ANGULAR 101

Scott Mathson
@smathson
http://smathson.github.io
@smathson
http://smathson.github.io
WHAT IS ANGULAR?
- Toolset for building web applications
- Model-View-Whatever
- Decoupled DOM manipulation and app logic
- Declarative templating via custom HTML tags
- Non-opinionated model (POJOs)
- Loosely coupled via Dependency Injection
- Highly testable
BOOTSTRAPPING &
TWO-WAY BINDING
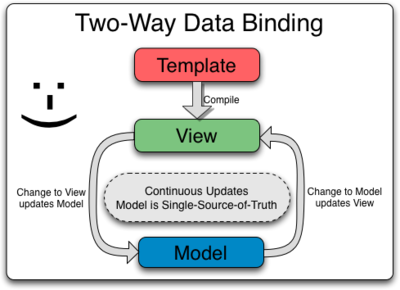
- THIS IS NOT MAGIC!
- Angular watches the model and updates the DOM
- $digest loop: dirty-check - Angular decides when
BUILT-IN DIRECTIVES
- ng-app - designate root element and bootstrap app
- ng-bind - evaluate expression and replace content
- ng-model - bind control value to scope variable
- ng-class - dynamically set CSS class of element
- ng-click - specify behavior on element click
- ng-show - show element when expression is true
- ng-hide - hide element when expression is true
-
ng-repeat - iterate over collection creating new
template for each item
EXPRESSIONS & FILTERS
- Inside bindings {{ }} or as an attribute value:
{{ foo }} or <div ng-bind="foo /> - No logic besides binary and ternary operators:
{{ foo && bar }} {{ bar || baz }} {{ foo ? bar : baz }} - Can be piped through filters (lowercase, date, etc)
{{ foo | lowercase }} - Can create custom filters to keep markup clean:
.filter('filterName', function() { return function(input) { // do work return output; } });
CONTROLLERS & SCOPE
- Scope: application model that will be exposed
to the view and evaluated for changes (view model) - All new scopes inherit from parent scope or $rootScope
- Controller: object that manages scope state an adds
behavior to the scope - Can be assigned declaratively in the view (ng-controller)
- Or linked to a view template via the $route service
- Defined via:
.controller('controllerName', function($scope) { // controller definition });
DEPENDENCY INJECTION
- Allows you to define components by name, define
their dependencies and then request them by
name as a dependency of another component
- DI system handles lifecycle of components and
dependency resolution - By name (not minifier-safe):
.factory('foo', function(fooService) { }); - With annotation (minifier-safe):
.factory('foo', ['fooService', function(fooService) { }]); - Build tools like ngmin will do annotation for you
SERVICES
- Lazily instantiated singleton objects for sharing
logic/state throughout the app:.factory('fooService', function($http) { var fooService = { // some behavior here using $http }; return fooService; }); - Great for containing business logic/server interaction
- Separation of Concerns: controller deals with view
state and behavior and depends on services for work - Combined with Dependency Injection, easy to mock
during testing and test components in isolation
DIRECTIVES
- This is where the DOM manipulation happens!
- Define new HTML tags or attributes with behavior:
.directive('myAwesomeThing', function() { return { restrict: 'A', template: '<div>{{ thing }}</div>', link: function(scope, element, attr) { // custom behavior and DOM manipulation here } } } - And use them in your views:
<div my-awesome-thing="thing"> - Test complicated DOM manipulation in isolation!
NEXT STEPS
- Greater depth with each concept in bite-sized vids:
- Learn how to organize and build an app:
-
https://github.com/angular-app/angular-app
-
http://blog.angularjs.org/2014/02/an-angularjs-style-guide-and-best.html
- Learn about the module system for grouping components and managing dependencies:
- Learn about $router and the ng-view directive:
- Check out AngularUI:
QUESTIONS?

ANGULAR 101
By Scott Mathson
ANGULAR 101
- 2,400



