Entropy methods
for the Boltzmann equation
and its quantum variant
Thomas Borsoni
Séminaire ANCS, LMB
June 19, 2025
CERMICS, École des Ponts, France
Motivation
Long-time behavior of solutions to the
Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
Main result
entropy inequality
Boltzmann
entropy inequality
Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
Tool
Entropy methods (functional inequalities)
Goal
Entropy inequalities for the Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
Outline
1. The (classical) Boltzmann equation
\(\mathrm{II})\) Trend to equilibrium
2. The (quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
\(\mathrm{I})\) Boltzmann equations
3. Entropies and equilibria
1. The entropy method
2. Overview of entropy inequalities
3. Transfer from Boltzmann to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
1. The (classical) Boltzmann equation
2. The (quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
\(\mathrm{I})\) Boltzmann equations
3. Entropies and equilibria
\(\mathrm{II})\) Trend to equilibrium
1. The entropy method
2. Overview of entropy inequalities
3. Transfer from Boltzmann to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
\(g \equiv g_{t,x}(v)\) density of molecules
the (classical) Boltzmann equation
Boltzmann equation:
Conservation laws
Collision operator:
(momentum)
(energy)
\(B \equiv B(v,v_*, \sigma) > 0 \) \(\leftrightarrow\) interaction potential
Collision kernel:


[A. Greg: Kinetic theory of gases, wikipedia.]
Statistical description of a monoatomic gas
\(g \equiv g_{t}(v)\) density of molecules
the space-homogeneous
(classical) Boltzmann equation
- Boltzmann equation
Conservation laws
(momentum)
(energy)



[A. Greg: Kinetic theory of gases, wikipedia.]















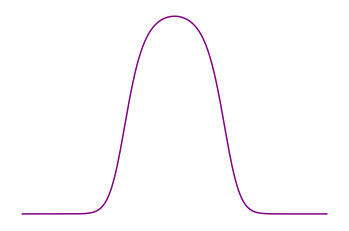
- Equilibrium
expected behaviour
Maxwellian
distribution
Entropy and equilibrium
The (classical) Boltzmann entropy functional \(H_{\textcolor{green}{0}} \)
2. \(D_{\textcolor{green}{0}}(g) = 0 \iff g =M_{\textcolor{green}{0}}^g \),
characterization of equilibrium
Boltzmann's H Theorem
1. If \(\partial_t g_t = Q_{\textcolor{green}{0}}(g_t)\), then
\(2^{nd}\) principle of thermodynamics
The (classical) Boltzmann entropy dissipation functional \(D_{\textcolor{green}{0}}\)
1. The (classical) Boltzmann equation
2. The (quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
\(\mathrm{I})\) Boltzmann equations
3. Entropies and equilibria
\(\mathrm{II})\) Trend to equilibrium
1. The entropy method
2. Overview of entropy inequalities
3. Transfer from Boltzmann to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
\(f \equiv f_{t}(v)\) density of fermions
the space-homogeneous
(quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
- Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
Conservation laws
(momentum)
(energy)
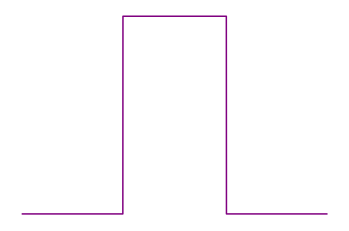
Pauli exclusion principle
- Collision operator
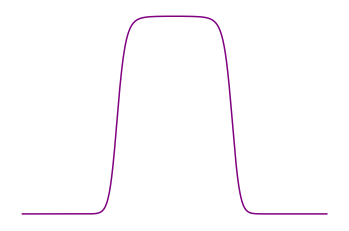
- Equilibrium
Fermi-Dirac
statistics
Entropy and equilibrium
2. \(D_{\textcolor{purple}{\delta}}(g) = 0 \iff g =M_{\textcolor{purple}{\delta}}^g \),
characterization of equilibrium
Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac H Theorem
1. If \(\partial_t f_t = Q_{\textcolor{purple}{\delta}}(f_t)\), then
\(2^{nd}\) principle of thermodynamics
The (quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac entropy dissipation functional \(D_{\textcolor{purple}{\delta}}\)
The (quantum) Fermi-Dirac entropy functional \(H_{\textcolor{purple}{\delta}} \)
1. The (classical) Boltzmann equation
2. The (quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
\(\mathrm{I})\) Boltzmann equations
3. Entropies and equilibria
\(\mathrm{II})\) Trend to equilibrium
1. The entropy method
2. Overview of entropy inequalities
3. Transfer from Boltzmann to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
Fermi-Dirac entropy
Boltzmann entropy
Equilibrium: Fermi-Dirac statistics
Equilibrium: Maxwellian
entropies and equilibria
Boltzmann
Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
Fermi-Dirac entropy
Equilibrium: Fermi-Dirac statistics
Equilibrium: Maxwellian
entropies and equilibria
Boltzmann
Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
entropy \(\displaystyle H : h \mapsto \int \Phi(h)\) \(\Phi\) \(\mathcal{C}^2\) st. convex
equilibrium
Boltzmann entropy
relative entropy to equilibrium
\(\displaystyle H : f \mapsto \int \Phi(f)\) \(\Phi\) \(\mathcal{C}^2\) st. convex
equilibrium
relative entropy to equilibrium
Proposition 1.
Taylor representation of the relative entropy to equilibrium
main theorem
Bonus: generalized \(L^p_\varpi\) Csiszár-Kullback-Pinsker
2024?
entropy
1. The (classical) Boltzmann equation
2. The (quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
\(\mathrm{I})\) Boltzmann equations
3. Entropies and equilibria
\(\mathrm{II})\) Trend to equilibrium
1. The entropy method
2. Overview of entropy inequalities
3. Transfer from Boltzmann to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
- Existence & stability of solutions to homogeneous BFD for cut-off hard potentials
Lu, Wennberg
Existence and uniqueness of solutions to inhomogeneous BFD for cut-off kernels
Dolbeault
- Relaxation to equilibrium of such solutions:
either \(f_0 =\) or \(f_t \; \underset{t \to \infty}{\rightarrow}\)
Derivation of the equation from particles system (partially formal)
Benedetto, Castella, Esposito, Pulvirenti
at which rate?

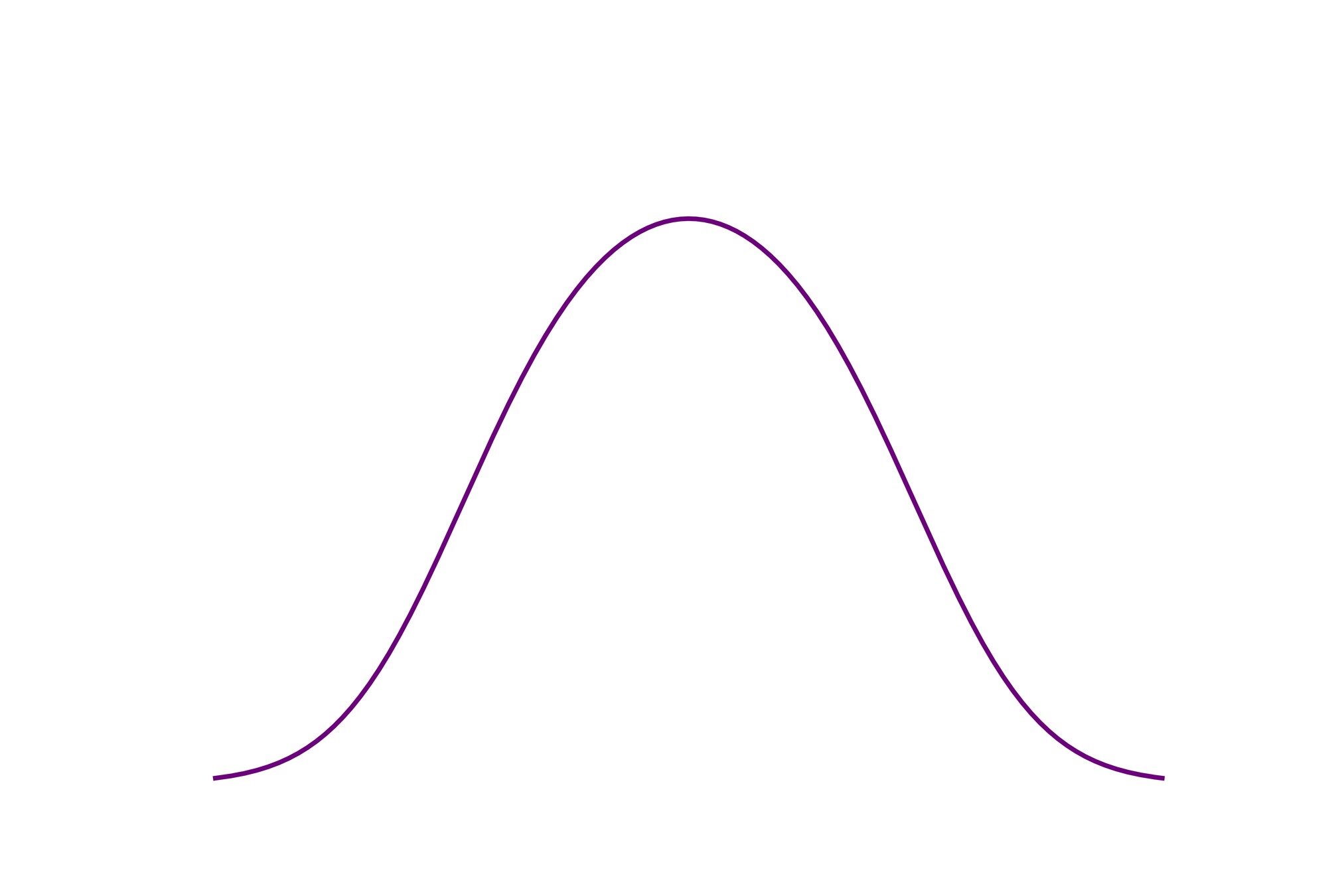
saturated state
Fermi-Dirac stat.
Some results on BFD
1. The (classical) Boltzmann equation
2. The (quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
\(\mathrm{I})\) Boltzmann equations
3. Entropies and equilibria
\(\mathrm{II})\) Trend to equilibrium
1. The entropy method
2. Overview of entropy inequalities
3. Transfer from Boltzmann to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
\(D(g) \gtrsim {H(g|M^g)}^{1+\alpha}\)
\(D(g) \geqslant C H(g|M^g)\)
the entropy method
Relative entropy to equilibrium:
\(H(f_t|M^{f_0}) \lesssim t^{-1/\alpha}\)
\(H(f_t|M^{f_0}) \lesssim e^{-Ct} \)
Csiszár-Kullback-Pinsker
1. The (classical) Boltzmann equation
2. The (quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
\(\mathrm{I})\) Boltzmann equations
3. Entropies and equilibria
\(\mathrm{II})\) Trend to equilibrium
1. The entropy method
2. Overview of entropy inequalities
3. Transfer from Boltzmann to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
Boltzmann
Carlen, Carvalho, Desvillettes, Toscani, Villani
1992 \(\to\) 2003
Landau
LAndau-Fermi-Dirac
Desvillettes, Villani
2000
Alonso, Bagland, Desvillettes, Lods
2020-2021
Boltzmann-FERMI-DIRAC
Overview of entropy inequalities for kinetic equations
Fokker-Planck
log-Sobolev inequality
Fokker-Planck-Fermi-Dirac
generalized
Gross
1975
+Kac, BGK
Toscani,...
\(\leq\) 1999
Carillo, Laurençot, Rosado
2009
our goal:
1. The (classical) Boltzmann equation
2. The (quantum) Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
\(\mathrm{I})\) Boltzmann equations
3. Entropies and equilibria
\(\mathrm{II})\) Trend to equilibrium
1. The entropy method
2. Overview of entropy inequalities
3. Transfer from Boltzmann to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
transfer of inequalities
We know:
entropy inequality for Boltzmann
entropy inequality for Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
We want:
Fermi-Dirac dissipation of \(f\)
Boltzmann dissipation of \( \displaystyle \frac{f}{1-\textcolor{purple}{\delta} f} \)
\( \gtrsim\)
?
(as soon as all terms make sense)
Boltzmann relative entropy to equilibrium of \(\displaystyle \frac{f}{1-\textcolor{purple}{\delta} f}\)
Fermi-Dirac relative entropy to equilibrium of \(f\)
Theorem 2.
For all
such that
and
and
comparison of relative entropies
TB 2024
Let
Then \(R_g\) is nonincreasing on \(\R_+\).
Proposition 3.
and
Proof of the theorem
proof of the proposition
Key elements:
- Taylor representation of the relative entropy to eq.
- general link between entropy and equilibrium
- fact that \(x \mapsto -\left(\frac{x}{1+\delta x} \right)^2\) is decreasing
Other technicalities:
- differentiability on \(\R_+^*\)
- continuity at \(\delta = 0^+\)
general considerations
specific use of Fermi-Dirac features
Show \(R_g' \leq 0\) on \(\R_+^*\) and \(R_g\) continuous on \(\R_+ \)
2024
Proposition 4.
For all
such that
and
Classical / Fermi-Dirac equivalence
For Boltzmann/BFD (& Landau/LFD) dissipations:
entropy inequality for Boltzmann
entropy inequality for Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
Conclusion
2024
Thank you for your attention!

TB: Extending Cercignani's conjecture results from Boltzmann to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation, J. Stat. Phys. (2024).
Bonus: generalized \(L^p_\varpi\) Csiszár-Kullback-Pinsker
General weighted \(L^p\) Csiszár-Kullback-Pinsker
Proposition.
(general entropy)
\(\displaystyle H(f) = \int\Phi(f)\), \(\Phi \; \; \mathcal{C}^2\) st. convex, \(M^f\) equilibrium, and
For any \(f\), any \(p \in [1,2]\) and \(\varpi\) weight,
Corollary.
For any \(0\leq f \in L^1_2\cap L \log L(\R^3)\), \(p \in [1,2]\) and \(\varpi : \R^3 \to \R_+\),
(Boltzmann entropy)
\(\displaystyle H_0\) Boltzmann entropy and \(M_0^f\) Maxwellian.
[simplified]
Presentation Besancon
By Thomas Borsoni
Presentation Besancon
- 42


