Image Generation
小社第四堂 25/12/23
回顧
目前為止我們講過⋯⋯
大型語言模型 (LLM)
回顧
目前為止我們講過⋯⋯
機器學習 (ML)
回顧
目前為止我們講過⋯⋯
AI 會不會造成經濟爆炸 & trends in AI development


Stable Diffusion
Midjourney
Nano Banana

不過我們好像沒有講過影像生成 (Image Generation)
Midjourney 伺服器
沒試過的可以試試看
打 /imagine 就可以輸入指令,生成圖片了喔
Diffusion 擴散

Diffusion 擴散
想像有一滴墨水滴到水杯裡了,
它就會進入擴散的過程,
直到整杯水都變成墨水的顏色。
擴散完成後,整杯水就看不出什麼差異了。
Diffusion 擴散
這就是啟發 影像生成技術的原理
假設 影像=水
雜訊=墨水
我們的目標就是要訓練模型拿從一張充滿隨機雜訊的圖片中,還原出一張符合使用者要求的圖片
Diffusion 擴散

I saw the angel in the marble and carved until I set him free
– Michaelangelo
我只是把困在石頭裡的大衛釋放出來
—米開朗基羅
我美術不好但大概是這個概念吧
把圖像從雜訊中釋放出來,而不是一個無中生有的過程
Diffusion Model 的核心精神是學習一個逐步 Denoise 的過程。
Forward
Diffusion
正向過程
Training Data
拿來訓練的圖片

⋯⋯
對它不斷加雜訊
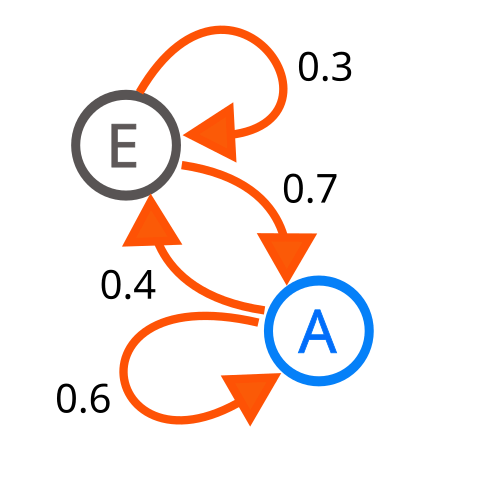
馬可夫鏈 Markov Chain
因俄國數學家安德烈·馬可夫得名,為狀態空間中經過從一個狀態到另一個狀態的轉換的隨機過程。該過程要求具備「無記憶」的性質:下一狀態的機率分布只能由當前狀態決定,在時間序列中它前面的事件均與之無關。這種特定類型的「無記憶性」稱作馬可夫性質。
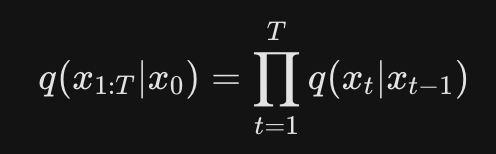
常態分佈 Normal/Gaussian Distribution
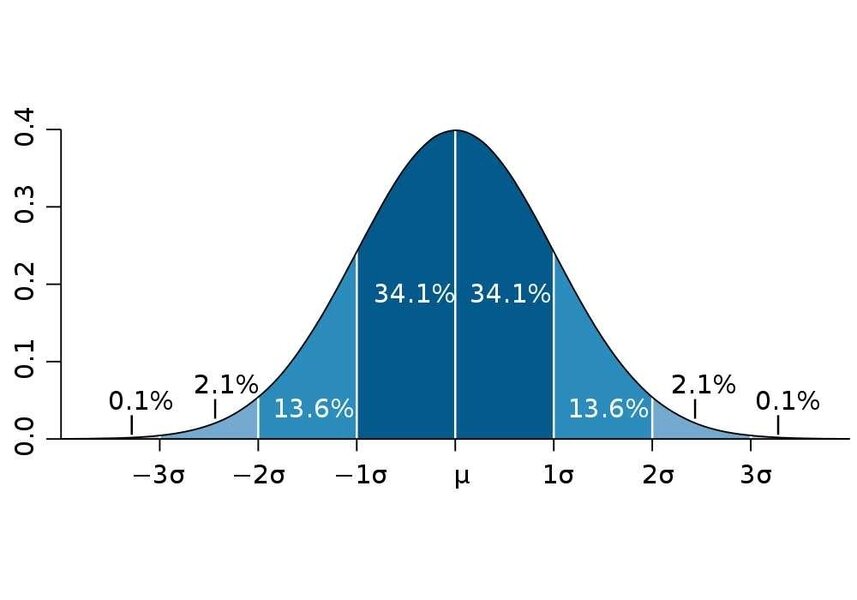
用來決定如何分佈雜訊
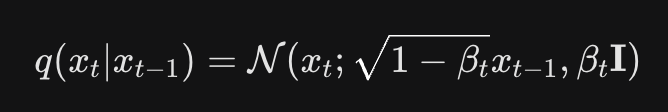
把前一個數的影響稍微降低
noise schedule
Current state(現在狀態)
noise schedule
scaling factor
noise strength
🌰
栗子
🌰
栗子
Reverse
Diffusion
逆向過程

⋯⋯

猜測移除雜訊後的樣子,以還原圖片
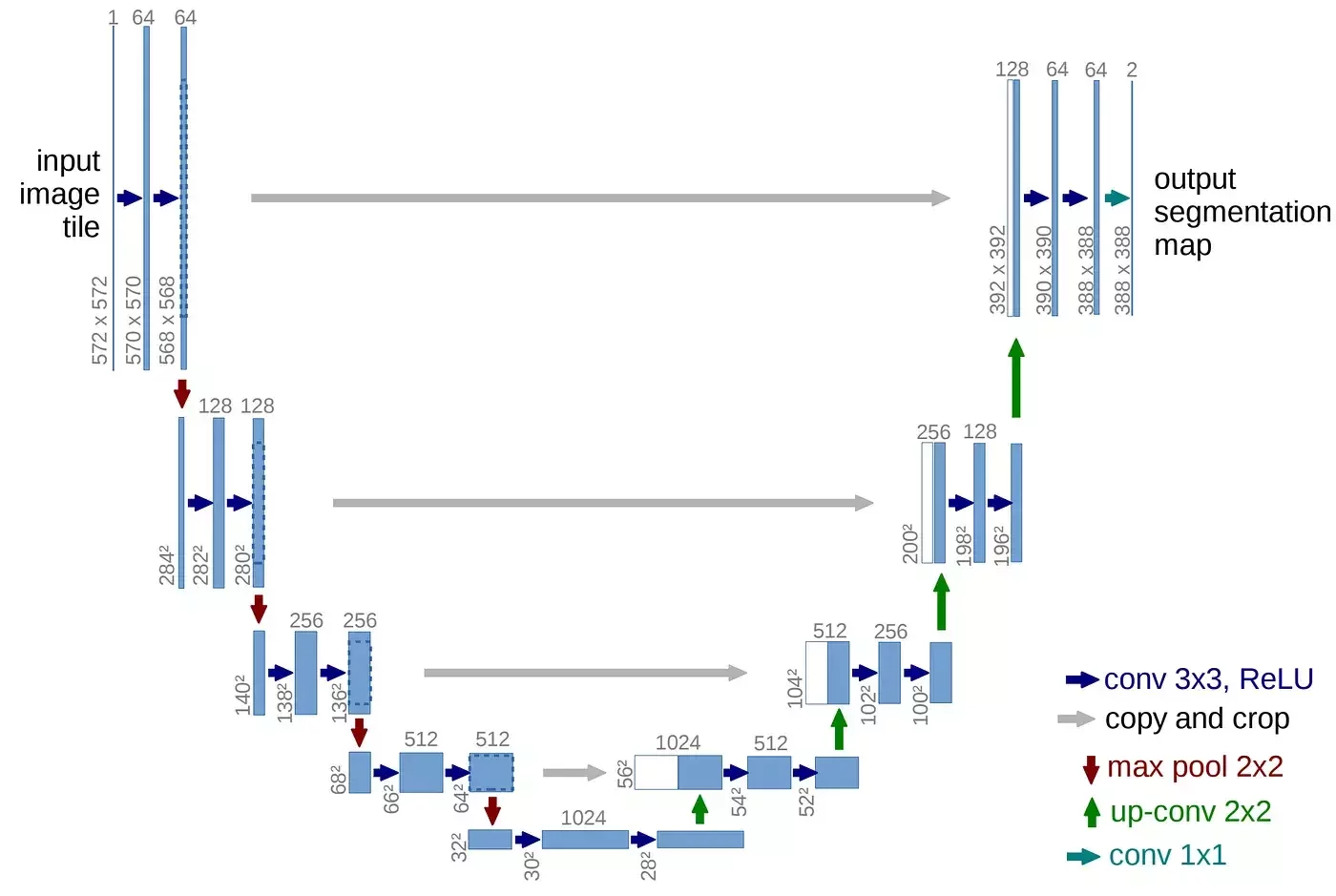
U-net structure
encoder
decoder
skip connection
Conditional
Diffusion
條件式擴散
條件式擴散模型(Conditional Diffusion Models)是在標準的「擴散模型」(Diffusion Models)基礎上增加控制能力,讓生成結果能遵循特定「條件」(例如文字描述、類別標籤、另一張圖片),實現更精準、更有用的數據生成(如特定內容的圖片、音樂),是現代生成式AI如DALL-E、Stable Diffusion的核心技術之一.
條件:指在生成過程中加入額外資訊,告訴模型要生成什麼。這些資訊就是「條件」
- 文字提示 (Text prompt)
- 圖片 (image to image)
⋯⋯等
Condition
Encoding
Condition
Integration
把條件變成模型看得懂的樣子
把條件寫進去
訓練過程中
Encoding
實作
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 用 T4 跑比較快
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
model_id,
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32
)
pipe = pipe.to(device)
intermediate_images = []
def callback_fn(pipe, step_index, timestep, callback_kwargs):
# 每五步展示一次
if step_index % 5 == 0:
latents = callback_kwargs["latents"]
with torch.no_grad():
# 0.18215 is the standard scaling factor for SD 1.5 latents
image = pipe.vae.decode(latents / 0.18215).sample
image = pipe.image_processor.postprocess(image, output_type="pil")[0]
intermediate_images.append(image)
return callback_kwargs
prompt = "輸入提示詞"
# markov chain
final_image = pipe(
prompt,
num_inference_steps=30,
callback_on_step_end=callback_fn
).images[0]
#當你呼叫 pipe 時,程式會隨機產生一個充滿 高斯噪音(Gaussian Noise) 的畫布
#num_inference_steps 代表逆向馬可夫鏈中,我們要進行幾次「降噪動作」
#步數越多,圖片通常越細緻,但運算時間也越長。
#callback_on_step 讓你在馬可夫鏈的 每一個步驟結束時 插入一個自定義函數(callback_fn)。它讓我們能把中間那些「半成品」抓出來#匯出圖表
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, len(intermediate_images) + 1, figsize=(20, 5))
for i, img in enumerate(intermediate_images):
axes[i].imshow(img)
axes[i].set_title(f"Step {i*5}")
axes[i].axis("off")
axes[-1].imshow(final_image)
axes[-1].set_title("Final Result")
axes[-1].axis("off")
plt.show()
Image Generation
By Suzy Huang
Image Generation
- 156



