First Steps In Building Custom Views
by Predko Silvestr
GDG Ternopil
-
What CustomView means? Difference between View and SurfaceView.
-
General drawing methods.
-
Draw components: Canvas, Paint, Path, Matrix, Rect …
-
How to create complex UI Element. (Custom ViewGroup, Touch processing).
-
Questions & Answers.
Сontent

Why should I create custom view?

SurfaceView
View
- Extends from View;
- Run in separate thread;
- Can be secure;
- SurfaceView punches a hole in window to allow its surface to be displayed;
- View is the base class for widgets
- Used to create interactive UI components
How to implement SurfaceView?
extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback1.
2.
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
thread = new Thread(holder);
thread.start();
}
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(
SurfaceHolder holder,
int format, int width, int height) {
// do something in drawing thread
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
if (thread != null) {
thread.interrupt();
thread = null;
}
}3.
// in your Thread
@Override
public void run() {
Canvas canvas = holder.lockCanvas();
// draw on canvas
holder.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas);
}General Drawing Methods
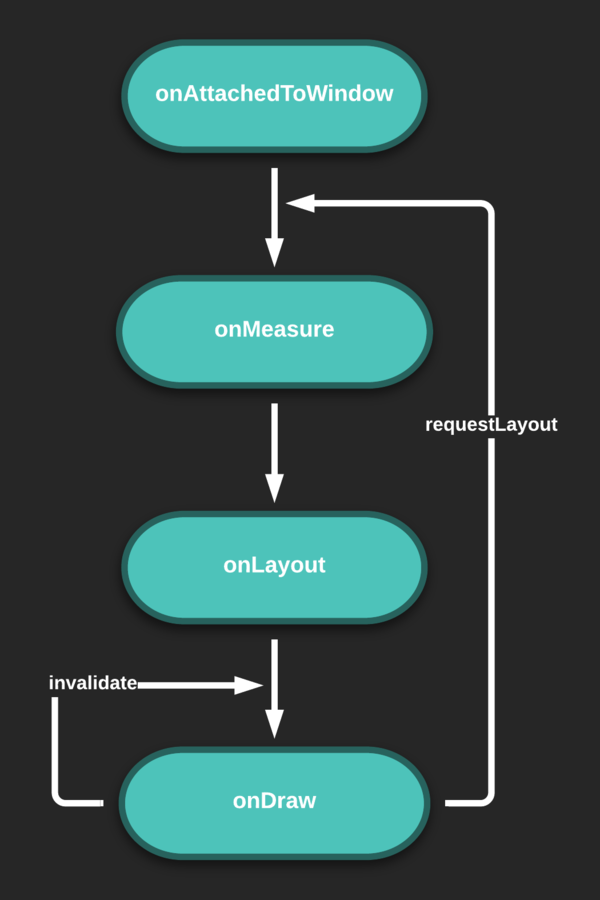
Progress Bar Example


@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
startAnimation();
}This is called when the view is attached to a window. At this point it has a Surface and will start drawing.
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight());
if (getMeasuredHeight() > getMeasuredWidth()) {
dotRadius = getMeasuredWidth() / DOT_AMOUNT / 4;
} else {
dotRadius = getMeasuredHeight() / 4;
}
bounceDotRadius = dotRadius + (dotRadius / 3);
float circlesWidth = (DOT_AMOUNT * (dotRadius * 2)) + dotRadius * (DOT_AMOUNT - 1);
xCoordinate = (getMeasuredWidth() - circlesWidth) / 2 + dotRadius;
}Measure the view and its content to determine the measured width and the measured height.
private void drawCircles(Canvas canvas, float radius) {
float step = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < DOT_AMOUNT; i++) {
if (dotPosition == i) {
canvas.drawCircle(xCoordinate + step,
getMeasuredHeight() / 2,
dotRadius + radius, paint);
} else {
if ((i == (DOT_AMOUNT - 1) && dotPosition == 0
&& !isFirstLaunch) || ((dotPosition - 1) == i)) {
canvas.drawCircle(xCoordinate + step,
getMeasuredHeight() / 2,
bounceDotRadius - radius, paint);
} else {
canvas.drawCircle(xCoordinate + step, getMeasuredHeight() / 2, dotRadius, paint);
}
}
step += dotRadius * 3;
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
drawCircles(canvas, animatedRadius);
}Implement this to do your drawing.
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
Paint paint = new Paint();
Bitmap btmp = new Bitmap();
...
} private void init() {
paint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG | Paint.DITHER_FLAG);
paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
paint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
paint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
paint.setStrokeWidth(20);
}

Draw Tools
-
Canvas
-
Paint
-
Path
-
Matrix
Canvas
The Canvas class holds the "draw" calls.
drawBitmap(Bitmap bitmap, Rect src, RectF dst, Paint paint)
drawCircle(float cx, float cy, float radius, Paint paint)
drawColor(int color)
drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY, Paint paint)
drawPath(Path path, Paint paint)
drawPicture(Picture picture, RectF dst)
...clipRect(int left, int top, int right, int bottom)Intersect the current clip with the specified rectangle, which is expressed in local coordinates.
Paint
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
paint.setDither(true);
paint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
paint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);The Paint class holds the style and color information about how to draw geometries, text and bitmaps.
Path
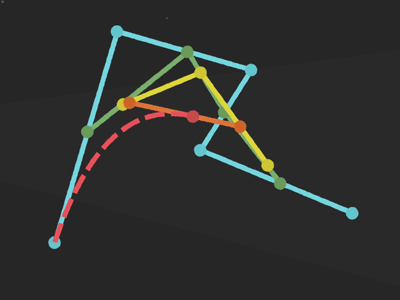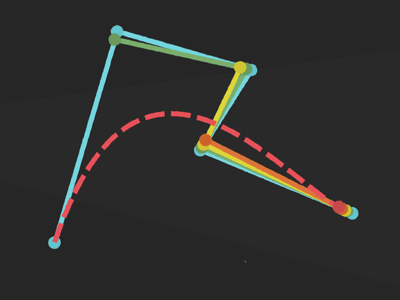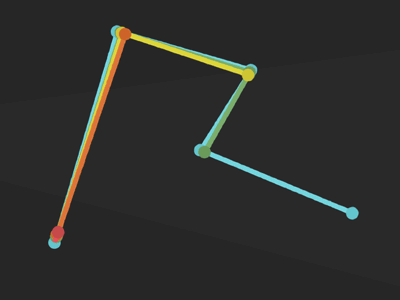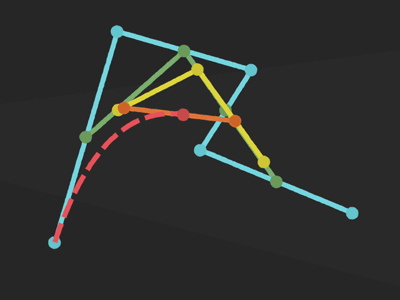
General methods:
public void lineTo (float x, float y)public void arcTo (RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle)public void quadTo (float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2)
public void moveTo (float x, float y)Set the beginning of the next contour to the point (x,y).
Add a line from the last point to the specified point (x,y). If no moveTo() call has been made for this contour, the first point is automatically set to (0,0).
Append the specified arc to the path as a new contour.
Add a quadratic bezier from the last point, approaching control point (x1,y1), and ending at (x2,y2).
Bézier curve

Matrix
The Matrix class holds a 3x3 matrix for transforming coordinates.
- translate
- scale
- rotate
- skew
matrix.reset();
matrix.setRotate(45, 400, 200);
matrix.postTranslate(500, 0);
path.transform(matrix, pathDst);
p.setColor(Color.GREEN);
canvas.drawPath(pathDst, p);
matrix.reset();
matrix.setRotate(45, 400, 200);
matrix.preTranslate(500, 0);
path.transform(matrix, pathDst);
p.setColor(Color.RED);
canvas.drawPath(pathDst, p);Example
Complex UI Element
For example

Touch processing
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
final int action = MotionEventCompat.getActionMasked(ev);
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: {
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: {
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: {
}
}
return true;
}Tracking Velocity
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker = null;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int index = event.getActionIndex();
int action = event.getActionMasked();
int pointerId = event.getPointerId(index);
switch(action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if(mVelocityTracker == null) {
// Retrieve a new VelocityTracker object to watch the velocity of a motion.
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
else {
// Reset the velocity tracker back to its initial state.
mVelocityTracker.clear();
}
// Add a user's movement to the tracker.
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
// When you want to determine the velocity, call
// computeCurrentVelocity(). Then call getXVelocity()
// and getYVelocity() to retrieve the velocity for each pointer ID.
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
// Log velocity of pixels per second
// Best practice to use VelocityTrackerCompat where possible.
Log.d("", "X velocity: " +
VelocityTrackerCompat.getXVelocity(mVelocityTracker,
pointerId));
Log.d("", "Y velocity: " +
VelocityTrackerCompat.getYVelocity(mVelocityTracker,
pointerId));
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
// Return a VelocityTracker object back to be re-used by others.
mVelocityTracker.recycle();
break;
}
return true;
}
}ViewDragHelper
Creating an instance
Once you’ve made your custom view extending ViewGroup, you need to create a ViewDragHelper instance. We’ll put it in onAttachedToWindow().
@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
mDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, 1.0f, new OurViewDragHelperCallbacks());
...
}Motion events
Before we look at the callbacks, let’s look at how they are activiated, and for that we look at onInterceptTouchEvent() and onTouchEvent().
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
boolean shouldInterceptTouchEvent = mDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
return shouldInterceptTouchEvent;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
mDragHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}ViewDragHelper callbacks
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View arg0, int pointerId) {
return true;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
return top;
}
@Override
public int getViewVerticalDragRange(View child) {
return parent.getMeasuredHeight() - child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
if (yvel > 0) {
mDragHelper.settleCapturedViewAt(
releasedChild.getLeft(),
parent.getMeasuredHeight() - releasedChild.getMeasuredHeight());
} else {
mDragHelper.settleCapturedViewAt(releasedChild.getLeft(), 0);
}
invalidate();
}Questions & Answers
Thanks for listening))
First Steps In Building Custom Views
By Silvestr Predko
First Steps In Building Custom Views
- 906

