Exploring the system impact of
automated taxis via simulation
Sebastian Hörl
17 May 2021


at CentraleSupélec
The street in 1900
http://www.loc.gov/pictures/item/2016800172/
The street today
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Atlanta_75.85.jpg
The street of tomorrow?
- Autonomous Mobility
- Mobility as a Service
- Mobility on Demand
- Electrification
- Aerial Mobility
Julius Bär / Farner
I. MATSim
Agent-based models
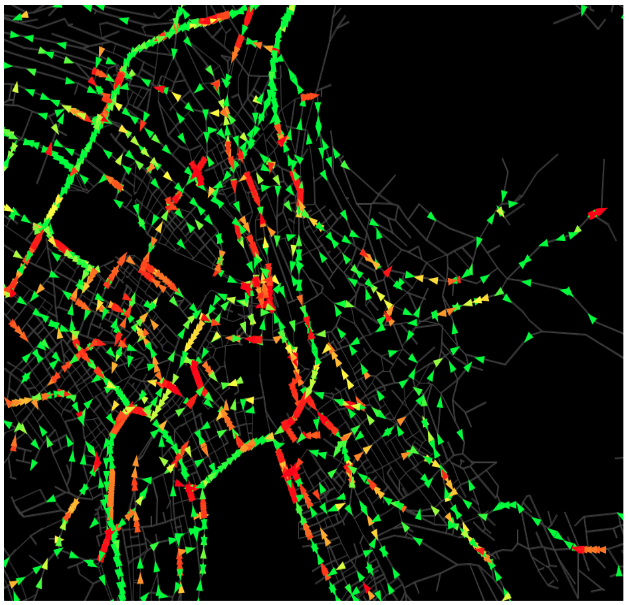
Senozon VIA

https://pixabay.com/en/traffic-jam-stop-and-go-rush-hour-143391/
MATSim
Senozon VIA
- Flexible, extensible and well-tested open-source transport simulation framework
- Used by many research groups and companies all over the world
- Extensions for parking behaviour, signal control, location choice, freight, ...

http://www.matsim.org
matsim-org/matsim-libs













MATSim
Mobility simulation
Decision-making
Analysis
Scenario
- Flexible, extensible and well-tested open-source transport simulation framework
- Used by many research groups and companies all over the world
- Extensions for parking behaviour, signal control, location choice, freight, ...
MATSim

Senozon VIA
MATSim
Home
Work
Shop
Home
until 8am
9am to 6pm
6:15m to 6:30pm
from 6:45pm
walk
public
transport
walk


Discrete mode choice


Discrete mode choice
https://pixabay.com/en/zurich-historic-center-churches-933732/
II. AMoD in Zurich
What do we know about automated vehicles?
Cost structures?
User preferences?
System impact?
Cost Calculator for automated mobility
Stated preference survey
MATSim simulation
1
2
3
AMoD Cost Calculator

Bösch, P.M., F. Becker, H. Becker and K.W. Axhausen (2018) Cost-based analysis of autonomous mobility services, Transport Policy, 64, 76-91
AMoD Survey
Felix Becker, Institute for Transport Planning and Systems, ETH Zurich.
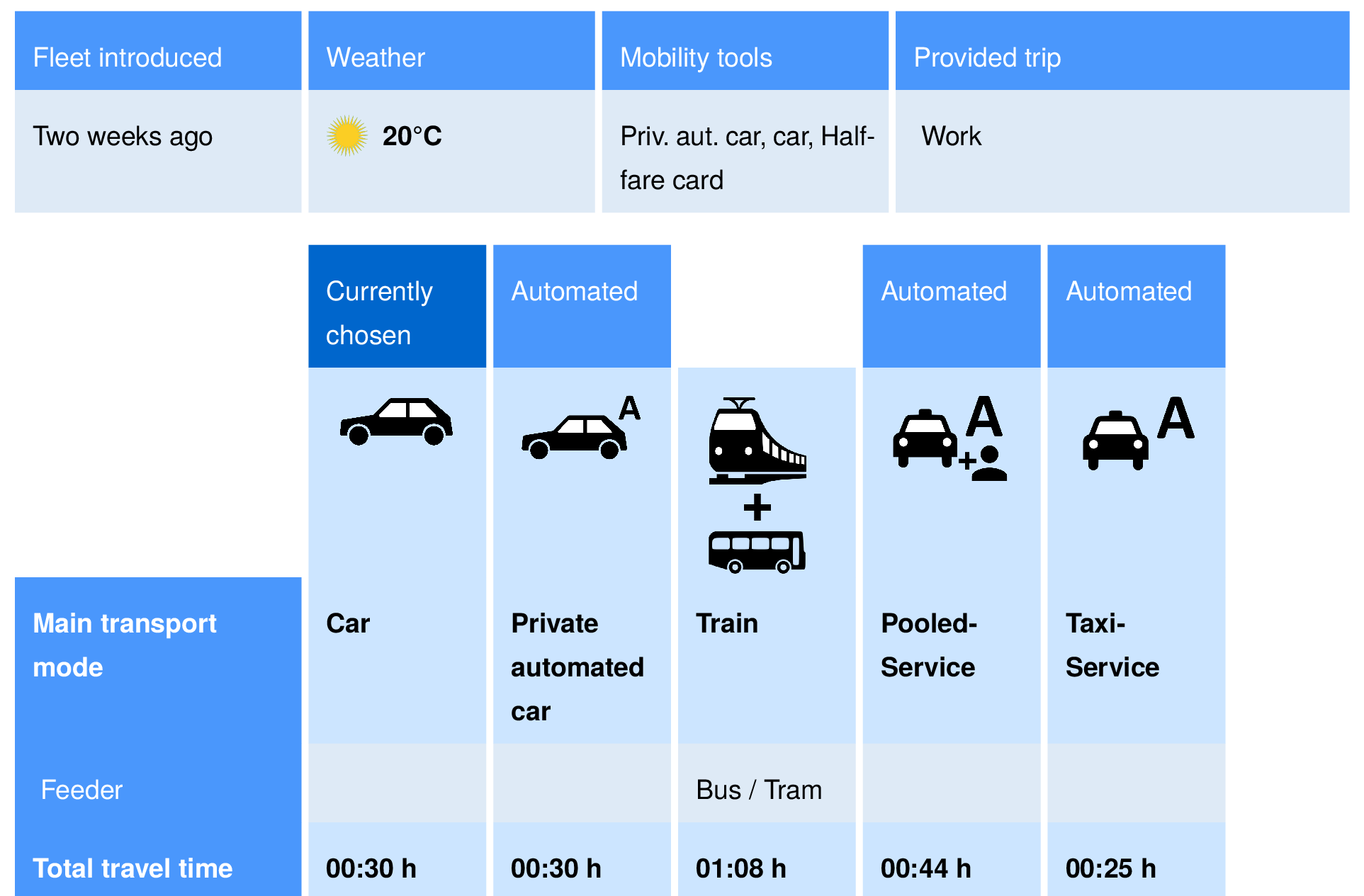
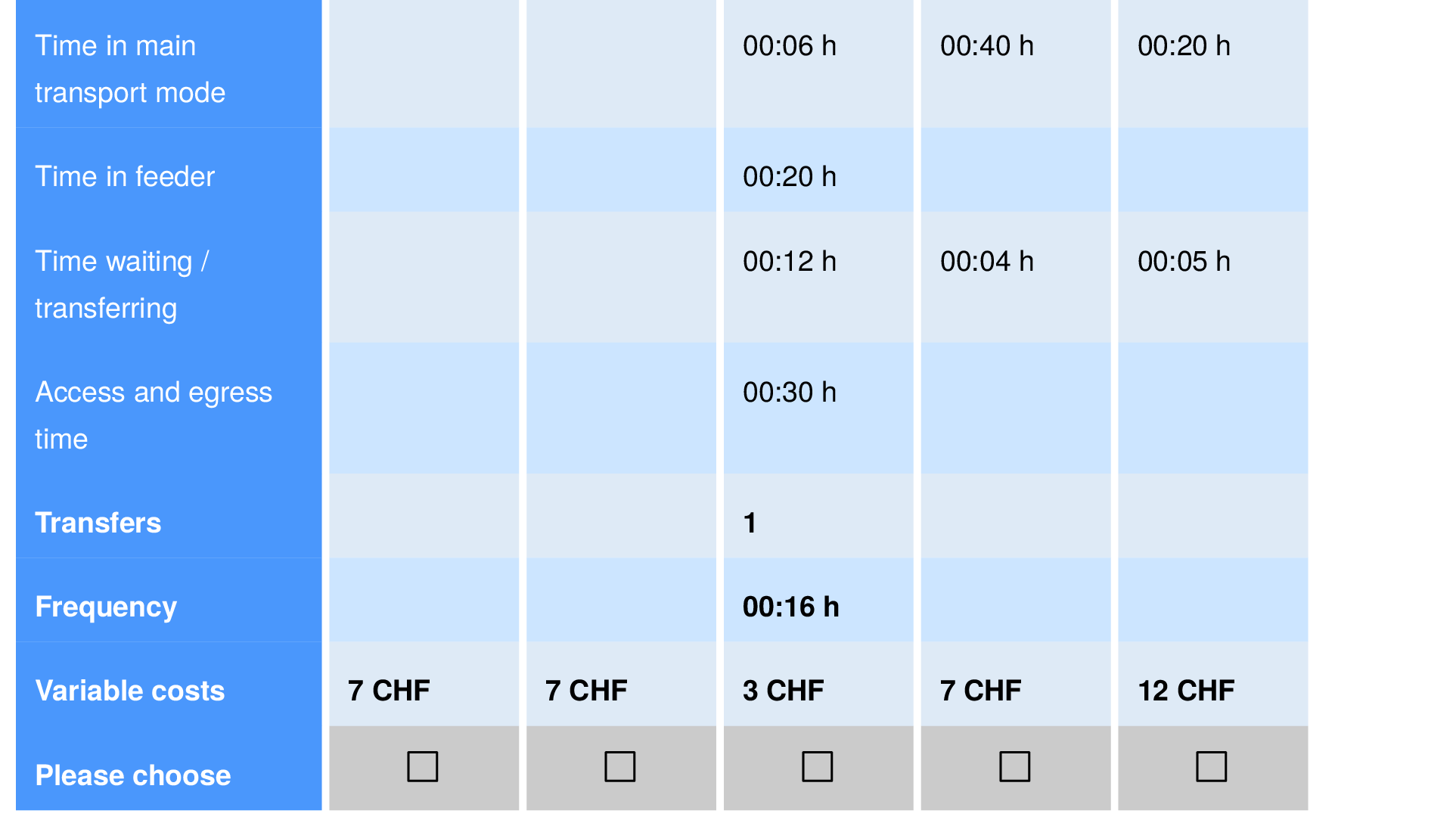
AMoD Survey
Felix Becker, Institute for Transport Planning and Systems, ETH Zurich.




AMoD Survey
AMoD Survey



13 CHF/h
AMoD
Taxi
19 CHF/h
Conventional
Car
12 CHF/h
Public
Transport
VTTS
Car by Adrien Coquet from the Noun Project
Bus by Simon Farkas from the Noun Project
Wait by ibrandify from the Noun Project
AMoD
AMoD Survey
Car by Adrien Coquet from the Noun Project
Bus by Simon Farkas from the Noun Project
Wait by ibrandify from the Noun Project



13 CHF/h
AMoD
Taxi
19 CHF/h
Conventional
Car
12 CHF/h
Public
Transport
VTTS

21 CHF/h
32 CHF/h
AMoD
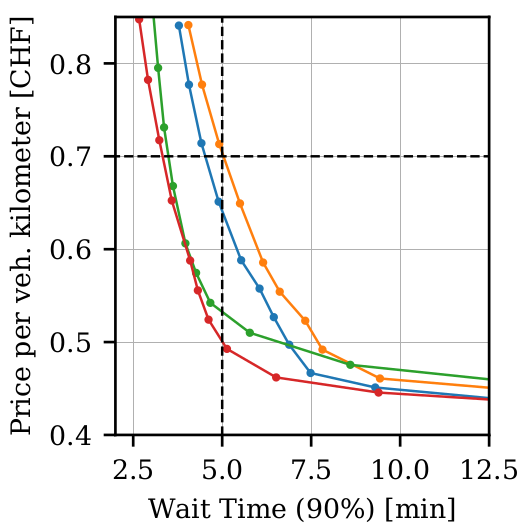
Calibration
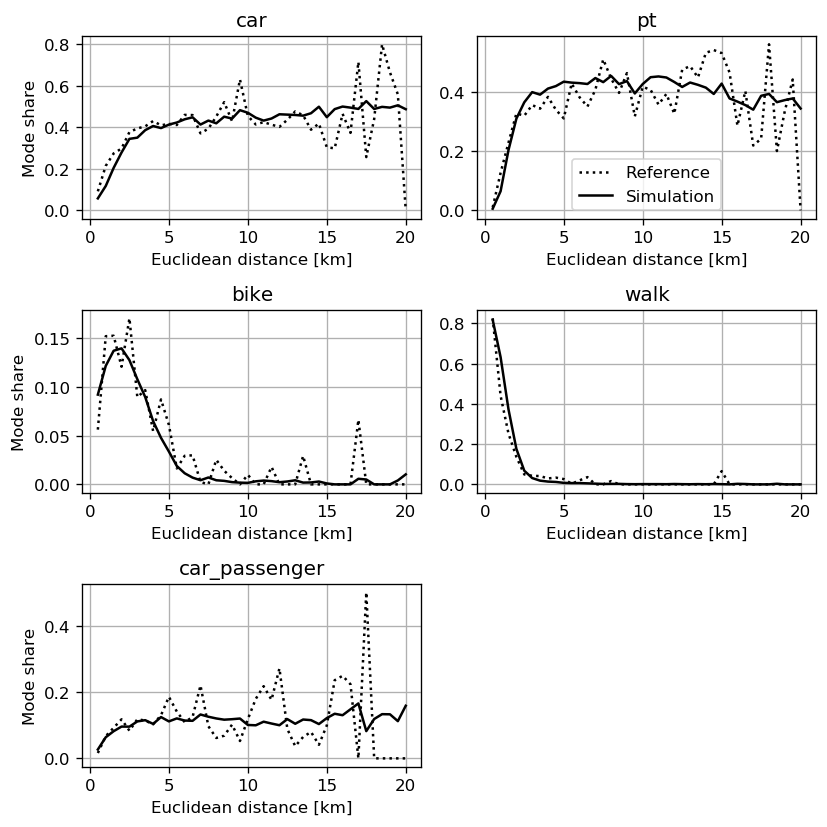
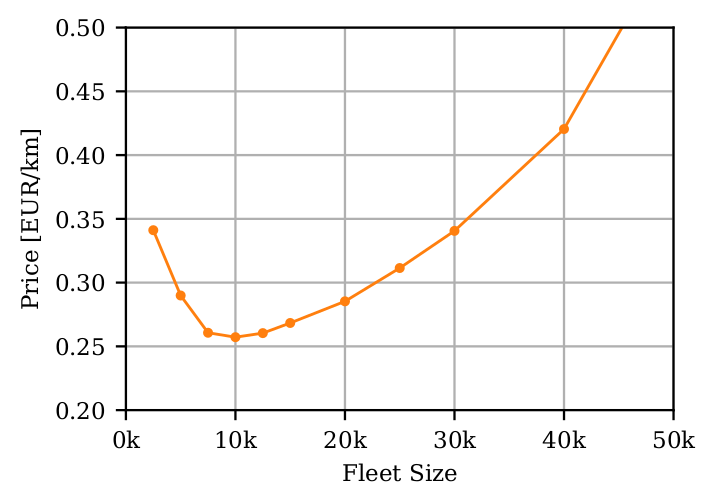
Fleet sizing with dynamic demand
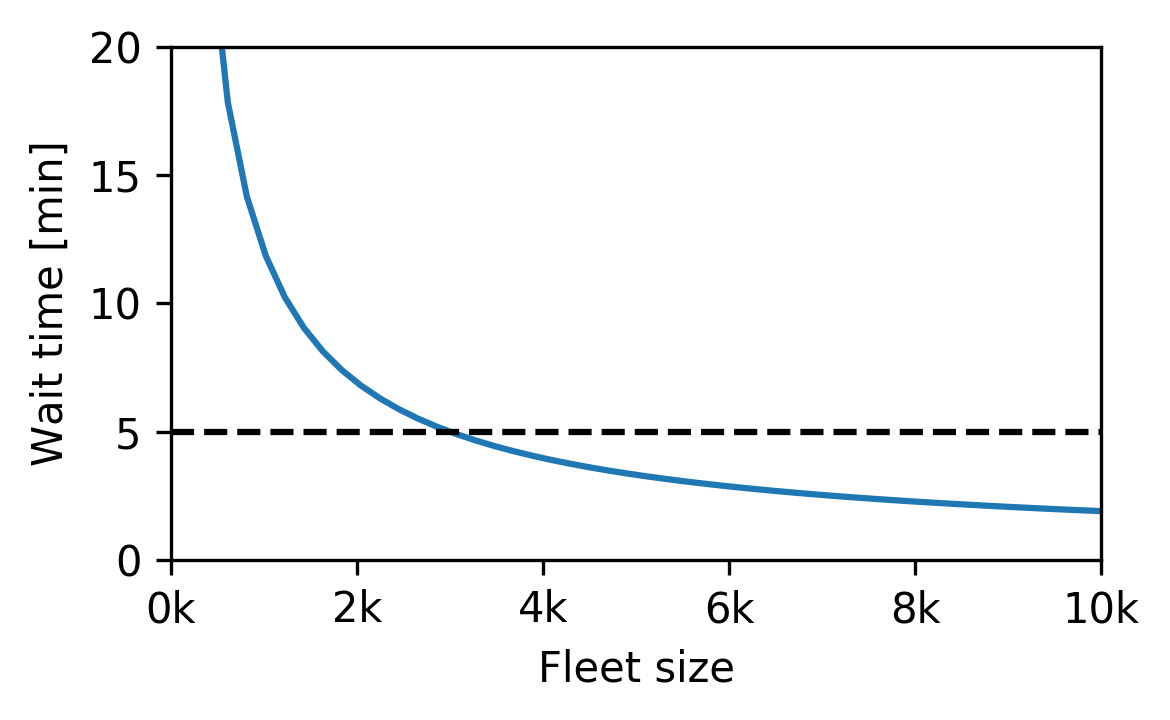


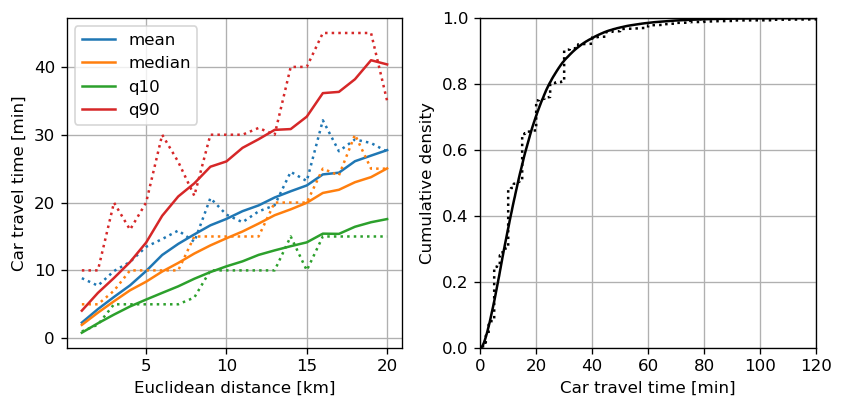
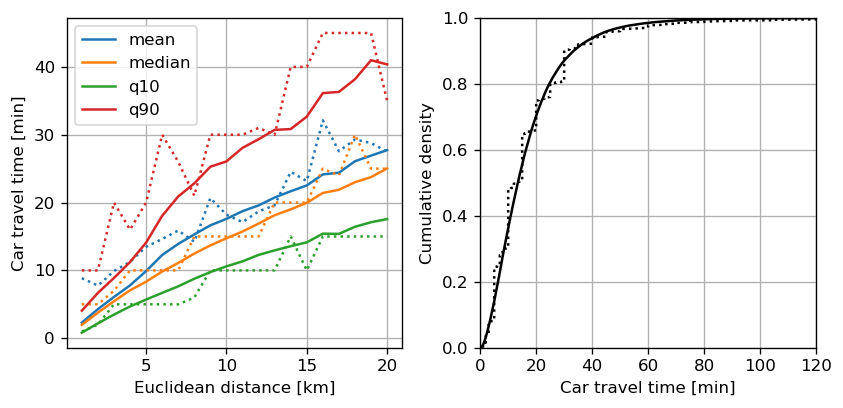
Fleet sizing with dynamic demand

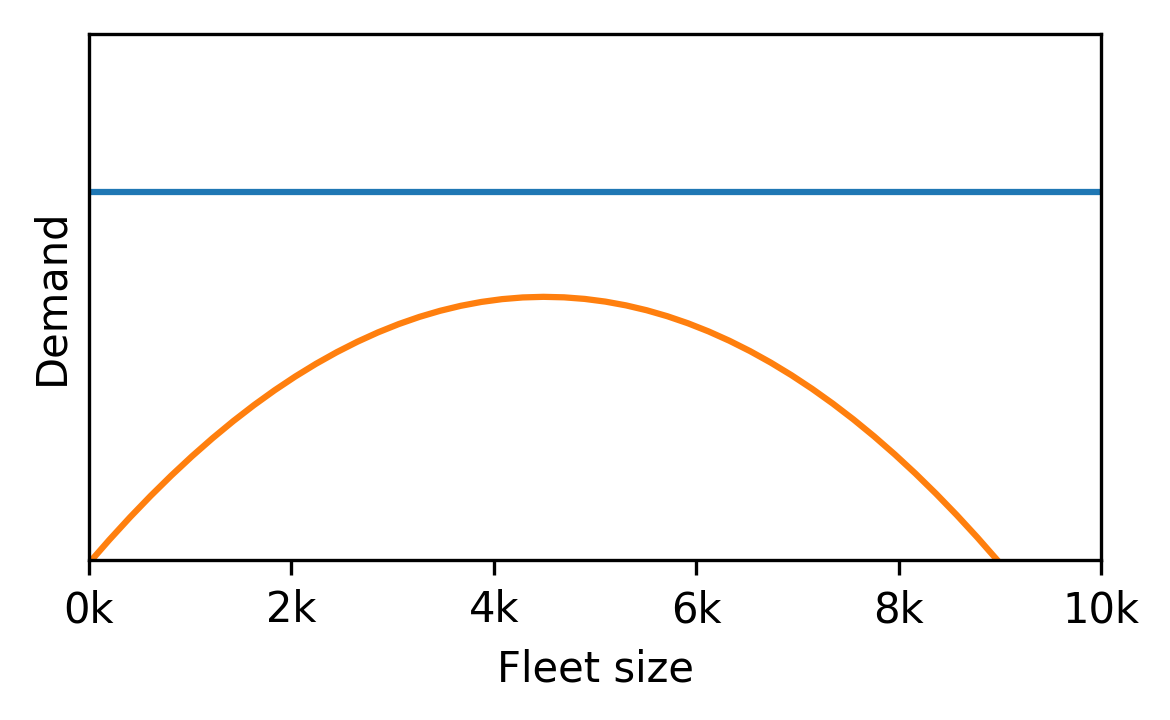
Fleet sizing with dynamic demand
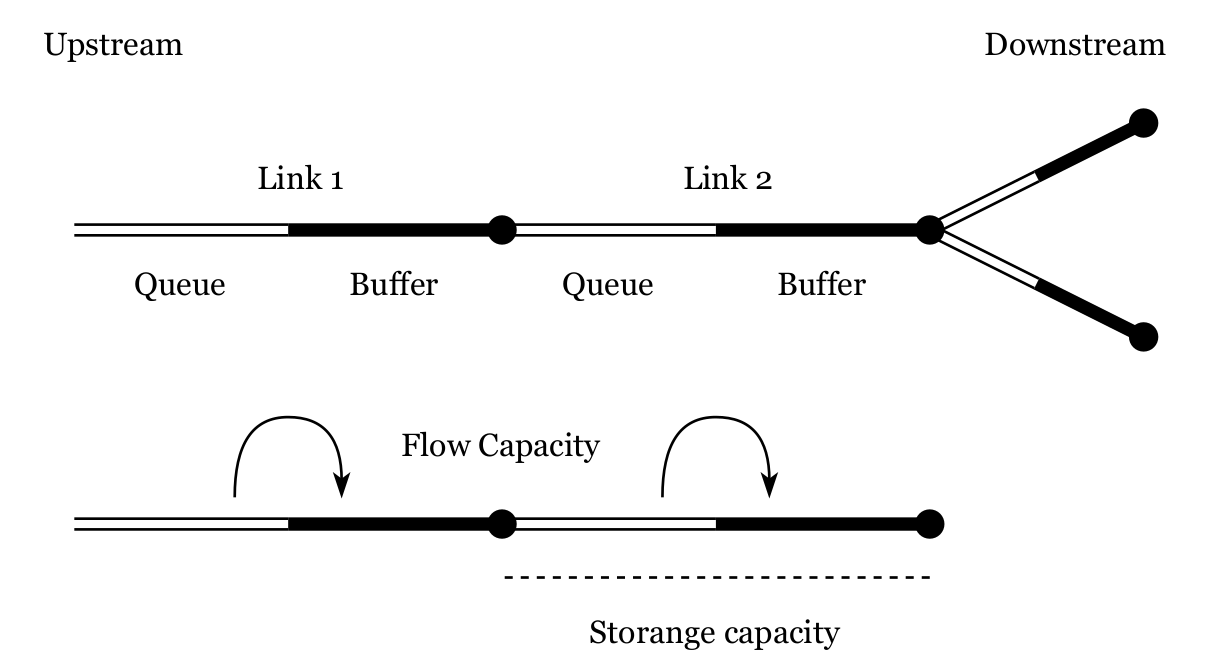
Model structure
Cost calculator
Plan modification
Discrete Mode Choice Extension
Mobility simulation
Prediction
Price
Trips
- Utilization
- Empty distance, ...
- Travel times
- Wait times, ...
Visualisation
Automated taxi
Pickup
Dropoff
Hörl, S., F. Becker and K.W. Axhausen (2020) Automated Mobility on Demand: A comprehensive simulation study of cost, behaviour and system impact for Zurich
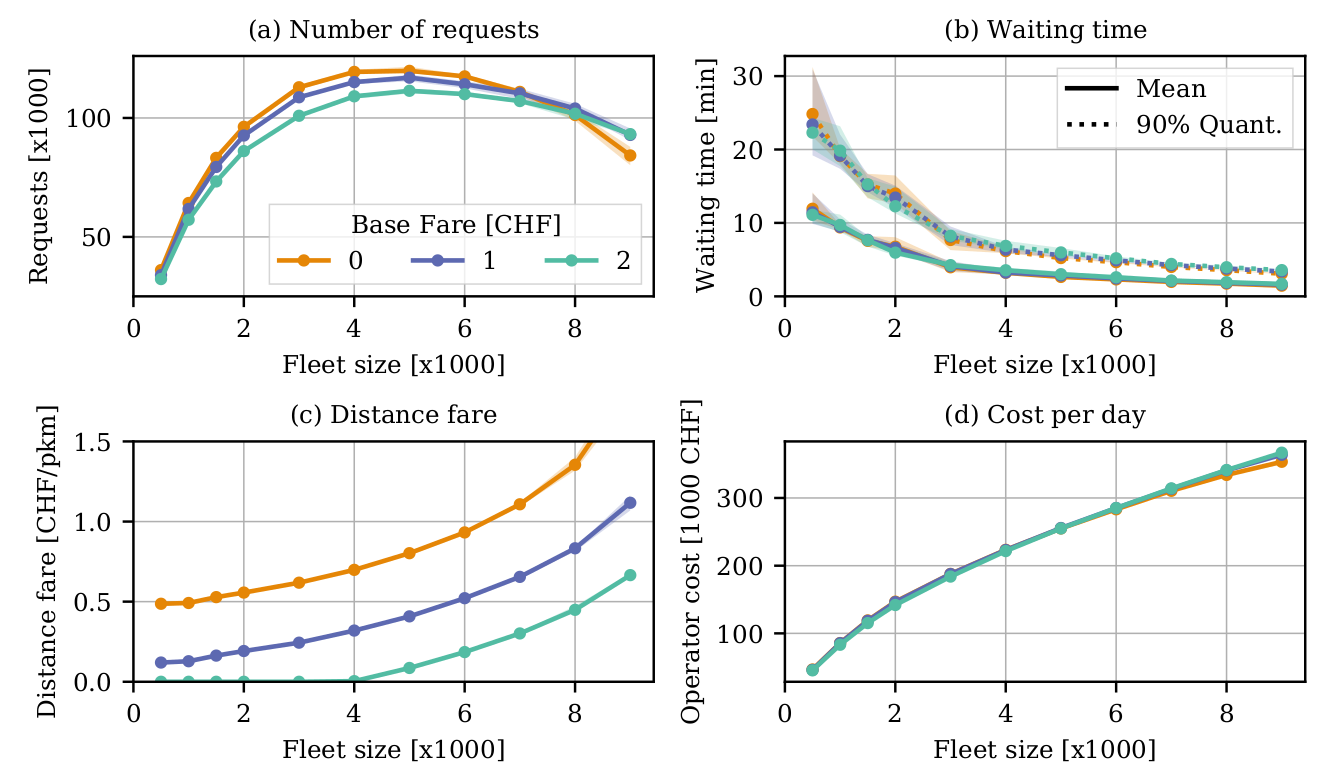
Hörl, S., F. Becker and K.W. Axhausen (2020) Automated Mobility on Demand: A comprehensive simulation study of cost, behaviour and system impact for Zurich
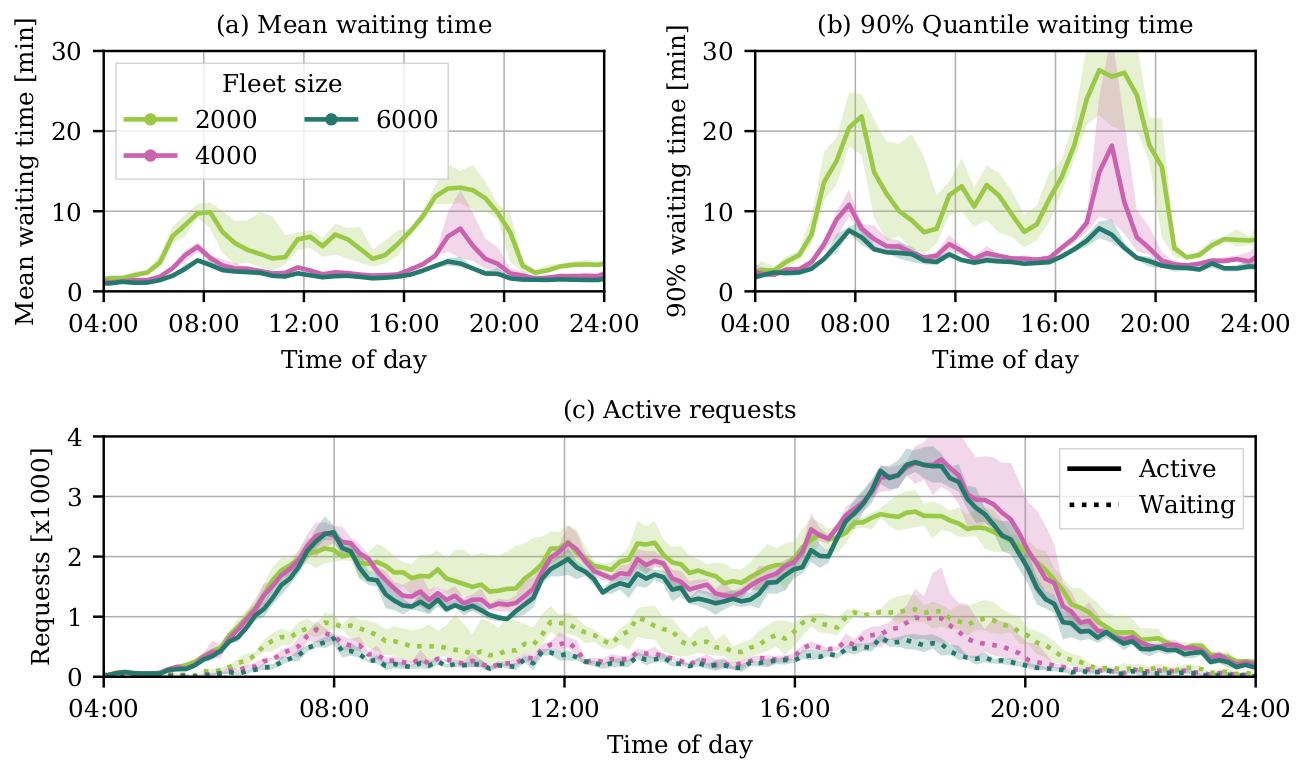
Hörl, S., F. Becker and K.W. Axhausen (2020) Automated Mobility on Demand: A comprehensive simulation study of cost, behaviour and system impact for Zurich
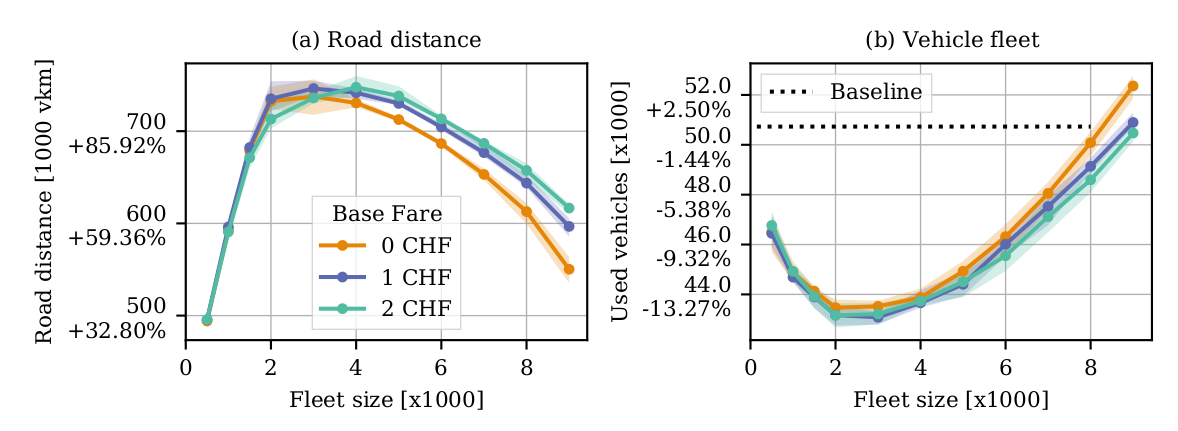
13% reduction in vehicles
100% increase in VKT
Fleet control
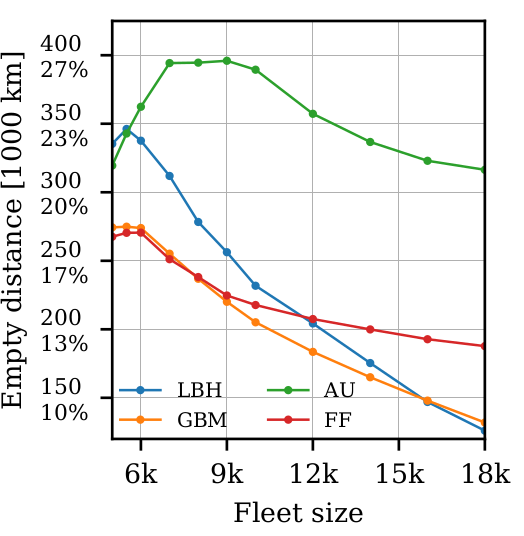
Hörl, S., C. Ruch, F. Becker, E. Frazzoli and K.W. Axhausen (2019) Fleet operational policies for automated mobility: a simulation assessment for Zurich, Transportation Research: Part C, 102, 20-32.
Fleet control
Load-balancing heuristic
Simple heuristic, fast runtime
Gloal Euclidean Bipartite Matching
Standard algorithm in Operations Research





?
?
Assignment
Car by Adrien Coquet from the Noun Project
Hail by Bradley Avison from the Noun Project
Example algorithms
Load-balancing heuristic
Undersupply
- More vehicles than requests
- When request pops up
find closest vehicle
Oversupply
- More requests than vehicles
- When vehicle gets available
find closest request

able to serve remote demand



able to serve remote demand


able to serve peek demand
Hörl, S., C. Ruch, F. Becker, E. Frazzoli and K.W. Axhausen (2019) Fleet operational policies for automated mobility: a simulation assessment for Zurich, Transportation Research: Part C, 102, 20-32.
Example algorithms
Global Bipartite Matching








- Find matching of vehicles and requests that minimizes total Euclidean (or network-based) empty distance
- Nice benchmark because sole objective is to minimize empty distance
Hörl, S., C. Ruch, F. Becker, E. Frazzoli and K.W. Axhausen (2019) Fleet operational policies for automated mobility: a simulation assessment for Zurich, Transportation Research: Part C, 102, 20-32.
Fleet control
Feedforward Fluidic Optimal Rebalancing Policy
Linear program matching a priori known trip rates
Adaptive Uniform Rebalancing Policy
Linear program distributing vehicles uniformly


Car by Adrien Coquet from the Noun Project
Hail by Bradley Avison from the Noun Project


?
?
?
?
Redistribution
Example algorithms
Feed-forward fluidic rebalancing strategy
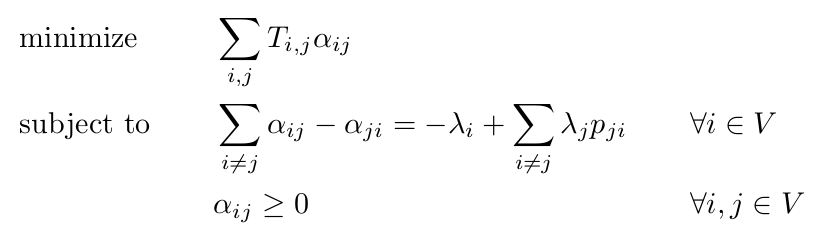
Travel time
Rebalancing flows
Arrival rate
Transition probability

Hörl, S., C. Ruch, F. Becker, E. Frazzoli and K.W. Axhausen (2019) Fleet operational policies for automated mobility: a simulation assessment for Zurich, Transportation Research: Part C, 102, 20-32.
Example algorithms
Feed-forward fluidic rebalancing strategy
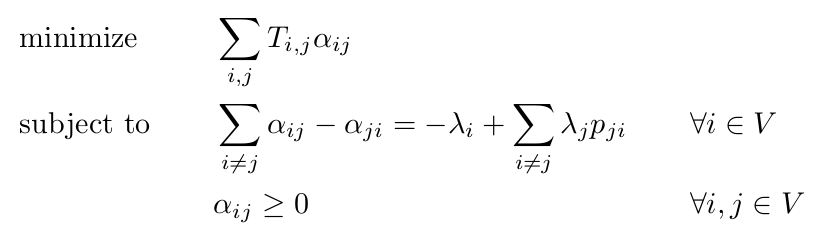
Travel time
Rebalancing flows
Arrival rate
Transition probability
- Informed algorithm from historical data
- Minimization of rebalancing time
- Minimization of waiting time?
Hörl, S., C. Ruch, F. Becker, E. Frazzoli and K.W. Axhausen (2019) Fleet operational policies for automated mobility: a simulation assessment for Zurich, Transportation Research: Part C, 102, 20-32.
Example algorithms
Adaptive Uniform Rebalancing Policy

Vehicles per zone
Current requests
- Minimization of rebalancing time
- Working on current information
- Uniform distribution of vehicles
Hörl, S., C. Ruch, F. Becker, E. Frazzoli and K.W. Axhausen (2019) Fleet operational policies for automated mobility: a simulation assessment for Zurich, Transportation Research: Part C, 102, 20-32.
III. Paris Scenario
https://pixabay.com/en/paris-eiffel-tower-night-city-view-3296269/
Two components = eqasim
Population synthesis
Travel demand synthesis
Mobility simulation
(MATSim)
- Framework to easily set up runnable MATSim (and other) simulations
- Collection of open source tools and algorithms for transport simulation
- Focus on process from raw data to final results for reproducible research
- Increase interoperability of models
Data
Analysis
The case of Île-de-France

Census data
Récensement de la population








RP
Icons on this and following slides: https://fontawesome.com // Background: Simunto VIA
The case of Île-de-France

Dispositif sur les revenus localisés sociaux et fiscaux
Income tax data

RP










FiLo
SoFi
The case of Île-de-France

RP: Flux de mobilité
Commuting data

RP



RP
Mob

FiLoSoFi






The case of Île-de-France
Enquête globale de transport
Household Travel Survey

RP
EGT

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

Enquête national transports et deplacements
Household Travel Survey
ENTD













The case of Île-de-France
Enquête globale de transport
Household Travel Survey

RP
EGT

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

Enquête national transports et deplacements
Household Travel Survey
ENTD










The case of Île-de-France
SIRENE
Enterprise census

RP
S

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob


EGT

ENTD










BD-TOPO
Address database
BD

The case of Île-de-France

RP

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

EGT

ENTD

SIRENE
Person ID
Age
Gender
Home (X,Y)
1
43
male
(65345, ...)
2
24
female
(65345, ...)
3
9
female
(65345, ...)


BD-TOPO
The case of Île-de-France

RP

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

EGT

ENTD

SIRENE
Person ID
Activity
Start
End
Loc.
523
home
08:00
(x,y)
523
work
08:55
18:12
(x,y)
523
shop
19:10
19:25
(x,y)
523
home
19:40
(x,y)

Person ID
Mode
Start
End
523
Public T.
08:55
523
Public T.
18:12
19:10
523
Walking
19:25
19:40
08:00

BD-TOPO
The case of Île-de-France
OpenStreetMap
Road network

RP
OSM

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob


EGT

ENTD
IDFm GTFS
Public transport schedule
GTFS


SIRENE

OSM

GTFS


BD-TOPO
The case of Île-de-France

RP

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

EGT

ENTD

SIRENE

OSM

GTFS


BD-TOPO
The case of Île-de-France

RP

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

EGT

ENTD

BPE

OSM

GTFS

DCM

The case of Île-de-France

RP

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

EGT

ENTD

BPE

OSM

GTFS

DCM
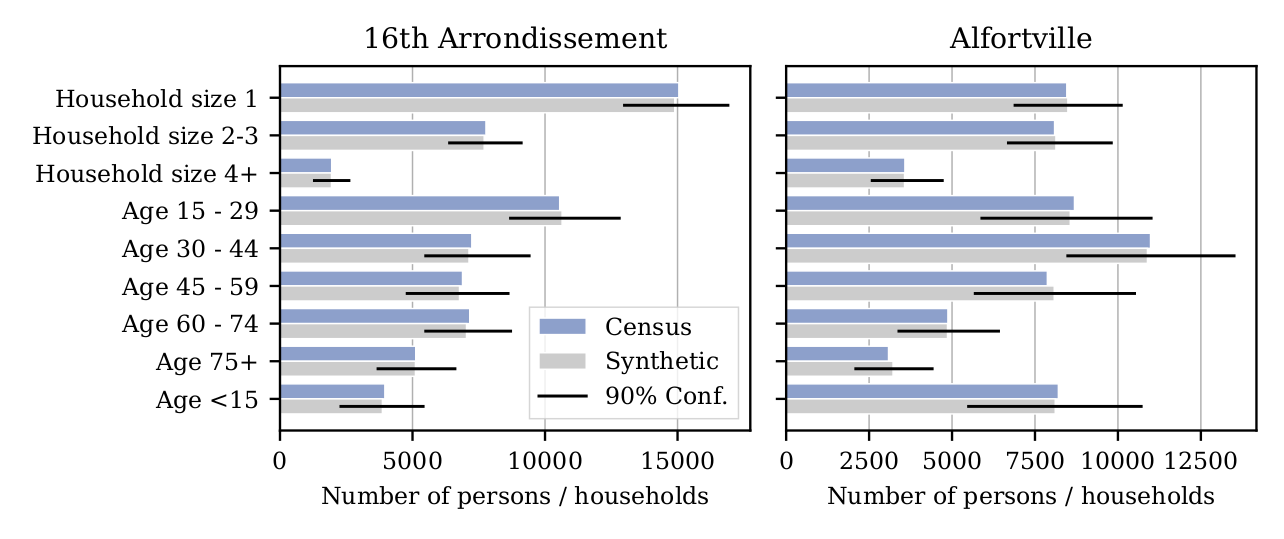
The case of Île-de-France

RP

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

EGT

ENTD

BPE

OSM

GTFS

DCM
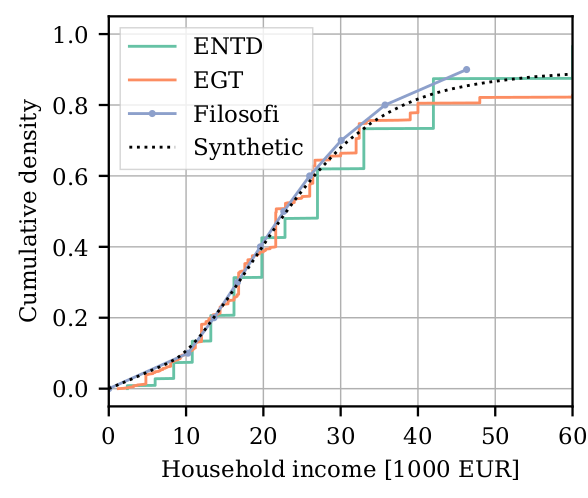
The case of Île-de-France

RP

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

EGT

ENTD

BPE

OSM

GTFS

DCM

The case of Île-de-France

RP

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

EGT

ENTD

BPE

OSM

GTFS

DCM

The case of Île-de-France
Open
Data


Open
Software
+
=
Reproducible research
Verifiable results
Integrated testing
- Detailed documentation of whole open-source pipeline is under preparation

RP

FiLoSoFi

RP Mob

EGT

ENTD

SIRENE

OSM

GTFS

BD-TOPO
IV. French use cases

The case of Île-de-France
CO2 Emmissions
The case of Île-de-France
Grand Paris Express
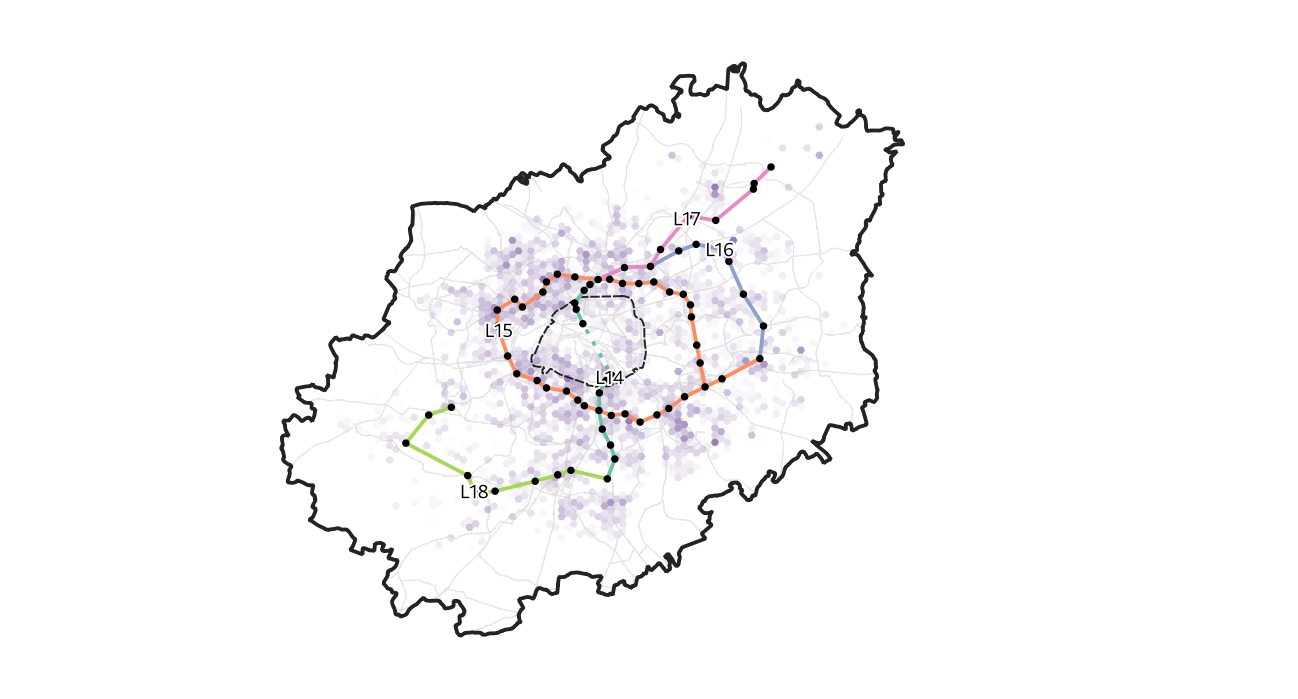
AMoD in Paris
Hörl, S., M. Balac and K.W. Axhausen (2019) Dynamic demand estimation for an AMoD system in Paris, paper presented at the 30th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, June 2019, Paris, France.
Travel Behaviour
Zurich model, calibrated
for Paris population
Cost sturcture
Adapted from Berlin
AMoD Simulation
Load-balancing heuristic
AMoD in Paris
Hörl, S., M. Balac and K.W. Axhausen (2019) Dynamic demand estimation for an AMoD system in Paris, paper presented at the 30th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, June 2019, Paris, France.
Travel Behaviour
Zurich model, calibrated
for Paris population
Cost sturcture
Adapted from Berlin
AMoD Simulation
Load-balancing heuristic
Maximum static demand: 2.3M trips
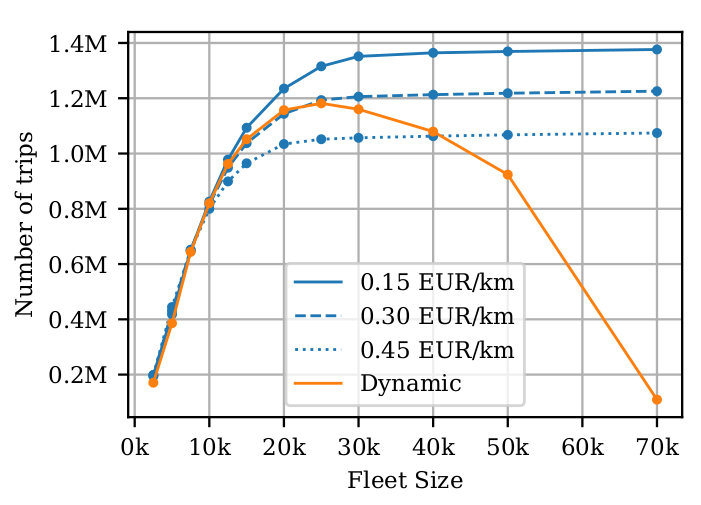
AMoD in Paris
Hörl, S., M. Balac and K.W. Axhausen (2019) Dynamic demand estimation for an AMoD system in Paris, paper presented at the 30th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, June 2019, Paris, France.
Travel Behaviour
Zurich model, calibrated
for Paris population
Cost sturcture
Adapted from Berlin
AMoD Simulation
Load-balancing heuristic
Maximum static demand: 2.3M trips
V. French community
Current use cases




Current use cases

Nantes (Univ Eiffel)
- Population synthesis
- Noise modelling
Current use cases
Lille (IMT Lille Douai)
- Park & ride applications

Current use cases
Toulouse (Odyssee)
- Shared offices

Current use cases
Paris / Île-de-France
- New mobility solutions for the quarter (LVMT / GRETTIA)
- Bicycle simulation (IFPen)
- Automated shuttles
(IRT SystemX)

Current use cases
Lyon (IRT SystemX)
- First / Last Mile Delivery


Thank you!
Questions ?

Contact: sebastian.horl@irt-systemx.fr

Exploring the system impact of automated taxis via simulation
By Sebastian Hörl
Exploring the system impact of automated taxis via simulation
CentraleSupélec, 17 May 2021
- 1,105



