Earthsys 144: Fundamentals of GIScience
GNSS/GPS and Data Collection
where is your data? gis.stanford.edu


If you registered late, are unable to access Google Earth Engine, or haven't received a Planet.com invite, fill out this form ASAP!!!

|
Spatial Question or Idea
What is the "where" of your project, and why does it matter to you? This could be the beginning reconnaissance on an archaeological site, a set of maps for you final project in another course, an interactive webmap that distributes information to the public about something useful, an art project to extract features from satellite imagery and use them in some interesting way (see: Jenny Odell), it's really wide open and up to your interests and creativity! |
|
2 pts |
|
Proposed Workflow
Don't try to be too technical or "GISciencey" here. Just a simple, "I'll measure the distance from something I'm interested in, to something I think influences some characteristic of it, and do a simple regression," or, "I will use high resolution satellite imagery and historic maps to look for buried features in an area I am interested in," or "I will create a geodatabase of layers relevant to my project, including new data digitized from historic maps," or "I will create a survey that collects some information from contributors and plots it to an interactive web map for public use," etc... |
|
2 pts |
|
Data Sources
This should be a straightforward list, with links, to data sources you have identified as useful, as well as your very brief idea about their application and utility. "Planet.com daily imagery - daily cadence allows mapping of hyperlocal flooding events," or "OpenStreetMap.org - water sources and clinic locations in Kibera, Kenya." |
|
2 pts |
|
Lit Review/Bibliography
A quick review of previous work (if any) that is similar, useful or influential to your project, with a bibliography. Again, keep it brief and cull to 4 or fewer most important sources for this proposal. |
|
2 pts |
|
GeoJSON file of your AOI
A polygon GeoJSON file (you can use QGIS, or geojson.io to create) of your Area of Interest (AOI). |
|
2 pts |
Project Proposals are DUE NEXT FRIDAY, APRIL 25!!
Be a KZSU DJ!!
We've set 3 dates for trainings this quarter (maybe more to come... time willing) on:
- Monday, April 29 from 5pm-9pm
- Friday, May 3 from 9:30pm-1:30pm
- Thursday, May 9 from 5pm-9pm



What is GNSS/GPS?



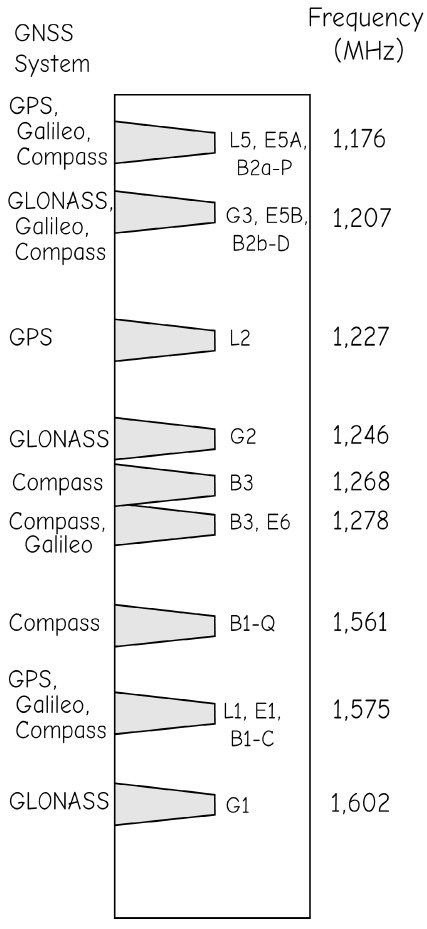
The military satellite navigation system called the Global Positioning System (GPS)/NAVSTAR, developed in the 1970s under the direction of Bradford W. Parkinson, Stanford professor of aeronautics and astronautics, and an U.S. Air Force colonel at the time.


NAVSTAR "GPS"
GLONASS
BeiDuo
Galileo
Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS)
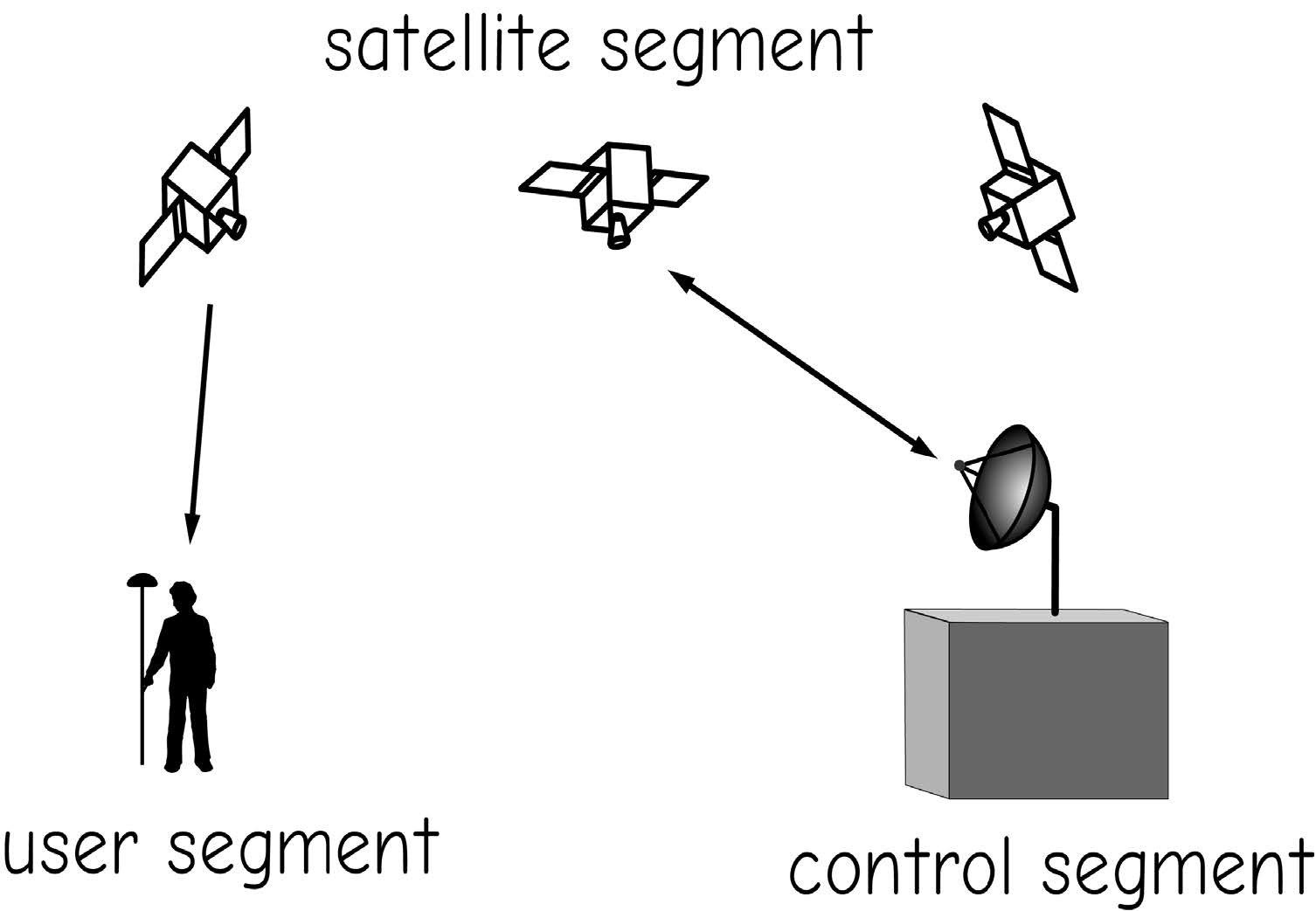
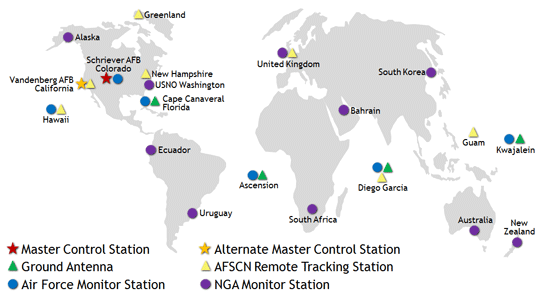
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) has 3 main components
- Receiver (User)
- Satellite Constellation
- Ground Stations (Control)


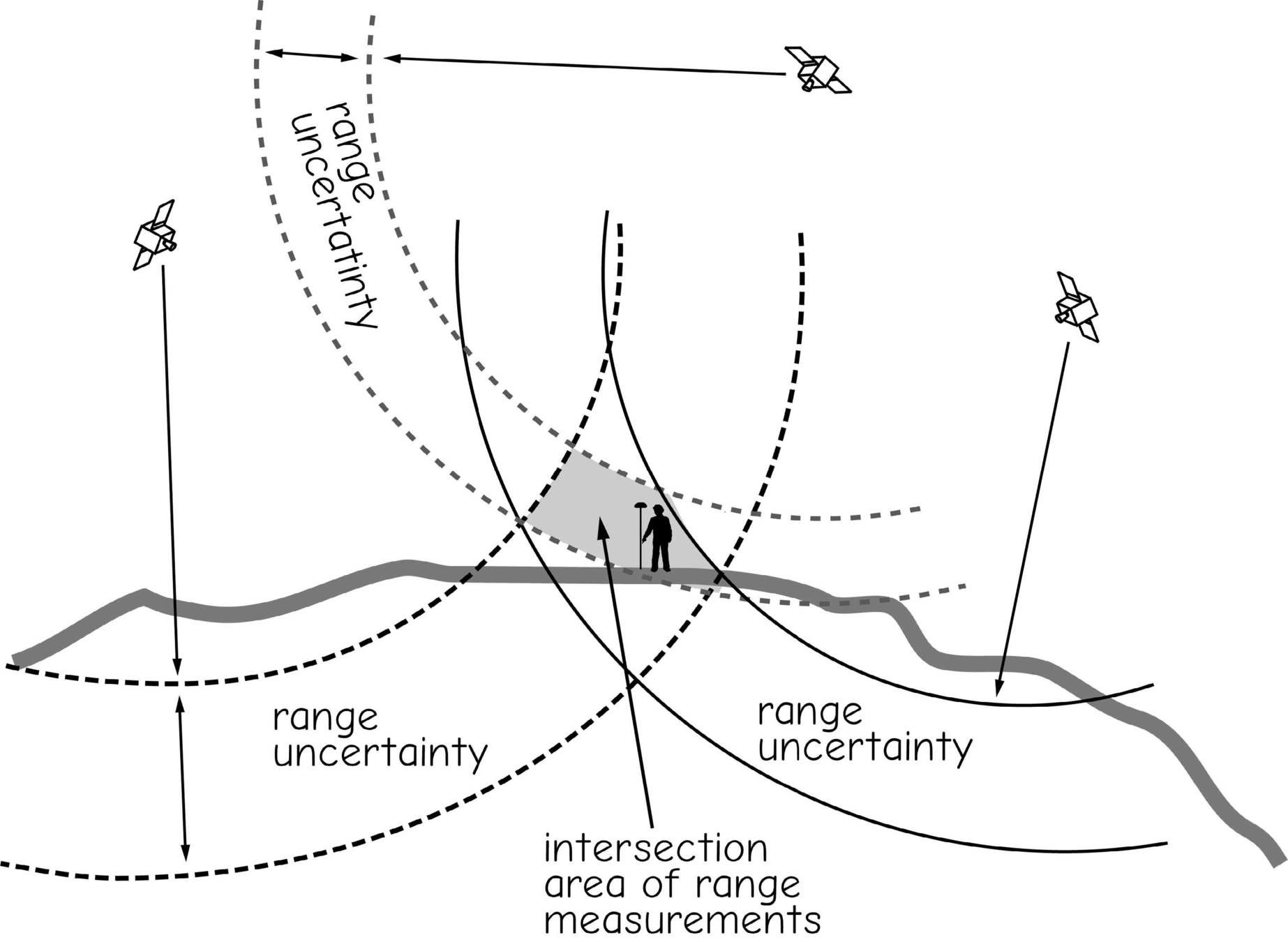
GNSS is based upon time converted into distance
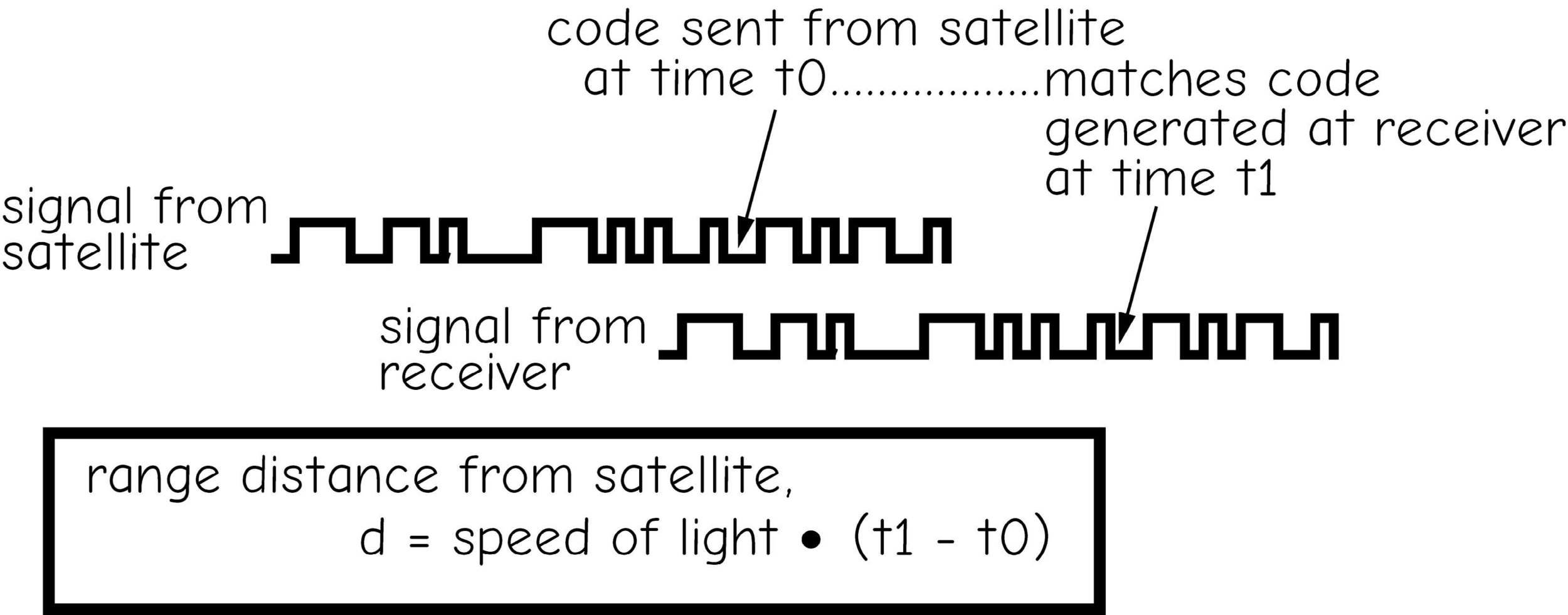
Trilateration
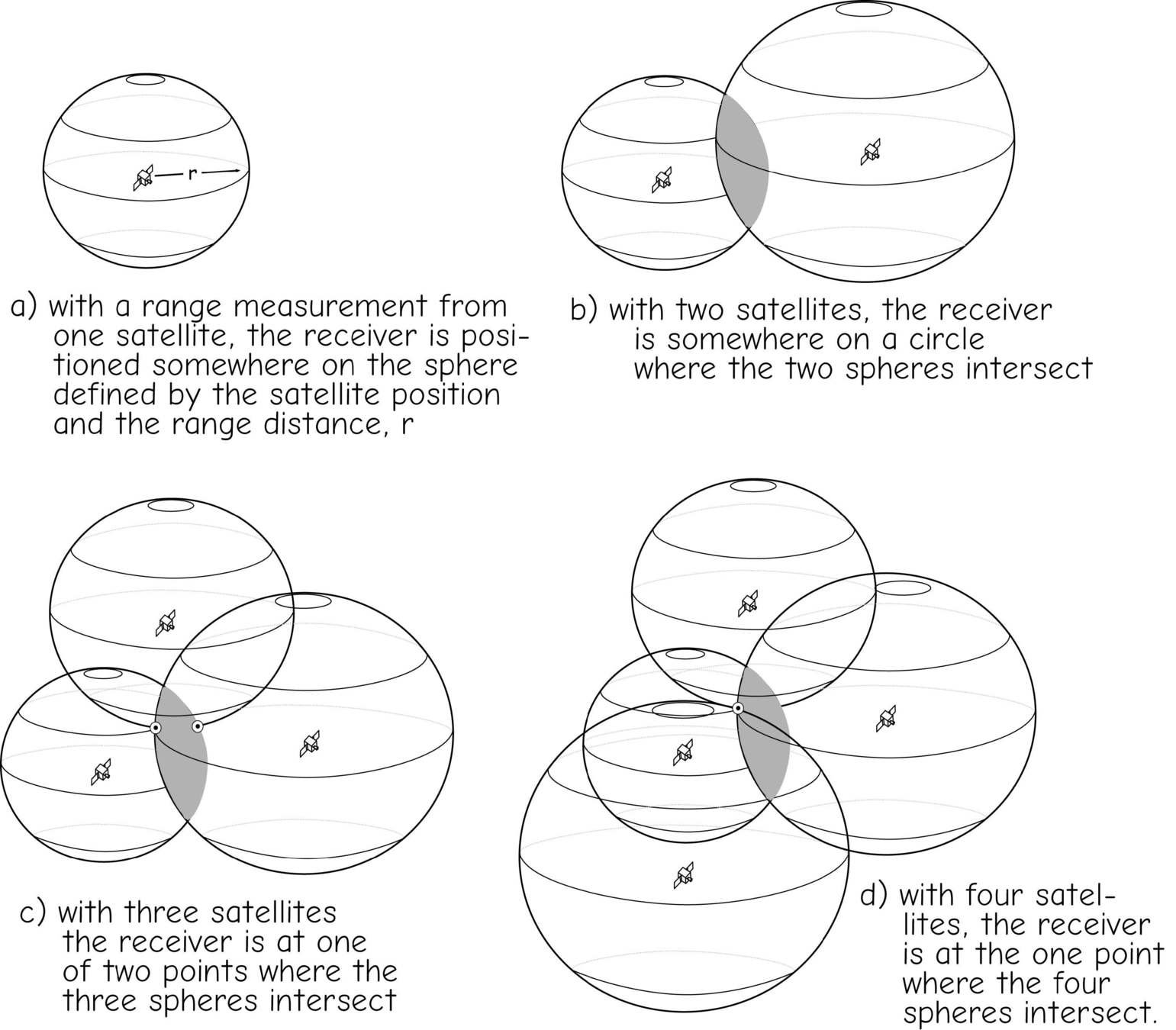
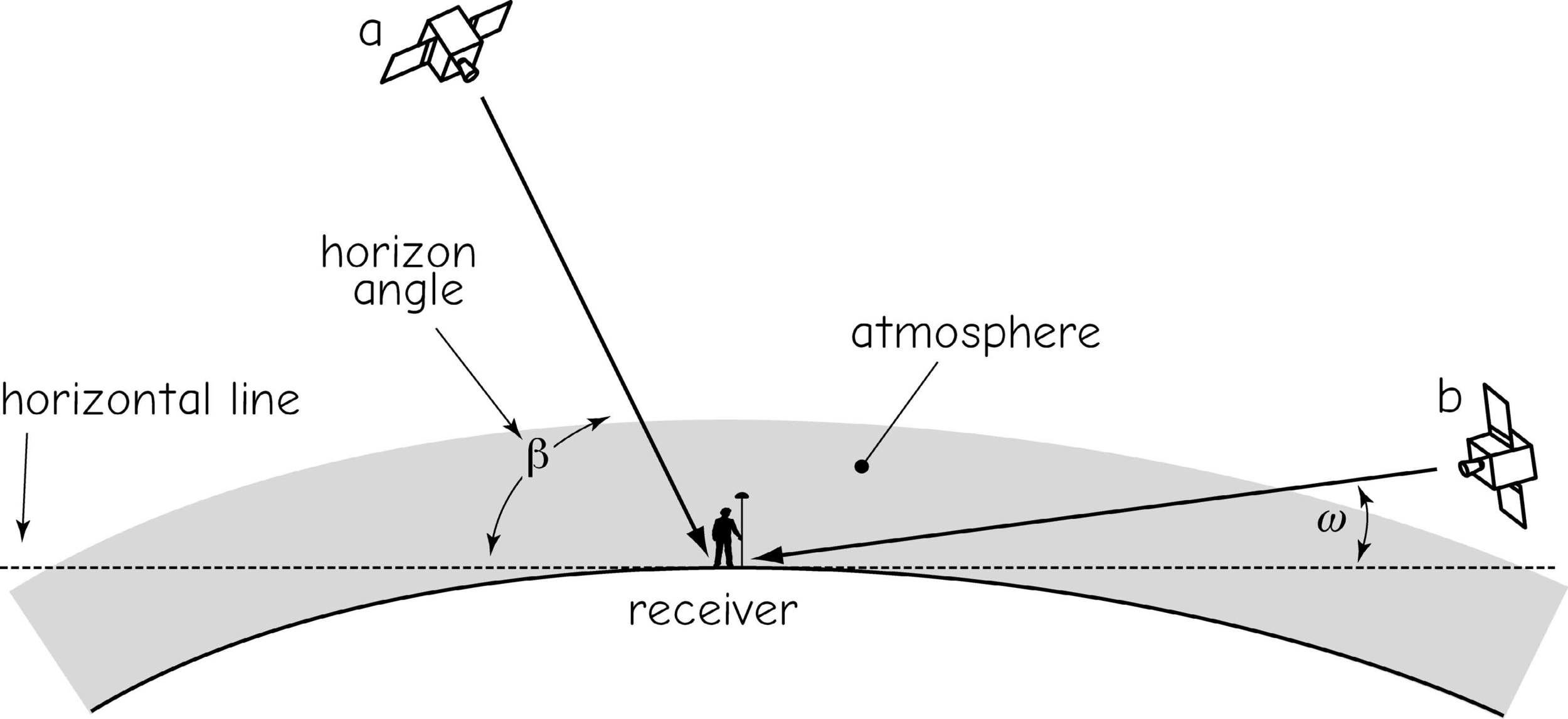
Sources of Error
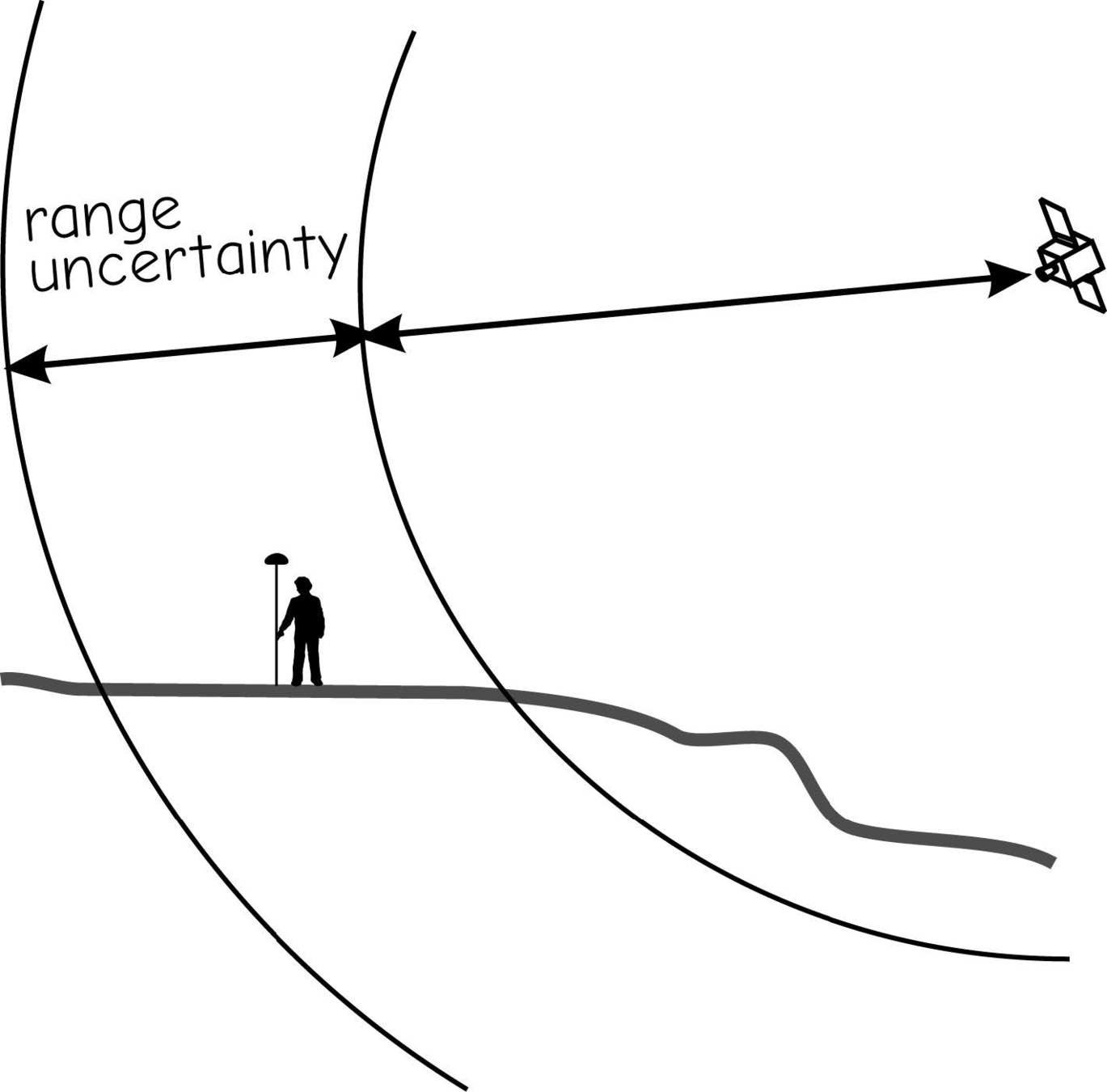
signal delays/range uncertainty
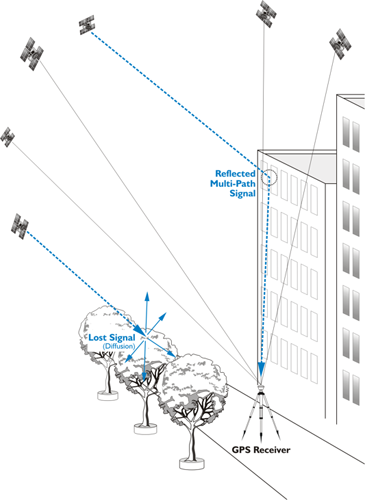
Multipathing
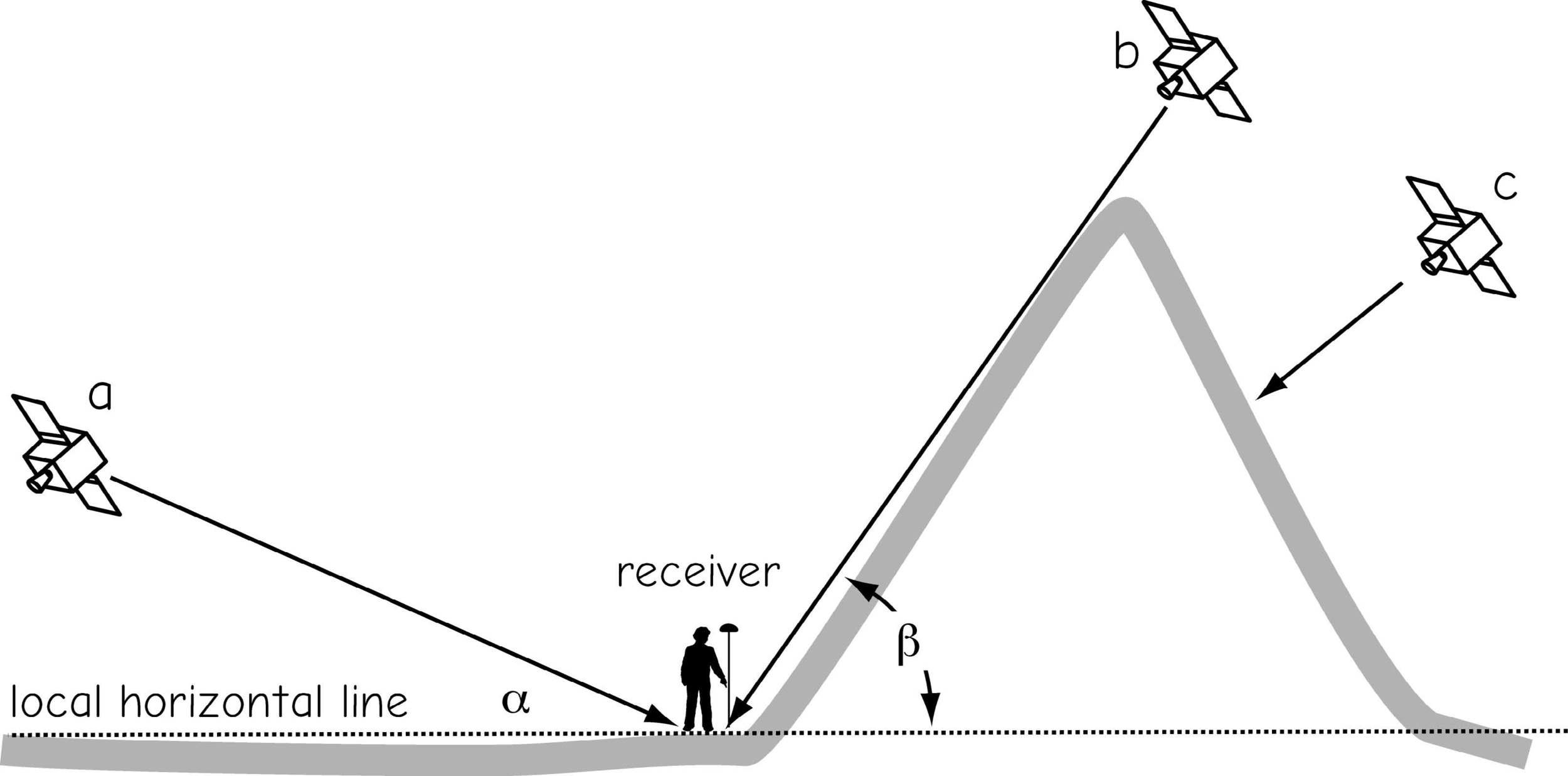
constellation geometry
constellation geometry
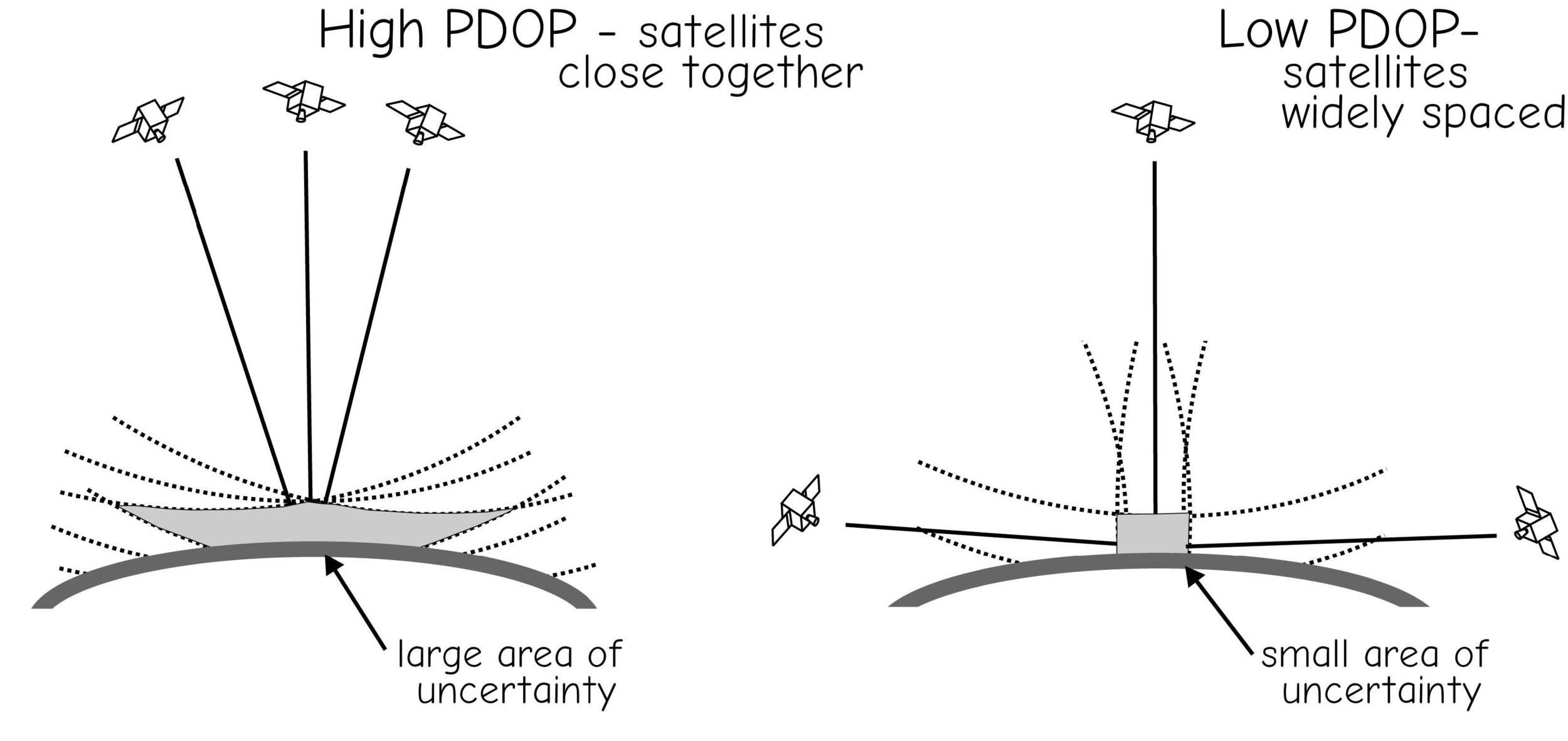
Dilution of Precision
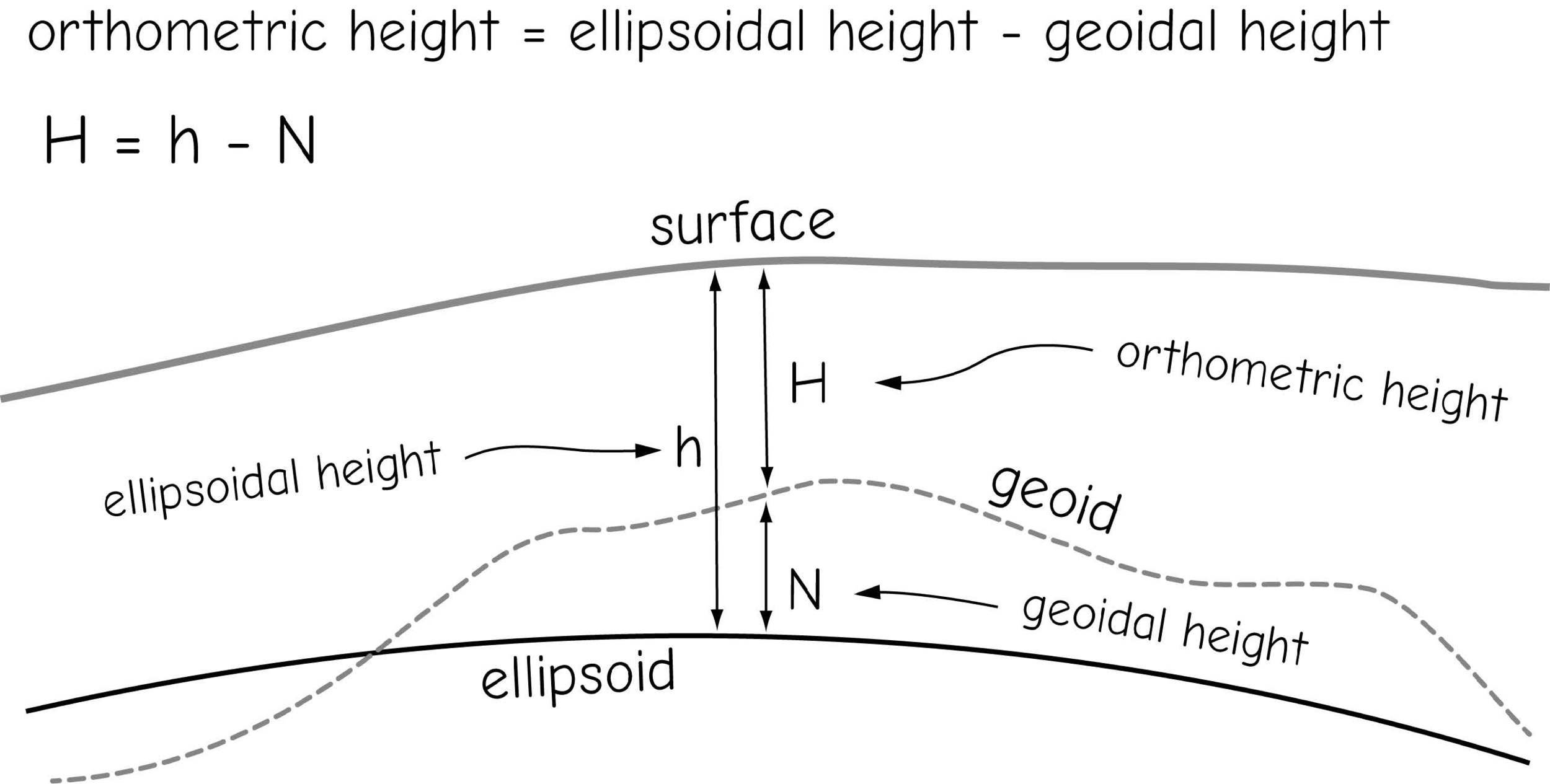
GNSS Height Measurement
Real-time Differential Correction & RTK
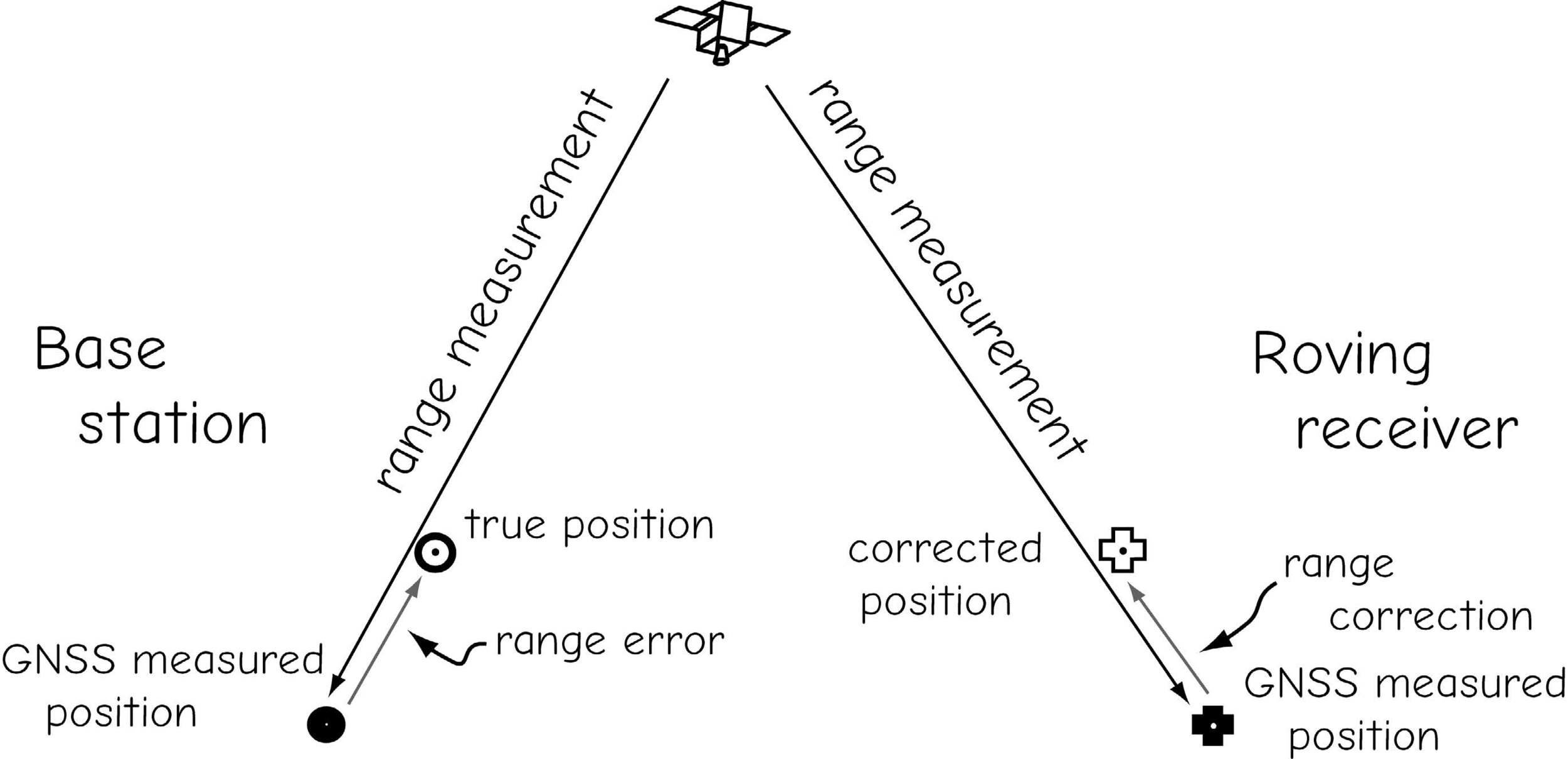
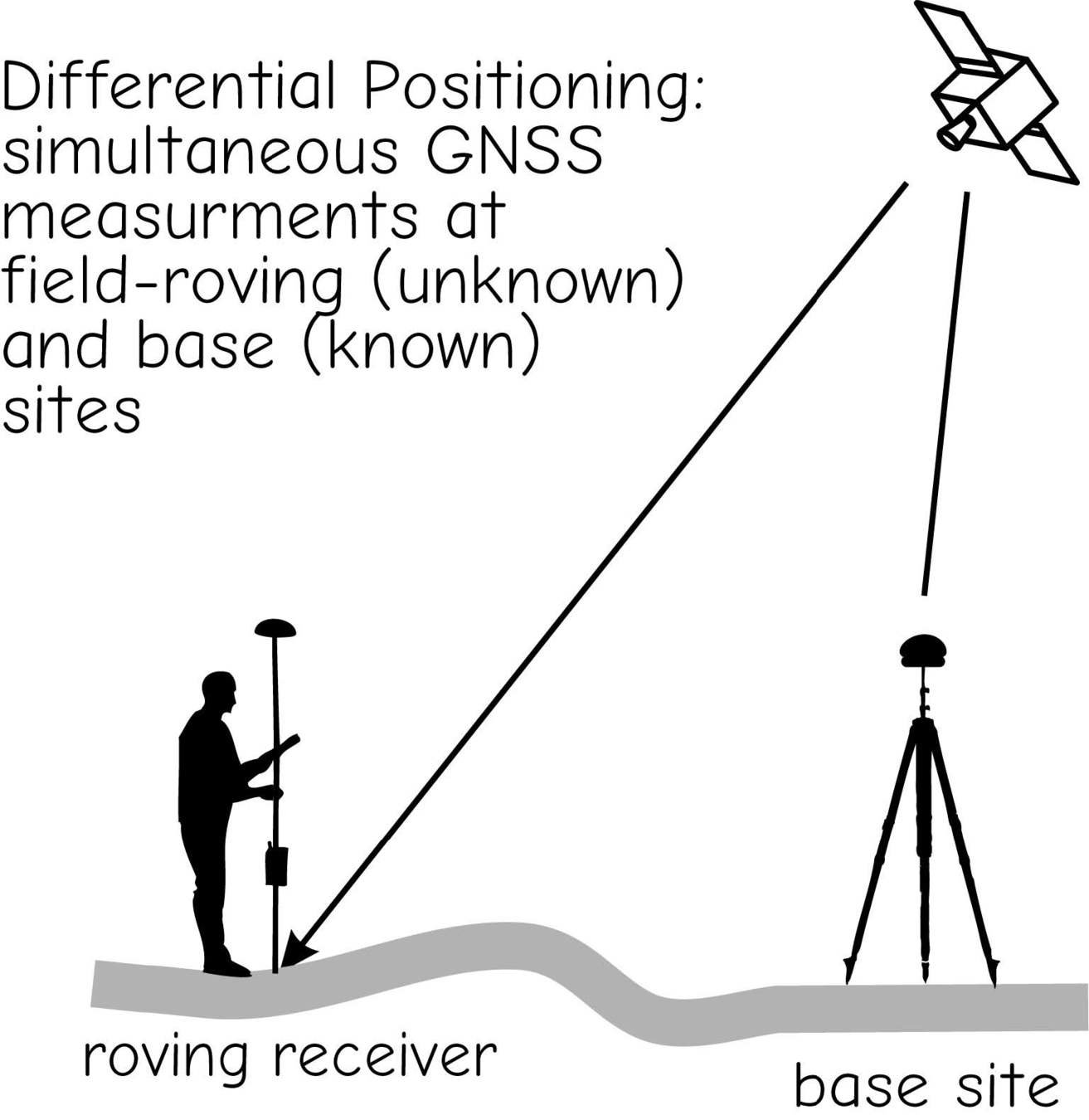
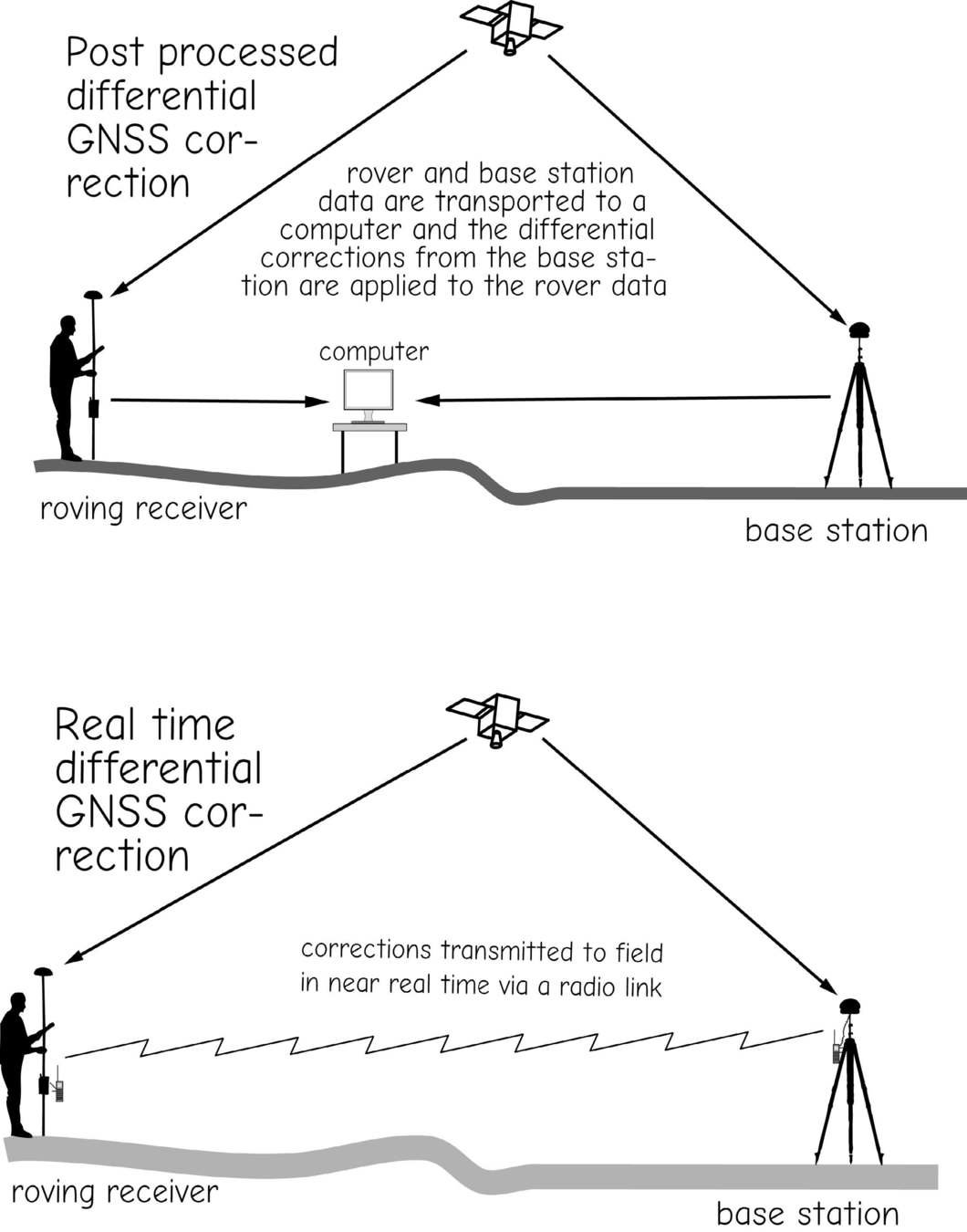
Post-Processing
vs
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK)
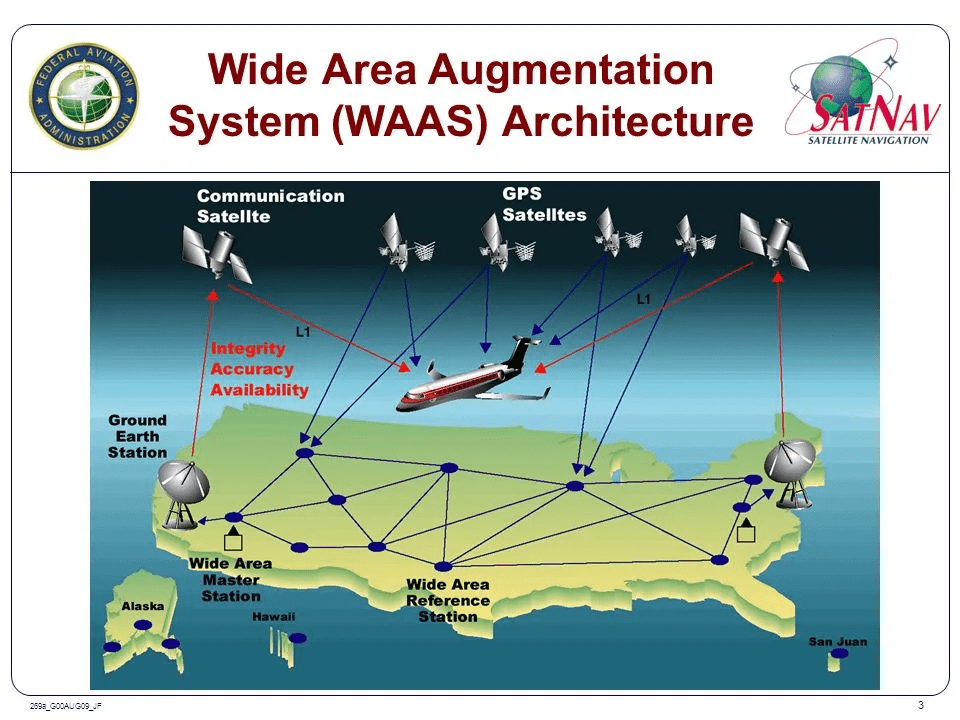
Optical (Total Station) Survey
Laser Theodolite

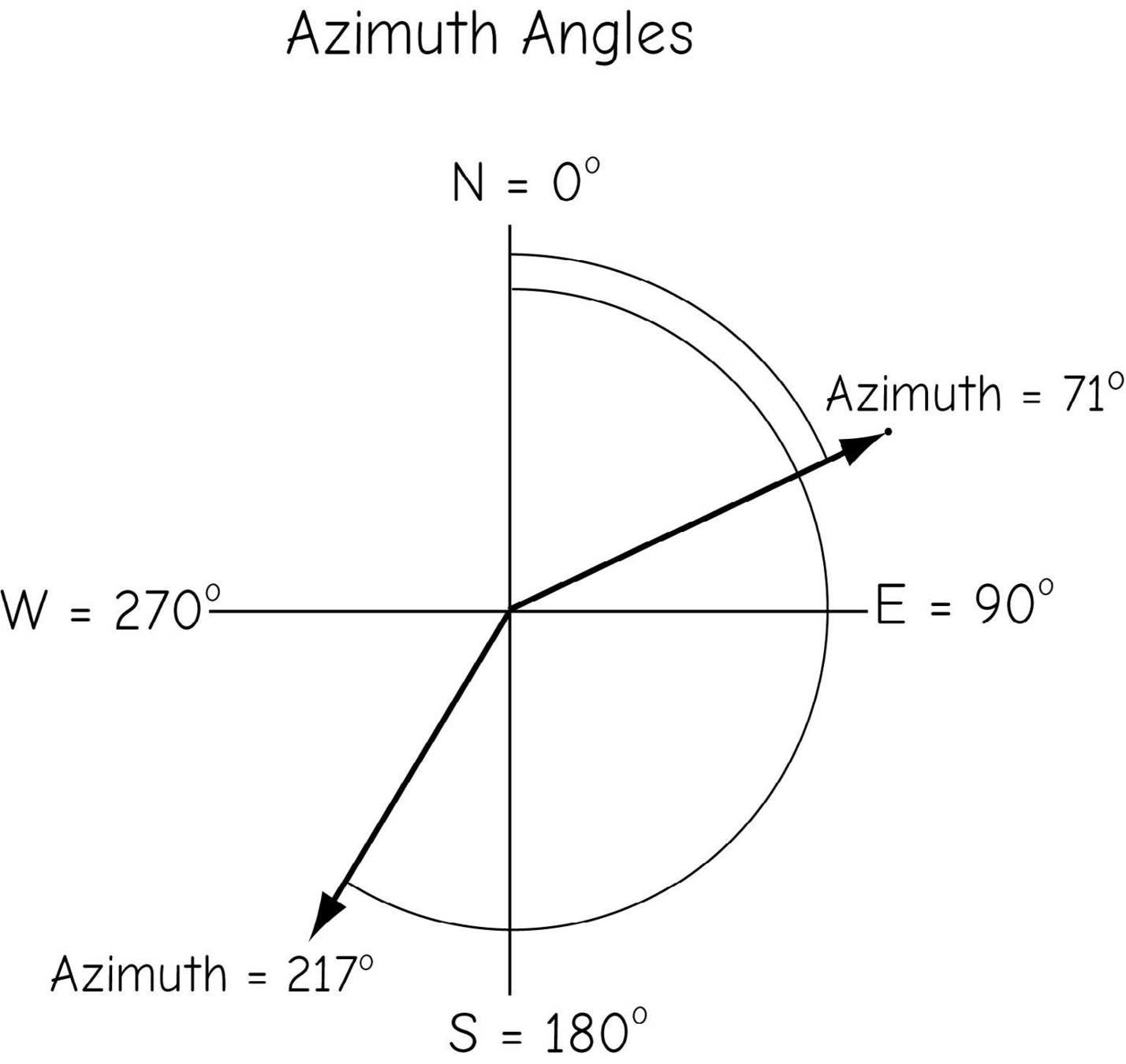

Azimuth vs Bearing


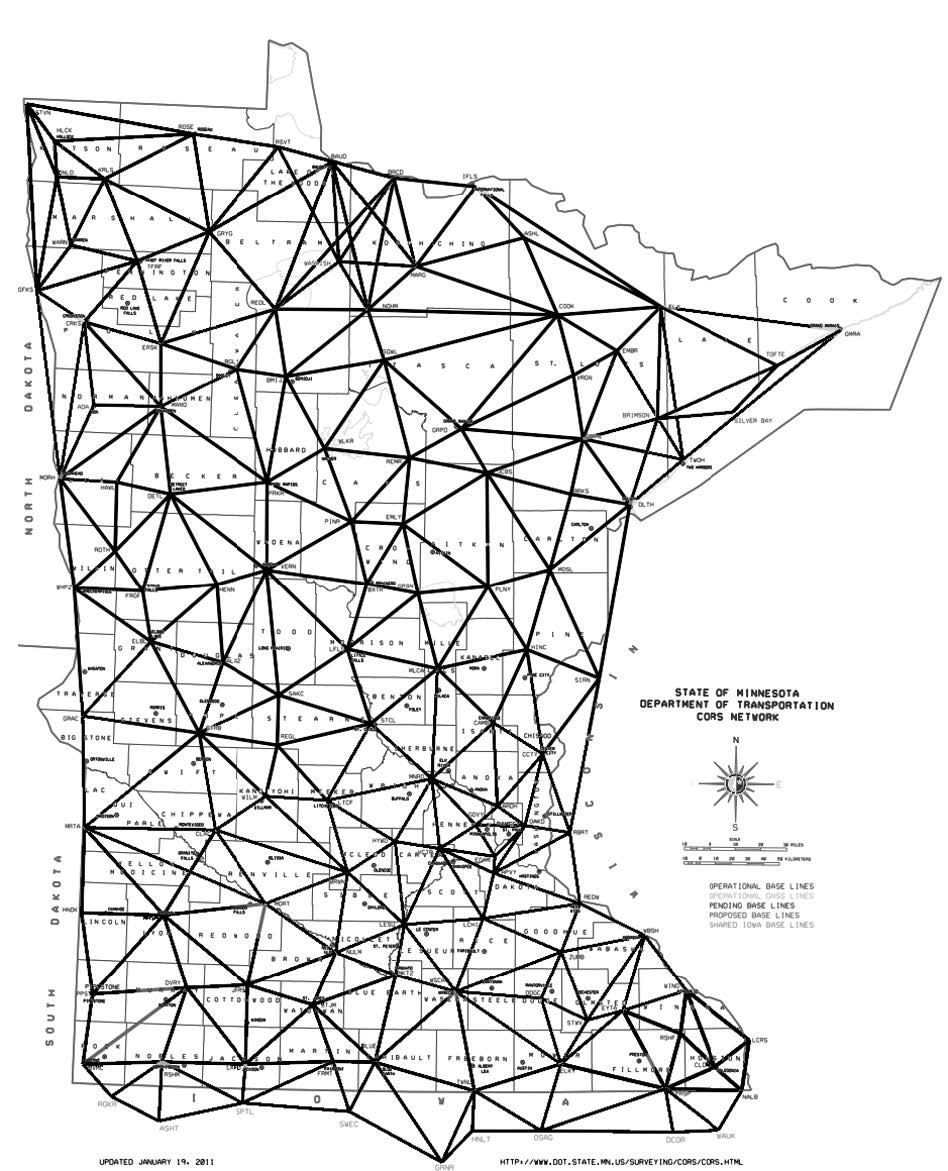
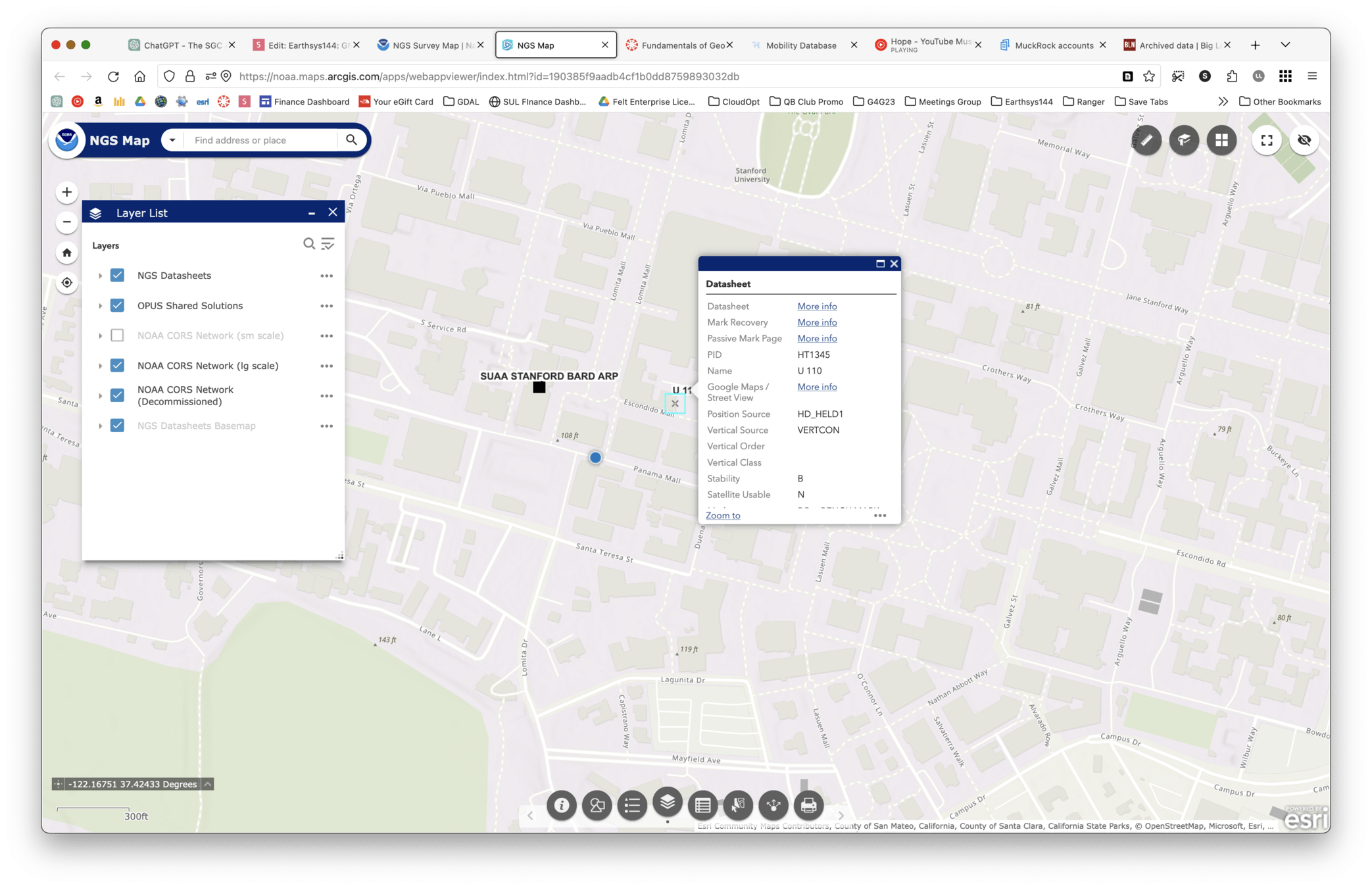
National Geodetic Survey (NGS)

Choosing Methods
GNSS vs Total Station


Choosing a GPS Unit
- Ruggedness
- Batteries
- Connectivity
- Functionality
Garmin vs Smartphones

Choosing a GPS App
- Basemaps
- Offline functionality
- Tracklogging
- Export / Interoperability
- Multi User management
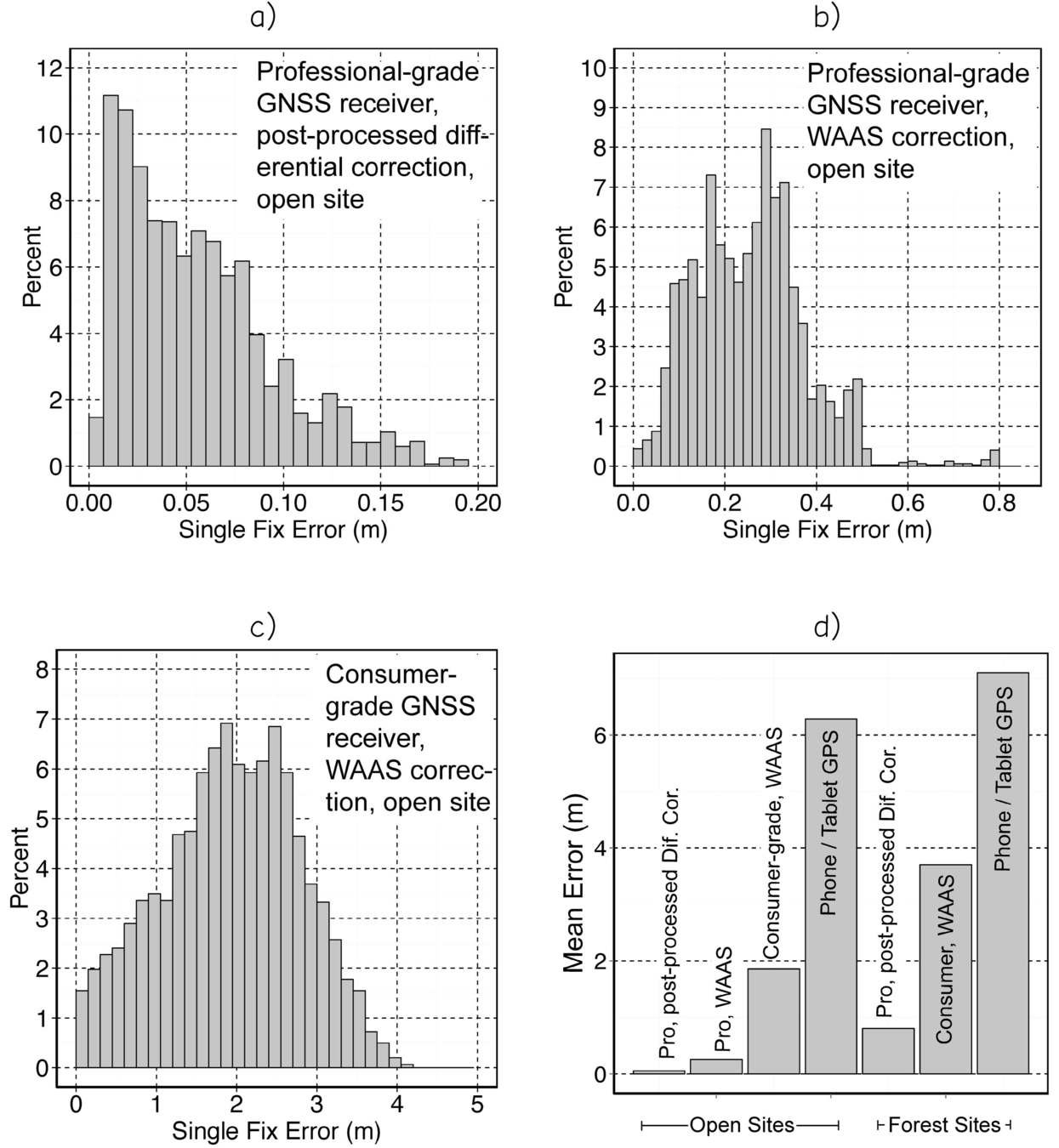
Pro GNSS vs Consumer GNSS
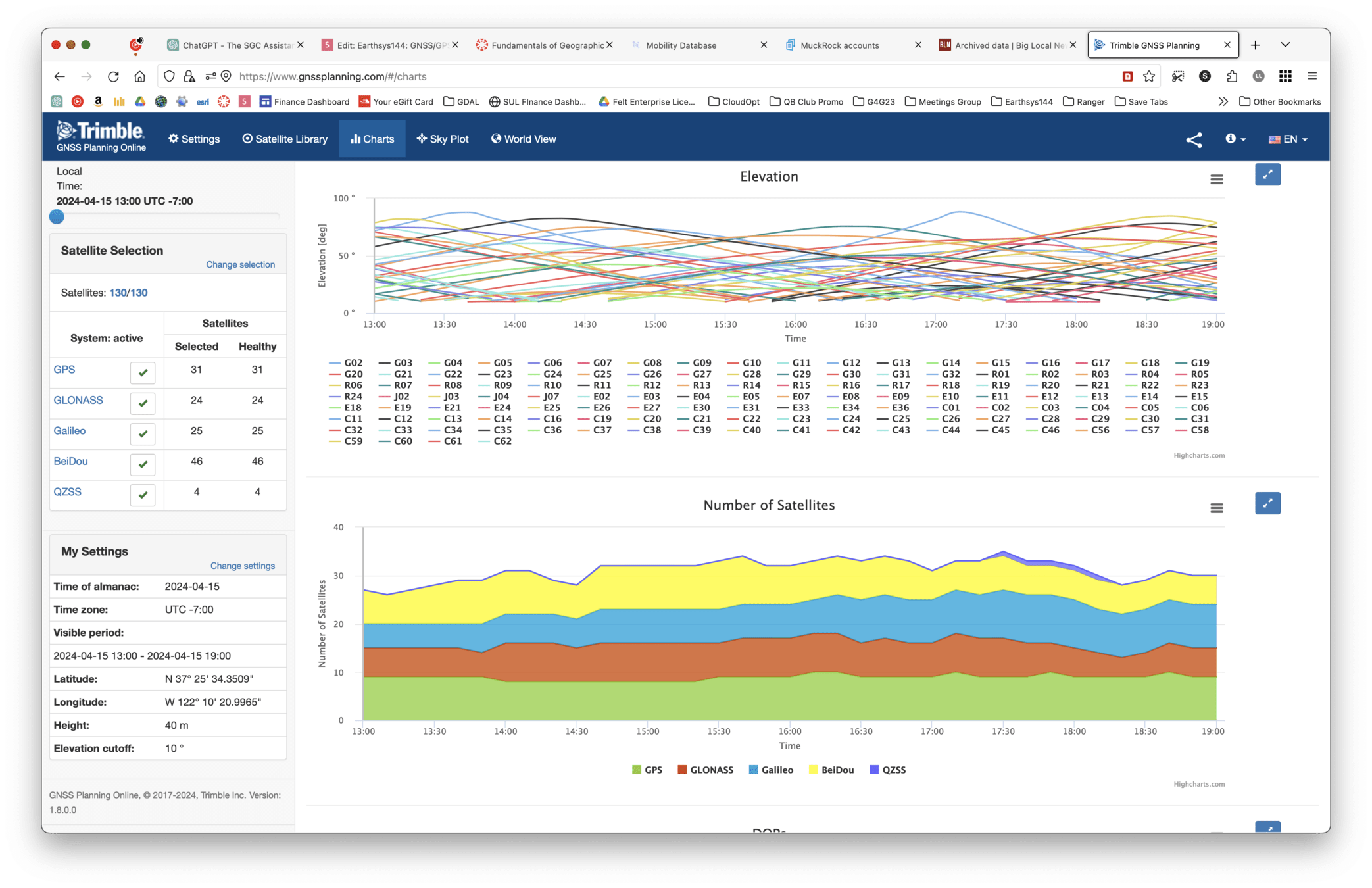
Planning a GPS Survey
- Trimble Planner
- Power
- Tracklogging
- Multi User management


If you registered late, are unable to access Google Earth Engine, or haven't received a Planet.com invite, fill out this form ASAP!!!

GNSS/GPS & Field Data Collection
By Stace Maples
GNSS/GPS & Field Data Collection
- 925



