Reference genomes
and
Common file formats
The Rockefeller University
Bioinformatics Resource Centre
Overview
-
Reference genomes and GRC.
-
Fasta and FastQ (Unaligned sequences).
-
SAM/BAM (Aligned sequences).
-
BED (Genomic Intervals).
-
GFF/GTF (Gene annotation).
-
Wiggle files, BEDgraphs and BigWigs (Genomic scores).
Are there we there yet?
-
The human genome isnt complete!
-
In fact, most model organisms's reference genomes are being regularly updated.
-
Reference genomes consist of mixture of known chromosomes and unplaced contigs called a " Genome Reference Assembly".
-
Major revisions to assembies result in change of co-ordinates.
-
Requires conversion between revisions.
-
The latest genome assembly for humans is GRCh38.
-
- Patches add information to the assembly without disrupting the chromosome coordinates . i.e GRCh38.p3
Genome Reference Consortium
- GRC is collaboration of institutes which curate and maintain the reference genomes for 3 model organims.
- Human - GRCh38.p3
- Mouse - GRCm38.p3
- Zebrafish - GRCz10
- Other model organisms are maintained separately.
- Drosophila - Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project, BDGP36
Why do we need to know about reference genomes
- Allows for genes and genomic features to be evaluated in their linear genomic context.
- Gene A is close to Gene B
- Gene A and Gene B are within feature C.
- Can be used to align shallow targeted high-thoughput sequencing to a pre-built map of an organisms genome.
Aligning to a reference genomes
DNA/cDNA
Fragment
DNA (PCR amplify)
Sequence DNA
Unaligned
sequence

Aligned sequences
Reference genome
A reference genome
- A reference genome is a collection of contigs.
- A contig is a stretch of DNA sequence encoded as A,G,C,T,N.
- Typically comes in FASTA format.
- ">" line contains information on contig
- Lines following contain contig sequence

High-throughput Sequencing formats
Unaligned sequence files generated from HTS machines are mapped to a reference genome to produce aligned sequence files.
-
FASTQ - Unaligned sequences
-
SAM - Aligned sequences
Unaligned Sequences
FastQ (FASTA with Qualities)
- "@" followed by identifier.
- Sequence information.
- "+"
- Quality scores encodes as ASCI.

Unaligned Sequences
FastQ - Header
- Header for each read can contain additional information
- HS2000-887_89 - Machine name.
- 5 - Flowcell lane.
- /1 - Read 1 or 2 of pair (here read 1)

Unaligned Sequences
FastQ - Qualities
- Qualities follow "+" line.
- -log10 probability of sequence base being wrong.
- Encoded in ASCI to save space.
- Used in quality assessment and downstream analysis

Aligned sequences
SAM format
- SAM - Sequence Alignment Map.
- Standard format for sequence data
- Recognised by majority of software and browsers.
Aligned sequences
SAM - Header
- SAM header contains information on alignment and contigs used.
- @HD - Version number and sorting information
- @SQ - Contig/Chromosome name and length of sequence.

Aligned sequences
SAM - Aligned Reads

- Contains read and alignment information and location
Aligned sequences
SAM

- Read name.
- Sequence of read.
- Encoded sequence quality.
Aligned sequences
SAM

- Chromosome to which read aligns.
- Position in chromosome to which 5' of read aligns.
-
Alignment information - "Cigar string".
- 100M - Continuous match of 100 bases
- 28M1D72M - 28 bases continuously match, 1 deletion from reference, 72 base match
Aligned sequences
SAM

-
Bit flag - TRUE/FALSE for pre-defined read criteria
- Paired? Duplicate?
- https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/explain-flags.html
- Paired read position and insert size
- User defined flags.
Summarised Genomic Features formats
Post alignment, sequences reads are typically summarised into scores over/within genomic intervals.
-
BED - Genomic intervals and information.
-
Wiggle/BedGraph - Genomic intervals and scores.
-
GFF - Genomic annotation with information and scores
Summarising in genomic intervals.
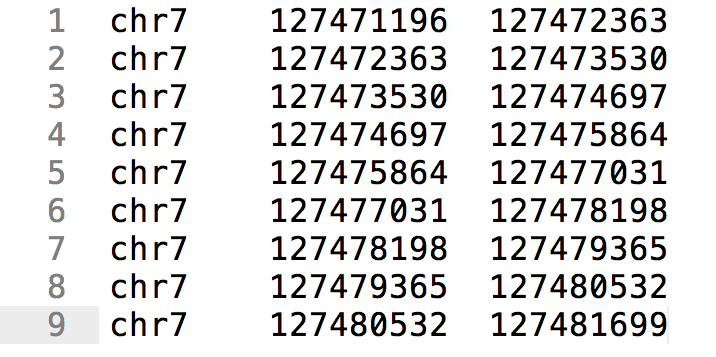
BED format (BED)
- Simple format
- 3 tab separated columns
- Chromsome, start, end
Summarising in genomic intervals.
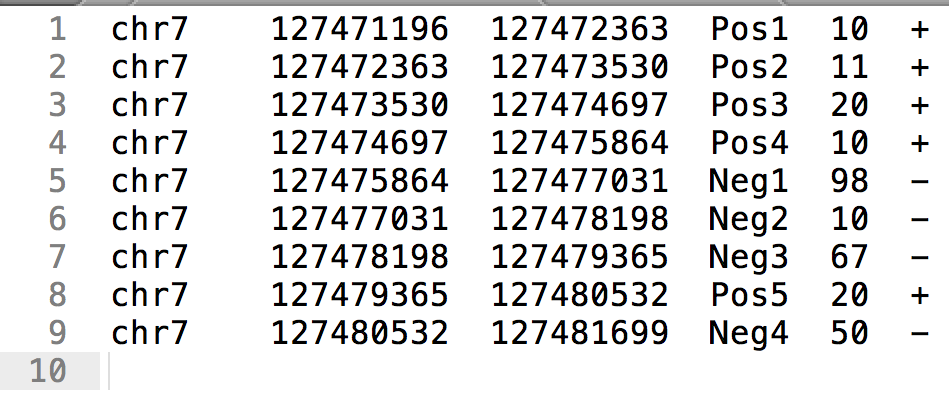
BED format (BED6)
- Chromosome, start, end
- Identifier
- Score
- Strand ("." for strandless)
Summarising in genomic intervals.
narrowPeak and broadPeak
- narrowPeak and broadPeak are extensions to BED6 used in Encode's peak calling.
- Contains p-values, q-values.
-
narrowPeak - BED 6+4
-
broadPeak - BED6+3
Signal at genomic positions
- Common practice to review signal over genome.
- Special formats exist for this
- Wiggle
- bedGraph
Signal at genomic positions
Wiggle
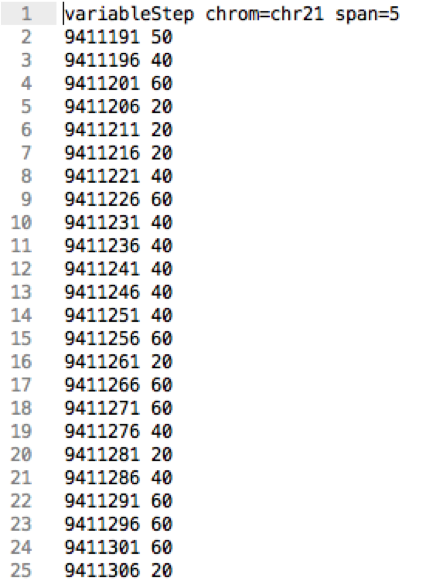
- Information line
- Chromosome
- Step size
- Step start position
- Score
Signal at genomic positions
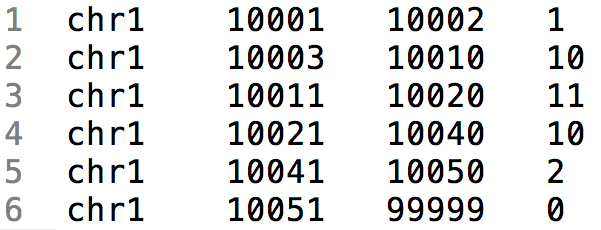
bedGraph
- BED 3 format
- Chromosome
- Start
- End
- 4th column - Score
Genomic Annotation
GFF

- Used to genome annotation.
- Stores position, feature (exon) and meta-feature (transcript/gene) information.
Genomic Annotation
GFF

- Chromosome
- Start of feature
- End of Feature
- Strand
Genomic Annotation
GFF

- Source
- Feature type
- Score
Genomic Annotation
GFF

- Column 9 contains key pairs (ID=exon01), separated by semi-colons ";"
- ID - Feature name.
- PARENT- Meta-feature name.
Saving time and space
bigWig, bigBED and TABIX
- Many programs and browsers deal better with compressed, indexed versions of genomic files
- SAM -> BAM (.bam and index file of .bai)
- Wiggle and bedGraph -> bigWig (.bw/.bigWig)
- BED -> bigBed (.bb)
- BED and GFF -> (.gz and index file of .tbi)
Getting help and more information
- UCSC file formats
- https://genome.ucsc.edu/FAQ/FAQformat.html
- IGV file formats
- https://www.broadinstitute.org/igv/FileFormats
- Sanger (GFF)
- https://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/software/gff/spec.html
genomeBrowserCourse
By tom carroll
genomeBrowserCourse
- 679



