
Introduction to interactive application development
by
Shubham Singh (@shobulive)
Agenda
- What is React Native?
- Why React Native?
- How does it work? Core concepts!
- Prerequisites - What you need to know
- RN Basics
- The Development Environment setup
- Basic Todo Application design
- Useful tools that come in handy
- Publishing your application
- Pros and Cons
- QnA
What is React Native?
That you already know
- It's a Javascript framework
- For building cross-platform
mobile/Web/Desktop applications - Works on React.
Some application that are build on RN
- Facebook Ads Manager
- Bloomberg
- AirBnB (used to)
- Gyroscope
- Myntra
- UberEats
- Discord
- Swiggy Driver App
- Walmart
Why React Native?
How does it work?
- Internal Design
- Virtual DOM
- Tree Reconciliation
- Component First Design
- JSX and not HTML
- State and Props
Internal
React Native Library
JS Engine
React JS
App Code (JS)
RN JS Library
Architecture
Native UI
Native APIs
Native / Bridge Interface
Virtual DOM
&
Tree Reconsiliation
- DOM traversal is a heavy process since JS is single-threaded.
- React internally maintains a Virtual DOM.
- On Update, makes a copy of the existing DOM with the update.
- Compares it with the older version.
- Updates only affected section the Actual DOM.
- Replaces the old Virtual DOM with the newer One.
Component First
Design
JSX
- You can use Javascript variables directly
HTML
- document.querySelector('#root').textContent = myVariable
State and Props
- Props are variables passed to it by its parent component
- The state is also a variable but managed and maintained by the Component.
- A state variable can also be passed to a child as a prop. So now the state variable of component is a prop to the child component.
- Why are these important?
Because React triggers tree reconciliation whenever either one of these change.
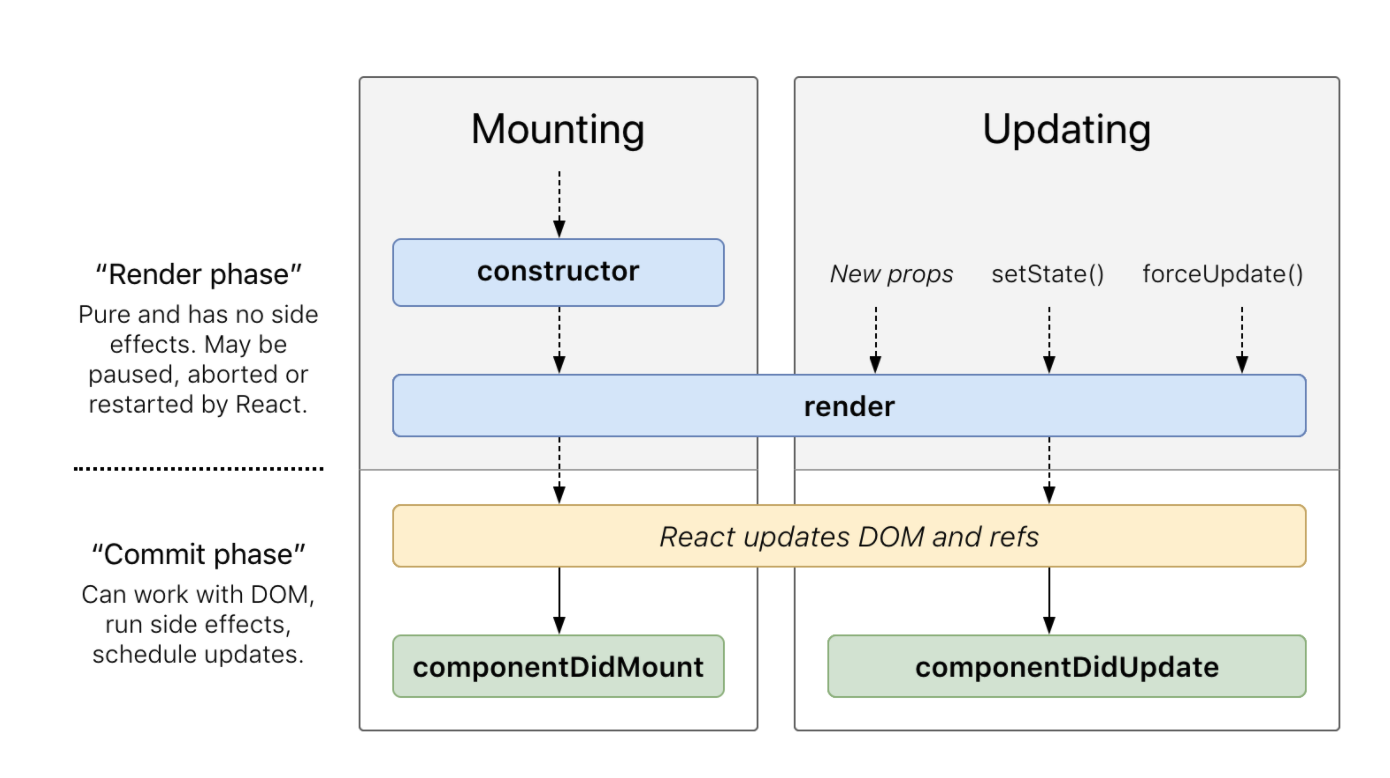
Life Cycle Functions
Context API

React.useContest()
Prerequesties
- React
- JavaScript
- CSS
- HTML
RN Basics
- State
- Props
- Components
- Hooks
- Context API
- Lifecycle functions
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import {
StyleSheet,
TouchableOpacity,
Text,
View,
} from 'react-native'
const TextComponent = ({count}) => (
<View>
<Text>
You clicked {count} times
</Text>
</View>
);
const App = () => {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.button}
onPress={() => setCount(count + 1)}
>
<Text>Click me</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
<TextComponent count={count}>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
},
button: {
alignItems: 'center',
backgroundColor: '#DDDDDD',
padding: 10,
marginBottom: 10
}
})
export default App;The Dev Environment Setup
- React Native CLI
- Create React Native Application (Expo)
Pre steps:
- Install NPM and Node.js
https://www.npmjs.com/get-npm - XCode
- Android Studio
React Native CLI
- npm install -g react-native-cli
- react-native init MyFirstRNTutorial
- react-native run-ios | react-native run-android
Create React Native Application
- npm install -g create-react-native-app
- create-react-native-app MyFirstRNTutorial
- npm run ios | npm run android | npm run web
- Uses Expo.
Let's see a Simple TODO app
Useful Libraries
- Redux | Mobux | Mobux State Tree
- React Navigation
- Native Base
- Emotion JS
Publishing your Application
- Using Expo
- Sign in to Expo
- Generate a QR Code for Application
- Share it across
- Without Expo
- Generate your APK(Android) and IPA (iOS) files
- Upload to respective stores
- Post that your apps can be downloaded from Stores
- React Native Code Push
Pons
- Faster development
- Easy deployment
- Cross platforms
- Large community support
Cons
- Still required Native devs
- Not very performant compared to it's alternatives
Alternative:
- Native Apps
- Flutter
- Others
QnA
@shobulive
- Github
Find Me :)
deck
By Shubham Singh
deck
- 488



