BioPerl and other useful Perl approaches for bioinformaticians
Toni Hermoso Pulido
Perlbrew
Install different Perl versions as a normal user
Install Perlbrew
\curl -L http://install.perlbrew.pl | bashInstall and use Perl versions
# Install a Perl version
perlbrew install perl-5.22.0
# Switch definitely to that version
perlbrew switch perl-5.22.0
# Use only during that session
perlbrew use perl-5.22.0Install Perl modules
cpanm (cpannmins)
#Install CSV
cpanm CSV
#Install BioPerl
cpanm BioPerlIf things do not work, you always have classical cpan (interactive commandline)
Update Perl modules
# Install cpanoutdated package
cpanm App::cpanoutdated
# Update list of outdated modules
cpan-outdated -p | cpanmReinstall modules between versions
# Use a specific Perl version
perlbrew use perl-5.8.8
# List installed modules
perlbrew list-modules
# Install modules of current Perl version into another specific one
perlbrew list-modules | perlbrew exec --with perl-5.16.2 cpanmPerl one-liners
awk/sed on steroids
Example file:
GTF (tab-separated-like format with gene structure information)
perl -e
perl -e 'print "Hello world!";'-e: execute
perl -p
perl -p -e '$_=~s/exon/intron/;' \
Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtf-p: print
perl -n
perl -p -n -e '$_= $_."\tMore"' \
Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtf
# Alternative
perl -n -e 'print $_."\tMore"' \
Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtf-n: handle newline characters
perl -l
perl -p -l -n -e '$_= $_."\tMore"' \
Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtf
# Alternative
perl -n -l -e 'print $_."\tMore"' \
Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtf-l: chomp newline characters
perl -a
-a: autosplit (default whitespaces). Put into @F array
perl -lane 'print $F[2].":".$F[6]' \
Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtfperl -F
perl -F\; -lane 'print $F[1]' \
Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtf
# Some extra processing
perl -F\; -lane '($num) = $F[1] =~/(\d+)/; \
print "Version: ".$num; ' \
Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtf-F: with autosplit (choice of separator)
perl -s
perl -s -F\; -lane '($num) = $F[1] =~/(\d+)/; \
print "$desc: $extra ".$num; ' -- -desc=Tal \
-extra=Number Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtf-s: Pass parameters
perl -i
perl -i.backup -p -lane 's/exon/intron/g;' \
Felis_catus.Felis_catus_6.2.82.gtf-in: Operate in-place
References
Code snippets at:
Useful Perl Modules
You don't need to reinvent the wheel
Data::Dumper
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use Data::Dumper;
# Data structure
my %gene = (
"gene" => "BRCA",
"position" => {
"start" => 4400,
"end" => 8005
}
);
# NO
print Dumper(%gene);
# YES
print Dumper(\%gene);
Text::Trim
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use Text::Trim qw( trim ltrim rtrim );
my $text = " That's all folks! ";
print "*".ltrim( $text )."*\n";
print "*".rtrim( $text )."*\n";
print "*".trim( $text )."*\n";
print "*".$text."*\n";
trim( $text );
print "*".$text."*\n";
Text::CSV (Text::CSV_XS)
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use strict;
use warnings;
use 5.010; #Version 5.10 at least
use Text::CSV;
my $file = $ARGV[0] // "file.csv";
my $csv = Text::CSV->new ( { binary => 1, sep_char => "\t",
quote_char => "", empty_is_undef => 1 } )
or die "Cannot use CSV: ".Text::CSV->error_diag ();
open my $fh, "<:encoding(utf8)", "$file" or die "$file: $!";
while ( my $row = $csv->getline( $fh ) ) {
if ( $row->[2] ) {
print $row->[2].": ".$row->[3]."-".$row->[4]."\n";
my $list = [ $row->[2], $row->[3], $row->[4] ];
push( @rows, $list );
}
}
close $fh;Text::CSV (Text::CSV_XS)
my $csvout = Text::CSV->new ( { binary => 1, sep_char => ",",
quote_char => '\"', eol => "\n" } )
or die "Cannot use CSV: ".Text::CSV->error_diag ();
open my $fhout, ">:encoding(utf8)", "out.csv" or die "out.csv: $!";
while ( my $row = shift( @rows ) ) {
$csvout->print($fhout, $row );
}
close $fhout;Other modules
- DBI (e.g. DBD::SQLite)
- GetOpt
- Config::JSON
- etc.
Access to (biological) webservices
Example
HTTP::Tiny
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use strict;
use warnings;
use Data::Dumper;
use HTTP::Tiny;
my $http = HTTP::Tiny->new();
my $server = 'http://rest.ensembl.org';
my $ext = '/taxonomy/id/9606?';
my $response = $http->get($server.$ext, {
headers => { 'Content-type' => 'application/json' }
});
die "Failed!\n" unless $response->{success};
print Dumper( $response );JSON (JSON::XS)
use JSON;
if(length $response->{content}) {
my $hash = decode_json($response->{content});
print $hash->{"scientific_name"}, "\n";
}BioPerl
Bio::Seq
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use Bio::Seq;
use Data::Dumper;
# http://search.cpan.org/dist/BioPerl/Bio/Seq.pm
my $seqobj = Bio::Seq->new( -display_id => 'MySEQ001',
-seq => "GATACAGATACA",
-desc => "New sequence"
);
print Dumper( $seqobj );Bio::Seq::Feature::Generic
use Bio::SeqFeature::Generic;
# http://search.cpan.org/dist/BioPerl/Bio/SeqFeature/Generic.pm
my $feat = Bio::SeqFeature::Generic->new(
-start => 10,
-end => 100,
-strand => -1,
-primary => 'repeat', # -primary_tag is a synonym
-source_tag => 'repeatmasker',
-display_name => 'alu family',
-score => 1000,
-tag => { new => 1,
author => 'someone',
sillytag => 'this is silly!' } );
$seqobj->add_SeqFeature($feat);
print Dumper( $seqobj );FASTA
>gi|5524211|gb|AAD44166.1| cytochrome b [Elephas maximus maximus]
LCLYTHIGRNIYYGSYLYSETWNTGIMLLLITMATAFMGYVLPWGQMSFWGATVITNLFSAIPYIGTNLV
EWIWGGFSVDKATLNRFFAFHFILPFTMVALAGVHLTFLHETGSNNPLGLTSDSDKIPFHPYYTIKDFLG
LLILILLLLLLALLSPDMLGDPDNHMPADPLNTPLHIKPEWYFLFAYAILRSVPNKLGGVLALFLSIVIL
GLMPFLHTSKHRSMMLRPLSQALFWTLTMDLLTLTWIGSQPVEYPYTIIGQMASILYFSIILAFLPIAGX
IENY>gi|2055231|dbj|AB000263.1| Homo sapiens mRNA for prepro cortistatin like peptide, complete cds
ACAAGATGCCATTGTCCCCCGGCCTCCTGCTGCTGCTGCTCTCCGGGGCCACGGCCACCGCTGCCCTGCC
CCTGGAGGGTGGCCCCACCGGCCGAGACAGCGAGCATATGCAGGAAGCGGCAGGAATAAGGAAAAGCAGC
CTCCTGACTTTCCTCGCTTGGTGGTTTGAGTGGACCTCCCAGGCCAGTGCCGGGCCCCTCATAGGAGAGG
AAGCTCGGGAGGTGGCCAGGCGGCAGGAAGGCGCACCCCCCCAGCAATCCGCGCGCCGGGACAGAATGCC
CTGCAGGAACTTCTTCTGGAAGACCTTCTCCTCCTGCAAATAAAACCTCACCCATGAATGCTCACGCAAG
TTTAATTACAGACCTGAAAmino acid sequence
Nucleotide sequence
Bio::SeqIO
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use Bio::SeqIO;
$in = Bio::SeqIO->new(-file => "nucl.fasta" ,
-format => 'Fasta');
while ( my $seq = $in->next_seq() ) {
print "* ", $seq->display_name(), " - ";
print $seq->desc(), "\n";
print $seq->seq(), "\n";
}Bio::SeqIO
use Bio::SeqIO;
my $outfasta = Bio::SeqIO->new(-file => ">myseq.fasta" ,
-format => 'Fasta');
$outfasta->write_seq($seqobj);
my $outembl = Bio::SeqIO->new(-file => ">myseq.embl" ,
-format => 'EMBL');
$outembl->write_seq($seqobj);FASTQ
@M03766:3:000000000-ADALA:1:1101:19359:1544 1:N:0:98
ACTACGGGAGGCTGCAGTAGGGAATCTTCGGCAATGGGGGCAACCCTGACCGAGCAACGCCGCGTGAGTGATGAAGGTTTTCGGATCGTAAAGCTCTTTTGTTATTTAAGAACGAGTGTCTGCGTGCACCTTTCTCACTTTCCCGGTACCTTACCAGAAACCCCCGCCTATCTACTTCCCACCAGCCGCGCTATTCCGTAGGTCCCGATCGTTGTCCGGTTTTCTTTGCCTTCAAGCGAGCCCTGCCGGTTCTTTAATTCTGTTTTTAATGCCTGTGCCTTCCCCTTTCTCCTCTTTTTTT
+
-8ACCE385>5=;===CE9EGGFFGGGGF@,FGCFGGA,@BFGD6FGGE6C68FFFF@F@FGGGGE,,CEA,<,,5C,,9AF:>+B78B,,:,9BE?,C<,:,9,,,,,,,,:+++8+:,,,,+8+++,,,3,:,3,:>,:,,:++3++5338>3,,,,,,,**5**/1*,7,,5,3,?<<,=,,,41*1*1**++322((*5:2/*0)-*2/*260**)1/1*3<+++-*2*+2*))(*()((/*.((2.(*)0**)2-1*)+*20.+)),.0*+++))++,20,0+)***+.030+,**!"#$%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNO
PQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~Quality
Bio::SeqIO - FASTQ
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use Bio::SeqIO;
use Data::Dumper;
# http://search.cpan.org/dist/BioPerl/Bio/SeqIO/fastq.pm
$in = Bio::SeqIO->new(-file => "example.fastq" ,
-format => 'Fastq');
while ( my $seq = $in->next_seq() ) {
# Bio::Seq::Quality object
# http://search.cpan.org/dist/BioPerl/Bio/Seq/Quality.pm
print "* ", $seq->display_name(), "\n";
print $seq->seq(), "\n";
print $seq->qual_text(), "\n";
print join( ",", @{$seq->qual()} ), "\n";
}Other modules
- Bio::Align and Bio::AlignIO (seq alignments)
- Bio::FeatureIO (read/write GTF, GFF, etc.)
- Bio::Ontology (Ontology terms, e. g. GO)
- Bio::Tree and Bio::TreeIO (phylogenetic trees)
- Bio::Tools (specific parsers or wrappers of applications)
NCBI Entrez
PubMed
cpanm Bio::Biblio
PubMed eutils retrieval
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use Bio::Biblio;
use Bio::Biblio::IO;
use Bio::Biblio::Ref;
my $biblio = Bio::Biblio->new( -access => 'eutils' );
$biblio->find("Hermoso A [au] OR Hermoso T [au]");
while ( my $xml = $biblio->get_next ) {
# Handling in Biblio IO
my $io = Bio::Biblio::IO->new( -data => $xml,
-format => 'medlinexml' );
# Handling Biblio Ref
while ( my $article = $io->next_bibref() ) {
print "* ", $article->title, "\n";
print $article->abstract, "\n\n";
}
}Get sequences from Genbank
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use Bio::DB::GenBank;
my $gb = Bio::DB::GenBank->new();
# http://search.cpan.org/dist/BioPerl/Bio/Seq/RichSeq.pm
my $seq = $gb->get_Seq_by_gi('5524211'); # GI Number
# my $seq = $gb->get_Seq_by_acc('AAD44166'); # Acc Number
# my $seq = $gb->get_Seq_by_version('AAD44166.1'); # Acc.version
# Get sequence and sequence information
print $seq->molecule(), "\n";
print $seq->display_name(), "\n";
print $seq->seq(), "\n";
print $seq->description(), "\n";
# Fasta file
my $out = Bio::SeqIO->new(-file => ">out.fasta" ,
-format => 'fasta');
$out->write_seq($seq->primary_seq);ENSEMBL Perl API
Installation Core API
# Assuming BioPerl is installed and installing in $HOME
cd $HOME
git clone https://github.com/Ensembl/ensembl-git-tools.git
export PATH=$PWD/ensembl-git-tools/bin:$PATH
git ensembl --clone api
# Load ENSEMBL Modules
export PERL5LIB=${PERL5LIB}:${HOME}/ensembl/modulesOverview
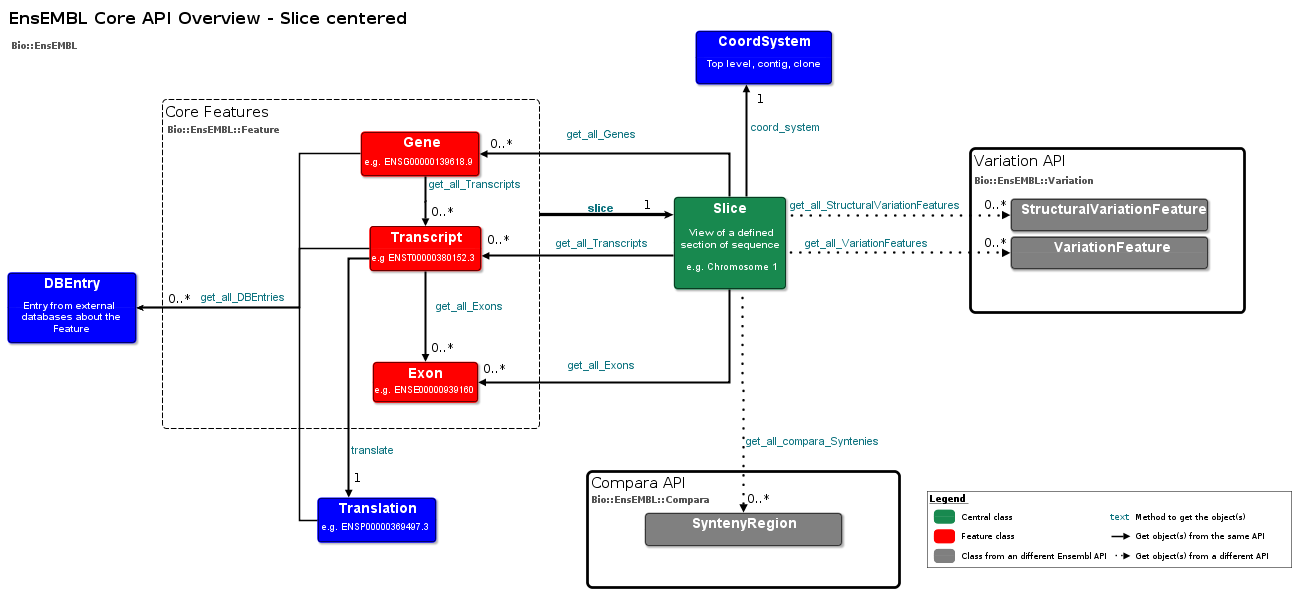
List adaptors
use Bio::EnsEMBL::Registry;
my $registry = 'Bio::EnsEMBL::Registry';
$registry->load_registry_from_db(
-host => 'ensembldb.ensembl.org',
-user => 'anonymous'
);
my @db_adaptors = @{ $registry->get_all_DBAdaptors() };
foreach my $db_adaptor (@db_adaptors) {
my $db_connection = $db_adaptor->dbc();
printf(
"species/group\t%s/%s\ndatabase\t%s\nhost:port\t%s:%s\n\n",
$db_adaptor->species(), $db_adaptor->group(),
$db_connection->dbname(), $db_connection->host(),
$db_connection->port()
);
}
Retrieval of genes and others
my $slice_adaptor = $registry->get_adaptor( 'Human', 'Core', 'Slice' );
my $slice = $slice_adaptor->fetch_by_region( 'chromosome', 'X', 1e6, 10e6 );
my $genes = $slice->get_all_Genes();
while ( my $gene = shift @{$genes} ) {
my $gstring = feature2string($gene);
print "$gstring\n";
my $transcripts = $gene->get_all_Transcripts();
while ( my $transcript = shift @{$transcripts} ) {
my $tstring = feature2string($transcript);
print "\t$tstring\n";
foreach my $exon ( @{ $transcript->get_all_Exons() } ) {
my $estring = feature2string($exon);
print "\t\t$estring\n";
}
}
}
Feature data
sub feature2string
{
my $feature = shift;
my $stable_id = $feature->stable_id();
my $seq_region = $feature->slice->seq_region_name();
my $start = $feature->start();
my $end = $feature->end();
my $strand = $feature->strand();
return sprintf( "%s: %s:%d-%d (%+d)",
$stable_id, $seq_region, $start, $end, $strand );
}ENSEMBL API Tutorial
Questions?
BioPerl and other useful Perl approaches for bioinformaticians
By Similis.cc
BioPerl and other useful Perl approaches for bioinformaticians
In this hands-on workshop (laptop recommended) we will introduce the following topics: perlbrew, Perl one-liners: awk/sed on steroids, some useful Perl modules for Bioinformatics, I/O of Bioinformatics formats, Access to Bioinformatics web services (NCBI Entrez, ENSEMBL)
- 4,739



