CSS
Objectives:
What is CSS?
- CSS is a "style sheet language" that lets you style the elements on your page.
- CSS can be embedded inside HTML, but it is not HTML itself.
What can it do?
http://csszengarden.com/?cssfile=http://my.tbaytel.net/vel_lanquibo/csszengarden/styles.css
VS
http://www.csszengarden.com/218/
CSS consists of "style rules". Each style rule consists of a "selector" and "declarations" of property-value pairs:

CSS can be embedded in HTML in several ways. One way is to include all CSS in a style tag, usually inside the head tag:
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
color: yellow;
background-color: green;
}
</style>
</head>The selector is used to select which elements in the HTML page will be given the styles inside the curly braces.
selector {
property: values;
}Types of Selectors:
- element
- id
- class
- psudo class
Using different selectors
<div>
<p>Make the background of this text orange</p>
<div>
<div id="red">make this red using an id</div>
<div class="purple">what color is this?</div>
<div id="red" class="purple">What color will this become with both id and class??</div>
</div>
</div>/*div {
background-color: blue;
}
div p {
background-color: orange;
}
.purple {
background-color: purple;
}
#red {
background-color: red;
}
*/The Main 3:
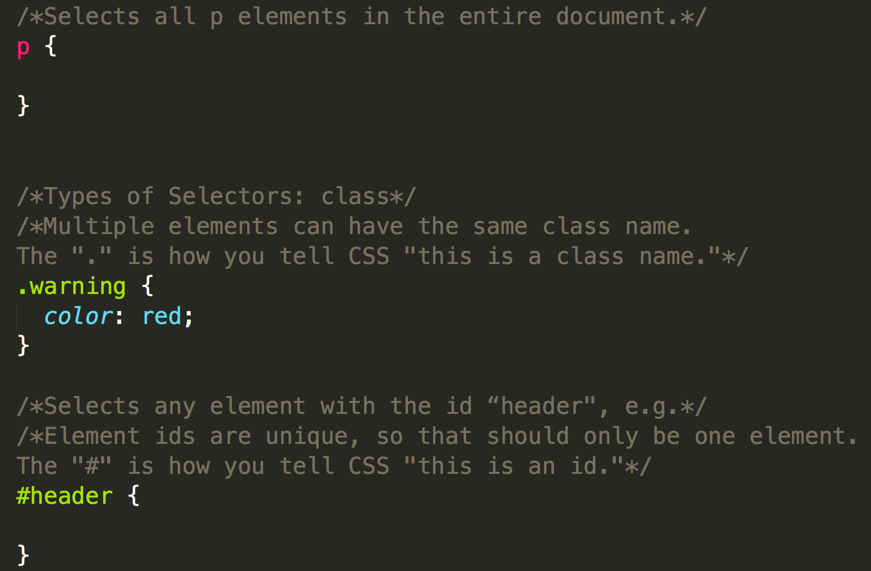
You can select descendent items with multiple selectors
Selects any <li> element that is a descendant of any element with an id that equals "related-brands."
#related-brands li {
color: gray;
}The difference between the "." and the space is very important!
li.a {
color: yellow;
}
li a {
color: red;
}<ul>
<li><a href="#rice">Rice Krispies</a></li>
<li class="a">NutriGrain</li>
</ul>A set of "pseudo classes" can style anchor elements depending on their state.
a:link { /* unvisited link */
color: red;
}
a:visited { /* visited link */
color: blue;
}
a:hover { /* moused over link */
color: green;
}
a:active { /* current link */
color: purple;
}
a:focus { /* focused link */
color: purple;
} Memorize or lookup --> lookup generally

Attribute Selectors
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
a[target="_top"] {
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The links with a target attribute gets a yellow background:</p>
<a href="http://www.zombocom.com">zombocom.com</a>
<a href="http://www.imgur.com" target="_blank">imgur.com</a>
<a href="http://theoatmeal.com/" target="_top">theoatmeal.com</a>
</body>
</html>it is possible to select attributes within an element (and useful!)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p:nth-child(odd) {
background: blue;
}
p:nth-child(even) {
background: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>The first paragraph.</p>
<p>The second paragraph.</p>
<p>The third paragraph.</p>
<p>The fourth paragraph.</p>
<p>The fifth paragraph.</p>
<p>The sixth paragraph.</p>
<p>The seventh paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>The :nth-child selector
allows you to select one or more elements based on their source order, according to a formula.
p:nth-child(3n+1) {
background: blue;
}Generally:
- id is more specific than a class, class is more specific than element.
- the longer the selector, the more specific it is
- If style rules are equally specific, the last one wins!
Some rules to follow when making IDs and class names:
- Describe the content, not the presentation ("warning", not "redbox").
- Use all lowercase, and hyphens ("header-info", not "headerInfo").
- Use hyphens to show that a class or ID is part of something else. (e.g. "footer", "footer-copyright", and "footer-logo").
Naming Conventions
CSS Box Model
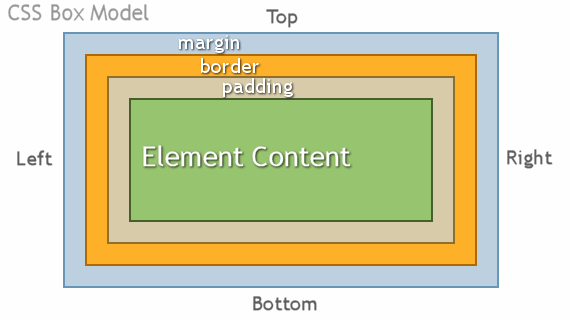

- Content - The content of the box, where text and images appear
- Padding - Clears an area around the content. The padding is transparent
- Border - A border that goes around the padding and content
- Margin - Clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent

<style>
div {
width: 300px;
padding: 25px;
border: 25px solid navy;
margin: 25px;
}
</style>Intermediate CSS
By Matthew Williams
Intermediate CSS
CSS
- 1,209



