Bioinformatics Team
MRC LMS
Thomas Carroll
The Bioinformatics Team.
- Tom Carroll (ex-Head of Bioinformatics)
- Gopuraja Dharmalingam (Epigenetics)
- Sanjay Khadayate (Genes and Metabolism)
- Yi-Fang Wang (Integrative Biology)
- Marion Dore (Genomics)
- TBD (Proteomics)
Websites
Where to find the team.
- ICTEM
- 2nd floor, MRC.
- Central aisle,
- Behind the printers.
Role
- Experimental design.
- Analysis
- Bioinformatics Infrastructure.
- Training.
Text
Experimental Design
“To consult the statistician after an experiment is finished is often merely to ask him to conduct a post mortem examination. He can perhaps say what the experiment died of.”
Fisher RA, 1938
- Work closely with Genomics Team to help with design questions
- Replicate number.
- Sequencing depth.
- Sequencing strategy.
Nice example experimental design
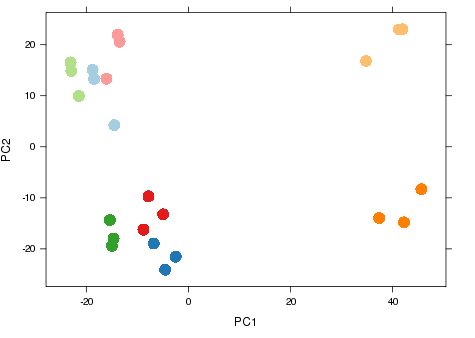
- RNA-seq experiment (2014)
- Graph shows major sources of variation.
- Samples from same groups close together.
- Samples from different experimental conditions separate.
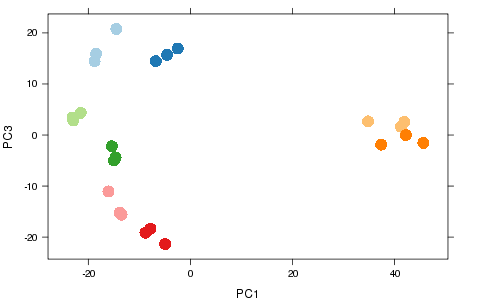
Nice example of experimental design
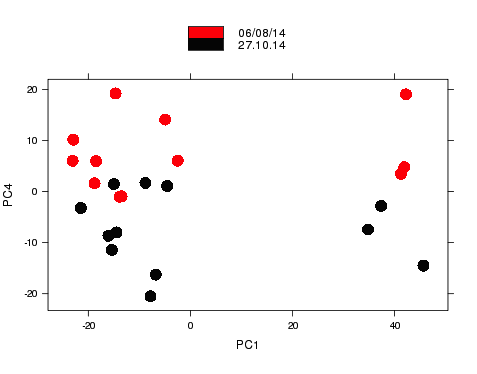
- Smaller sources of variance relating to other metadata.
- Samples group according to the day that RNA was extracted on.
- Known effects can be removed from analysis.
Analysis
- Initial data processing and QC.
- Advice and support as needed.
- Support throughout project.
Increased demand for long term support.
Authorships in > 30 publication since 2014
Analysis support
- Increased use of high throughput techniques in projects.
- Greater use for bioinformatics in projects.
- Analysis across project lifetime or individual elements.
- Requires reproducible research.
Reproducible research
- Reproducible results from computational methods should be straight forward.
- Common problems.
- Version and software changes.
- Lack of analysis documentation.
rMarkdown
- rMarkdown converted R (or python/many languages') code to dynamic reports.
- Code, results and versions are reported within the same page.
- HTML allows for inclusion of dynamic elements.
A do it yourself guide
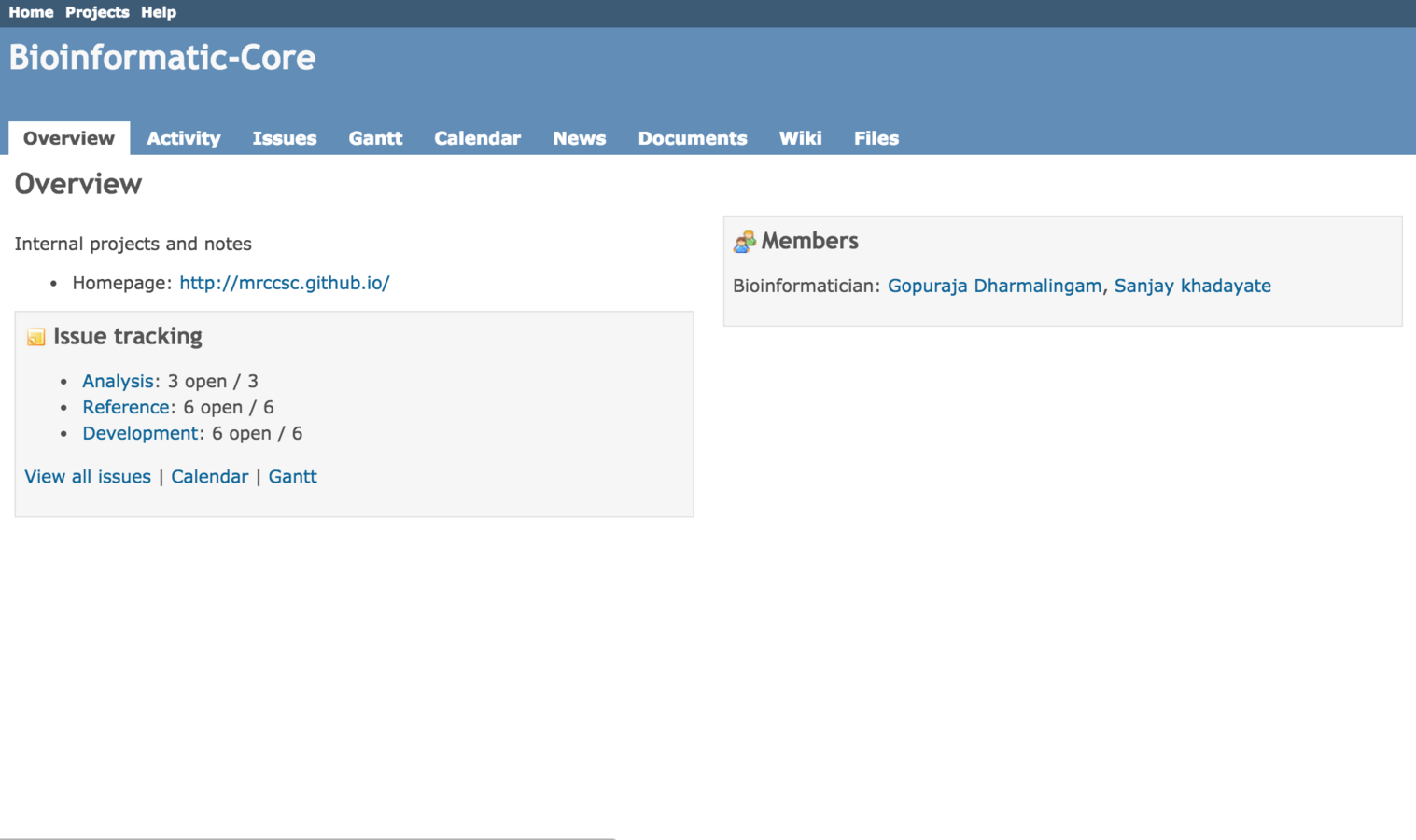
Project tracking
- Use Redmine software.
- Multiple user interface to record project information.
- Repository to version control scripts (SVN).
- Wiki for internal documentation.
Infrastructure
- Analysis pipelines.
- Data delivery.
- Software development.
ChIP-seq and RNA-seq
pipelines.
- Common analysis steps can be automated.
- Optimised for local resources.
- Reproducible and comparable.
- ChIP-seq and RNA-seq pipeline to automate alignment and quality control.
- Freely available for use or customisation on github
Genomics Pipeline
- Joined forces with Genomics to better automate some processes of basecalling/demultiplexing data.
- Basecalling - Convert optical data to sequence information.
- Demultiplexing - Split sequence data by a sequence tag (index) which is unique per sample
- Process is
- Users submit indexed samples and a sample sheet containing sample/index information.
- Genomics provide a set of QCed sample sequence files for further analysis.
Why?
- Reduce time consuming steps.
- Sample sheet templates often misinterpreted by users or incorrectly filled out.
- Thankfully not very originally and common errors can be automatically caught.
- Manual creation of basemasks for index/read layout.
- Remove dependence on Illumina's Windows' point and click software - Sequencing Analysis Viewer (SAV).
- Reduce copy and paste.
- Remove sources of potential error.
- An automated process will be more consistent (in both accuracy and error).
- Reduce copy and paste errors.
The MRC-LMS Genomics Pipeline
- Automate samplesheet cleaning and updating.
- Create basemasks or index/read description.
- Parse results from basecalling/demultiplexing
- Binary files from Real Time Analysis software.
- XML files from BCL2fastq version 2.17 or above.
- Summarise results to provide to user alongside resulting sequence files in fastq format.
- Written in R, moved to Bioconductor in May 2017.
Others in the pipeline
- Internal RNA-seq/ChIP-seq pipeline
- Written in R.
- Easily installed, maintained.
- Allows Core to move between systems easily (both install and parallelisation).
- Released soon.
- Basecalling to ChIP/RNA-seq QC/initial analysis all in one reproducible, version controlled report.
- Proteomics data pipeline?
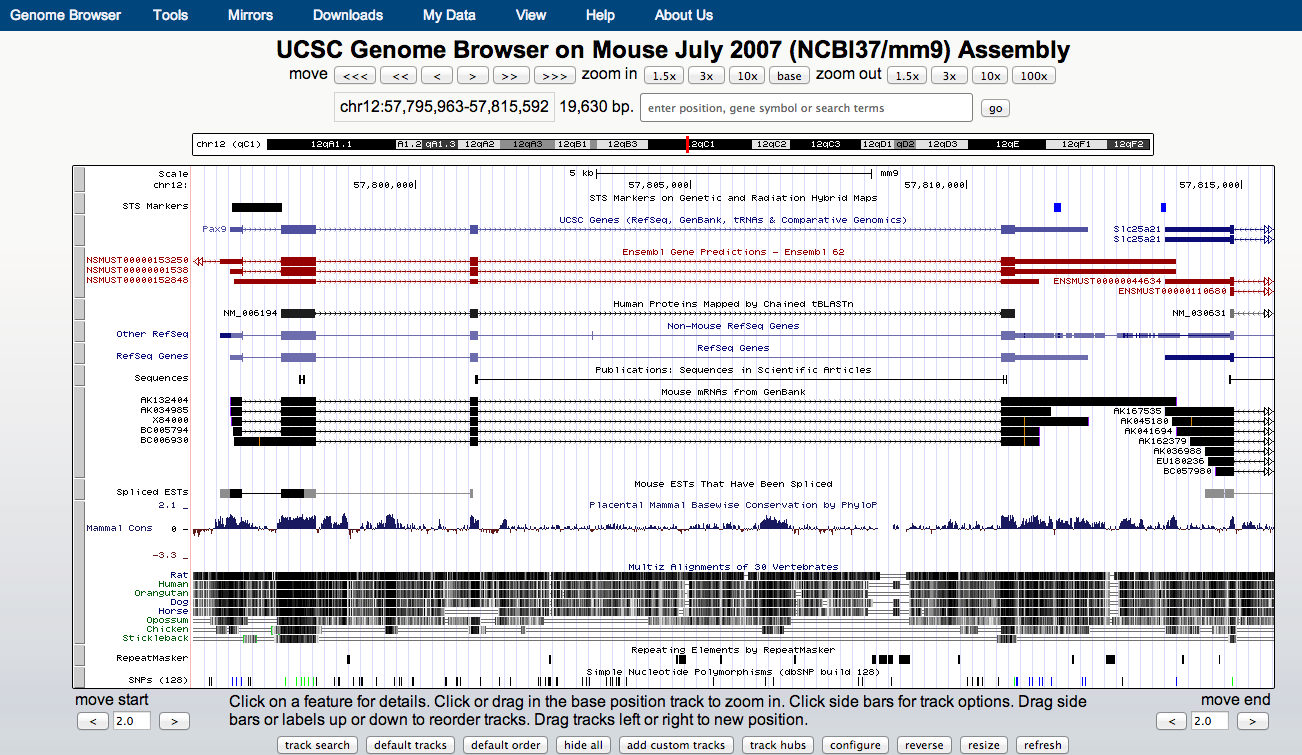
UCSC genome browser
- UCSC allows for visualisation of a range of genomics data types.
- Public instances can be very slow.
- CSC public instance maintained by Bioinformatics team.
-
web: http://ucsc
FTP: ftp://ucsc
Software
- Develop and maintain software relevant to our work.
- R packages and javascript toolsets.
-
Release software to public (peer-reviewed) repositories.
- Reviews improves code quality
- Collaborative feedback.
- Automated build reports and checking.
ChIPQC
- Lack of suitable R/Bioconductor quality control tools for ChIP-seq.
- Require methods to assess quality across high volumes of samples
- ChIPQC developed and tested on 500 public datasets.
- IGV is an popular alternate to UCSC.
- Allows for inclusion of per sample metadata and complex sample display types.
- Tracktables creates standalone and rMarkdown compliant tables.
Tracktables
Simple Example - Loading data
Simple Example - Loading data
Simple Example - Loading data
Simple Example - Loading data
- Visualising genomics data over regions of the genome.
- Allows for rapid generation of profiles and subsetting by IDs or other regions.
- Arithmetic operations between and within profiles allows for rapid, iterative investigation of hypotheses.
Soggi
- Peak calling in R is convenient.
- Many peak callers in R have unwieldy input and far from optimised.
- triform contains a reliable peak calling algorithm in need of optimisation for speed and long marks.
- MRC CSC took over maintenance of triform in 2015
triform
basecallQC
- Automate basecalling and demultiplexing.
- Less manual intervention.
- No dependence on proprietary software.
- Customised for MRC-LMS use
Training
-
Aim to develop courses to meet MRC Clinical Sciences requirements.
-
R (8 courses)
-
Python (1 courses)
-
High throughput sequencing analysis. (3 courses)
-
-
Relevant and targeted training.
-
Real world examples.
-
Taught courses and material for online learning.
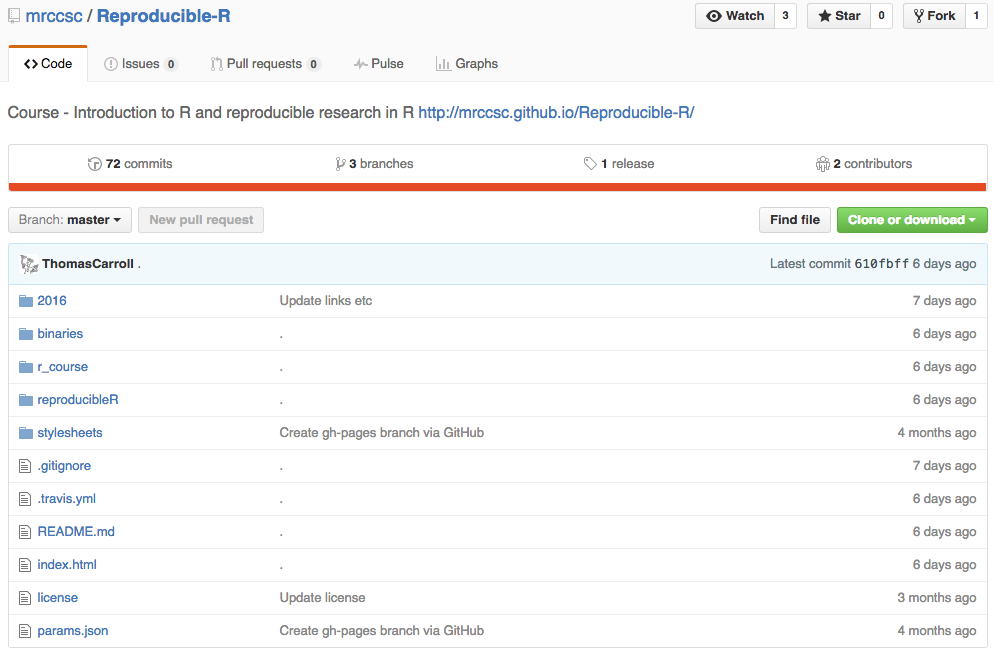
Material Repository
- 2014 (R Basics)
- Intro to R course.
- Reproducible R.
- 2015 (Basics of Bioinformatics)
- ChIP-seq.
- RNA-seq.
- Bioconductor.
- Genome Browsers and File Formats.
- 2016 (Intermediate R and Bioinformatics)
- Intermediate R.
- Alignments and Counting.
- Visualising High Throughput Sequeuncing Data
- Introduction to Python
CSC Bioinformatics Course
- Current and upcoming Bioinformatics training material can be found at our site
http://mrccsc.github.io/training.html
Github/Github.io/Travis/Appveyor and Training in 2017
- All training is hosted on Github.
- All pages automatically synced to Github.io
- Training courses automatically tested on windows/mac/linux after any changes.

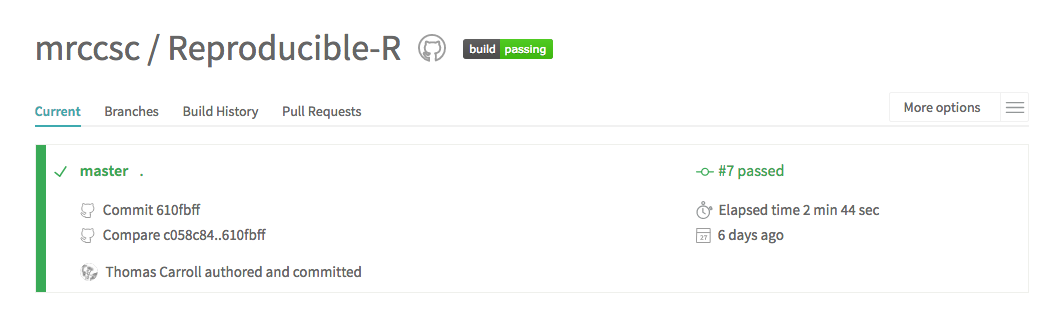
Training Collaborations
- All material is open source (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
- Free to distribute or collaborate.
- No commercial use.
- No remixes.
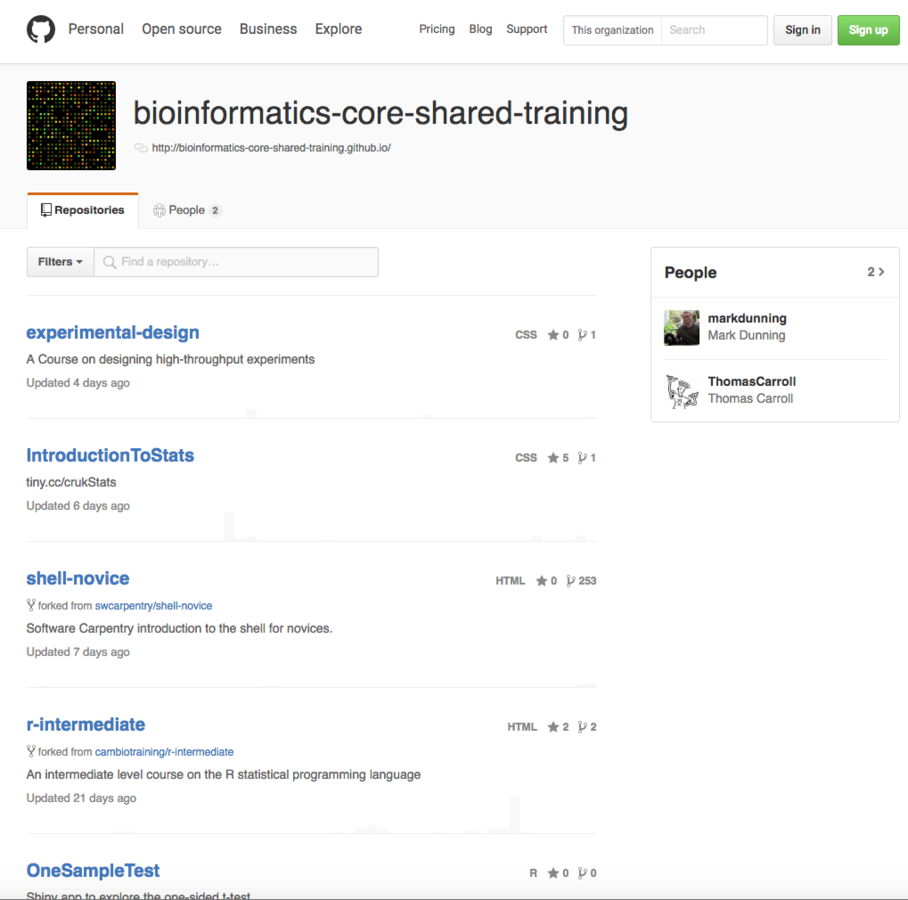
- Bioinformatics Core Shared Training (with Mark Dunning)
- Genomic File Formats
- Intermediate R
- ChIP-seq ->
- IGV ->
- -> Experimental Design
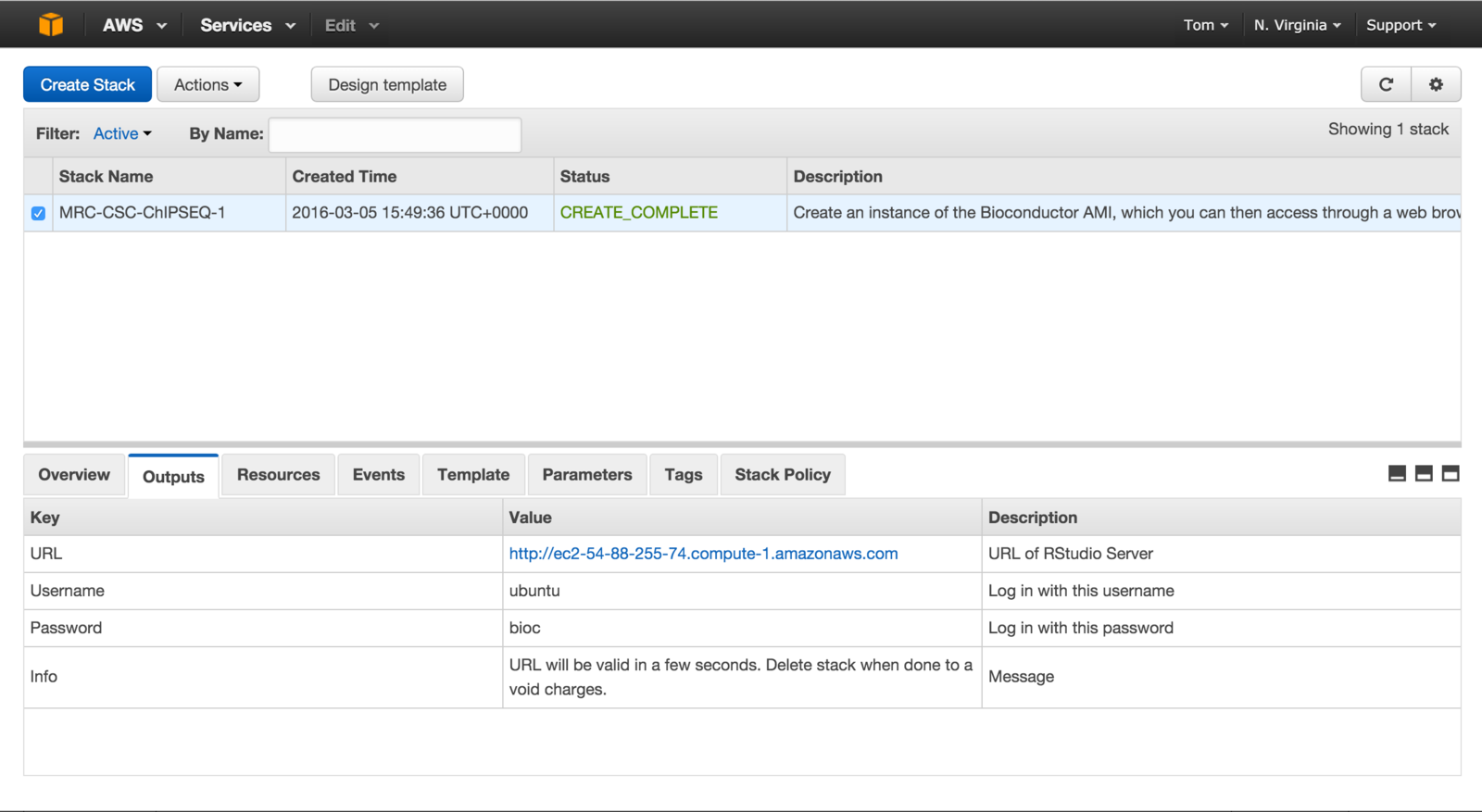
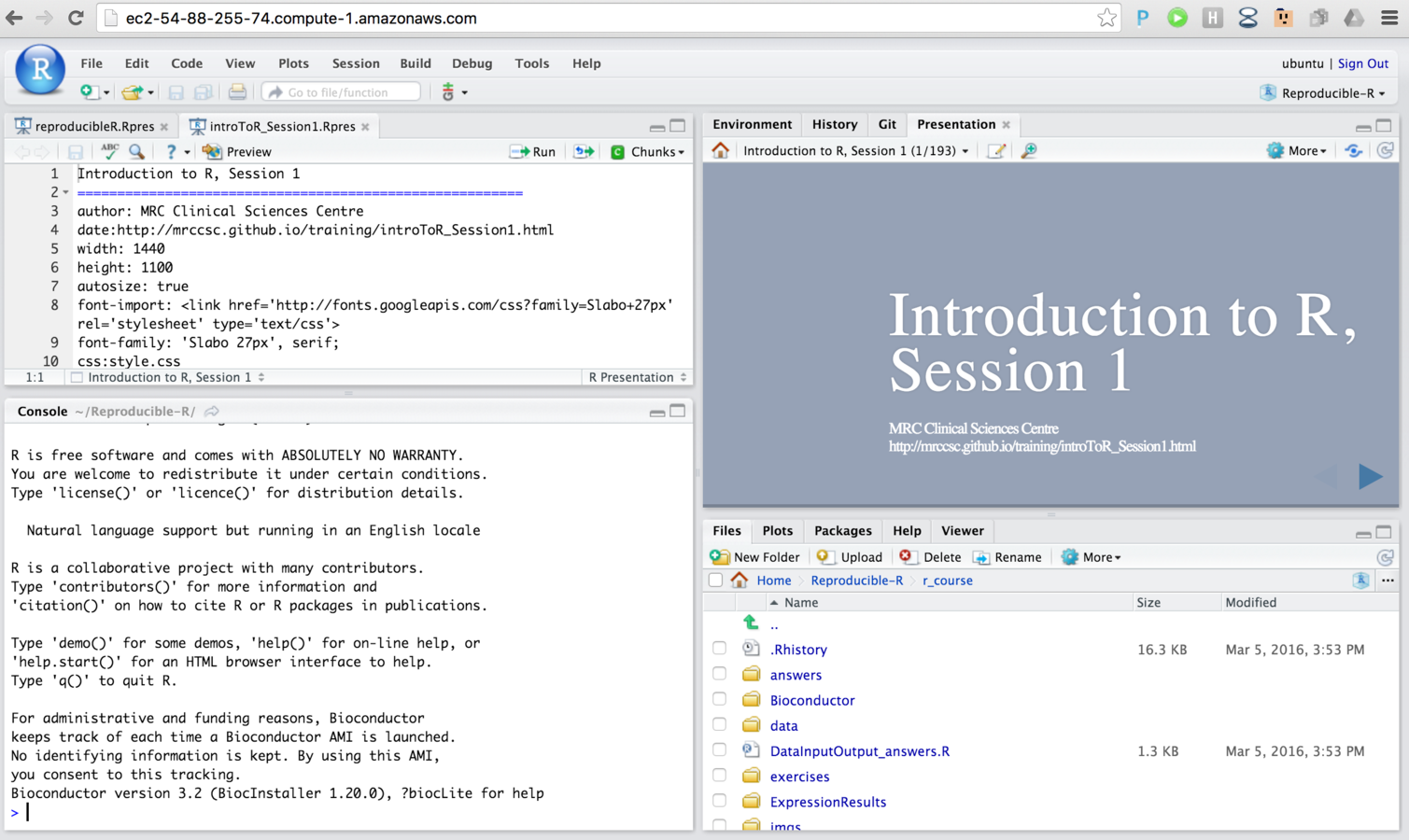
Training on the cloud.
- Awarded grant from Amazon Web Services.
- Use virtual linux servers to host R and RStudio pre-loaded with course material.
- Allow for larger, real world analysis tasks during training.
- No need for dedicated classroom - train from anywhere.
Future!
- Release and link RNA-seq and ChIP-seq pipelines.
- Submit samples and get QCed, aligned data back.
- Support proteomics and analysis of other MRC high throughput technologies.
- Training updates
- More python!
- More non-programmer courses (e.g. Deeptools)!
- Julia and other languages?!
- Interactive online training!!
- More analysis!!!
Have a great week!
Bioinformatics Team
Tom - thomas.carroll@imperial.ac.uk
Gopu - gopuraja.dharmalingam@imperial.ac.uk
Sanjay - sanjay.khadayate@imperial.ac.uk
Yi-Fang - yifang.wang@imperial.ac.uk
Marion - marion.dore@imperial.ac.uk

Bioinformatics2017
By tom carroll
Bioinformatics2017
- 522



