Build microservice with gRPC in Golang
David Chou


We are Umbo Computer Vision
We build autonomous video security system


Cyberlink
TrendMicro
Umbo CV
Google I/O Extend
Golang Taipei


A high performance, open source, general purpose standards-based, feature-rich RPC framework.

O(10^10) RPCs per second at Google
gRPC: Motivation
- Google has its internal RPC called Stubby
- All applications and systems built using RPCs
- Over 10^10 RPCs per second
- Tightly couple with internal infrastructure
- Not suitable for open source community
gRPC: Status
-
A high performance, universal RPC framework
-
Google open sourced it in Feb 2015
- Being 1.0 in Aug 2016
- Latest version: v1.3.2
-
Already been adpoted in
- CoreOS, Netflix, Square, Cisco, Juniper
gRPC: Features
- Bi-directional streaming over HTTP/2
- Support multi-language, multi-platform
- Simple service definition framework
Bi-directional streaming over HTTP/2
- Single TCP connection for each client-server pair
- Support bi-directional streaming
Support multi-language, multi-platform
- Use protoc as the code generator
- Native implementations in C/C++, Java, and Go
- C stack wrapped by C#, Node, ObjC, Python, Ruby, PHP
- Platforms supported: Linux, MacOS, Windows, Android, iOS
- Currently, no browser side support. #8682
Simple service definition framework
-
Use Protocol Buffer IDL
-
Service definition
-
Generate server and client stub code
-
-
Message definition
-
Binary format
- Much better performace than json
-
syntax = "proto3";
package pb;
message EchoMessage {
string msg = 1;
}
service EchoService {
rpc Echo(EchoMessage) returns (EchoMessage);
}
Protobuf IDL: EchoService
BenchmarkToJSON_1000_Director-2 500 2512808 ns/op 560427 B/op 9682 allocs/op
BenchmarkToPB_1000_Director-2 2000 1338410 ns/op 196743 B/op 3052 allocs/op
BenchmarkToJSONUnmarshal_1000_Director-4 1000 1279297 ns/op 403746 B/op 5144 allocs/op
BenchmarkToPBUnmarshal_1000_Director-4 3000 489585 ns/op 202256 B/op 5522 allocs/op
Json vs Protobuf performance
- Marshalling: 2x faster, 65% less memory
- Unmarshalling: 2.6x faster, 50% less memory

Example: DemoService
gRPC Service Definition
message Demo {
string value = 1;
}
service DemoService {
rpc SimpleRPC(Demo) returns (Demo);
rpc ServerStream(Demo) returns (stream Demo);
rpc ClientStream(stream Demo) returns (Demo);
rpc Bidirectional(stream Demo) returns (stream Demo);
}
gRPC Service Definition
- gRPC supprots 4 kinds of service methods
- Unary RPC
- Server streaming RPC
- Client streaming RPC
- Bidirectional RPC
Generate client and server code
- Install relevant tools
-
Run protoc to generate client/server interfaces
- $ protoc --go_out=plugins=grpc:. demo.proto
- protoc will generate demo.pb.go
demo.pb.go
type Demo struct {
Value string `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=value" json:"value,omitempty"`
}
// Client API for DemoService service
type DemoServiceClient interface {
SimpleRPC(ctx context.Context, in *Demo, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*Demo, error)
ServerStream(ctx context.Context, in *Demo, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (DemoService_ServerStreamClient, error)
ClientStream(ctx context.Context, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (DemoService_ClientStreamClient, error)
Bidirectional(ctx context.Context, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (DemoService_BidirectionalClient, error)
}
// Implementation of DemoService client
type demoServiceClient struct {
cc *grpc.ClientConn
}
func NewDemoServiceClient(cc *grpc.ClientConn) DemoServiceClient {
...
}
// Server API for DemoService service
type DemoServiceServer interface {
SimpleRPC(context.Context, *Demo) (*Demo, error)
ServerStream(*Demo, DemoService_ServerStreamServer) error
ClientStream(DemoService_ClientStreamServer) error
Bidirectional(DemoService_BidirectionalServer) error
}
Go Server
type server struct{}
func (this *server) SimpleRPC(c context.Context, msg *Demo) (*Demo, error) {
msg.Value = "Hello" + msg.Value
return msg, nil
}
func (this *server) ServerStream(msg *Demo, stream DemoService_ServerStreamServer) error {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
err := stream.Send(&Demo{value: "Hello"})
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err: %s\n", err.Error())
}
time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
}
return nil
}
func main() {
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", "localhost:12345")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to listen: %v", err)
}
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer()
RegisterDemoServiceServer(grpcServer, &server{})
grpcServer.Serve(lis)
}Go Client: SimpleRPC
func main() {
grpcAddr := "localhost:12345"
conn, err := grpc.Dial(grpcAddr)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Dial(%s) = %v", grpcAddr, err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := NewDemoServiceClient(conn)
msg := &Demo{value: "World"}
reply, err := client.SimpleRPC(context.Background(), msg)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("SimpleRPC(%#v) failed with %v", msg, err)
}
println("received message " + reply.Value)
}
Go Client: ServerStream
func main() {
grpcAddr := "localhost:12345"
conn, err := grpc.Dial(grpcAddr)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Dial(%s) = %v", grpcAddr, err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := NewDemoServiceClient(conn)
stream, err := client.ServerStream(context.TODO(), &Demo{
Value: "Hello",
})
for {
msg, err := stream.Recv()
if err == io.EOF {
break
}
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", msg)
}
}

Let's go deeper
gRPC build-in authentication
Two types of Credentials objects
- Channel credentials
- Call credentials
Channel credentials
- Credentials are attached to a Channel
- Ex: SSL credentials
tls := credentials.NewClientTLSFromCert(nil, "")
conn, err := grpc.Dial(serverAddr, grpc.WithTransportCredentials(tls))
creds, err := credentials.NewServerTLSFromFile(certFile, keyFile)
server := grpc.NewServer(grpc.Creds(creds))
server.Serve()TLS on server side
TLS on client side
Call credentials
- Credentials are attached to each RPC call
- Token based authentication, ex: OAuth, JWT
func unaryInterceptor(ctx context.Context, req interface{}, info *grpc.UnaryServerInfo, handler grpc.UnaryHandler) (interface{}, error) {
if err := authorize(ctx); err != nil {
return err
}
return handler(ctx, req)
}
func authorize(ctx context.Context) error {
if md, ok := metadata.FromContext(ctx); ok {
if checkJWT(md["jwt"][0]) {
return nil
}
return AccessDeniedErr
}
return EmptyMetadataErr
}
grpc.NewServer(grpc.UnaryInterceptor(unaryInterceptor))TLS on server side
type JWTCreds struct {
Token string
}
func (c *JWTCreds) GetRequestMetadata(context.Context, ...string) (map[string]string, error) {
return map[string]string{
"jwt": c.Token,
}, nil
}
grpc.Dial(target, grpc.WithPerRPCCredentials(&JWTCreds{
Token: "test-jwt-token",
}))TLS on client side
gRPC load balance
Approaches to Load Balancing
- Server-side LB
- Client-side LB
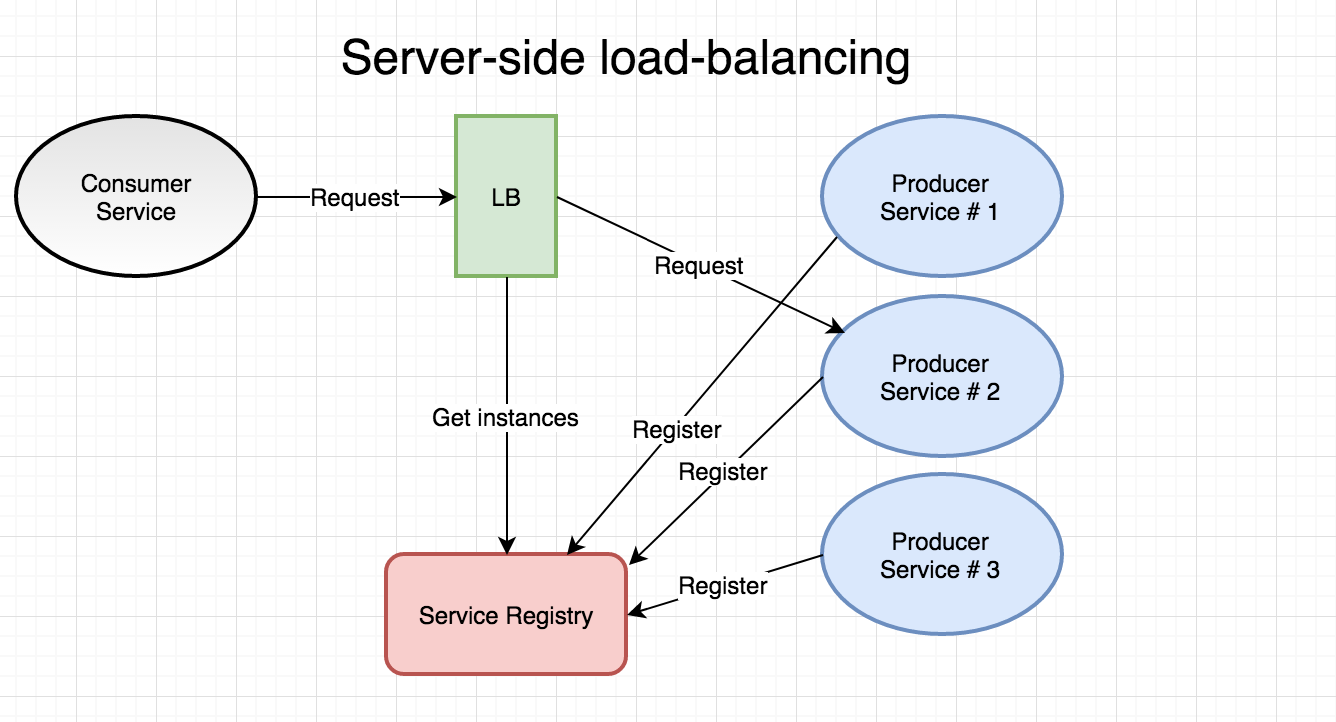
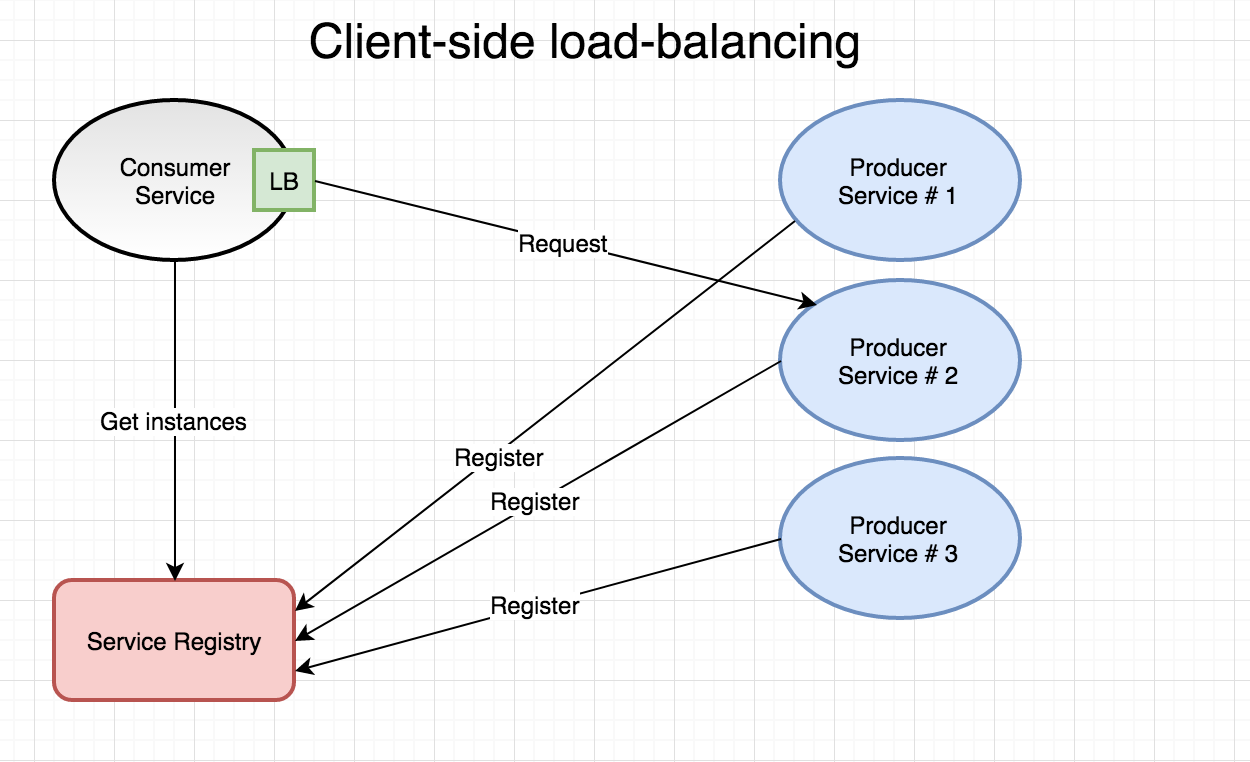
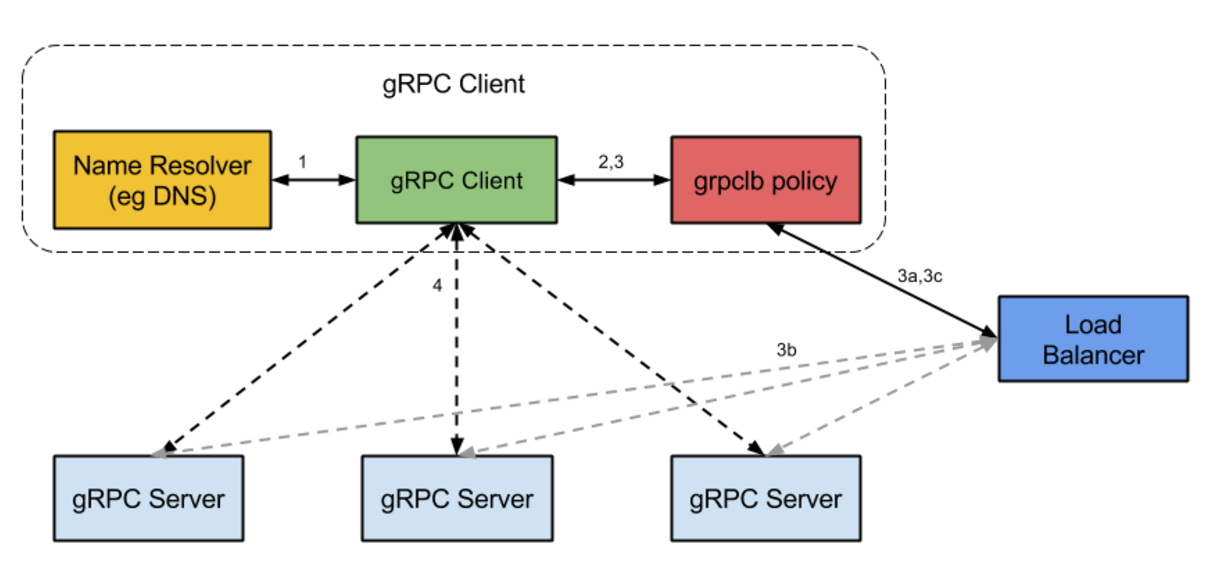
Load Balancing in gRPC
Any Question?


Build microservice with gRPC in Golang
By Ting-Li Chou
Build microservice with gRPC in Golang
- 634



