Airy beams
How to make laser beam turn
Claude-Alban
RANÉLY-VERGÉ-DÉPRÉ



Outline
- Introduction
- Simulation
- Applications
- Conclusion
Introduction
What are Airy beams anyway...?
Many answers are possible
Solution of Schrödinger equation for a free particule
i\hbar\frac{\partial}{\partial t} \Psi(\mathbf{r},t) = \left [ \frac{-\hbar^2}{2\mu}\nabla^2 + V(\mathbf{r},t)\right ] \Psi(\mathbf{r},t)
iℏ∂t∂Ψ(r,t)=[2μ−ℏ2∇2+V(r,t)]Ψ(r,t)
Caustics
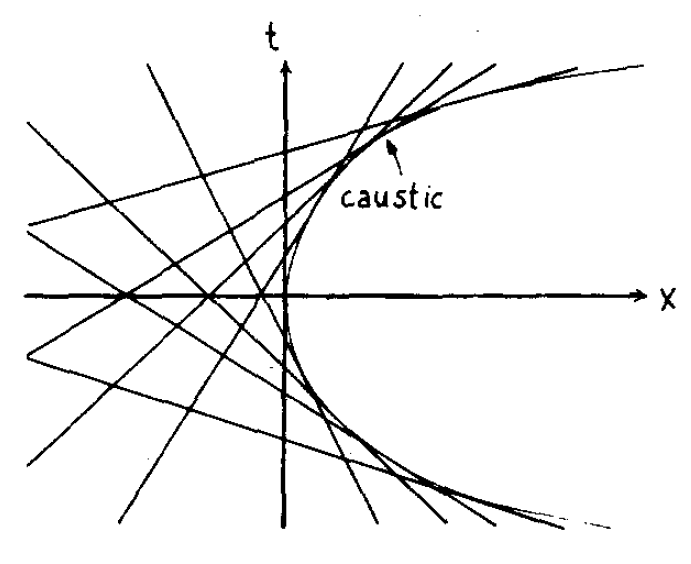
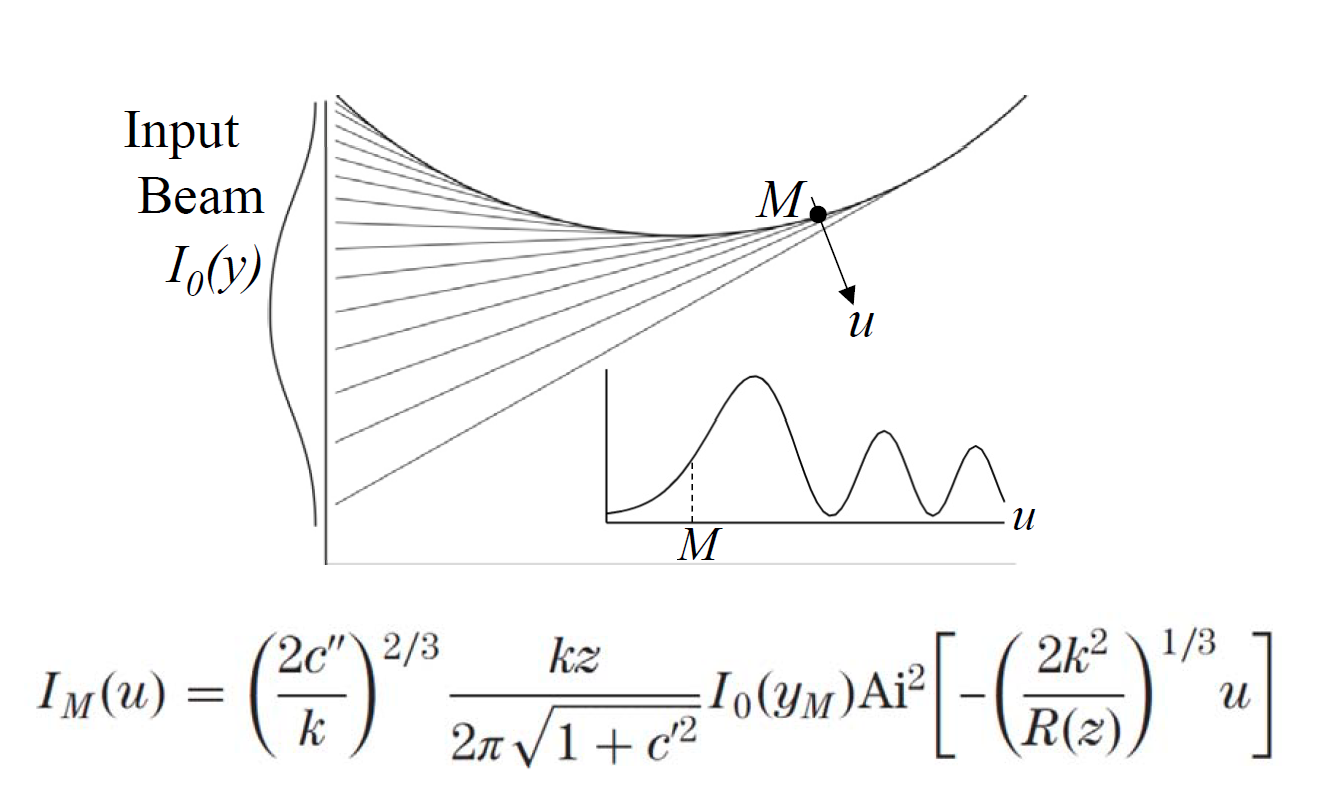
How can we generate them?
Fourier Optics !


Experimental setup
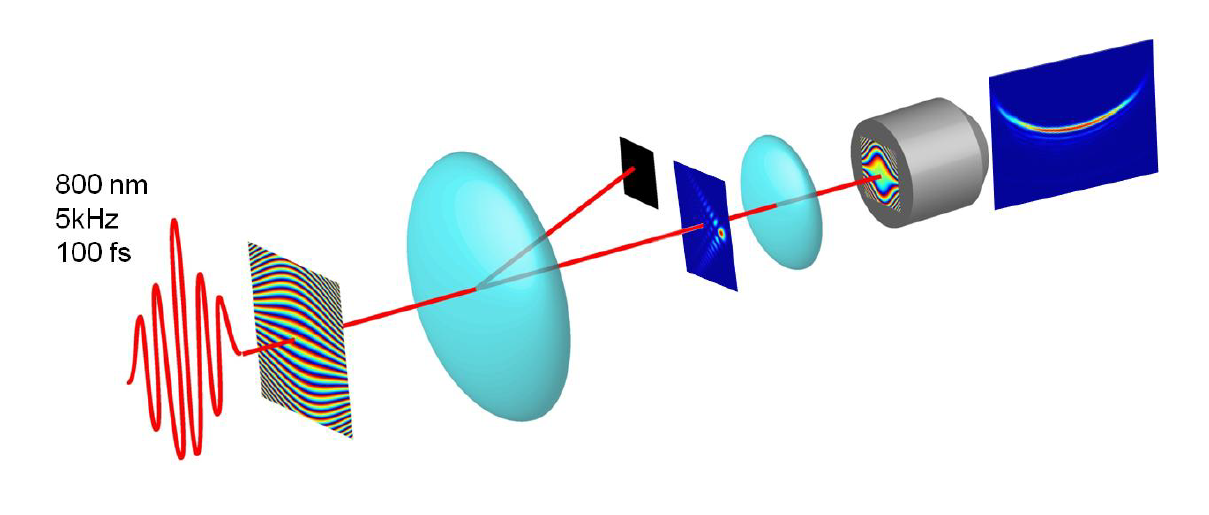
F. Courvoisier, Journées Nationales du réseau Optique et Photonique, 2012
Simulations
Analytical expression
There is often many ways of doing something but the best one is the one that works"
\phi(s,\xi) = Ai\left[ s - \left(\frac{\xi}{2}\right)^2\right] \exp\left[i \frac{s\xi}{2}-i\frac{\xi^3}{12}\right]
ϕ(s,ξ)=Ai[s−(2ξ)2]exp[i2sξ−i12ξ3]
Show us some code !
Trajectoire = @(s,kzi) airy(s-(kzi./2).^2);
Phase = @(s,kzi) exp(1i*s*kzi./2 - 1i*kzi.^3/12);
Phi = @(s,kzi) Trajectoire(s,kzi).*Phase(s,kzi);
The result
Applications
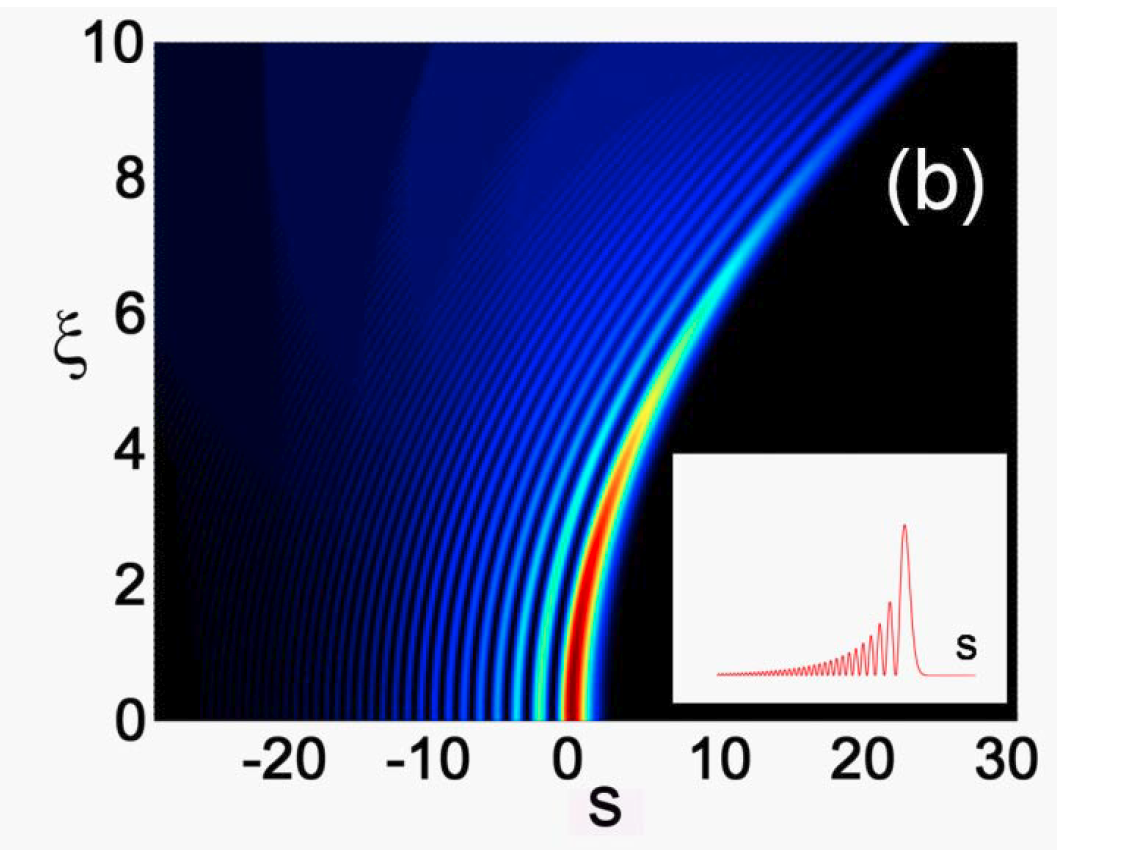
Finite beam
PRL 99, 213901 (2007)
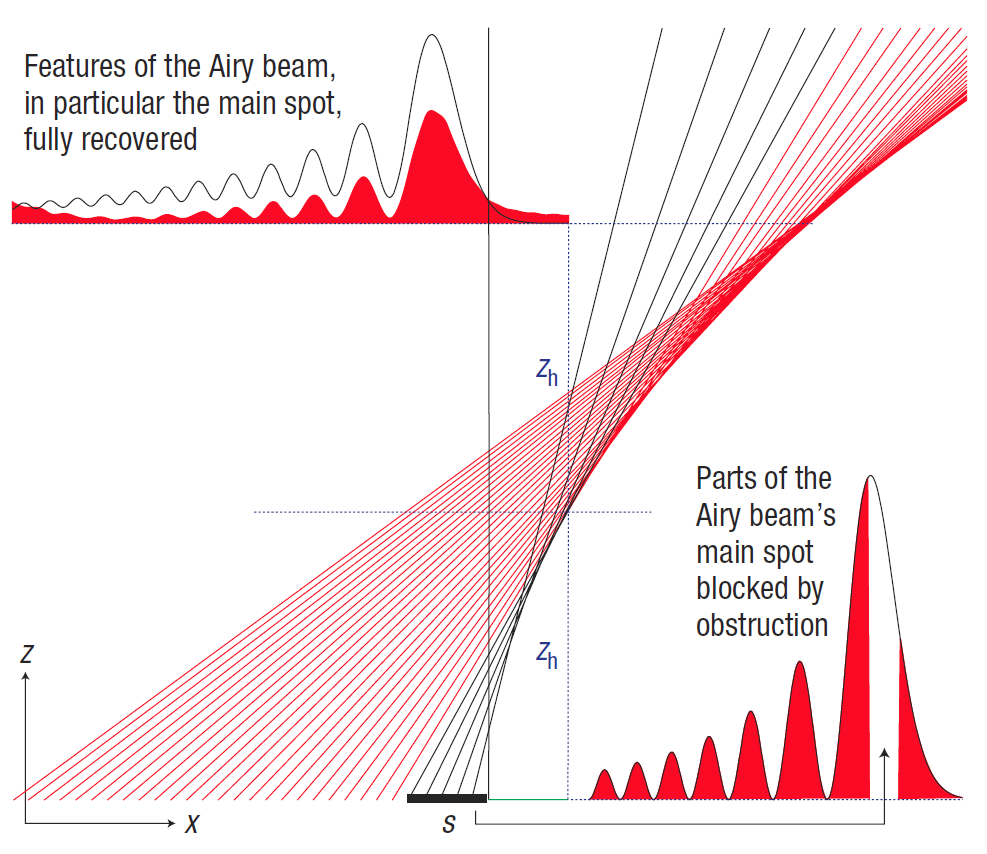
Regeneration of the beam
doi:10.1038/nphoton.2008.201
Optical tweezers
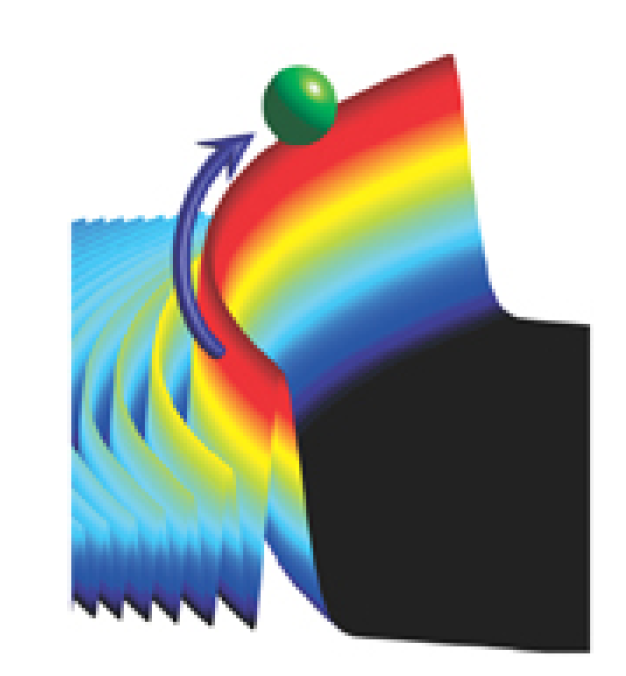
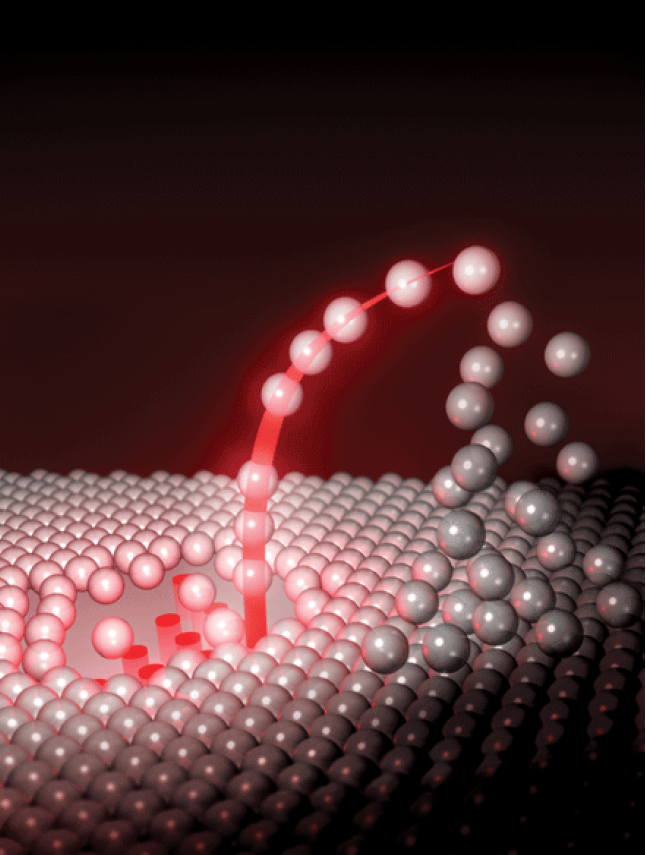
doi:10.1038/nphoton.2008.201
doi:10.1038/nphoton.2008.201
Curve-made manufacturing
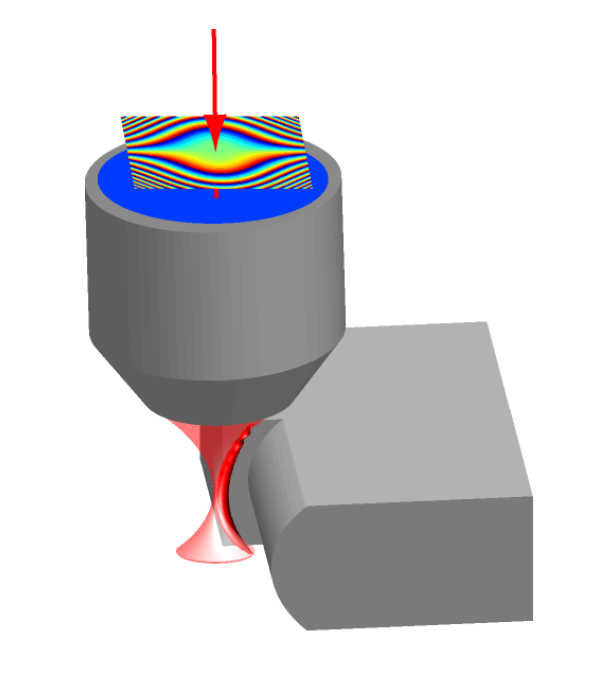
F. Courvoisier, Journées Nationales du réseau Optique et Photonique, 2012
Conclusion
Airy beams
By Claude-Alban RANÉLY-VERGÉ-DÉPRÉ
Airy beams
Présentation de Procédés Laser
- 39



