
@attheodo
Cracking a 3rd party iOS framework for fun & profit
Assembly Primer


Assembly Primer

CPU Registers
-
Little "hardware variables" very close to the CPU that are blazing fast
CPU Instructions
-
Single purpose "functions" that operate on/with CPU registers
-
They can perform arithmetic, moving values etc
Memory
-
A continuous, volatile space of "storage slots" (words) that can be addressed by the CPU
-
It's mostly where your program lives when it's running
Assembly Primer

CPU Registers
-
Specific to each architecture
-
x86_64 uses 16 general purpose registers
| RAX | A extended | Typically return values |
| RBX | B extended | Callee-saved |
| RCX | C extended | 4th arg to functions |
| RDX | D extended | 3rd argument to functions |
| RDI | Destination Index | 1st arg to functions |
| RSI | Source Index | 2nd arg to functions |
| RSP | Stack pointer | |
| RBP | Base Pointer (start of stack) | |
| R8 - R15 |
Assembly Primer

CPU Instructions
-
mov (Move - Copies the data refered by one item to the other)
-
Push (Places stuff on top of the stack)
-
pop (Removes stuff from the top of the stack)
-
...
Data Movement
- add (Integer addition)
- sub (Integer subtraction)
- inc, dec (Increment/Decrement)
- ...
Arithmetic
- jmp (Jump - Transfers flow to the instruction at a memory location)
- jCondition(je/jne/... - JumpWhenEqual/JumpWhenNotEqual according to the "machine status word"
- cmp (Compare - Sets the "machine status word" according to the comparison
- ...
Control flow
Assembly Primer

Memory
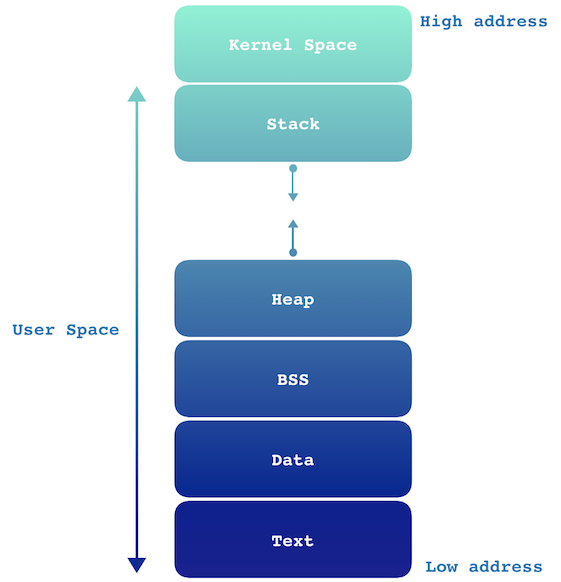
Assembly Primer

Memory
Stack
-
LIFO Datastructure
-
Usually grows downwards to lower addresses
-
Stores all the data required by a function call
-
Everytime a new function is execute, a new stack frame is being created at the top of the stack
-
When it finishes, the stack from is poped from the stack
-
The stack frame contains all the functions parameters, the return address back to the caller of the function and any variables local to that function.
-
Assembly Primer

Memory
Heap
-
A memory segment for dynamic memory allocation
-
All reference types created by malloc/new
-
Uses the brk and sbrk system calls to adjust its size
-
-
Heap is used:
-
Memory size is dynamically allocated at run-time
-
Scope is not local to a function
-
Allocated size is large
-
Assembly Primer

Memory
BSS (Block Started by Symbol)
-
An unitialized data segment
-
Data in this segment is usually initialized by the kernel before the program starts its execution
-
I.e static let index = 0 will be allocated in the BSS
Assembly Primer

Memory
Data
-
This segment contains initialized global and static variables which have a pre-defined value and can be modified.
-
It has a read-only and a read-write space.
-
Let's just say it holds global variables
Text
-
A segment where basically assembly instructions are stored.
-
This is read-only
Assembly Primer

Memory
How stack frames work
Questions?


Cracking an iOS Framework for fun
By Thanos Theodoridis
Cracking an iOS Framework for fun
- 278



