

LEAD Living Lab Demo: Lyon
Sebastian Hörl
13 December 2021
Lyon Living Lab

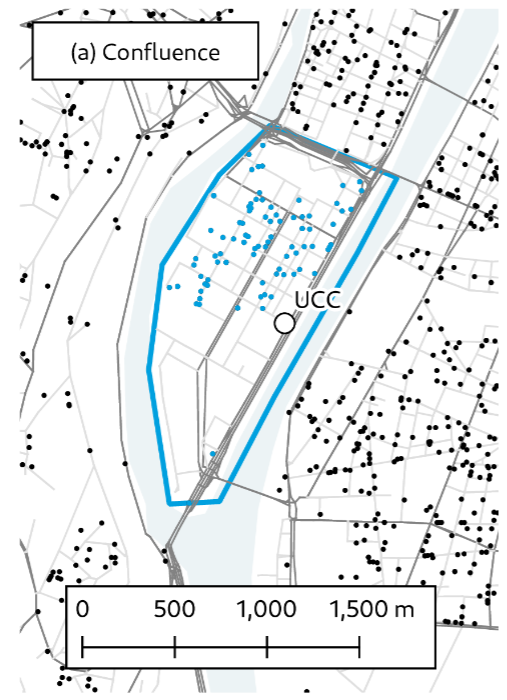
- Peninsula Confluence between Saône and Rhône
- Interesting use case as there are limited access points
- Implementation of an urban consolidation center (UCC) to collect the flow of goods and organize last-mile distribution
- using cargo-bikes
- using electric robots
- and others
- Analysis and modeling through
- Flow estimation through cameras
- Simulation of future scenarios
- Focus on parcel deliveries due to data availability

Modeling methodology

- Main question: What is the impact on traffic and population of implementing an Urban Consolidation Center in Confluence?
- Focus on B2C parcel deliveries due to data availability

Modeling methodology

Agent-based simulation of Lyon
- Main question: What is the impact on traffic and population of implementing an Urban Consolidation Center in Confluence?
- Focus on B2C parcel deliveries due to data availability

Modeling methodology

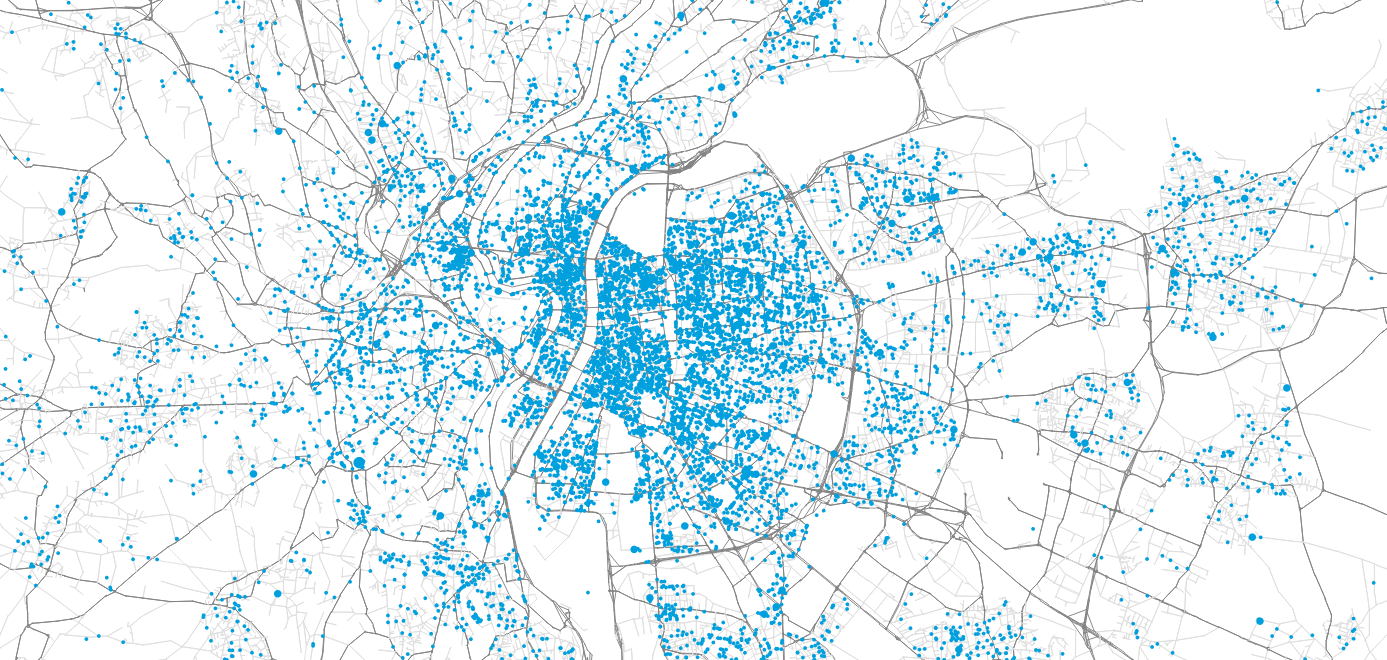
Agent-based simulation of Lyon
Demand in parcel deliveries
- Main question: What is the impact on traffic and population of implementing an Urban Consolidation Center in Confluence?
- Focus on B2C parcel deliveries due to data availability

Modeling methodology


Agent-based simulation of Lyon
Demand in parcel deliveries
- Main question: What is the impact on traffic and population of implementing an Urban Consolidation Center in Confluence?
- Focus on B2C parcel deliveries due to data availability


Route optimization


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)
National HTS (ENTD)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
Methodology: Synthetic travel demand


EDGT
Synthetic travel demand has been generated for Lyon in order to perform agent-based mobility simulation of all residents' movements.


Methodology: Synthetic travel demand
Open
Data


Open
Software
+
=
Reproducible research
Integrated testing

Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)
National HTS (ENTD)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)


EDGT
Synthetic travel demand has been generated for Lyon in order to perform agent-based mobility simulation of all residents' movements.


Methodology: Synthetic travel demand

Open
Software
=
Reproducible research
Integrated testing
Paper published July 2021
Open
Data


Open
Software
+
=
Reproducible research
Integrated testing

Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)
National HTS (ENTD)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)


EDGT
Synthetic travel demand has been generated for Lyon in order to perform agent-based mobility simulation of all residents' movements.

Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
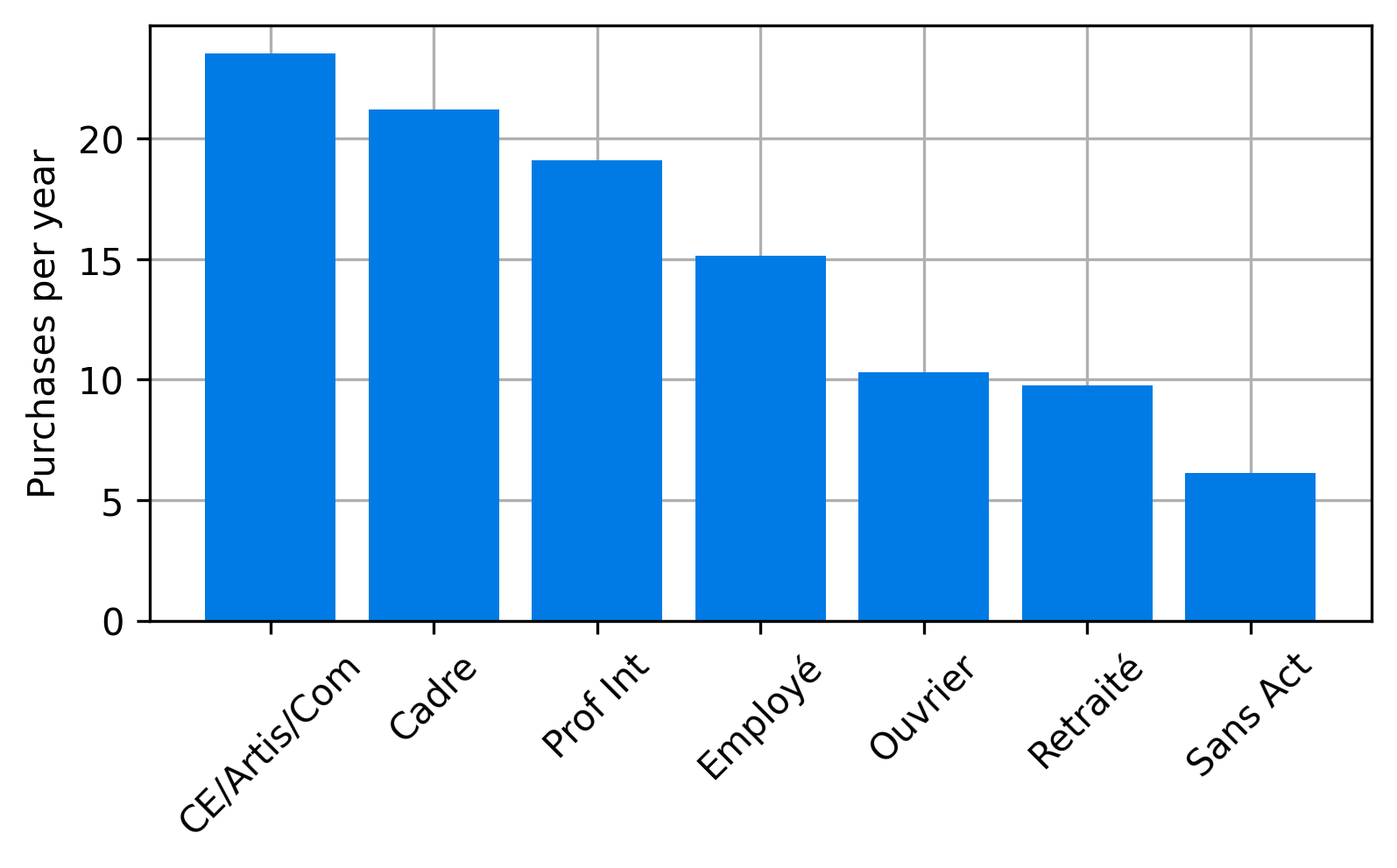
Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.


Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.



Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
Iterative proportional fitting (IFP)
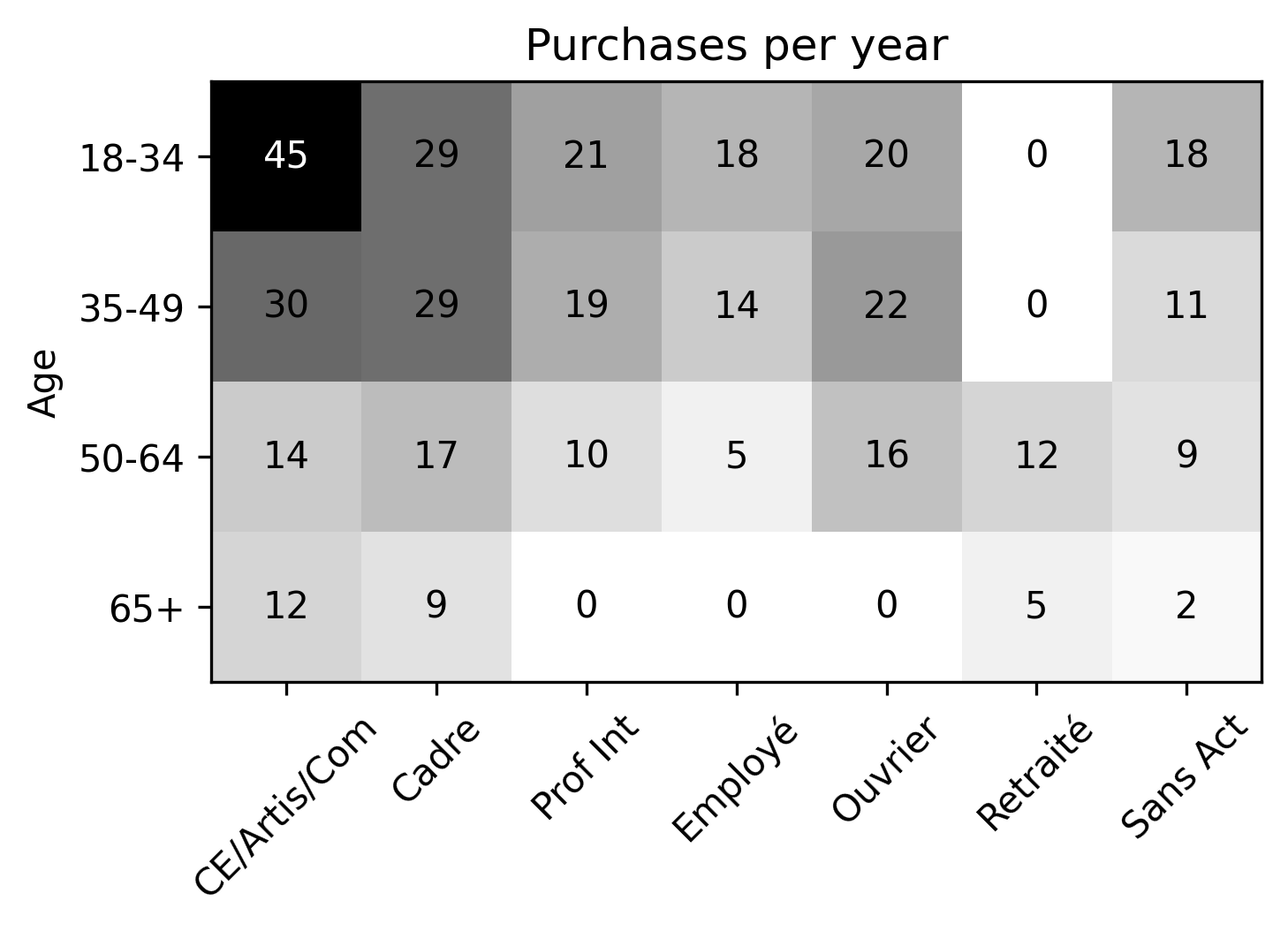
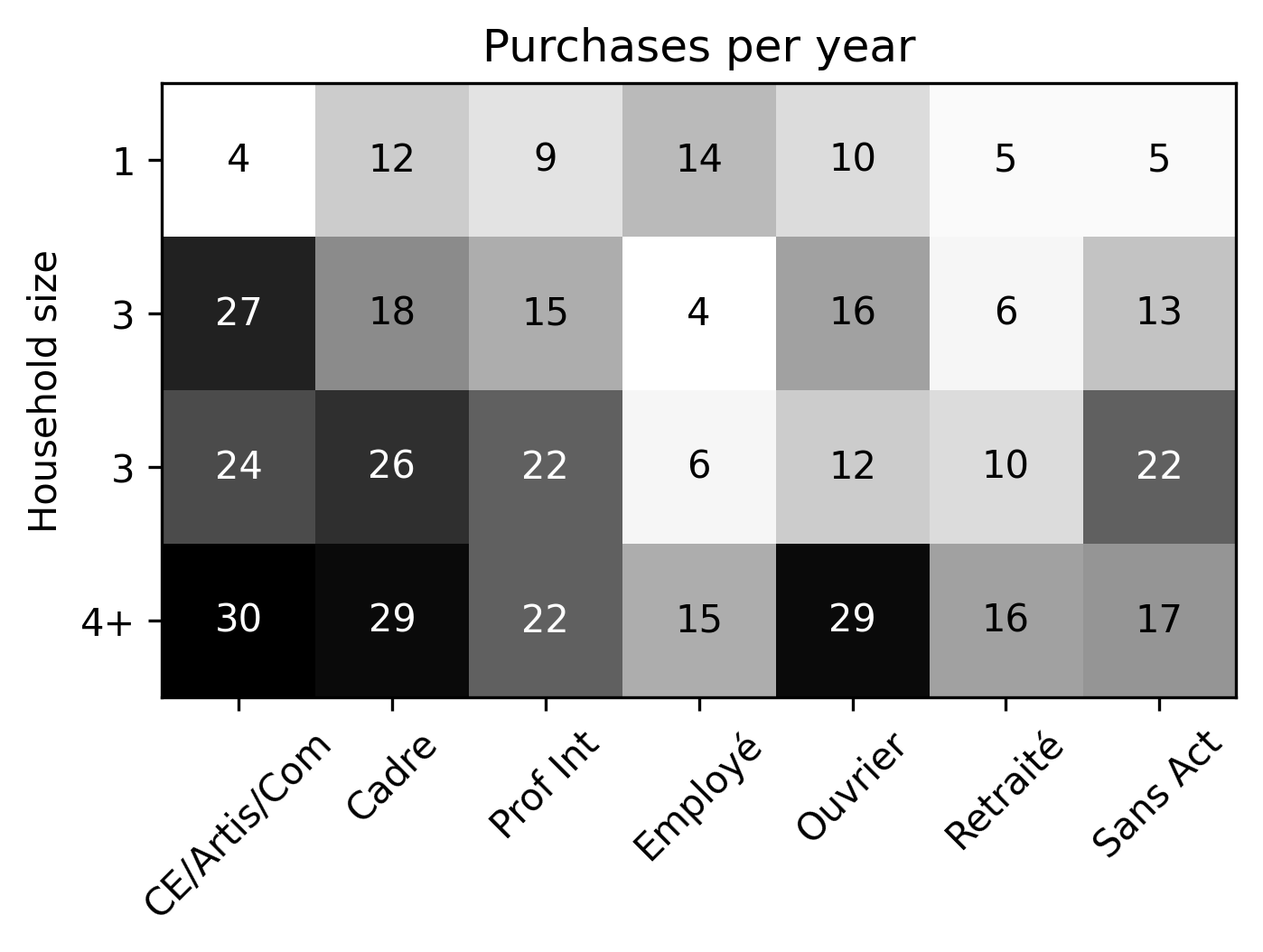
- Based on synthetic population, find average number of purchases delivered to a household defined by socioprofesional class, age of the reference person and household size per day.
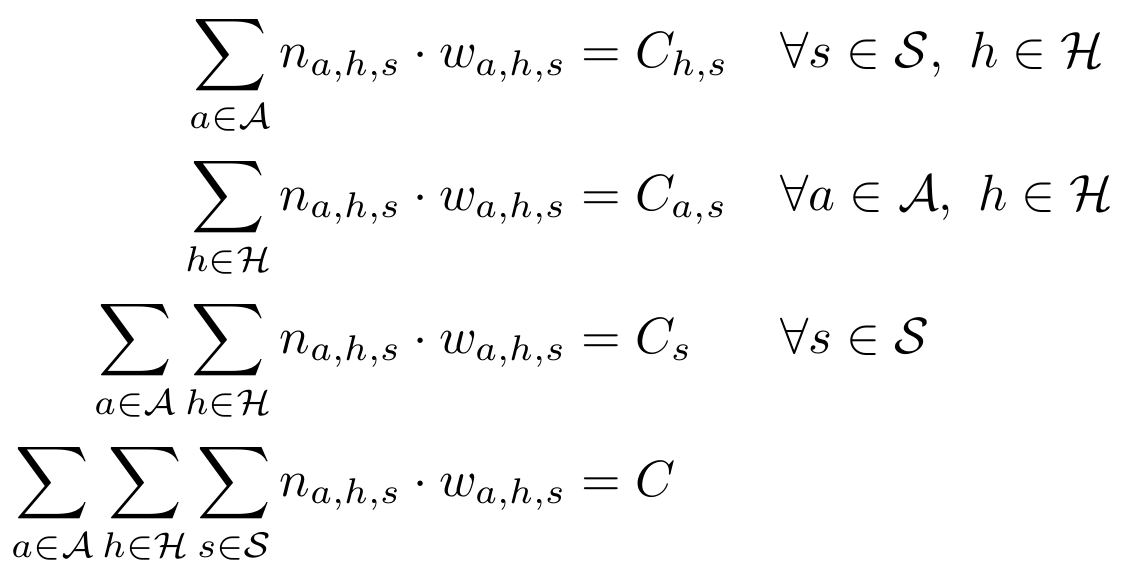
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
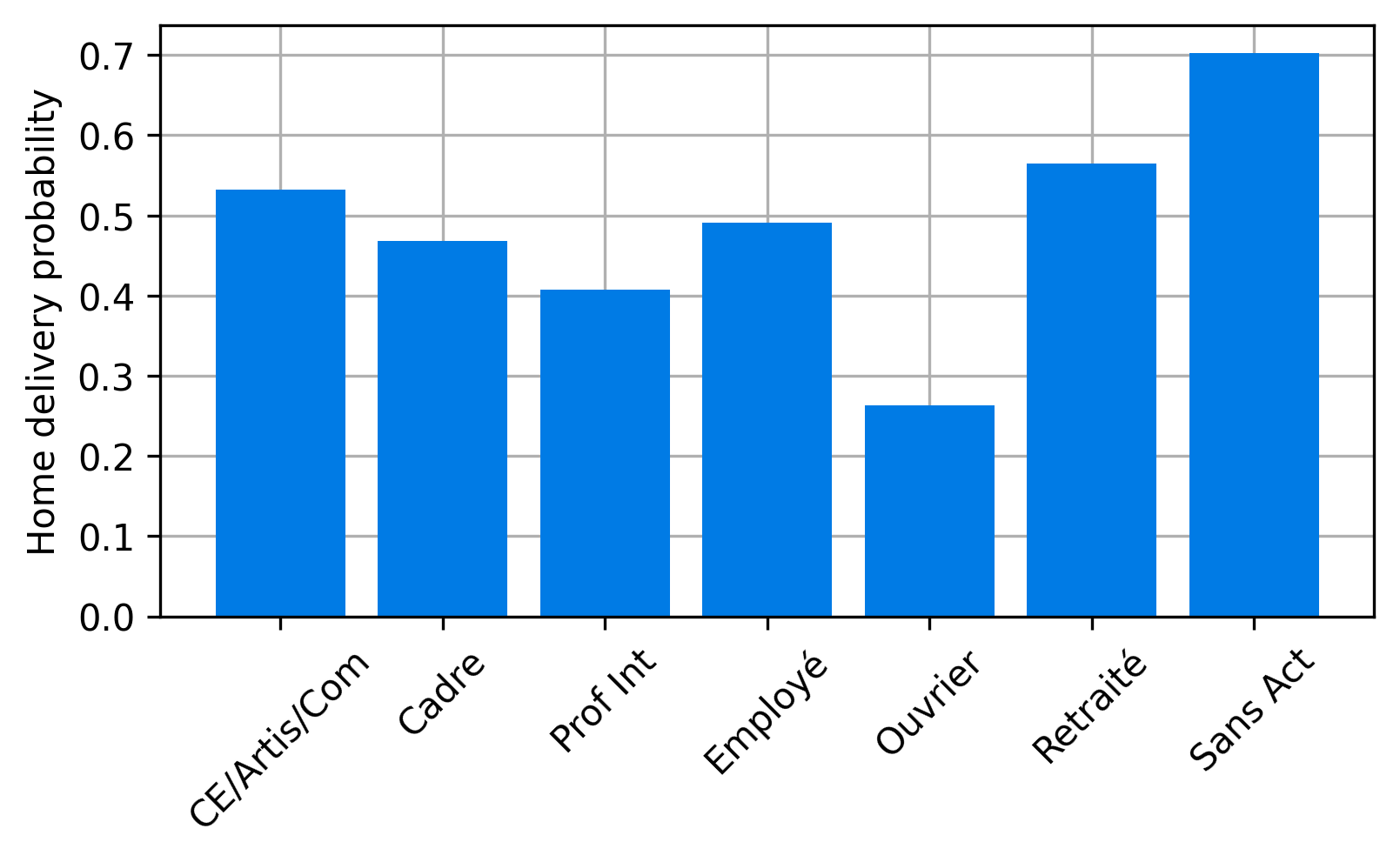
Maximum entropy approach
- We now the average number of parcels, but we do not now the distribution of the number of parcels for a household on an average day.
- We know it must be non-negative, and we know the mean.
- Without additional data, we assume maximum entropy distribution, which is Exponential in this case.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.

Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
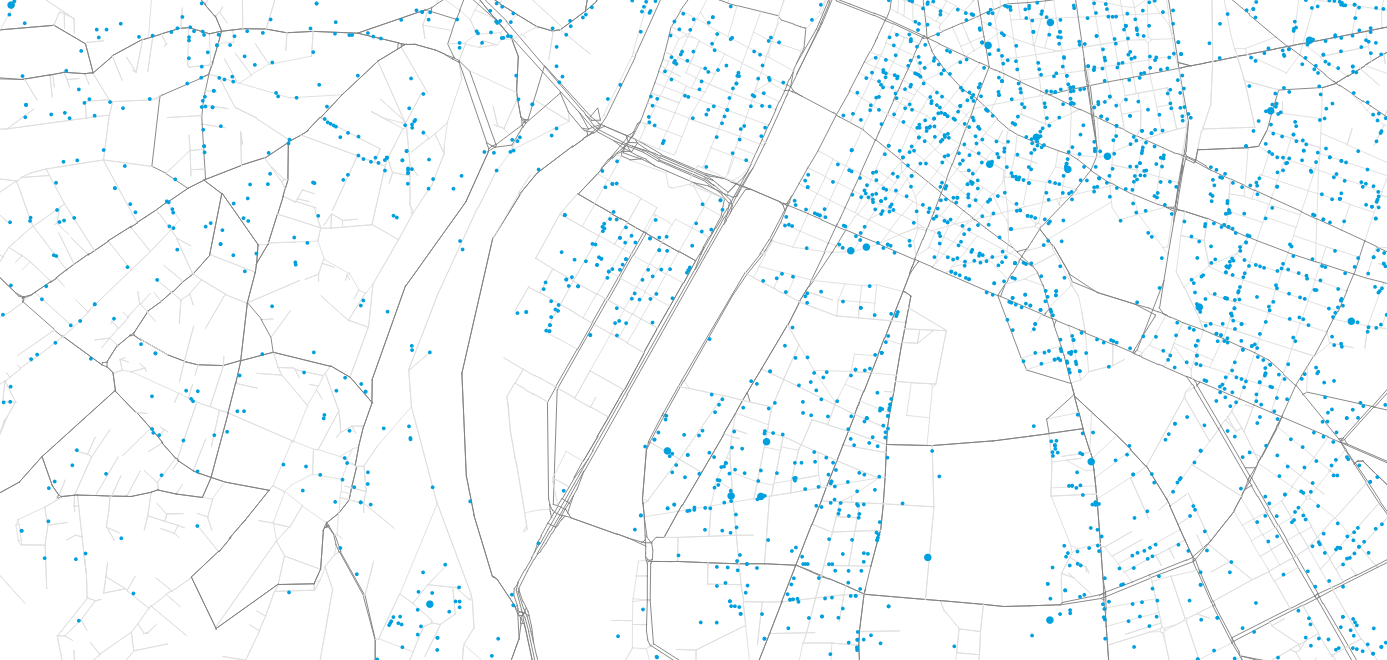
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
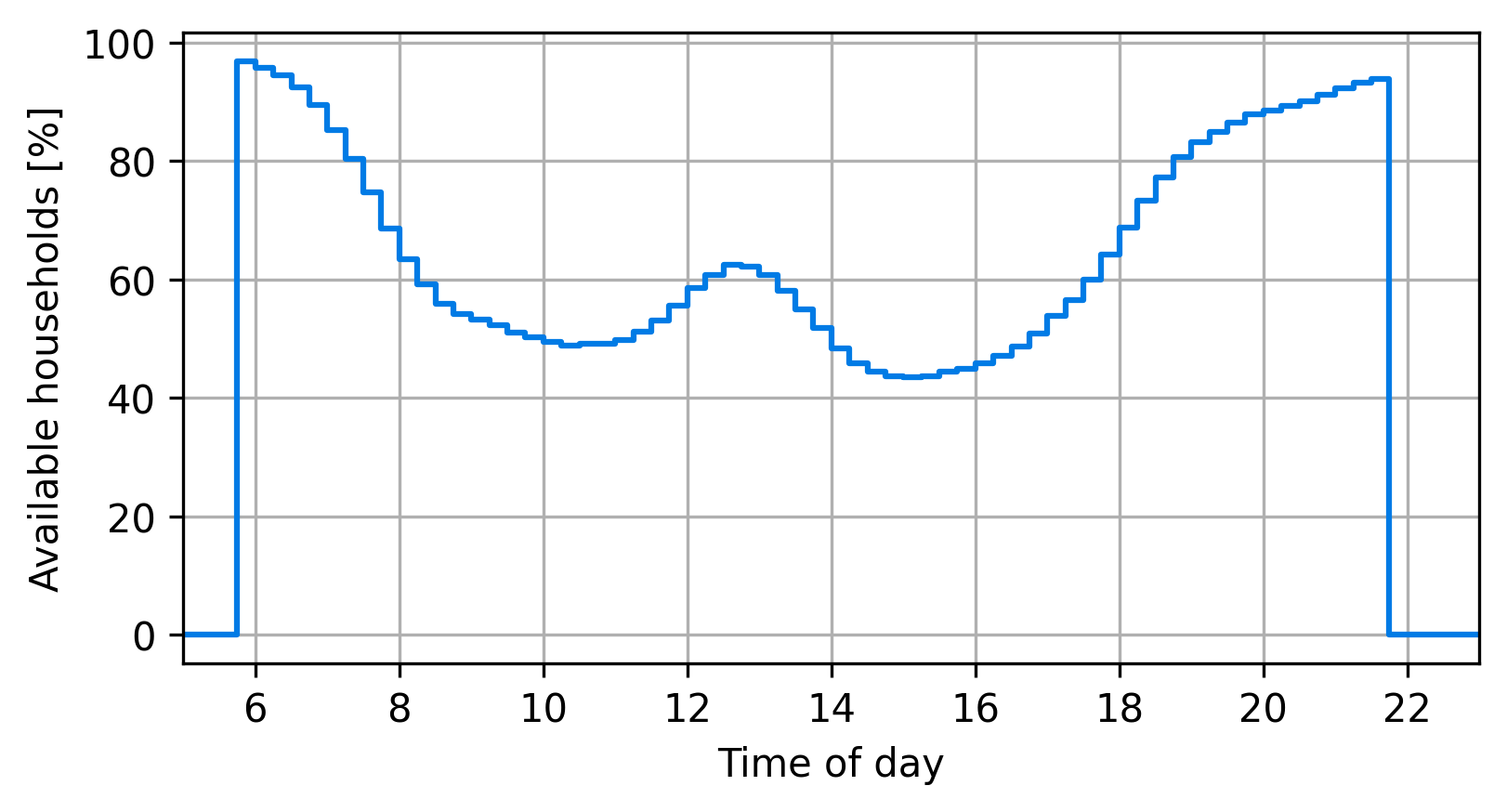
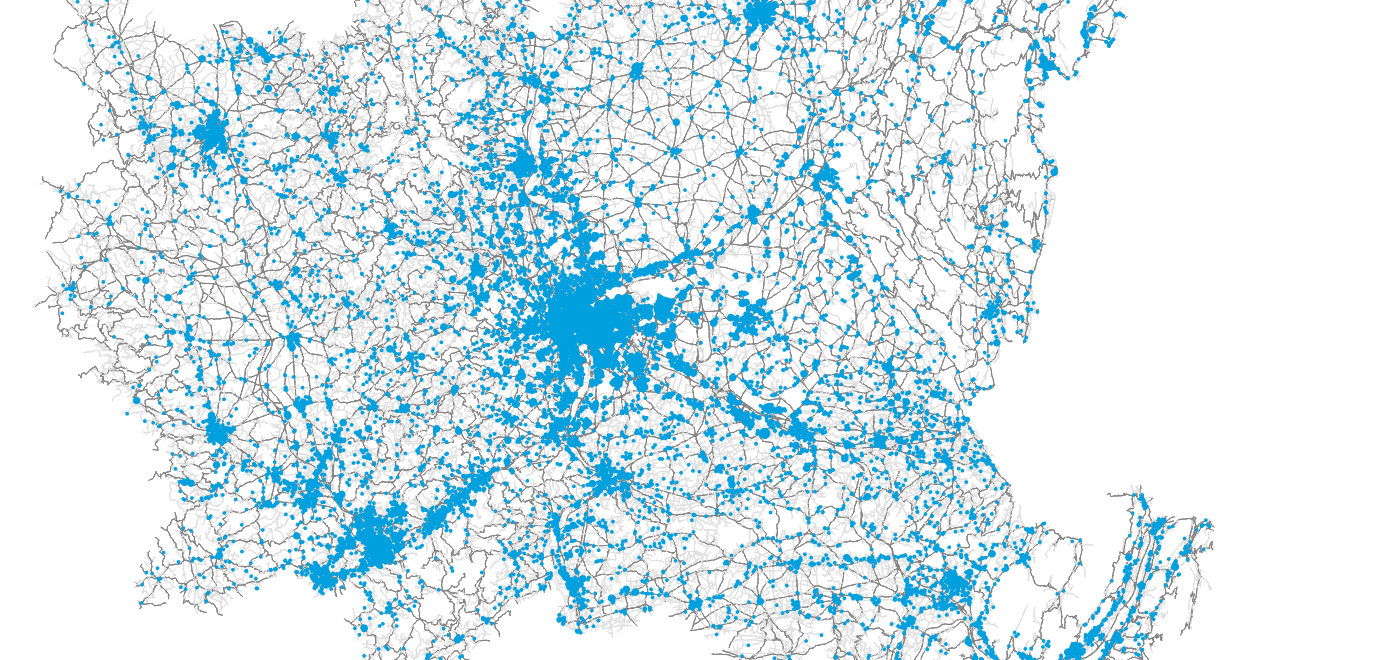
Presence of household members
First case study



Hörl, S. and J. Puchinger (2021) From synthetic population to parcel demand: Modeling pipeline and case study for last-mile deliveries in Lyon, Working paper.
Solve VRP-TW based on generated parcels and household presence
JSprit
First case study


Hörl, S. and J. Puchinger (2021) From synthetic population to parcel demand: Modeling pipeline and case study for last-mile deliveries in Lyon, Working paper.

Solve VRP-TW based on generated parcels and household presence
JSprit
First case study


Hörl, S. and J. Puchinger (2021) From synthetic population to parcel demand: Modeling pipeline and case study for last-mile deliveries in Lyon, Working paper.

Solve VRP-TW based on generated parcels and household presence
JSprit

Main use case for Lyon


List of scenario characteristics


-
Operator
- Per vehicle Types
- Number of vehicles
- Distance covered
- Stops performed (per veh. and driver)
- Vehicle size (capacity)
- Per vehicle Types
-
Scenario
- Number of parcels
- Population size
- Analysis period (1 day)
-
Traffic
- Congestion
- Delays per person (car)
- Average speed
- Occupancy of public space (spatial and temporal)
- Congestion
-
Environmental
- Emissions (CO2, NOx, PM)
- Noise
- Energy consumption
-
Economic
- Number of drivers
- Cost of consolidation center (assumption)
- Cost per vehicle, distance, and time
- Cost per delivery
List of scenario parameters


Policy
- Access restrictions
- Road types
- Area shapes
- Opening hours
- Access fees (for large-scale scenarios)
Consolidation centers
- Number of centers
- Position of centers
Vehicle types
- Electric vans
- Cargo-bikes
- Delivery robots
- Potentially mixed
Vehicle properties
- Capacity
- Speed
Demand
- Population growth
- Share of parcels
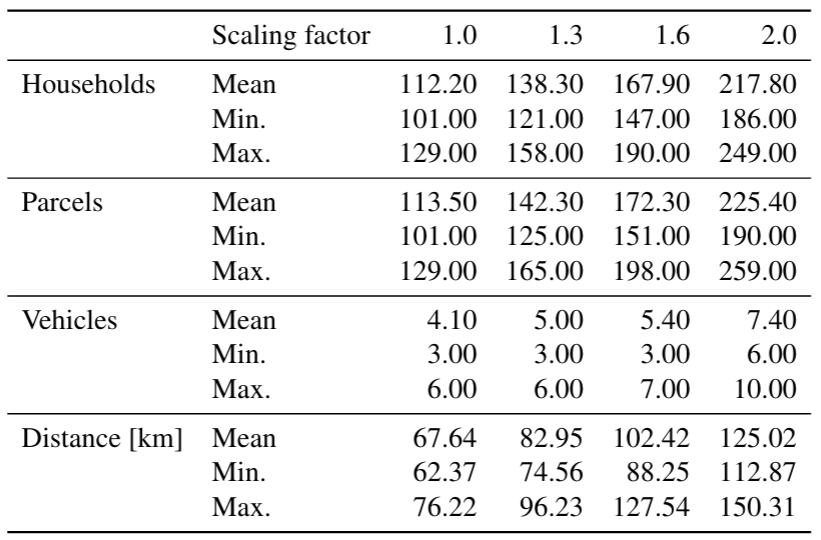
Scaling up: City-wide baseline


Using shares of customer preference, parcels are assigned to operators and the closest distribution centers.

SIRENE: Delivery centers


Advanced use case


Using shares of customer preference, parcels are assigned to operators and the closest distribution centers.

SIRENE: Delivery centers


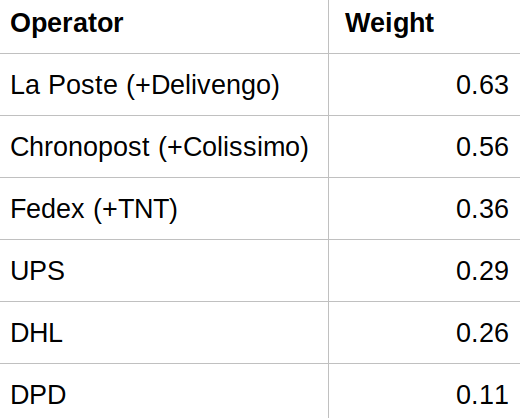
Assignment of parcels to operators based on customer preference survey (sendcloud)
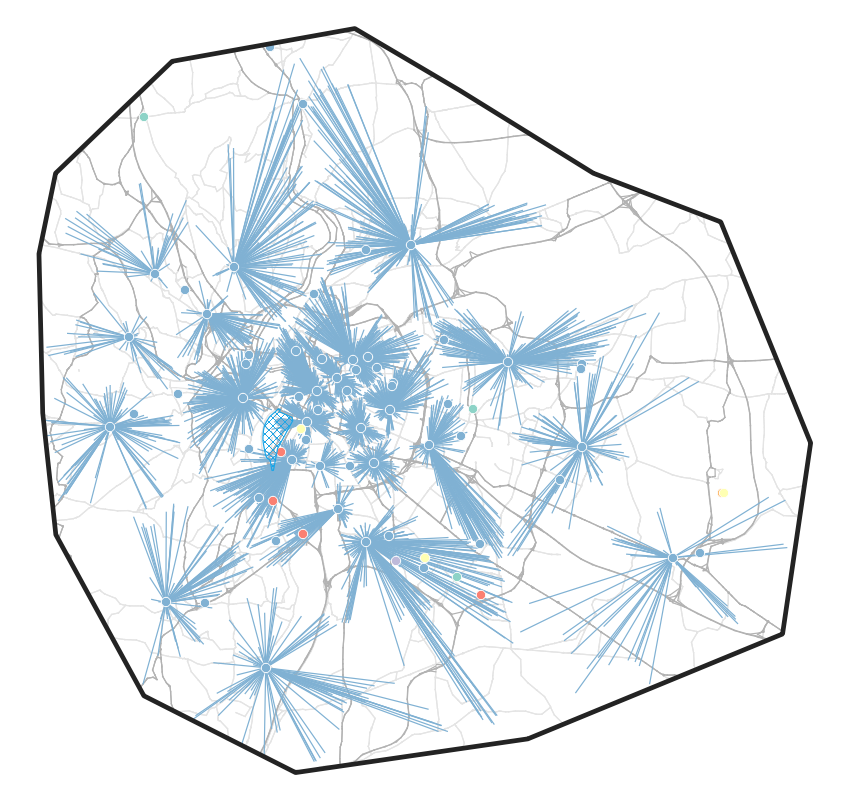
Scaling up: City-wide baseline
Advanced use case


Using shares of customer preference, parcels are assigned to operators and the closest distribution centers.

SIRENE: Delivery centers


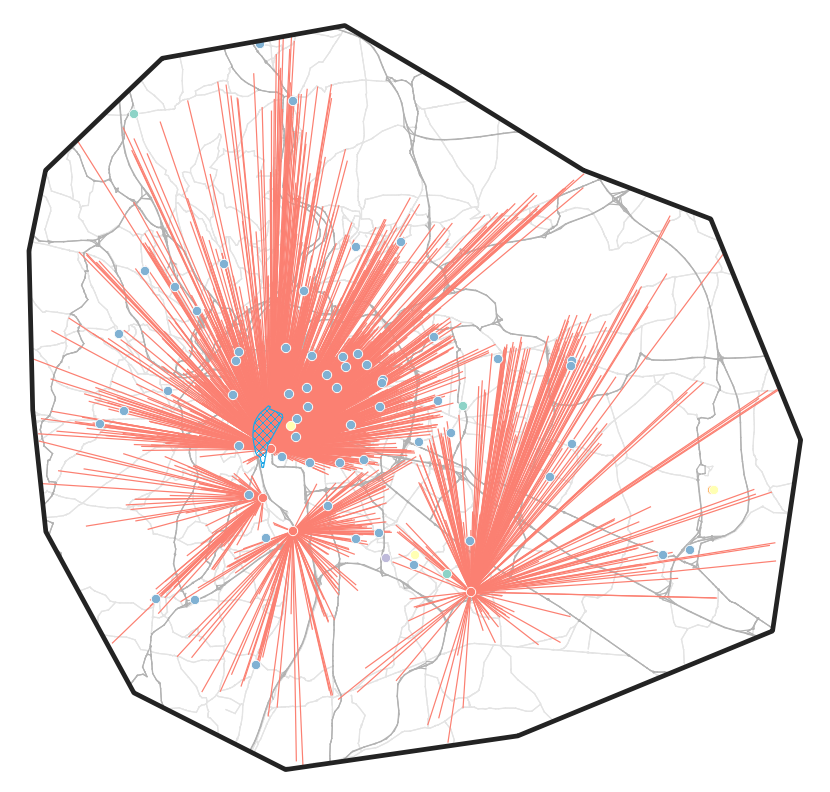
Assignment of parcels to operators based on customer preference survey (sendcloud)

Scaling up: City-wide baseline
Advanced use case


Advanced use case
Scaling up: City-wide baseline

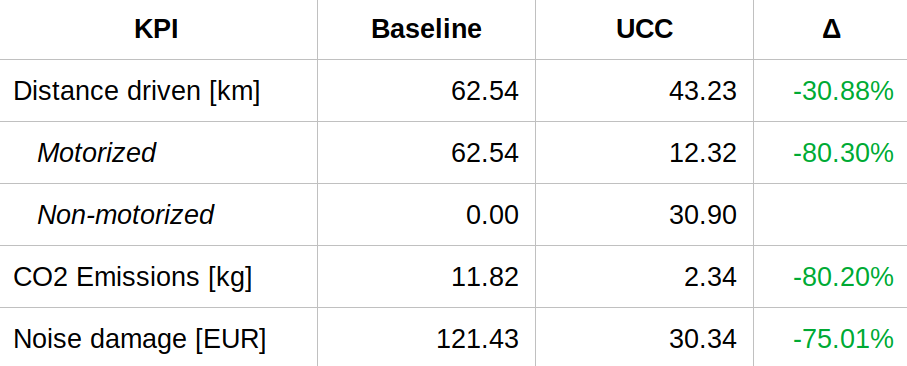
- Estimate on the total distance driven for delivery operations in Lyon
- Allows us to cut out a better baseline scenario for Confluence


Advanced use case 2
Experimental: MATSim and MASS-GT
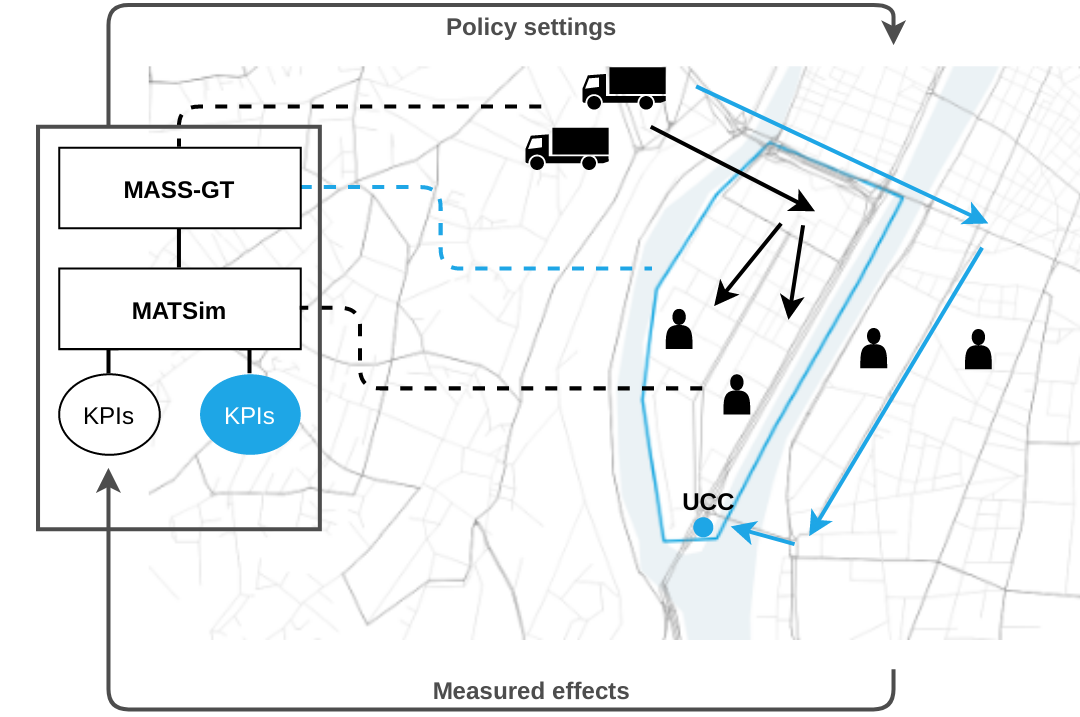
- Simulation of Lyon (and Rhônes-Alpes) with influence of traffic, including freight traffic
- Simulation of shipper behaviour (B2C and B2B)


Technical description
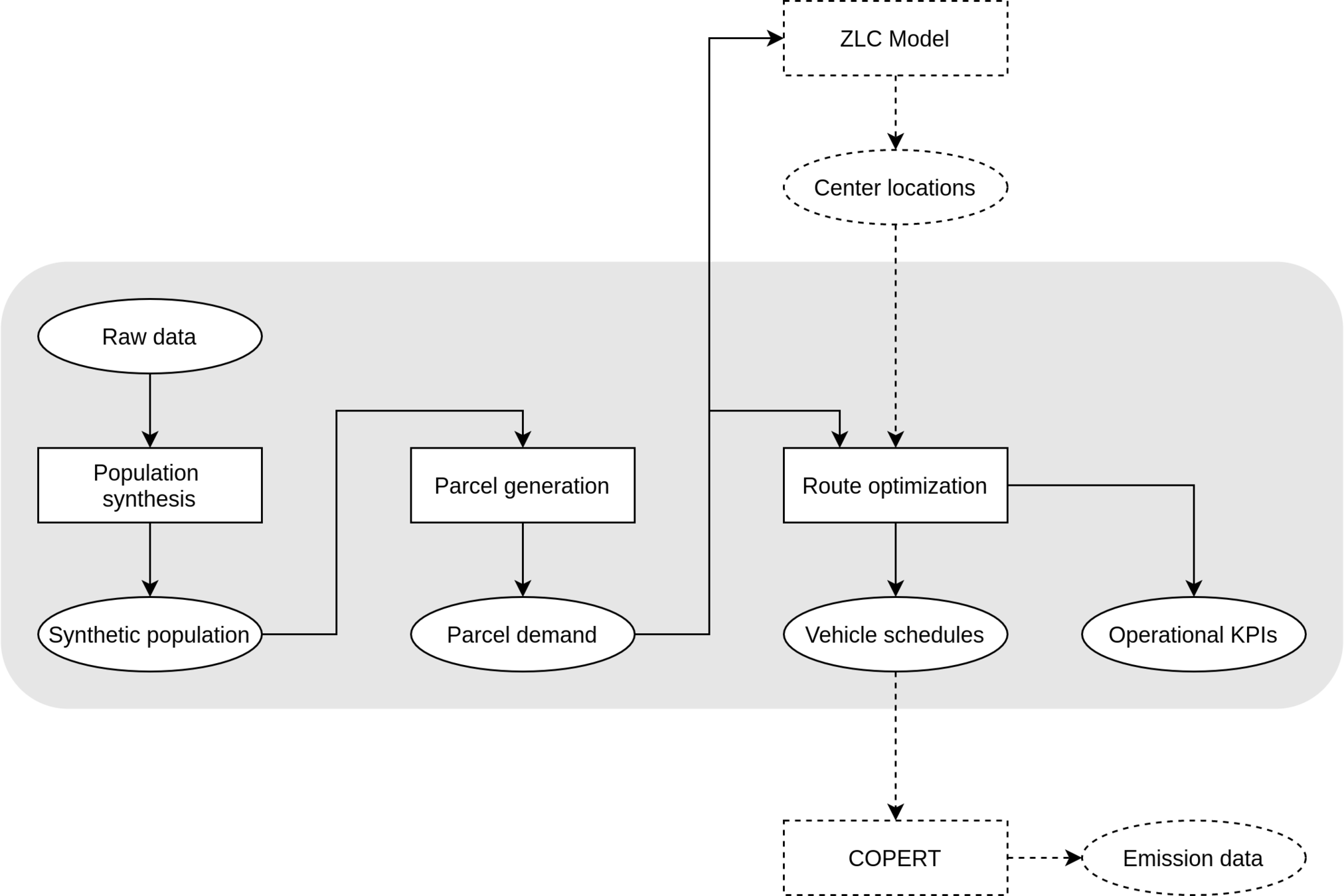
1
Main use case


Technical description

1
2
Main use case


Technical description

1
2
3
Main use case


(1) Population synthesis
1) Data preparation
- Documented in the Github repository
- Completely based on open data
- We can provide all files together
2) Setting up the environment
- We provide an Anaconda environment definition to install all Python dependencies
- Osmosis must be installed and accessible via the path (or later set up in the configuration file)


(1) Population synthesis
3) Preparing the configuration file
- Default config file is provided by the repositoy
- Modifications for the specific case of Lyon are described in the repository
4) Running population synthesis
- After the previous steps, things should go automatically by calling
python3 -m synpp config.yml
Potential options
- Random seed
- (Different scenarios in France)


(1) Population synthesis
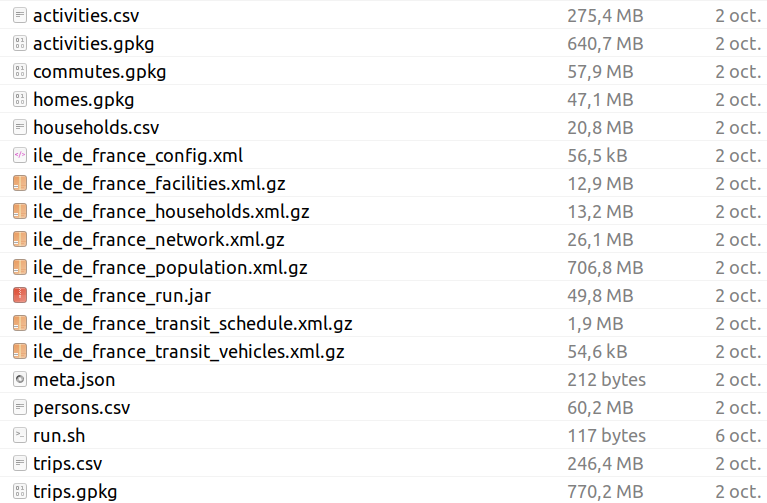
Output files


(1) Population synthesis
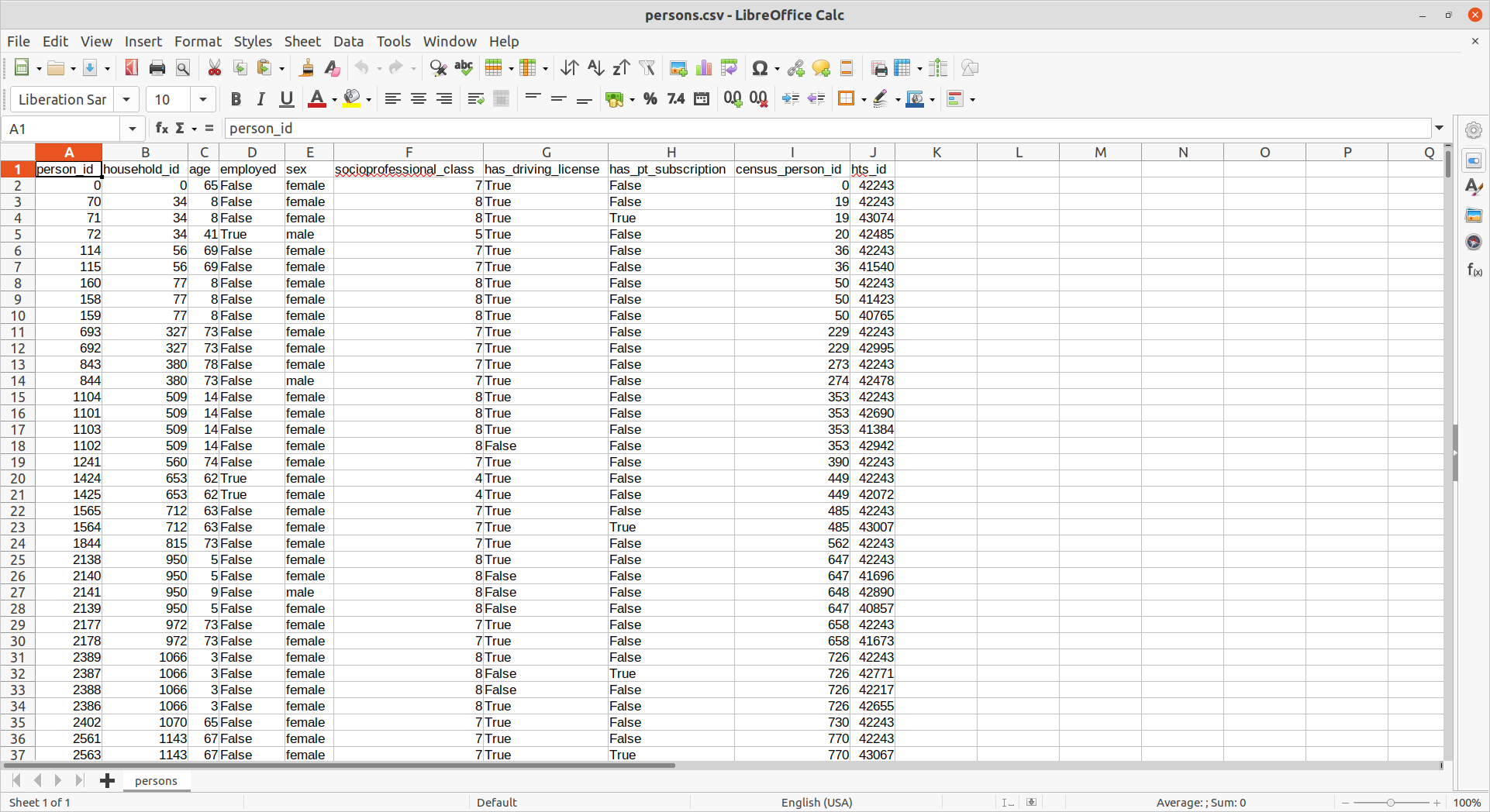
Example: persons.csv


(1) Population synthesis
Example: activities.csv
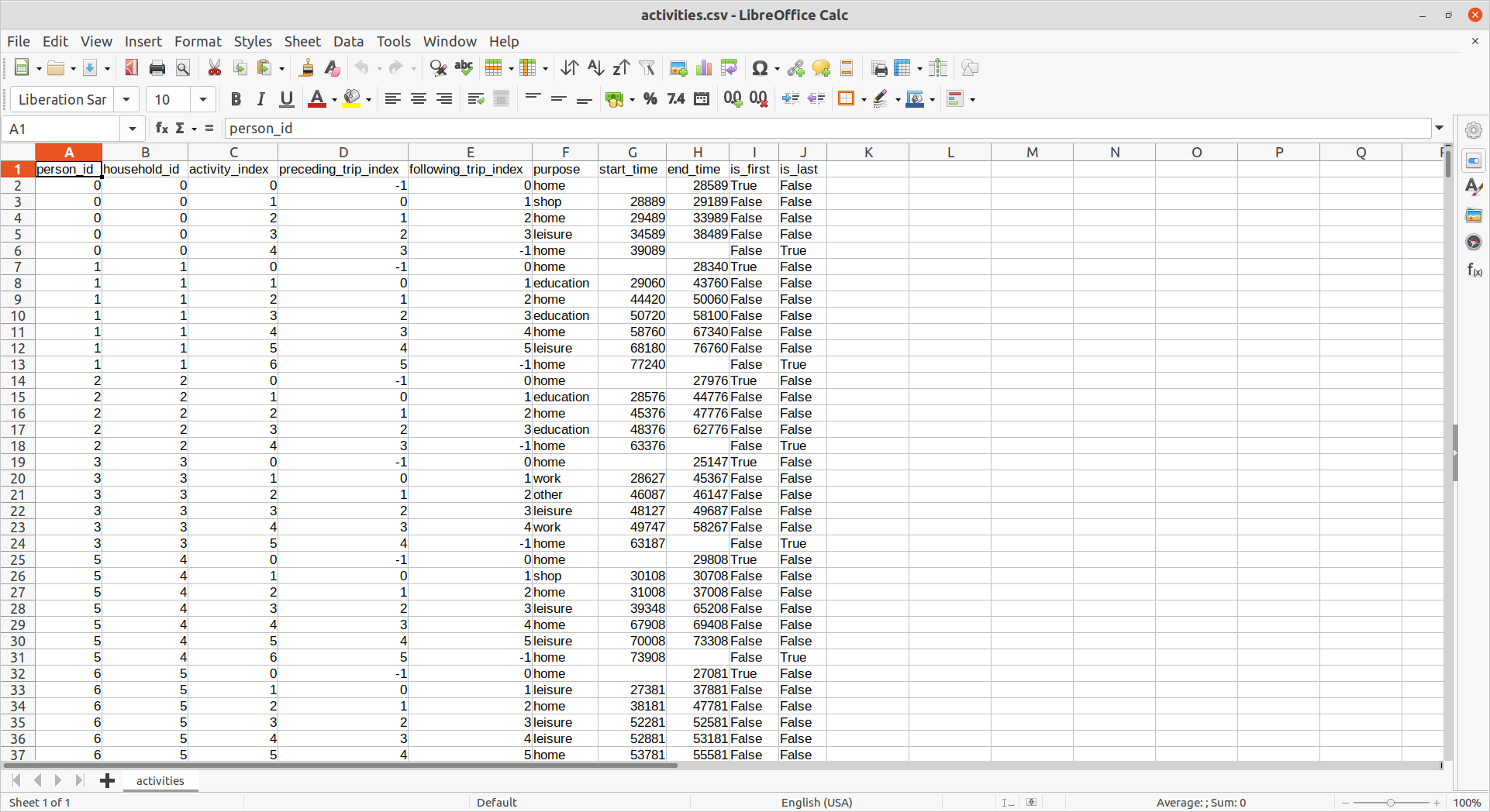


(2) Parcel generation
1) Collecting the data
- OpenStreetMap data
- Population data (persons, home locations, and activities)
- Here from the population synthesis pipeline
2) Setting up the environment
- Code is provided in our lead-lyon Github repository in parcels directory
- Repository provides environment file for Anaconda
3) Running the demand synthesis
- Put data in "input" directory
- Run Jupyter notebook
Generate Parcels.ipynb
Potential options
- Random seed
- Scaling factor for parcel demand
- Earliest/Latest delivery time


(2) Parcel generation
Output
- Parcel demand data
- Slots for household time windows
ZLC solver



(3) Solving the VRP
1) Collecting the data
- Demand data (step 2)
- Home locations (step 1, for filtering)
- OpenStreetMap data of the region
- Perimeter of the study area (shipe file)
2) Setting up the environment
- Code is in lead-lyon repository
- Same environment as before (in repository)
- Java 11 and Maven are needed



(3) Solving the VRP
3) Preparing the solver
- Iead-java contains a Maven package that needs to be built
4) Running the solver
- Call Java with the built classes and pass the input data
ZLC's distribution center location
mvn clean package
java -cp lead-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar lead.RunOptimization \
--deliveries-path temp/vrp_deliveries.csv \
--costs-path temp/vrp_distances.csv \
--depot-node ${depot_node} \
--output-path output/vrp_solution.csv


(3) Solving the VRP
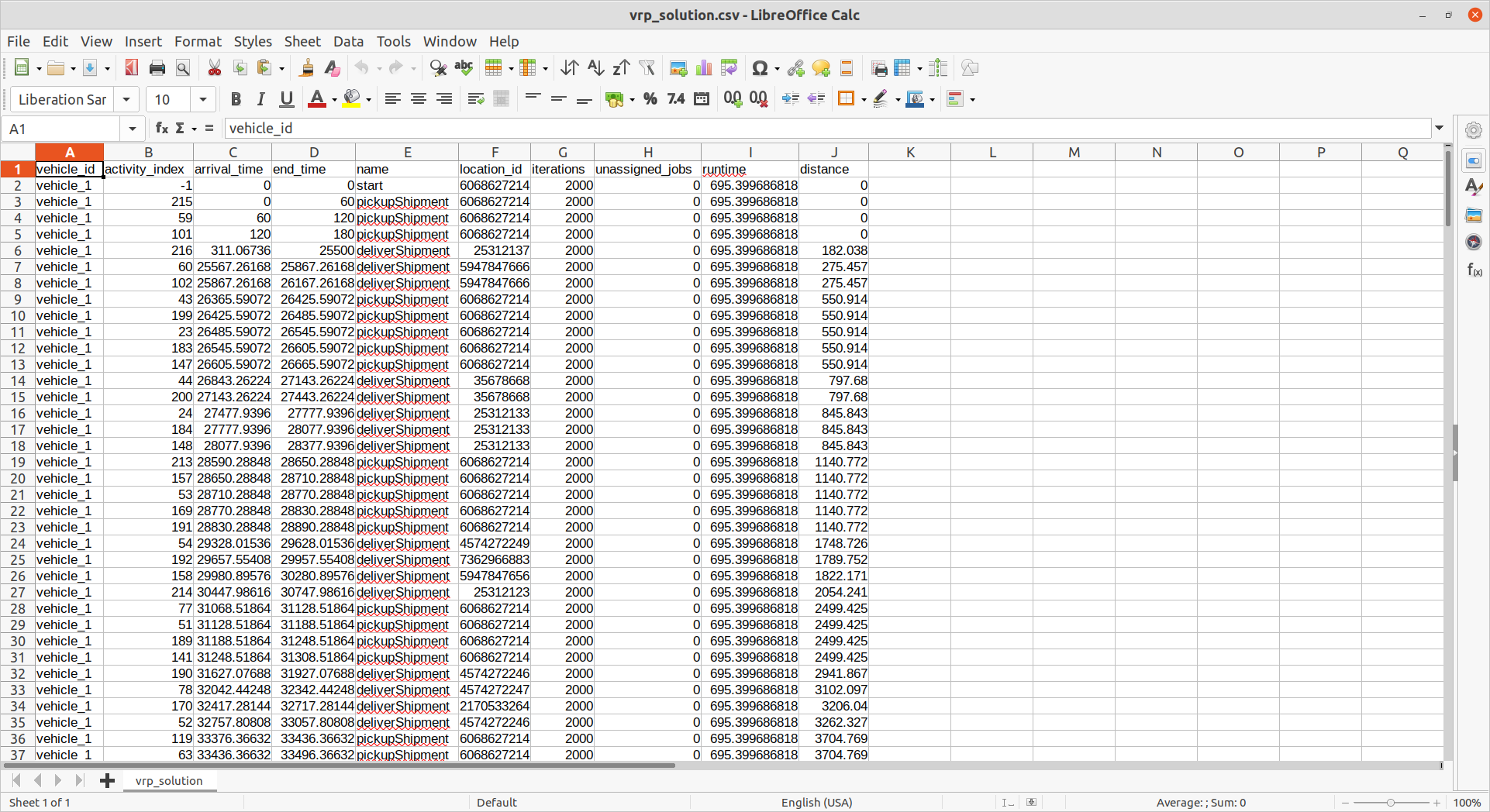
Output
- Vehicle schedules
COPERT


Library
- Whole process available in library folder in our repository
- Each stage contains a bash script to setup and run the model
- Specific data sets expected in input folder, output written to output folder
- Whole process can be run with run_all.sh
If all input data is put into raw_data folder
Tools used
- miniconda to set up independent Anaconda environments
- Adoptium Java distro
- papermill to automate Jupyter notebooks
Verified environment
- Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS
- Need to install build-essential
Questions?



LEAD Living Lab Demo
By Sebastian Hörl
LEAD Living Lab Demo
13 December 2021
- 989



