Lecture 8 Convex Sets and Functions
(Supporting slides)
Shen Shen
Feb 23, 2021
ORF363/COS323 Computing and Optimization


Convex Sets
Def: A set \(\Omega\) is a convex set if
\(\lambda x+(1-\lambda) y \in \Omega, \) \(\forall x,y \in \Omega, \forall \lambda\in[0,1]\)
convex combination of \(x\) and \(y\)
convex combination coefficient
Simple examples
Convex Sets
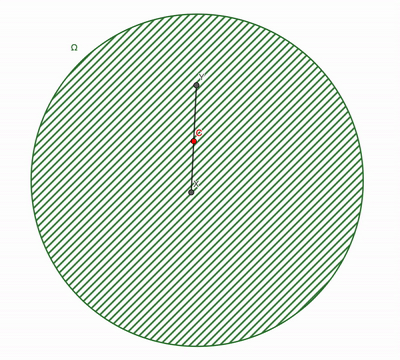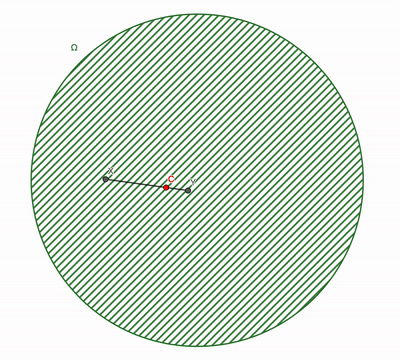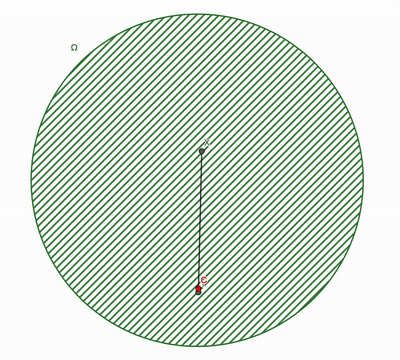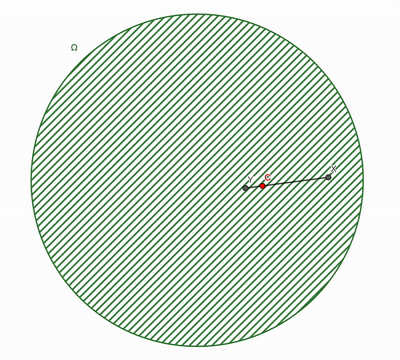
Simple examples
Non-convex Sets




because...
Common Convex Sets in Optimization
- Hyperplanes: \(\left\{x \mid a^{T} x=b\right\}\left(a \in \mathbb{R}^{n}, b \in \mathbb{R}, a \neq 0\right)\)
- Halfspaces: \(\left\{x \mid a^{T} x \leq b\right\} \left(a \in \mathbb{R}^{n}, b \in \mathbb{R}, a \neq 0\right)\)

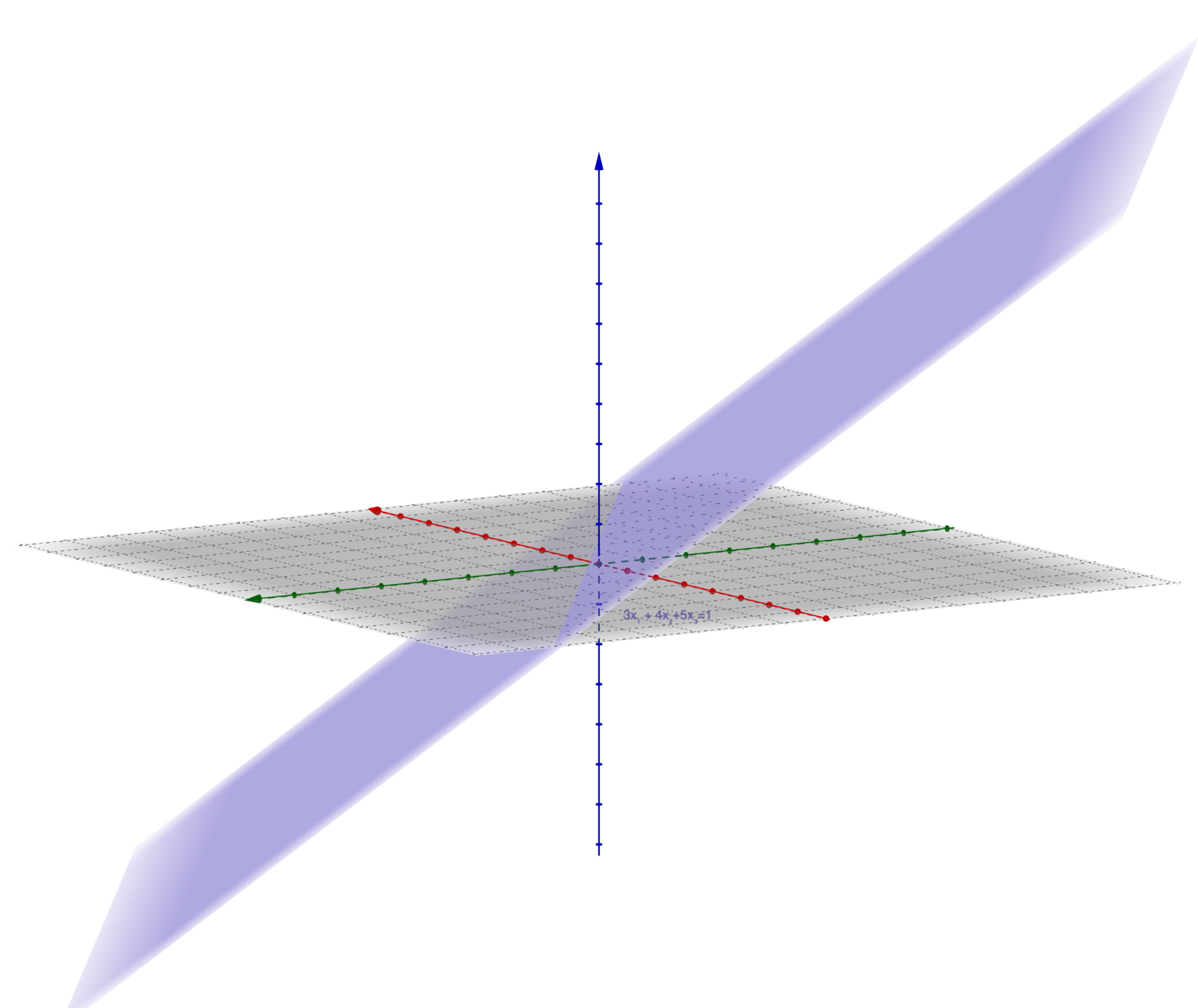
\(n=3: 3x_1+4x_2+5x_3=1\)
\(n=2: 3x_1+4x_2+\leq 2\)
Common Convex Sets in Optimization
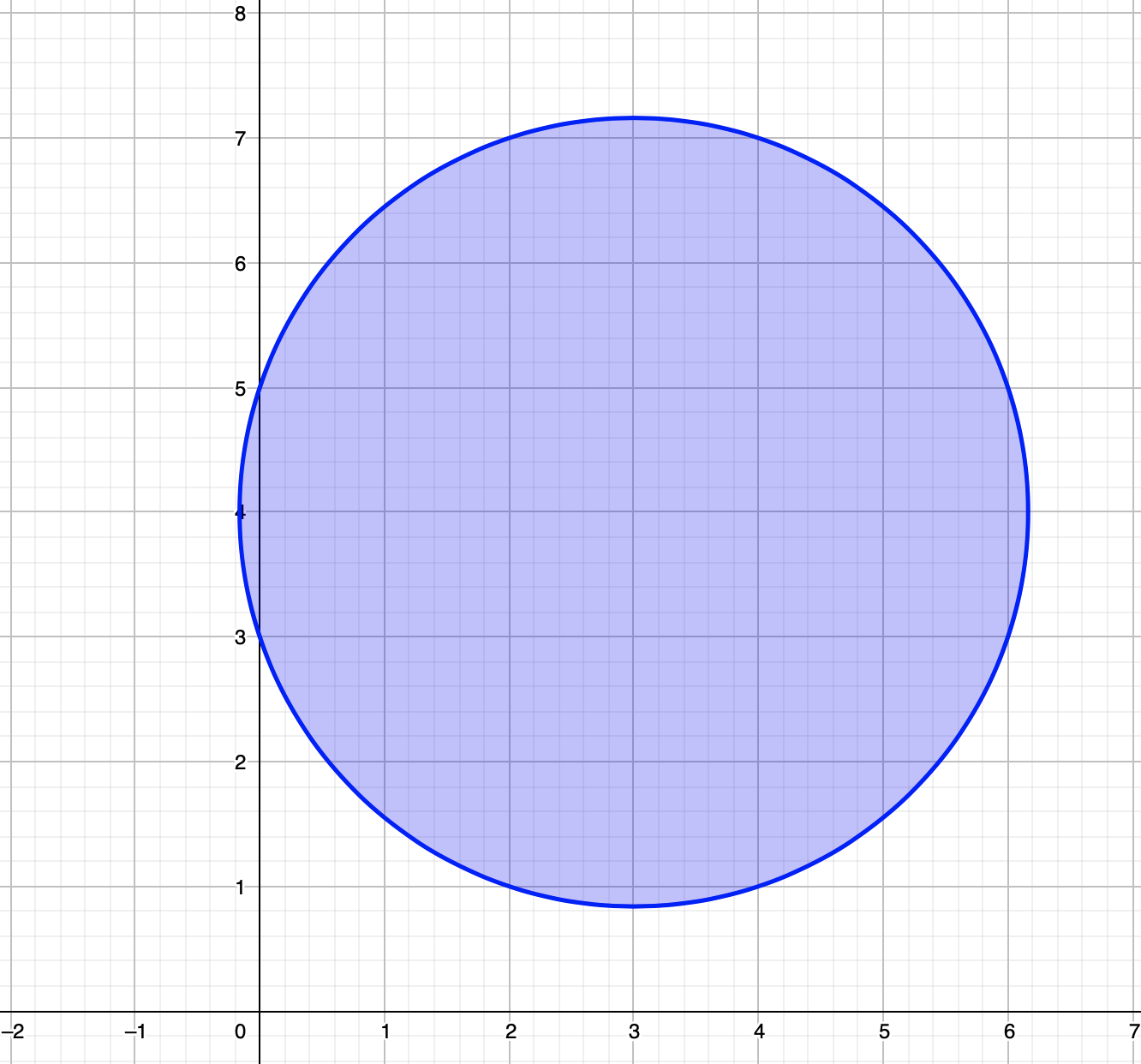
- Euclidean balls: \(\left\{x \mid \left||x-x_{c}\right|| \leq r\right\} \) \( (x_{c} \in \mathbb{R}^{n}, r \in \mathbb{R},\|.\|\) 2-norm)
- Ellipsoids: \(\left\{x \mid\left(x-x_{c}\right)^{T} P\left(x-x_{c}\right) \leq r\right\}\left(x_{c} \in \mathbb{R}^{n}, r \in \mathbb{R}, P \succ 0\right)\)
\(n=2\)
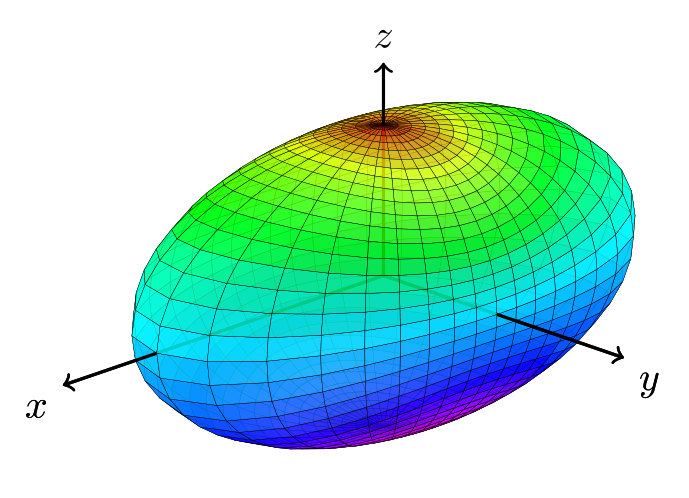
\(n=3\)
Common Convex Sets in Optimization
- The set of PSD matrices
- The set of co-positive matrices (HW)
A common recipe
1. Pick two arbitrary members, say \(x\) and \(y\), from \(\Omega\)
2. Write out the convex combination \(c\)
3. Make use of that \(x\) and \(y\) are from \(\Omega\), and \(\lambda \in [0,1]\)
4. Claim the \(c\) also belongs in \(\Omega\)
Proof of the PSD claim:
Pick \(A\succeq 0, B\succeq 0\)
N.t.s \(\lambda A+(1-\lambda) B \succeq 0\)
i.e., \(x^T(\lambda A+(1-\lambda) B)x \geq 0 \forall x\)
\(=\lambda x^{T} A x+(1-\lambda) x^{T} B x\)
\(x^T(\lambda A+(1-\lambda) B)x\)
\(\geq 0\)
\(\geq 0\)
\(\geq 0\)
Intersections of convex sets
Useful fact: \(\Omega_{1}\) convex, \(\Omega_{2}\) convex \(\Rightarrow \Omega_{1} \cap \Omega_{2}\) convex.
- Proof in last lecture.
- The union of convex sets may not be convex


- Polyhedrons: \(\{x \mid A x \leq b\}\) are convex sets
e.g. m =4 (4 halfspaces), n=2 (2d)
\(A=\left[\begin{array}{rr}-1 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 \\ 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 1\end{array}\right], b=\left[\begin{array}{l}0 \\ 0 \\ 1 \\ 3\end{array}\right]\)
Convex Functions
Def: A function \(f: \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) is convex if its domain is a convex set and
\(f(\lambda x+(1-\lambda) y) \leq \lambda f(x)+(1-\lambda) f(y)\) \(\forall x,y \in \text{domain}(f), \forall \lambda\in[0,1]\)
Simple examples
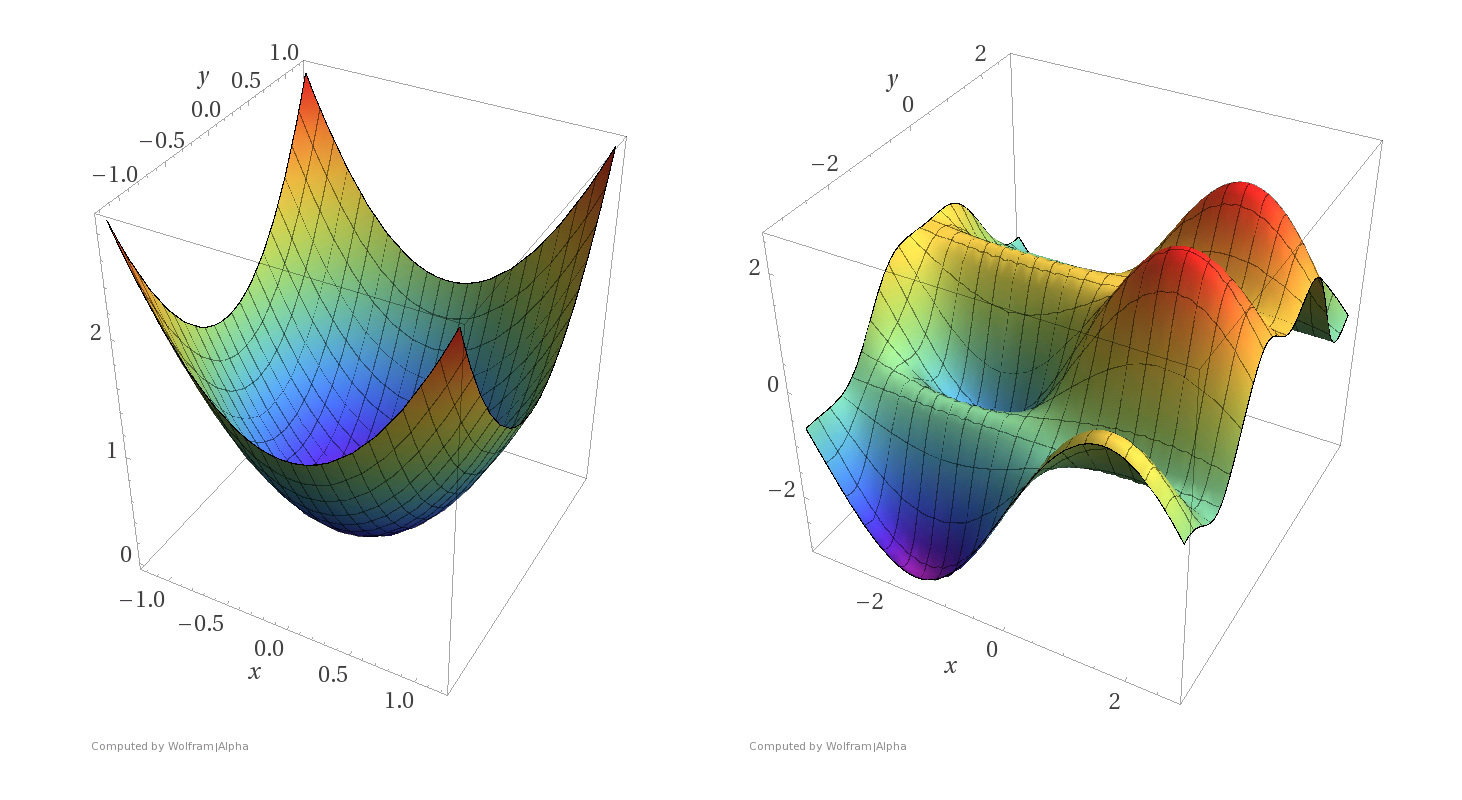
Convex functions
Non-convex functions

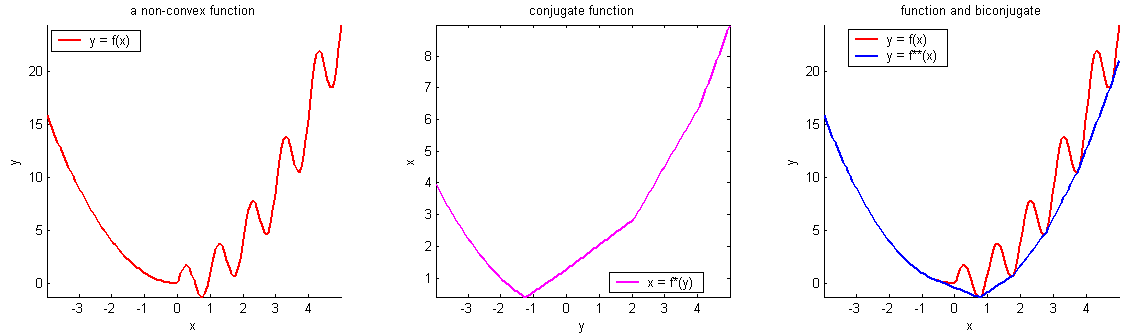
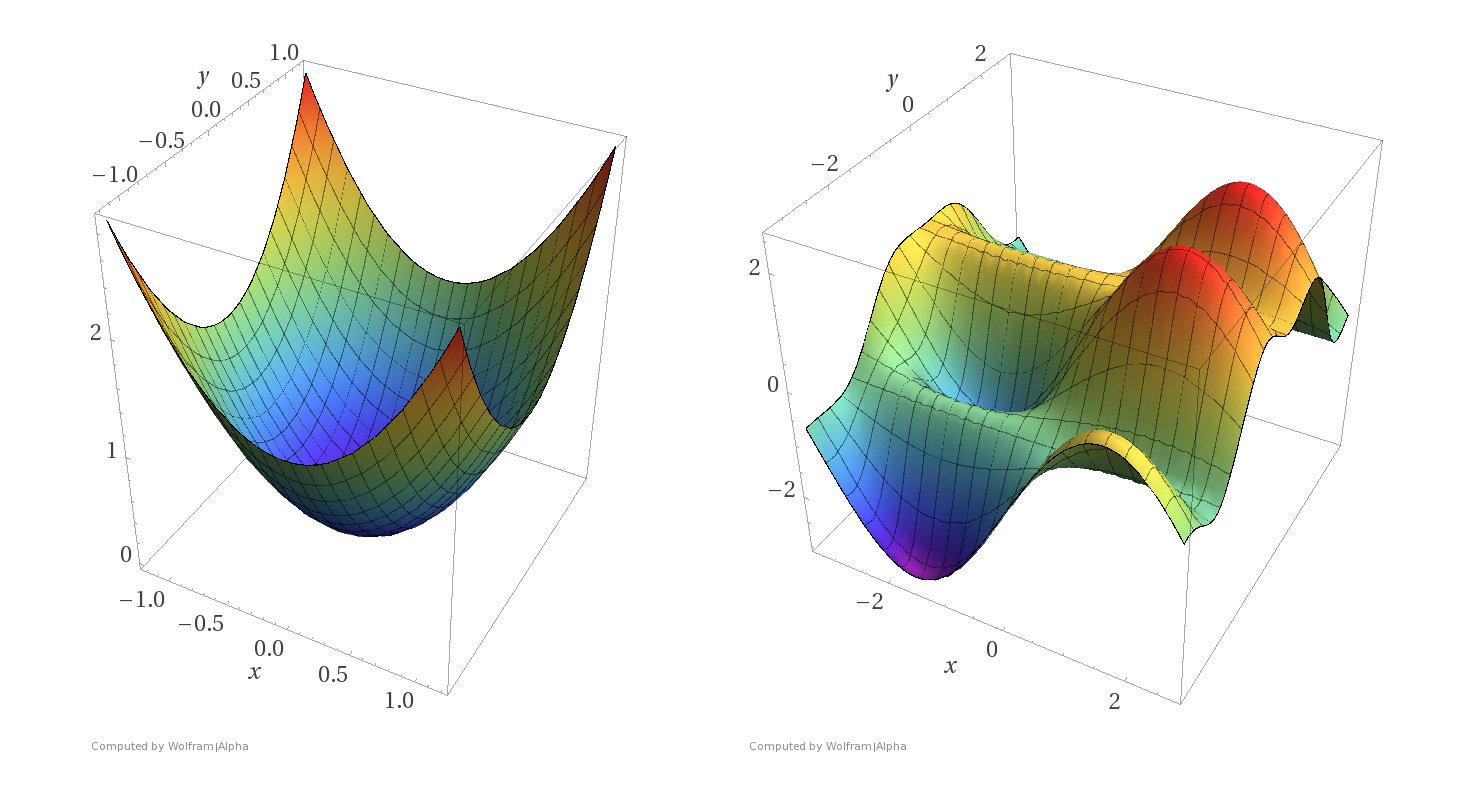
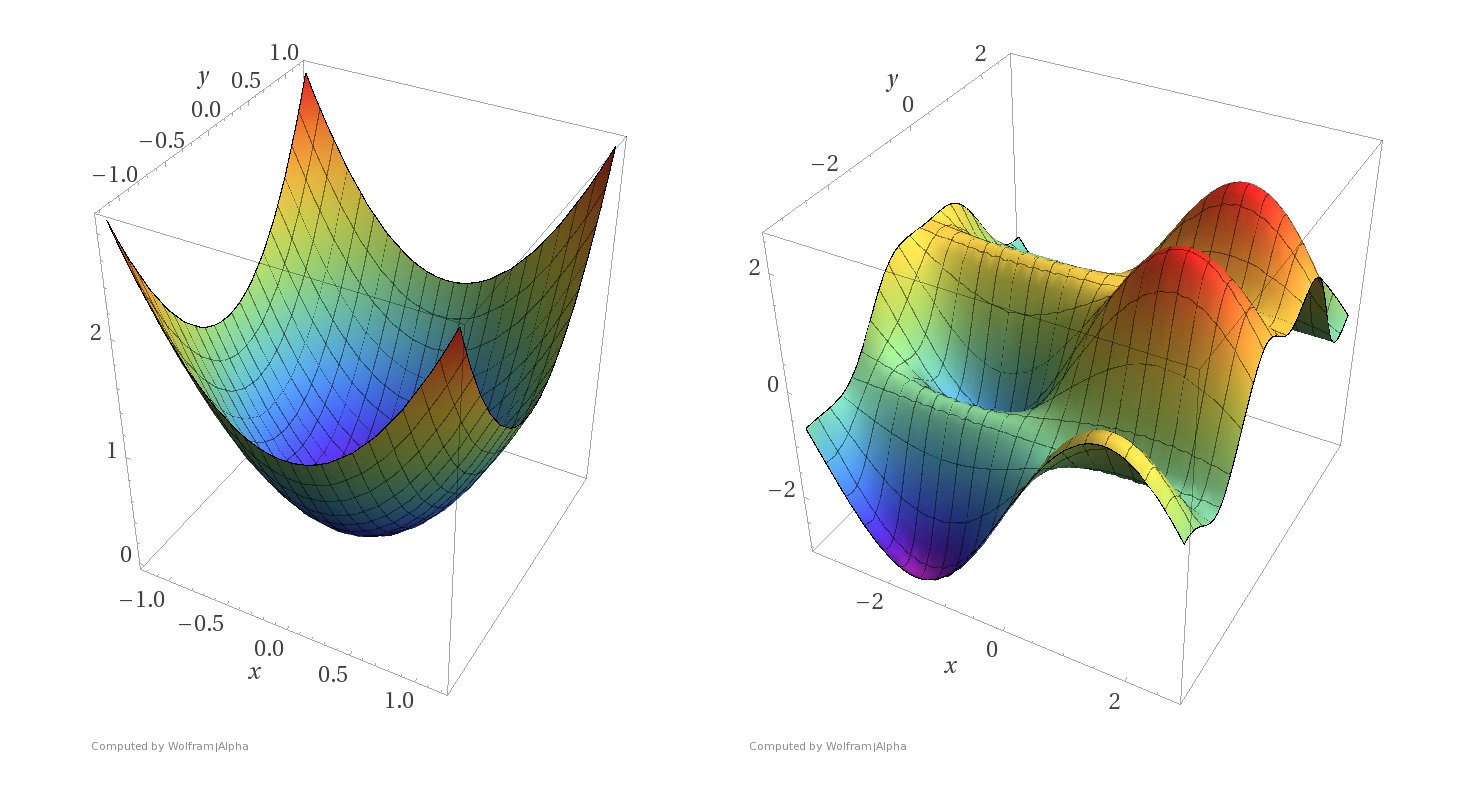


\(f\) is called a concave function if \(-f\) is convex
Common convex functions in optimization
- All affine functions \(f(x)=a^{T} x+b \quad\) (for any \(\left.a \in \mathbb{R}^{n}, b \in \mathbb{R}\right)\)
- Some quadratic functions (details later)
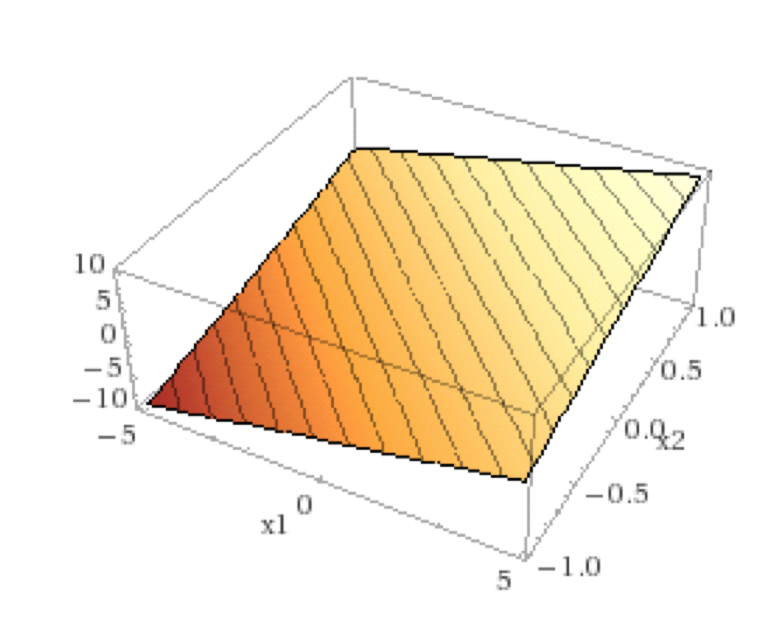


Common convex functions in optimization
- All norms
Recall norm is a function \(f\) that satisfies:
a. \(f(\alpha x)=|\alpha| f(x), \forall \alpha \in \mathbb{R}\)
b. \(f(x+y) \leq f(x)+f(y)\)
c. \(f(x) \geq 0, \forall x, f(x)=0 \Rightarrow x=0\)
\(f(\lambda x+(1-\lambda) y) \)
\(= \lambda f(x)+(1-\lambda) f(y)\)
b.c. (b)
b.c. (a) and \(\lambda \geq 0\)
Proof (convexity of any norm):
\(\leqslant f(\lambda x)+f((1-\lambda) y)\)
Connection btw Convex Sets and Convex Functions
Theorem: If a function \(f: \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) is convex, then all its sublevelsets are convex sets.
- Recall the sub-levelsets definition:
The \(\alpha\) -sublevel set of a function \(f: \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) is the set \(S_{\alpha}=\{x \in \operatorname{domain}(f) \mid f(x) \leq \alpha\}\)
Connecting Convex Sets and Convex Functions
Theorem: If a function \(f: \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) is convex, then all its sublevelsets are convex sets.
- Recall the sub-levelsets definition:
The \(\alpha\) -sublevel set of a function \(f: \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) is the set \(S_{\alpha}=\{x \in \operatorname{domain}(f) \mid f(x) \leq \alpha\}\)

- Instead, a function whose sub-levelsets are convex sets is called quasiconvex.
- The converse is not true:
First and second order characterizations of convex functions
Theorem: Suppose \(f: \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) is twice differentiable over its domain.
Then, the following are equivalent:
(i) \(f\) is convex.
(ii) \(f(y) \geq f(x)+\nabla f^{T}(x)(y-x), \quad \forall x, y \in \operatorname{dom}(f)\)
(iii) \(\nabla^{2} f(x) \succeq 0, \quad \forall x \in \operatorname{dom}(f)\) (i.e., the Hessian is psd \(\left.\forall x \in \operatorname{dom}(f)\right)\).
Intuition for (ii) \(f(y) \geq f(x)+\nabla f^{T}(x)(y-x), \quad \forall x, y \in \operatorname{dom}(f)\)
Intuition for (iii) \(\nabla^{2} f(x) \succeq 0, \quad \forall x \in \operatorname{dom}(f)\) (i.e., the Hessian is psd \(\left.\forall x \in \operatorname{dom}(f)\right)\).
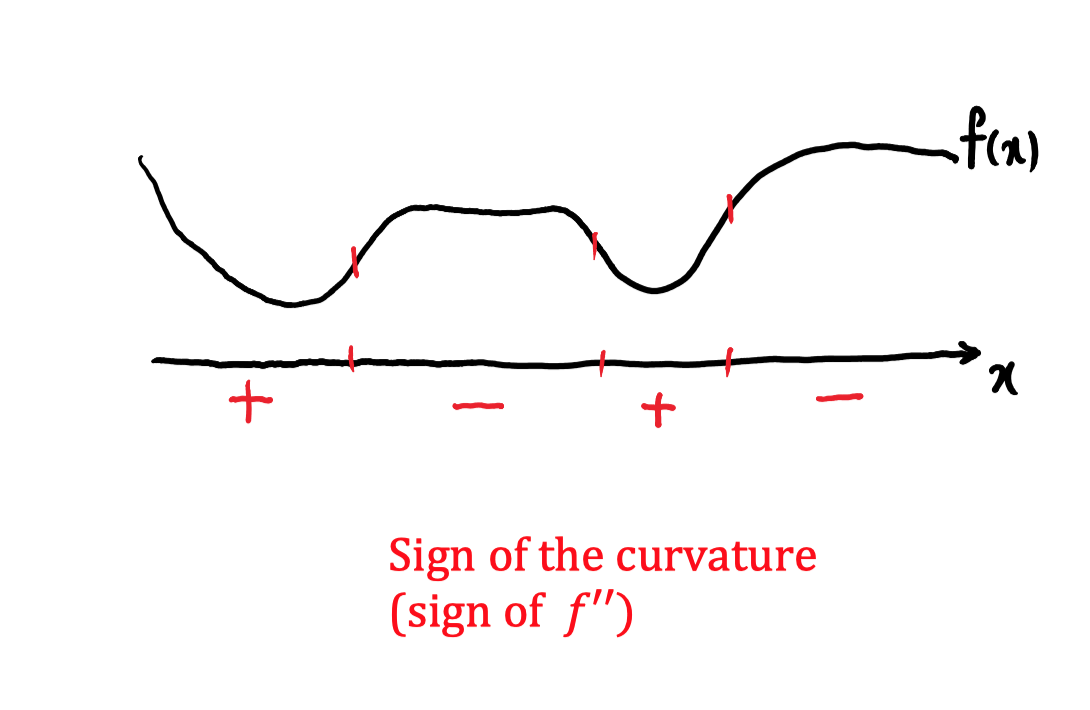
Function has nonnegative curvature everywhere: "it curves up"
Recall we said, some quadratic functions are convex, this second order characterization makes identifying the "some" really easy
In one dimension: \(f^{\prime \prime}(x) \geq 0, \forall x \in \operatorname{dom}(f)\)
Recall theorem says \(f\) convex \(\Leftrightarrow \nabla^{2} f(x) \succeq 0, \quad \forall x \in \operatorname{dom}(f)\)
Consider a quadratic function \(f(x)=x^{T} A x+b x+c \quad\) (A symmetric)
when is \(f\) convex?
we know \(\nabla^{2} f(x)=2 A\)
Text
\(f\) convex \(\Leftrightarrow A \succeq 0\) (independent of \(b, c)\)
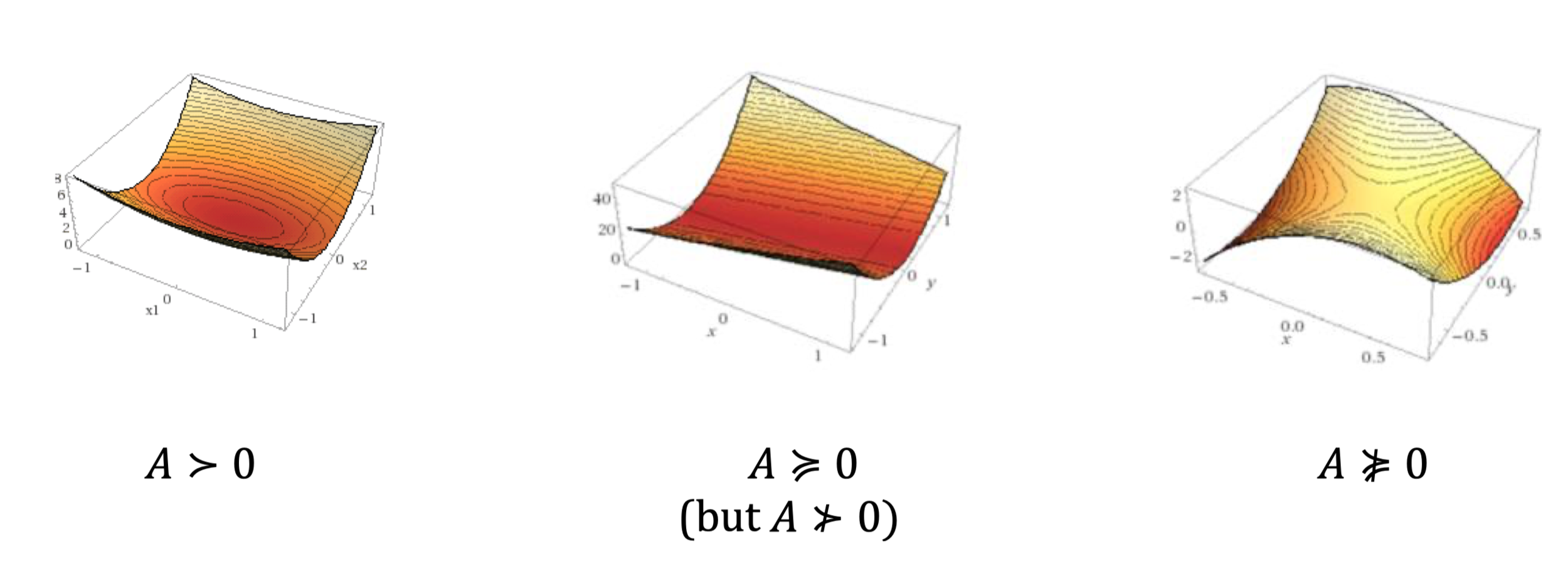
Convexity of quadratic functions
Convexity-preserving Rules
(for convex functions)
- Think of as shortcuts or stepping-stones
- Rules take in some convex functions, perform certain operations, and spit out a convex function
- Makes identifying convex functions a lot easier
- We'll present 4 such rules
Rule 1: Nonnegative weighted sum
If \(f_{1}, \ldots, f_{n}\) are convex functions and \(\omega_{1}, \ldots, \omega_{n} \geq 0,\) then
\(f(x)=\omega_{1} f_{1}(x)+\cdots+\omega_{n} f_{n}(x)\) is also convex.
Rule 2: Point-wise maximum
If \(f_{1}, \ldots, f_{m}\) are convex functions then their pointwise maximum
\(f(x)=\max \left\{f_{1}(x), f_{2}(x), \ldots f_{m}(x)\right\}\)
with \(\operatorname{dom}(f)=\operatorname{dom}\left(f_{1}\right) \cap \operatorname{dom}\left(f_{2}\right) \cap \cdots \cap \operatorname{dom}\left(f_{m}\right),\) is also convex.
Rule 3: Composition with an affine mapping
Suppose \(f: \mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{n}} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}, \mathrm{A} \in \mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{n} \times \mathrm{m}}\) and \(b \in \mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{n}}\). Define \(g: \mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{m}} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) by
\(g(x)=f(A x+b)\)
with \(\operatorname{dom}(g)=\{x \mid A x+b \in \operatorname{dom}(f)\}\). Then, if \(f\) is convex, so is \(g\); if \(f\) is concave so is \(g\).
Rule 4: Restriction to a line
Let \(f: \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) be a convex function and fix some \(a, b, \in \mathbb{R}^{n} .\) Then, the function \(g: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) given by \(g(x)=f(ax+b)\) is convex.

Convex sets and convex functions
By Shen Shen
Convex sets and convex functions
- 649



