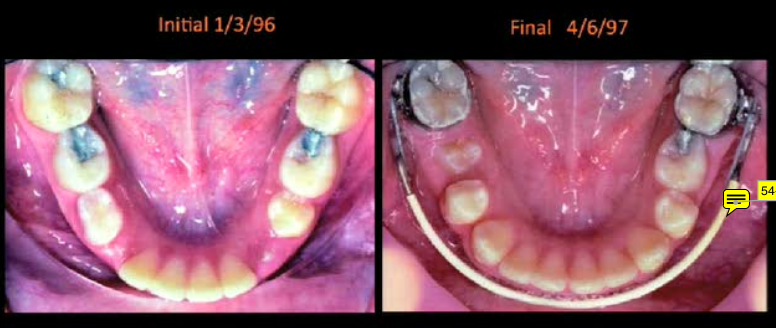
Mandibular Bumper (crowding)
Growth and Development
By Saj Arora
Growth and Development
- 698


