Reflections on tech
Stephen Merity
(@smerity)
that may or may not be useful ^_^
---
Dislcaimer:
Confused? Fascinated? Interested? Stop and ask me!
If you don't I might as well have recorded this from SF :)
Dislcaimer:
If you wanted to talk about lower or higher level details, let's do it!
Reminders/claims
Don't rely on others for your reasoning or direction
Technology is magical abstractions, both good and bad
Deep learning is declarative and can get better as your compute does
Luck surface area
"Luck is what happens when preparation meets opportunity"
Luck is like a rare raindrop
Maximize the surface area to maximize your chances of catching it
Smerity Reflections
(that may or may not be useful)
Main tip:
keep a diary
Better tip:
write into an open blog
(and maybe Twitter*)
Smerity Reflections
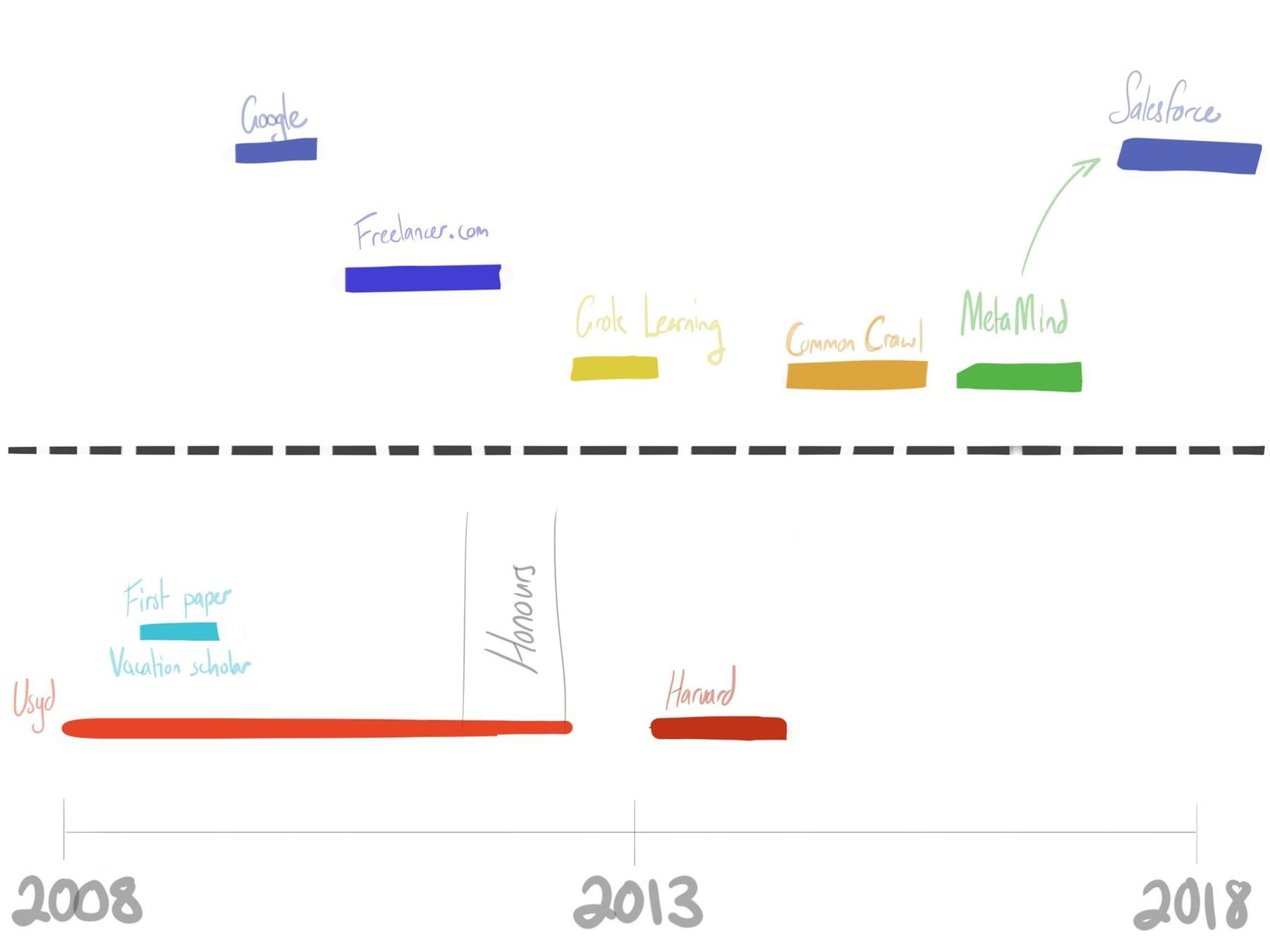
2008
2018
2013
AU
US
Smerity @ 2008
First year university:
stunningly good mentors but knew a direction I wanted to learn
Natural language processing (NLP):
trying to understand language through computing
Smerity @ 2008
I enjoyed NLP and wanted to learn,
so did a research course where I got no credit
Ugh -_-
Luckily the learning made up for it!
Smerity @ 2008/9
NLP Vacation Scholar with my mentor
(Dr James Curran)
First paper
(though it required staying up until 4+am and then he had a lecture at 10)
◉_◉
Smerity @ 2009/10
("Google Internship Reflection", 2010)
Good: scale, tools, technique, LGTM
Bad: cog in a machine
(not true for everyone but was for me)
Smerity @ 2010/11
Freelancer.com internship
Startup is so very different from big co
No longer a cog,
I was the data scientist
(before the term even existed)
Smerity @ 2010/11
Freelancer.com internship
Matt Barrie sent me a great deal of confidential material
(he was also the lecturer of compnetsec and startup course)
Smerity @ 2011/12
Honours year (I think?)
Mentor advice:
carrot and stick until you solve what you need to
Smerity @ 2013
Lost direction for a while,
applied for US university
Only applied for one, got rejected, damned fool :)
Smerity @ 2013
First employee at Grok Learning
They currently teach 15k+ high school students around Australia!
(same team that taught me Python when I was in high school)
Smerity @ 2013
Side note:
dropped a production database
...
Oops?
You will screw up, everyone does
Smerity @ 2013/14
Harvard <3
Introduction to the US ecosystem
Masters in one year means little sleep
Smerity @ 2013/14
Favourite course was one I was never technically enrolled in:
The Founder's Journey
Ask. Never be afraid of asking. The worst you can get is a no.
Smerity @ 2013/14
Favourite project: Google Analytics
analysis using
Common Crawl

Smerity @ 2013/14
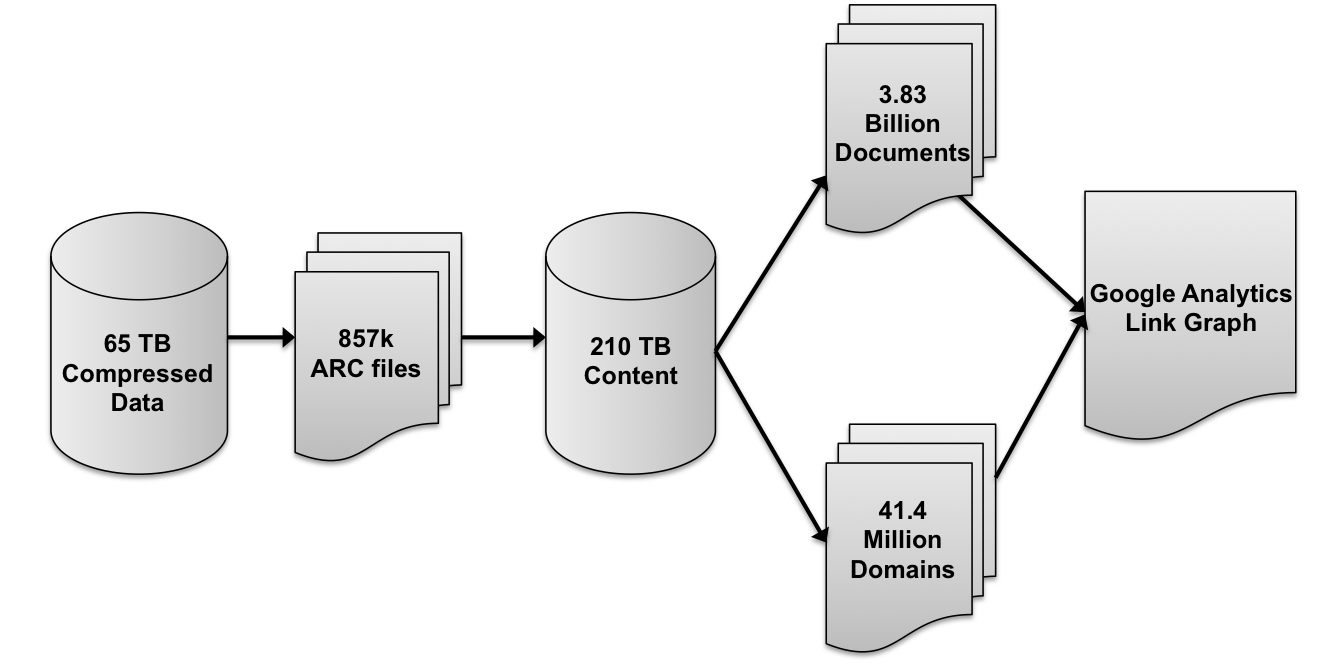
Smerity @ 2013/14
1600 CPUs
doing
nothing
Smerity @ 2013/14
(this was not the first, last, or millionth time I have been a fool)

Pro-tip: practice being foolish so you know how to avoid it when it matters :)
2014/15 @ CommonCrawl
Crawling ~35 billion pages (~2.5 PB)
as a lone engineer:
"I've seen things you people wouldn't believe.
DDoSed servers on fire off the shoulder of Tumblr."
ಠ_ಠ
Introduction to
San Francisco and Silicon Valley :)
2014/15 @ CommonCrawl
Good: big data, learning opportunities, presentation opportunities, perfect flexible intro to the US West Coast
Bad: I wasn't well suited to the role
Jumping from
big data hype to AI hype
My aim the entire time:
Use the insane capabilities that computing affords us to solve our problems
(true since first year / Freelancer.com)
2015/16 @ MetaMind
Jumped from big data engineer to research scientist (thanks Usyd!)

2017/18 @ Salesforce
Acquired back into a big co :)
Good: Great research environment, good pay, good visibility, flexibility, ...
Bad: I eventually wanted something new again :)
Reminders/claims
Don't rely on others for your reasoning or direction
Technology is magical abstractions, both good and bad
Deep learning is declarative and can get better as your compute does
Reminders/claims
Don't rely on others for your reasoning or direction
I could have done many of the same things and not done what I enjoy
Allow yourself to drift in the directions you want to go
Most of life is a two-way door,
take advantage of that
People are more wrong than right
Reminders/claims
Technology is magical abstractions, both good and bad
It's horrible, it's complex, it's barely usable, you will have sleepless nights...
yet it's all worth it when you get it working on the task you care about
Beliefs
Computers are being used horrifically ineffectively
Beliefs
Don't worry about that,
worry about
solving your task effectively
Good news: you have machines with seemingly infinite computer with which to solve your task :)
Beliefs
Part of computing is becoming comfortable with knowing
you don't know
but realizing you're smart enough to work it out if you need to
Allergory Time
Sorcerer's Apprentice
Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time

Allergory Time
Sorcerer's Apprentice...
Whose fault was it?
Mickey did darn well
Five minutes of mentoring and/or better directions and there'd be no problem
Beliefs
Irrational optimism - this world we've built has so many faulty perceptions and assumptions
By checking your assumptions you learn either way - why they're true or why they're not
Beliefs
Irrational optimism works for those who are already skilled and also for those with imposter syndrome
Reminders/claims
Deep learning is declarative and can get better as your compute does
Next section :)
Main take-away
Computing should feel intuitive
(same is true for deep learning)
If it doesn't feel like that
- someone has explained it wrong,
- someone misunderstood it,
- a library or paper has overcomplicated it
Before I begin,
let's take a step back...
What do we want
in computing?
We want our programs to be flexible, re-usable, and produce expected output
Desire:
Our programs are
flexible, re-usable, and produce expected output
Reality:
Sequence modeling and
deep learning may allow all:
flexible, re-usable, and
expected output
Heretical claim:
As programmers, functions are
our fundamental building blocks
We as humans define the logic
We also hence decide what information flows from input to output
Take input, apply logic, produce output
Functions define our
level of abstraction
We can't influence what came before
We can't be influenced by
what happens after
This is a problem
Our tasks are defined by
objectives and data
Objectives are lossy
past abstraction boundaries
Language Modeling
Given a sequence of tokens (context),
predict the next N tokens
The flight from Sydney to New ____
We analyze a massive set of data and follow the patterns we've already seen
Machine Translation
p(strong tea) > p(powerful tea)
Speech Recognition
p(speech recognition) > p(speech wreck ignition)
Question Answering / Summarization
p(President X attended ...) is higher for X=Obama
Query Completion
p(Michael Jordan Berkeley) > p(Michael Jordan basketball)
By accurately assigning probability to a sequence you can improve many tasks:
N-grams
Have we seen this sequence before?
If so, how many times?
Bob ate the ____
Zomicron ate the ____
N-grams
Have we seen this sequence before?
If so, how many times?
Bob ate the ____
张伟 (Zhang Wei) ate the ____
Contextual N-grams
<name> ate the ____
... but now we have a bajillion edge cases to try to capture ...
<name:male> was <verb:run> through the <city:Sydney> <street:plural>
A bajillion edge cases isn't sane for a human
... yet it's what we likely need to do well
In brief: deep learning
Explaining DL to my parents
over a cup of tea (link)

DL is just functions
Define the input, the output,
and the "architecture"
(i.e. equations the fn computes with)
The logic is decided by the
input and expected output
given to the program
Linear regression
Input: beds, baths, square feet
Logic:
N = X * bed + Y * bath + Z * footage
Output: N (approximate house price)
We now have weights {X, Y, Z}
"Learn" {X, Y, Z} to minimize the error
Linear regression
Logic:
X * bed + Y * bath + Z * footage
We don't set {X, Y, Z} ourselves
We use backpropagation to nudge them
(= fancy way of asking the eqn how best to change a parameter to reduce our error)
Stack these blocks
The computation is whatever we want
We don't care as long as our desired program is a subset of the possible computation
Typically a matrix multiplication
followed by an "activation function"
(allows for decisions to be made)
Stack these blocks


Confused? Uncertain?
You don't need to understand specifics
Deep learning is a
declarative programming language
State what you want in terms of
input, output, and the type of compute the model may use
Response from parents
"This seems ... overly simple?"
"Indeed it is - the scary thing is that the principle scales up. The same general tactics work for images, text, you name it..! Instead of three parameters though, I’m doing this over MILLIONS or BILLIONS of parameters. Backpropagation still works!"
A billion edge cases isn't sane for a human
... yet it's what we likely need to do well
So let's get the computer to do it :)
In brief: deep learning
Learn to trust the abstraction
(just as you trust your database*)

In brief: deep learning
Learn to trust the abstraction
(just as you trust your compiler*)

In brief: deep learning
Learn to trust the abstraction
(just as you trust your CPU*)

In brief: deep learning
Learn how much you can trust an abstraction then trust it
Learn to trust deep learning
as an abstraction
The only scary thing is
a human didn't write the logic ...
🤔
Neural Language Modeling
So what does this look like for LM?
First, let's think of our objective:
given previous word,
we want to predict the next word,
on repeat
We want a function akin to:
memory, next_word = f(current_word, memory)
Neural Language Modeling
So what does this look like for LM?
First, let's think of our objective:
given previous word,
we want to predict the next word,
on repeat
We want a function akin to:
memory, next_word = f(current_word, memory)
Neural Language Modeling
We define the architecture
(or equations the function may use)
We want each word to be represented by a vector, let's say 400 floating point numbers
Our "running memory" will also be
400 floating point numbers
Neural Language Modeling
Our model will learn the best value for each of those 400 numbers for all our words
Our model will learn what type of logic the functions should run to create and manipulate the hidden state (memory) to guess the
next word
Neural Language Modeling

Top: Output
Middle: Logic (Blue)
Bottom: Input
Neural Language Modeling

Embed:
Each word has a representation of 400 floating point numbers
words['The'] = [0.123, 0.621, ..., -0.9]
Neural Language Modeling

Recurrent Neural Network (RNN):
A function that takes two inputs,
word (400 numbers) and memory (400 numbers),
and produces two outputs (word and memory)
Neural Language Modeling

Recurrent Neural Network (RNN):
(h = hidden state, or our memory)
Neural Language Modeling

How do you start out the weights?
Random.
(Maybe pre-trained weights but that's later...)
Neural Language Modeling

Why is the RNN hidden state important?
It's how we pass along context
(i.e. you said "flew" a few words back and "New" right before this word)
As each word is added,
our hidden state (memory) changes
Visualizing word vectors

Visualizing word vectors

Contextual N-grams
"... but now we have a bajillion edge cases to try to capture ..."
<name:male> was <verb:run> through the <city:Sydney> <street:plural>
The computer learned how to do those bajillion edge cases
from random numbers and context
Our programs are
flexible, re-usable, and produce expected output
An aside:
Let's do HTML parsing
Let's say we want to
extract content from the web
Boss: Your objective is to collect links for a web crawler
Huzzah! I can do that!
How about I use ...
Regex for HTML 😡
Are you MAD?!?!?
import requests
import re
data = requests.get('http://smerity.com/articles/2018/limited_compute.html').text
links = re.findall('<a href="([^"]+)">([^<]+)</a>', data)Now is this wrong?
Not exactly.
What it does catch is correct.
It just misses oh so many edge cases ...
(= so much missed or lost context)
Success!
It isn't perfect, but it does
work for the task at hand ^_^
Now your boss, excited with your progress, asks you to extract text from the same webpages you just processed.
It should be easy, right..?
Answer: 😭
"Proper" parser for HTML
Recursive descent parser (RDP)
You go all in and write an RDP
(If you don't know what it is, you keep track of the opening and closing HTML tags)
Wait, boss, what text do you want? All text, including navigation? Only article text as if it were a news article? Sidebar text?
!?!?!??!?!
This is a problem
Our tasks are defined by
objectives and data
Our objective is vague yet
those specifics are key to success
Success!
It isn't perfect, but it does
work for the task at hand ^_^
Now your boss, excited with your progress, asks you to convert that text to a Markdown equivalent.
Your answer: 😭
At least a butcher, baker, or candlestick maker have clear objectives
Worse, what about errors?
Constructing programs resilient to
bad input is hard
You've likely had to deal with some horrific code in your lifetime.
Now imagine having to deal with an entire
web worth of silly people...
The architecture of the Web has several languages in it - there's HTTP, there's HTML, URLs are a language, there's CSS, and there's the scripting language. They're all in there and at they can all be embedded in each other and they all have different quoting and escaping and commenting conventions. And they are not consistently implemented in all of the browsers. Some of them are not specified anywhere.
- Douglas Crockford (of Javascript and JSON)
My time @ Common Crawl
Crawling ~35 billion pages (~2.5 PB)
as a lone engineer:
"I've seen things you people wouldn't believe.
DDoSed servers on fire off the shoulder of Tumblr."
ಠ_ಠ
LMing for HTML 🤔
(Heretical claim reminder)
Sequence modeling and
deep learning may allow all:
flexible, re-usable, and
expected output
Neural Language Modeling

Why is the RNN hidden state important?
It's how we pass along context
(i.e. you said "flew" a few words back and "New" right before this word)
As each word is added,
our hidden state (memory) changes
LMing for HTML 🤔
We know LMs learn useful context

We can introspect the RNN's hidden state
to guess the function of a given memory cell
LMing for HTML 🤔
Let's look what it does to C code

This is the same "program" as trained on English - but this model was trained on C.
LMing for HTML 🤔

The model learns to capture the depth of an expression by performing LM'ing on C code.
Depth is exactly what we need for HTML.
Neural Language Modeling

How does hidden state change exactly?
Depends on everything.
The data, the input, the architecture, ...
Active area of research as we don't really know.
As each word is added,
our hidden state (memory) changes
Neural Language Modeling
Example: a few days ago a paper trying to work out how different RNNs count with their memory

Reminder: DL is declarative
Ask it to learn language modeling?
Your model learns counting as a sub-task

What happens with errors?
The LM gets progressively more upset
Forget a semicolon/bracket/closing tag/.../?
The LM will become uncertain
(we can measure the entropy)
and can even intelligently suggest
where you went wrong
Remember that at this stage the model has only one broad objective:
guess what comes next
Now add more objectives as you want
(mark <a href>, get text, remember if in <b> tag)
The model will learn how to balance objectives given the resources available and data seen
Deep learning is a
declarative programming language
How far can we take this?
Is it only surface level features?

The team at OpenAI performed character level language modeling on Amazon reviews.
This is a single neuron.
How far can we take this?
With different mechanisms
An attention based model (i.e. pull information from words based on my word) learns anaphora resolution as part of translation

How far can we take this?
Translation with no parallel corpus
Translate between language A and B
without a single shared sentence
How?
Convert a sentence from A => B => A'
Ensure A == A'
Language models are implicit compression
What about my work?
My research has been used in areas
I never could have imagined
I wrote a language model that was fast
and which achieved state of the art results.
I released the code open source.
It has been trained on dozens of other languages, serves as the basis of Github's Semantic Code Search, audio processing, bio-informatics, ...
Our tasks are defined by
objectives and data
Deep learning models
define their operation based on both
Deep learning is closer to
growing a garden
than
enumerating logic
The result depends on the substrate (data) and
what you put in (type/structure of compute)
It had no explicit English knowledge injected and few constraints to make it better work on English.
Hence, it is re-usable across data.
The language model is trained based upon the data it sees.
What if tomorrow your program had to work in only 100MB of RAM? A 100 Mhz CPU? Could only use adds but no mults?
In deep learning you re-train the model and see what trade-offs have been made
My work
Quasi-Recurrent Neural Network
(Bradbury*, Merity*, Xiong, Socher)

"This bit is slow so why don't we try a
less powerful but faster part?"
"Wait ... it works just as well? O_o"
Sequence modeling and
deep learning may allow all:
flexible, re-usable, and
expected output
Heretical claim:
No-one knows how efficient it could be
or what knowledge we could extract
No-one has tried this in field / task X
A single GPU can beat a cluster
You don't need a deep theory background
The potential
New York Times (2012):
"How Many Computers to Identify a Cat?
16,000 (CPU cores)"
One year later: "three servers each with two quad-core CPUs and four Nvidia GeForce GTX 680 GPUs"
The potential
Neural Architecture Search:
"32,400-43,200 GPU hours"
Just over a year later:
"single Nvidia GTX 1080Ti GPU, the search for architectures takes less than 16 hours"
The potential
If this type of programming isn't introduced
in first year alongside functions and DBs,
we're doing students a disservice
The implementation is hard, the use is easy
I am not saying this due to the hype,
I am saying this due to how easy it can be
and what can be delivered with it
Most heretical
Advice for undergrads
By smerity
Advice for undergrads
- 2,577



