Intro to WebVR
XR


About Me
Matt Stow
@stowball
Lead UX Engineer at
National Rugby League



VR
AR
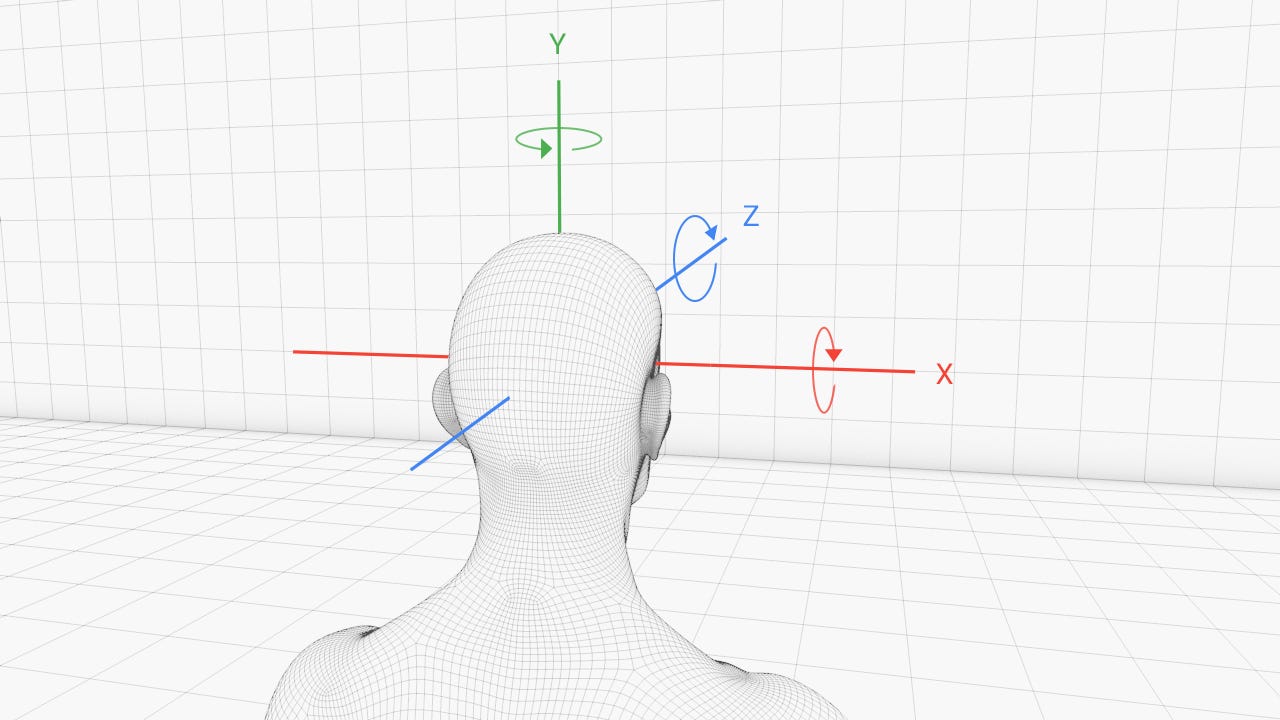
3DoF
6DoF
1977
1982
1987
1991


1992
1995
1998
2002
2011
2012
2014
2015
2016
2018
Unique experiences
FIFA World Cup 2018
Keep Talking & Nobody Explodes
VR Arcades, Japan
Zero Latency, Melbourne
Luke W’s AR Examples




What is WebXR?
- A draft, official spec and experimental JavaScript API that supports VR devices
- Basically, it provides performant
Stereoscopic Rendering and Positional Tracking
- It doesn‘t do graphics. You need WebGL
- It extends the Gamepad and a few other APIs
Developing for XR
What you'll need




Vanilla
if (navigator.xr) {
navigator.xr.requestDevice()
.then(xrDevice => {
// Advertise the AR/VR functionality to get a user gesture.
})
.catch(err => {
if (err.name === 'NotFoundError') {
// No XRDevices available.
console.error('No XR devices available:', err);
} else {
// An error occurred while requesting an XRDevice.
console.error('Requesting XR device failed:', err);
}
})
} else{
console.log("This browser does not support the WebXR API.");
}xrPresentationContext = htmlCanvasElement.getContext('xrpresent');
let sessionOptions = {
// The immersive option is optional for non-immersive sessions;
// the value defaults to false.
immersive: false,
outputContext: xrPresentationContext
}
xrDevice.requestSession(sessionOptions)
.then(xrSession => {
// Use a WebGL context as a base layer.
xrSession.baseLayer = new XRWebGLLayer(session, gl);
// Start the render loop
})xrSession.requestFrameOfReference('eye-level')
.then(xrFrameOfRef => {
xrSession.requestAnimationFrame(onFrame(time, xrFrame) {
let pose = xrFrame.getDevicePose(xrFrameOfRef);
if (pose) {
for (let view of xrFrame.views) {
// Draw something to the screen.
}
}
// Input device code will go here.
frame.session.requestAnimationFrame(onFrame);
}
}
// Oh, and don't forget to load the polyfill
// https://github.com/immersive-web/webxr-polyfillvar scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth/window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 );
var renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize( window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight );
document.body.appendChild( renderer.domElement );
var geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry( 1, 1, 1 );
var material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( { color: 0x00ff00 } );
var cube = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
scene.add( cube );
camera.position.z = 5;
var animate = function () {
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
cube.rotation.x += 0.01;
cube.rotation.y += 0.01;
renderer.render( scene, camera );
};
animate();Unity
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.VR;
public class UpdateEyeAnchors : MonoBehaviour
{
GameObject[] eyes = new GameObject[2];
string[] eyeAnchorNames = { "LeftEyeAnchor", "RightEyeAnchor" };
void Update()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
// If the eye anchor is no longer a child of us, don't use it
if (eyes[i] != null && eyes[i].transform.parent != transform)
{
eyes[i] = null;
}
// If we don't have an eye anchor, try to find one or create one
if (eyes[i] == null)
{
Transform t = transform.Find(eyeAnchorNames[i]);
if (t)
eyes[i] = t.gameObject;
if (eyes[i] == null)
{
eyes[i] = new GameObject(eyeAnchorNames[i]);
eyes[i].transform.parent = gameObject.transform;
}
}
// Update the eye transform
eyes[i].transform.localPosition = InputTracking.GetLocalPosition((VRNode)i);
eyes[i].transform.localRotation = InputTracking.GetLocalRotation((VRNode)i);
}
}
}private void OnEnable ()
{
m_VrInput.OnSwipe += HandleSwipe;
}
private void HandleSwipe(VRInput.SwipeDirection swipeDirection)
{
// If the game isn't playing or the camera is fading, return and don't handle the swipe.
if (!m_MazeGameController.Playing)
return;
if (m_CameraFade.IsFading)
return;
// Otherwise start rotating the camera with either a positive or negative increment.
switch (swipeDirection)
{
case VRInput.SwipeDirection.LEFT:
StartCoroutine(RotateCamera(m_RotationIncrement));
break;
case VRInput.SwipeDirection.RIGHT:
StartCoroutine(RotateCamera(-m_RotationIncrement));
break;
}
}
// Export with Mozilla's Unity WebVR Assets plugin
// https://github.com/mozilla/unity-webvr-exportBabylonJS
var scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
var vrHelper = scene.createDefaultVRExperience();
// Initial camera before the user enters VR
vrHelper.deviceOrientationCamera;
// WebVR camera used after the user enters VR
vrHelper.webVRCamera;
// One of the 2 cameras above depending on which one is in use
vrHelper.currentVRCamera;
vrHelper.onControllerMeshLoaded.add((webVRController)=>{
var controllerMesh = webVRController.mesh;
webVRController.onTriggerStateChangedObservable.add(()=>{
// Trigger pressed event
});
});
vrHelper.enableInteractions();var myBox = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox('myBox', {
height: 5, width: 2, depth: 0.5,
}, scene);
var mySphere = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateSphere('mySphere', {
diameter: 2, diameterX: 3,
}, scene);
var myPlane = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreatePlane('myPlane', {
width: 5, height: 2,
}, scene);
var myGround = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround('myGround', {
width: 6, height: 4, subdivsions: 4,
}, scene);PlayCanvas
var LookCamera = pc.createScript('lookCamera');
LookCamera.attributes.add("mouseLookSensitivity", {
type: "number", default: 0, title: "Mouse Look Sensitivity", description: "",
});
LookCamera.attributes.add("touchLookSensitivity", {
type: "number", default: 0, title: "Touch Look Sensitivity", description: "",
});
LookCamera.prototype.initialize = function () {
// Camera euler angle rotation around x and y axes
var quat = this.entity.getLocalRotation();
this.ex = this.getPitch(quat) * pc.math.RAD_TO_DEG;
this.ey = this.getYaw(quat) * pc.math.RAD_TO_DEG;
this.targetEx = this.ex;
this.targetEy = this.ey;
this.moved = false;
this.lmbDown = false;
// Disabling the context menu stops the browser displaying a menu when
// you right-click the page
this.app.mouse.disableContextMenu();
this.addEventCallbacks();
this.lastTouchPosition = new pc.Vec2();
this.on("destroy", function () {
this.removeEventCallbacks();
});
if (this.app.vr && this.app.vr.display) {
this.app.vr.display.on("presentchange", this.onVrPresentChange, this);
}
this.startCameraOrientation = this.entity.getLocalRotation().clone();
};

React 360
import {
StyleSheet,
Text,
View,
VrButton,
} from 'react-360';
class HelloWorld extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.wrapper}>
<VrButton style={styles.button}>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>
Hello World
</Text>
</VrButton>
</View>
);
}
}

What is A-Frame?
- A web framework for quickly and easily building cross-platform VR experiences
- Created by Mozilla in 2014
- Built on top of and provides a declarative structure to three.js
- Bloody awesome
A-Frame
<script src="https://aframe.io/releases/0.8.2/aframe.min.js"></script>
<a-scene>
<a-box
position="-1 0.5 -3" rotation="0 45 0" color="#4cc3d9" shadow
></a-box>
<a-sphere
position="0 1.25 -5" radius="1.25" color="#ef2d5e" shadow
></a-sphere>
<a-cylinder
position="1 0.75 -3" radius="0.5" height="1.5" color="#ffc65d" shadow
></a-cylinder>
<a-plane
position="0 0 -4" rotation="-90 0 0" width="4" height="4" color="#7bc8a4" shadow
></a-plane>
</a-scene>How it works
<script src="https://aframe.io/releases/0.8.2/aframe.min.js"></script>
<a-scene>
<a-box
position="-1 0.5 -3" rotation="0 45 0" color="#4cc3d9" shadow
></a-box>
<a-sphere
position="0 1.25 -5" radius="1.25" color="#ef2d5e" shadow
></a-sphere>
<a-cylinder
position="1 0.75 -3" radius="0.5" height="1.5" color="#ffc65d" shadow
></a-cylinder>
<a-plane
position="0 0 -4" rotation="-90 0 0" width="4" height="4" color="#7bc8a4" shadow
></a-plane>
</a-scene>Handles 3D boilerplate, VR setup, default camera, lighting and controls
Convenient HTML element called a primitive
It's a wrapper around the generic
<a-entity>
<a-box
></a-box>
Attributes are called components.
Dimension attribute values are in metres
Components can be standalone (shadow), accept a simple string (position), or accept multiple properties via an inline style syntax ("foo: bar; baz: qux;")
position="1 0.75 -3" radius="0.5" height="1.5" color="#ffc65d" shadow
<script src="https://aframe.io/releases/0.8.2/aframe.min.js"></script>
<a-scene>
</a-scene>Primitives
- <a-box>
- <a-camera>
- <a-circle>
- <a-collada-model>
- <a-cone>
- <a-cursor>
- <a-curvedimage>
- <a-cylinder>
- <a-dodecahedron>
- <a-gltf-model>
- <a-icosahedron>
- <a-image>
- <a-light>
- <a-link>
- <a-obj-model>
- <a-octahedron>
- <a-plane>
- <a-ring>
- <a-sky>
- <a-sound>
- <a-sphere>
- <a-tetrahedron>
- <a-text>
- <a-torus-knot>
- <a-torus>
- <a-triangle>
- <a-video>
- <a-videosphere>
Components
- camera
- collada-model
- cursor
- daydream-controls
- debug
- embedded
- fog
- gearvr-controls
- geometry
- gltf-model
- hand-controls
- keyboard-shortcuts
- laser-controls
- light
- line
- link
- look-controls
- material
- obj-model
- oculus-touch-controls
- pool
- position
- raycaster
- rotation
- scale
- screenshot
- shadow
- sound
- stats
- text
- tracked-controls
- visible
- vive-controls
- vr-mode-ui
- wasd-controls
- windows-motion-controls
A-Frame Inspector!
Ctrl+Alt+I
const box = document.querySelector('a-box');
const sphere = document.querySelector('a-sphere');
const cylinder = document.querySelector('a-cylinder');
const plane = document.querySelector('a-plane');
setTimeout(() => {
box.setAttribute('color', 'dodgerblue');
}, 500);
setTimeout(() => {
sphere.setAttribute('radius', 1.75);
}, 1000);
setTimeout(() => {
cylinder.setAttribute('position', '1 2 -3');
}, 1500);
setTimeout(() => {
plane.setAttribute('visible', false);
}, 2000);Imperative 😬

Declarative 🤔
Declarative!
<div id="app">
<a-scene background="color: #333">
<a-box
position="-1 0.5 -3" rotation="0 45 0" shadow
v-bind:color="boxColor"
></a-box>
<a-sphere
position="0 1.25 -5" color="#ef2d5e" shadow
v-bind:radius="sphereRadius"
></a-sphere>
<a-cylinder
radius="0.5" height="1.5" color="#ffc65d" shadow
v-bind:position="cylinderPosition"
></a-cylinder>
<a-plane
position="0 0 -4" rotation="-90 0 0" width="4" height="4" color="#7bc8a4" shadow
v-bind:visible="planeVisibility.toString()"
></a-plane>
</a-scene>
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data() {
return {
boxColor: '#4cc3d9',
sphereRadius: 1.25,
cylinderPosition: '1 0.75 -3',
planeVisibility: true,
};
},
mounted() {
setTimeout(() => { this.boxColor = 'dodgerblue'; }, 1000);
setTimeout(() => { this.sphereRadius = 1.75; }, 1500);
setTimeout(() => { this.cylinderPosition = '1 2 -3'; }, 2000);
setTimeout(() => { this.planeVisibility = false; }, 2500);
},
});
Declarative!
<a-box
color="#fff"
depth="0.2"
height="0.5"
position="0 3.5 -4"
ref="button"
width="1"
></a-box>
…
mounted() {
this.$refs.button.addEventListener('mouseenter', this.reset);
}
<a-box
color="#fff"
depth="0.2"
height="0.5"
position="0 3.5 -4"
width="1"
v-on:mouseenter="reset"
></a-box>Declarative?
vue-aframe-directives
// my-component.vue
<a-entity
v-a-bind:color="color"
v-a-bind:depth="depth"
v-a-bind:position="`0 ${positionY} 2`"
v-a-bind:rotation="rotation"
v-a-bind:scale="scale"
v-a-bind:visible="visible"
></a-entity>
// app.vue
<my-component
v-bind:color="#fff"
v-bind:depth="0"
v-bind:position-y="1"
v-bind:rotation="{ x: 45 }"
v-bind:scale="[3, 2, 1]"
v-bind:visible="false"
></my-component>
// behind the scenes
el.setAttribute('color', '#fff');
el.setAttribute('depth', 0.001);
el.object3D.position.set(0, 1, 2);
el.object3D.rotation.x = 45;
el.object3D.scale.set(3, 2, 1);
el.object3D.visible = false;WIP
2-day hackathon PoC
One last thing…
<script src="aframe-ar.min.j></script>
<a-scene
arjs="debugUIEnabled: false; sourceType: webcam;"
embedded
>
<a-box
color="#fff"
depth="1.1"
height="1.1"
material="opacity: 0.3"
width="1.1"
/>
<a-sphere
radius="0.5"
src="earth_atmos_4096.jpg"
>
<a-animation
attribute="rotation"
dur="5000"
easing="linear"
repeat="indefinite"
to="0 360 0"
></a-animation>
</a-sphere>
<a-marker-camera preset="hiro"></a-marker-camera>
</a-scene>A-Frame AR!
Where to next?
- Learn more at A-Frame School
- Learn how to design for VR (Link 1, Link 2)
- Design 3D models with Vectary or Blender
- Have fun!
Thank you!
@stowball
Intro to WebXR
By Matt Stow
Intro to WebXR
A brief history of VR and how you can use A-Frame to quickly build and prototype VR experiences in the browser
- 4,405



