
Open synthetic travel demand for France
Sebastian Hörl
13 September 2023
14 September 2023
EDF/SMACH Seminar
IRT SystemX

- Research institute situated in Paris Saclay
- Fostering digital transformation in France
- Current research domains:
- Cybersecurity
- Transport
- Circular economy
- Health
- Three project types:
- Individual industry projects
- Collaborative industry projects
- European projects
IRT SystemX


IRT SystemX



Why agent-based transport simulation?

- Zones
- Flows
- Peak hours
- User groups
Aggregated
Why agent-based transport simulation?











0:00 - 8:00
08:30 - 17:00
17:30 - 0:00
0:00 - 9:00
10:00 - 17:30
17:45 - 21:00
22:00 - 0:00





- Discrete locations
- Individual travelers
- Individual behaviour
- Whole day analysis
Disaggregated
Icons on this and following slides: https://fontawesome.com
Agent-based transport simulation

Robotaxis
Rabattement
Intermodality
Decarbonation
Agent-based transport simulation

- Flexible, extensible and well-tested open-source transport simulation framework
- Used by many research groups and companies all over the world
- Extensions for parking behaviour, signal control, location choice, freight, ...

matsim-org/matsim-libs













Agent-based transport simulation

Synthetic demand
Agent-based transport simulation

Mobility simulation
Synthetic demand
Agent-based transport simulation

Decision-making






10:00 - 17:30
17:45 - 21:00
22:00 - 0:00


Mobility simulation
Synthetic demand
Agent-based transport simulation

Decision-making
Mobility simulation
Synthetic demand

Agent-based transport simulation

Decision-making
Mobility simulation
Analysis
Synthetic demand
Scenarios
Synthetic travel demand


Population census (RP)








> Truncate-Replicate-Sample (TRS)


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)










Synthetic travel demand
> Imputation by quantile


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)









Synthetic travel demand
> Direct sampling from OD matrix


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)

Household travel survey (EDGT)










0:00 - 8:00
08:30 - 17:00
17:30 - 0:00
0:00 - 9:00
10:00 - 17:30
17:45 - 21:00
22:00 - 0:00





Synthetic travel demand
> Assignment of activity chains through statistical matching


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)

Household travel survey (EDGT)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)











Address database (BD-TOPO)
Synthetic travel demand
> Specifically designed approach to find secondary locations
Hörl, S., Axhausen, K.W., 2021. Relaxation–discretization algorithm for spatially constrained secondary location assignment. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/23249935.2021.1982068


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)

Household travel survey (EDGT)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
Person ID
Age
Gender
Home (X,Y)
1
43
male
(65345, ...)
2
24
female
(65345, ...)
3
9
female
(65345, ...)
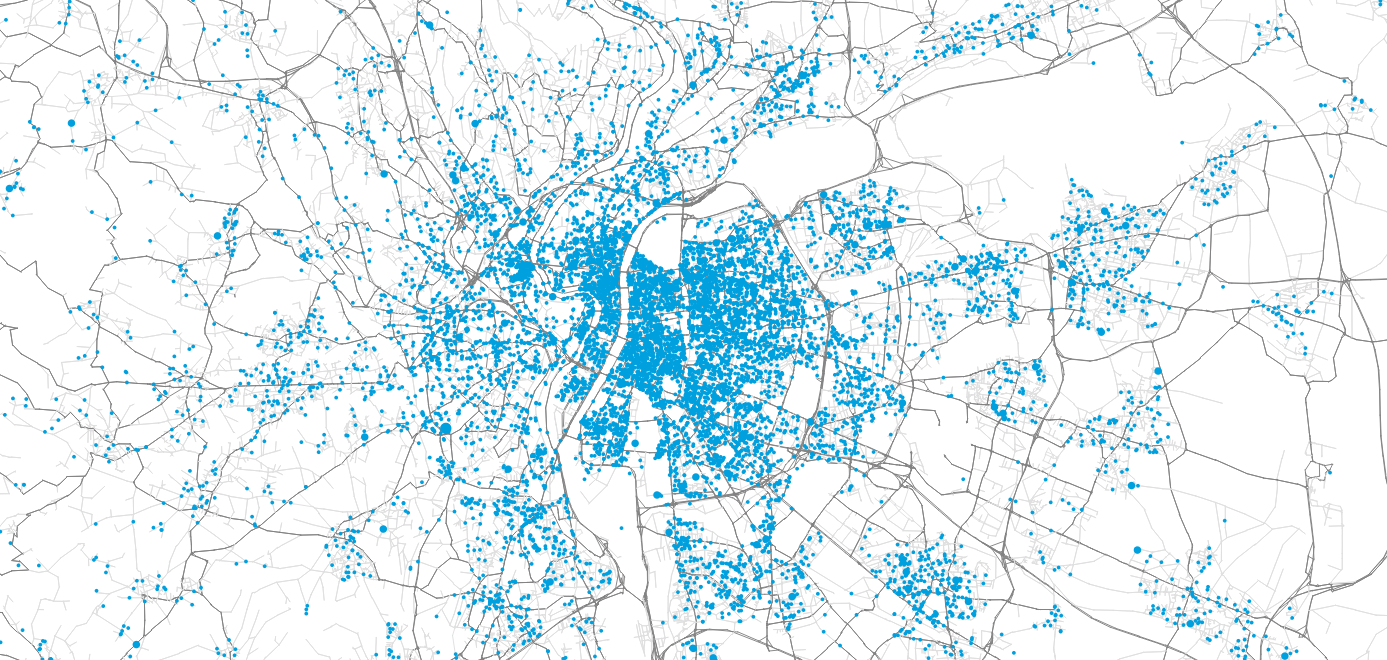
Synthetic travel demand


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)

Household travel survey (EDGT)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
Person ID
Activity
Start
End
Loc.
523
home
08:00
(x,y)
523
work
08:55
18:12
(x,y)
523
shop
19:10
19:25
(x,y)
523
home
19:40
(x,y)

Synthetic travel demand


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)

Household travel survey (EDGT)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
Synthetic travel demand


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)

Household travel survey (EDGT)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
Synthetic travel demand


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)
National HTS (ENTD)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
Synthetic travel demand


EDGT


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
Synthetic travel demand
Open
Data


Open
Software
+
=
Reproducible research
Integrated testing
National HTS (ENTD)


EDGT


Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
Synthetic travel demand
Open
Data


Open
Software
+
=
Reproducible research
Integrated testing
National HTS (ENTD)


EDGT

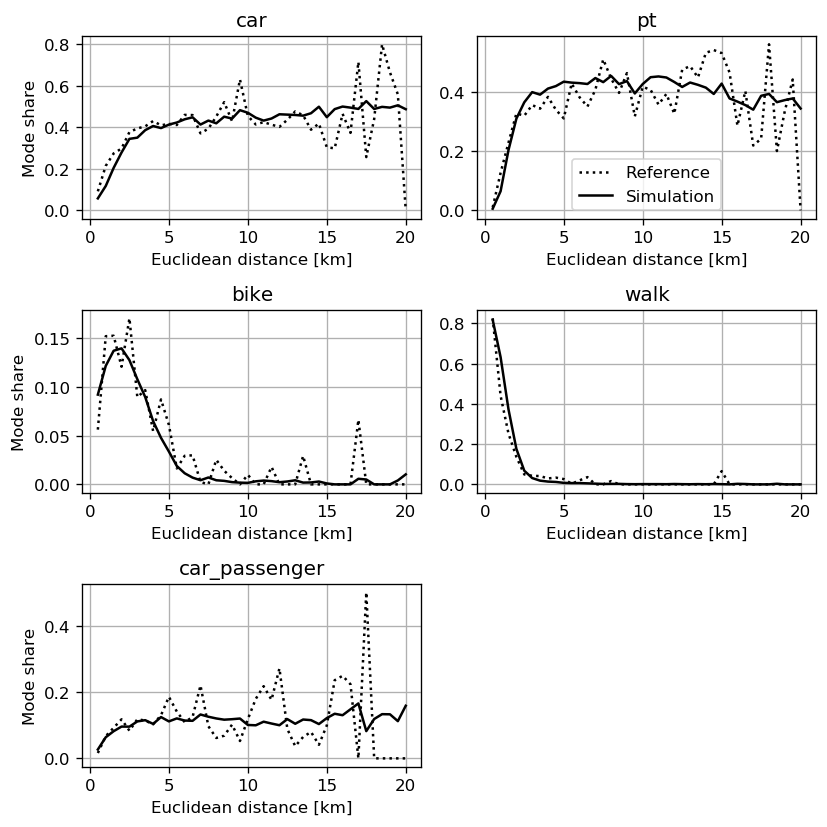
Evaluation

- Comparison of population attributes

Evaluation

- Activity chains

Sampling




Current use cases


Nantes
- Noise modeling

Current use cases

Lille
- Park & ride applications
- Road pricing



Current use cases


Toulouse
- Placement and use of shared offices

Current use cases

Rennes
- Micromobility simulation



Current use cases



Paris / Île-de-France
- Scenario development for sustainable urban transformation
- New mobility services
Mahdi Zargayouna (GRETTIA / Univ. Gustave Eiffel)
Nicolas Coulombel (LVMT / ENPC)

Current use cases


Paris / Île-de-France
- Cycling simulation

Current use cases


Paris / Île-de-France
- Simulation of dynamic mobility services
- Fleet control through reinforcement learning

Current use cases



Lyon (IRT SystemX)
- Low-emission first/last mile logistics

Current use cases




Current use cases


Balac, M., Hörl, S. (2021) Synthetic population for the state of California based on open-data: examples of San Francisco Bay area and San Diego County, presented at 100th Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board, Washington, D.C.
Sallard, A., Balac, M., Hörl, S. (2021) Synthetic travel demand for the Greater São Paulo Metropolitan Region, based on open data, Under Review
Sao Paulo, San Francisco Bay area, Los Angeles five-county area, Switzerland, Montreal, Quebec City, Jakarta, Casablanca, ...

Current use cases
- Latest addition: Cairo
- Germany work-in-progress
Replicability

- Reproducibility
- Low in transport modelling / simulation, especially with agent-based models
- Can increase acceptance, uptake and more widespread use of these models
- Increasingly available open data sources make reproducibility possible, but processes aren't standardized or not easily accessible as open source
- Our goal: Have pipeline from raw data to a calibrated large-scale agent-based transport simulation that is nearly 100% replicable with reproducible results.

Work in progress

- Continuously updated
- Example: Integrating buildings
- Open data: BAN (Base d'addresses nationale)
- Open data: BD-TOPO building census
- Benchmarking methodology
- Bayesian networks, HMMs, deep learning, ...
Anthropolis Chair 3

Questions?


Open synthetic travel demand for France
By Sebastian Hörl
Open synthetic travel demand for France
EDF/SMACH Seminar, 14 September 2023
- 574



