Priority Queue
Agenda
- Priority queue
- Naive way : O(n)
- grouping :
- heap : O(log(n))
Priority Queue
- Recover previous data structure
- stack: last in first out
- queue: first in first out
- What if we want to pop the biggest(smallest) "weight", rather than first in or last in?
- priority queue
- note: for convenience, elements are integer, "weight" comparison is just number comparison.
Priority Queue
- Basic operations
- push: push an element into the priority queue
- top: ask for the element with the biggest value in the priority queue
- pop: take the biggest value element out of the priority queue.
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
| 5 | 3 | 12 | 1 | 6 |
|---|
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
| 5 | 3 | 12 | 1 | 6 |
|---|
push 2
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
| 5 | 3 | 12 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
|---|
push 2
We just put it in to the array: O(1)
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
| 5 | 3 | 12 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
|---|
top: find the maximum
Iterating and found: O(n)
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
| 5 | 3 | 12 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
|---|
pop: find the maximum and pop
Iterating and found: O(n)
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
|---|
pop: find the maximum and pop
Iterating and found: O(n)
Put the last element to the empty position: O(1)
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
| 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 6 |
|---|
pop: find the maximum and pop
Iterating and found: O(n)
Put the last element to the empty position: O(1)
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
- Better way, make sure the first element is the largest.
| 12 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
|---|
push 2: O(1)
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
- Better way, make sure the first element is the largest.
| 12 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
|---|
push 2: O(1)
Compare to the maximum. O(1)
generally O(1)
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
- Better way, make sure the first element is the largest.
| 12 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
|---|
top: O(1)
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
- Better way, make sure the first element is the largest.
| 12 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
|---|
pop: just remove the first one
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
- Better way, make sure the first element is the largest.
| 3 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
|---|
pop: just remove the first one
And find the maximum in the array
Implement - array
- Push every elements into array
- Better way, make sure the first element is the largest.
| 6 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 |
|---|
pop: just remove the first one: O(1)
And find the maximum in the array O(n)
Move the maximum to the first-place O(1)
And use the last element to the empty place O(1)
Generally O(n)
Implement - array
- Push every element into array
- push: O(1)
- top: O(n)
- pop: O(n)
- The better way, make sure the first element is the largest.
- push: O(1)
- top: O(1)
- pop: O(n)
- Pop operation is too slow both ways.
Implement - Grouping
- Divide the sequence into k numbers a group, and record the maximum in each group
- ex. k=2, and put the maximum in each group at the front.
| 5 | 4 |
|---|
| 2 |
|---|
| 7 | 3 |
|---|
| 6 | 1 |
|---|
Implement - Grouping
- Divide the sequence into k numbers a group, and record the maximum in each group
- ex. k=2, and put the maximum in each group at the front.
| 5 | 4 |
|---|
| 2 |
|---|
| 7 | 3 |
|---|
| 6 | 1 |
|---|
push 9
Implement - Grouping
- Divide the sequence into k numbers a group, and record the maximum in each group
- ex. k=2, and put the maximum in each group at the front.
| 5 | 4 |
|---|
| 2 | 9 |
|---|
| 7 | 3 |
|---|
| 6 | 1 |
|---|
push 9
- push into array O(1)
Implement - Grouping
- Divide the sequence into k numbers a group, and record the maximum in each group
- ex. k=2, and put the maximum in each group at the front.
| 5 | 4 |
|---|
| 9 | 2 |
|---|
| 7 | 3 |
|---|
| 6 | 1 |
|---|
push 9
- push into the array: O(1)
- Compare to the maximum in its group: O(1)
- Generally: O(1)
Implement - Grouping
- Divide the sequence into k numbers a group, and record the maximum in each group
- ex. k=2, and put the maximum in each group at the front.
| 5 | 4 |
|---|
| 9 | 2 |
|---|
| 7 | 3 |
|---|
| 6 | 1 |
|---|
top
Compare maximums of groups
O(n/k)
Implement - Grouping
- Divide the sequence into k numbers a group, and record the maximum in each group
- ex. k=2, and put the maximum in each group at the front.
| 5 | 4 |
|---|
| 9 | 2 |
|---|
| 7 | 3 |
|---|
| 6 | 1 |
|---|
pop
find the maximums of groups and pop it
O(n/k)
Implement - Grouping
- Divide the sequence into k numbers a group, and record the maximum in each group
- ex. k=2, and put the maximum in each group at the front.
| 5 | 4 |
|---|
| 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 7 |
|---|
| 6 | 1 |
|---|
pop
find the maximums of groups and pop it
O(n/k)
Use the last element to replace it.
Implement - Grouping
- Divide the sequence into k numbers a group, and record the maximum in each group
- ex. k=2, and put the maximum in each group at the front.
| 5 | 4 |
|---|
| 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 7 |
|---|
| 6 | 1 |
|---|
pop
find the maximums of groups and pop it
O(n/k)
Use the last element to replace it.
Find the maximum in its group. (may need to exchange)
Implement - Grouping
- Divide the sequence into k numbers a group, and record the maximum in each group
- ex. k=2, and put the maximum in each group at the front.
| 5 | 4 |
|---|
| 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 7 |
|---|
| 6 | 1 |
|---|
pop
find the maximums of groups and pop it
O(n/k)
Use the last element to replace it. : O(1)
Find the maximum in its group. (may need to exchange) O(k)
Generally O(n/k) + O(k), depends on k's magnitude.
Time complexity
- push: O(1)
- top: O(n/k)
- pop: O(n/k) + O(k)
if we choose
Another way, maintain all maximums a the first group, think.
heap
heap Definition
heap Definition
Imagination: a complete binary tree.
The value of the parent node is no less than its child nodes.
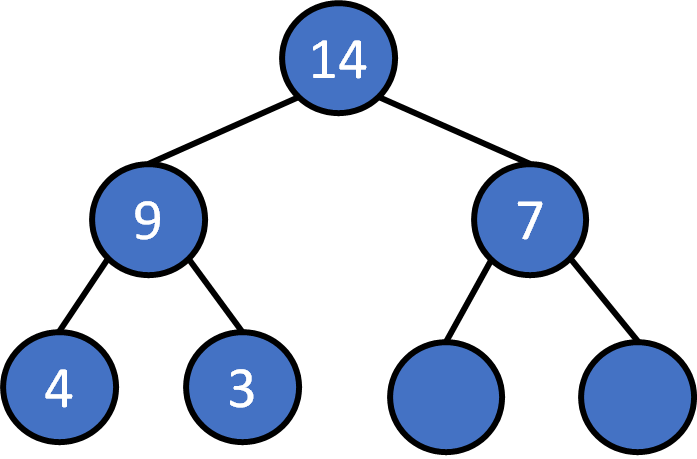
heap push
Push 8
Put the element into tree : O(1)
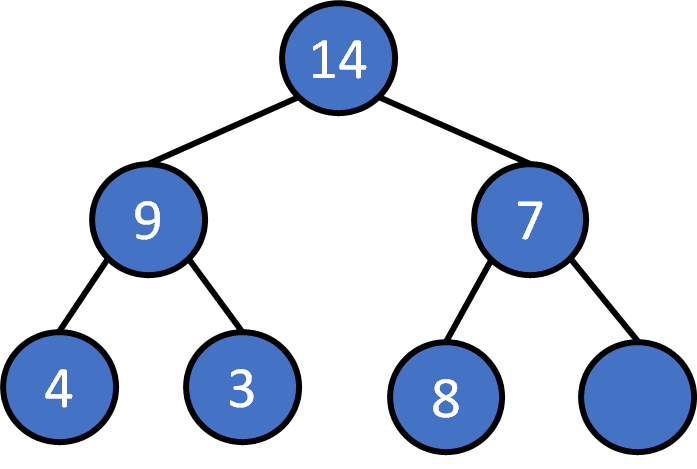
heap push
Push 8
Put the element into tree: O(1)
Compare with the parent: O(1)
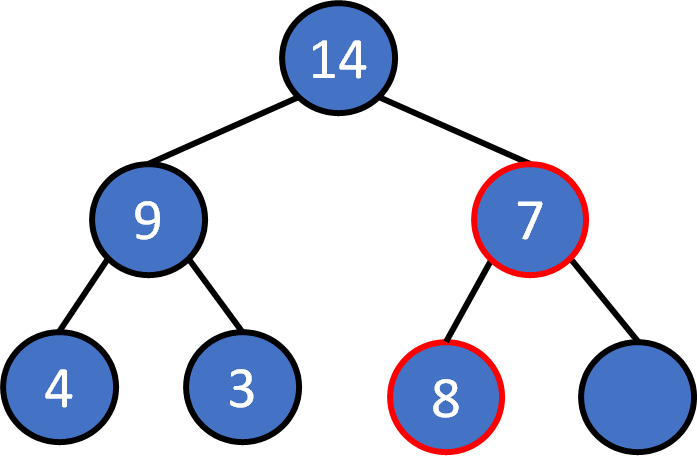
heap push
Push 8
Put the element into tree: O(1)
Compare with the parent: O(1) * log(N)
Keep float upward until the value is less than the value of parent node
Float at most log(N) times.
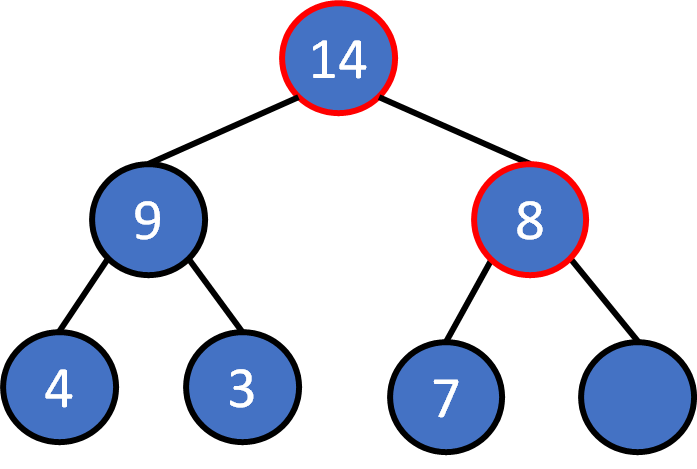
heap push
Push 8
Put the element into tree: O(1)
Compare with the parent: O(1) * log(N)
Keep float upward until the value is less than the value of parent node
Float at most log(N) times.

Generally log(N)
heap top
Top
O(1)
The root must be the largest one.
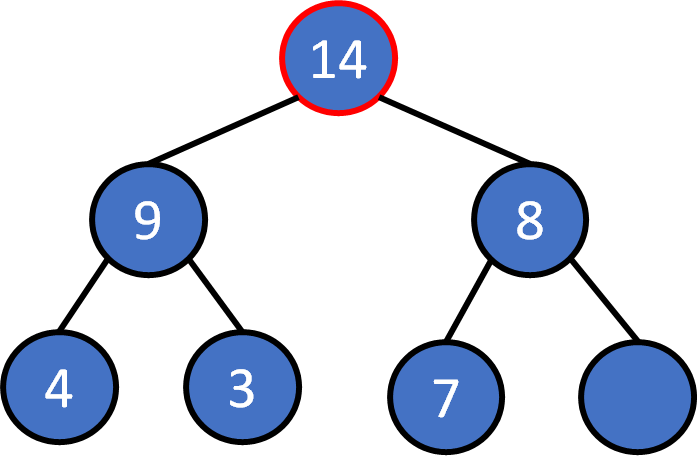
heap pop
Pop

heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it
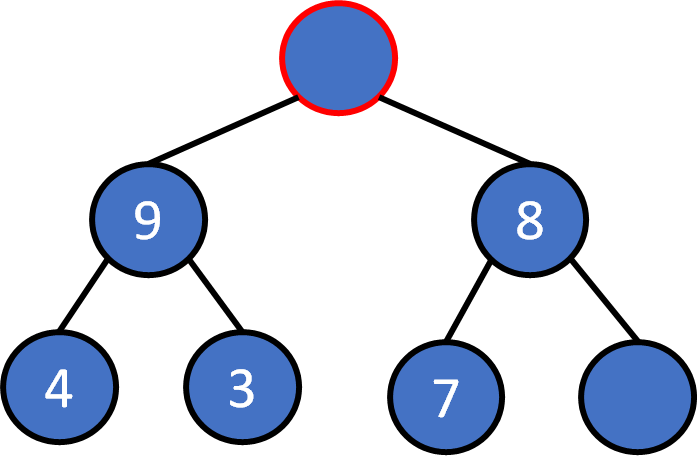
heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it

heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it
Compare two child nodes, the larger one floats up.
Keep comparing, at most log(N) times.
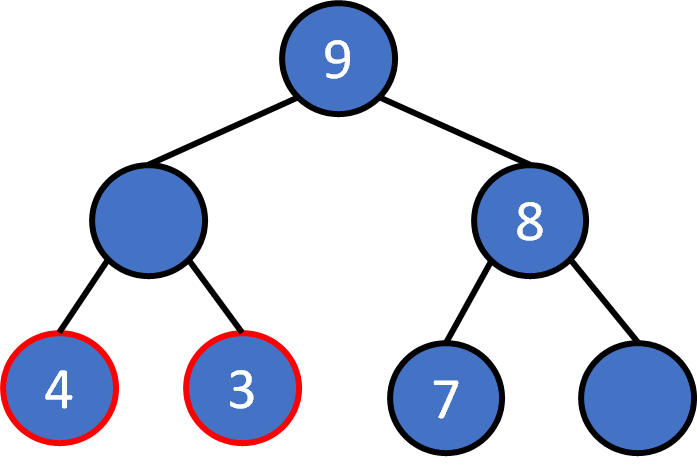
heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it
Compare two child nodes, the larger one floats up.
Keep comparing, at most log(N) times.
The empty place uses the last element to replace it.
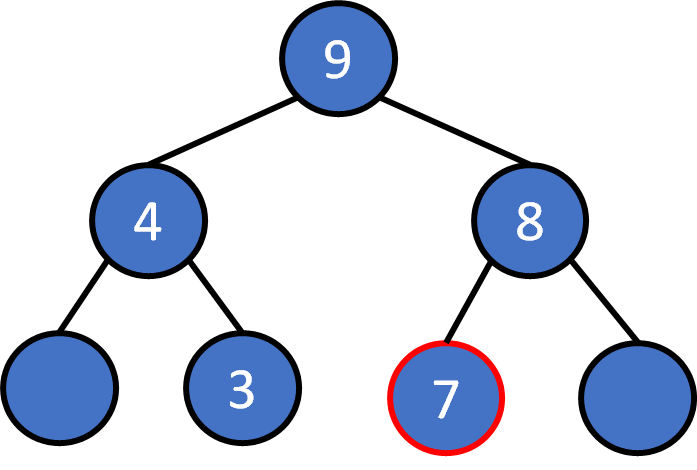
heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it
Compare two child nodes, the larger one floats up.
Keep comparing, at most log(N) times.
The empty place uses the last element to replace it.
After replacement, it may needs to float up again
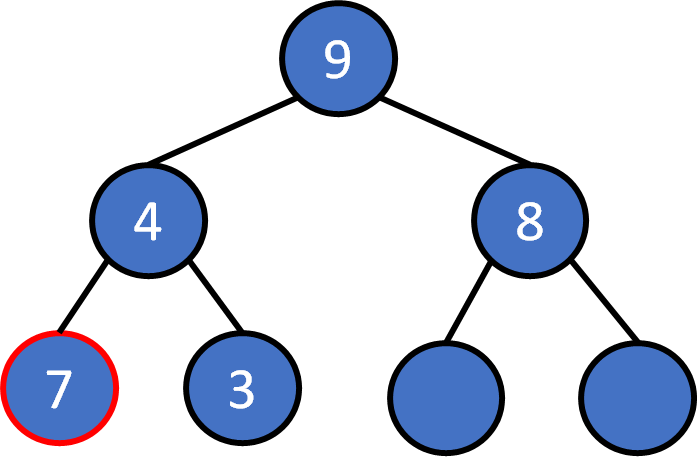
heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it
Compare two child nodes, the larger one floats up.
Keep comparing, at most log(N) times.
The empty place uses the last element to replace it.
After replacement, it may needs to float up again

heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it

heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it
Put the last element on the root.
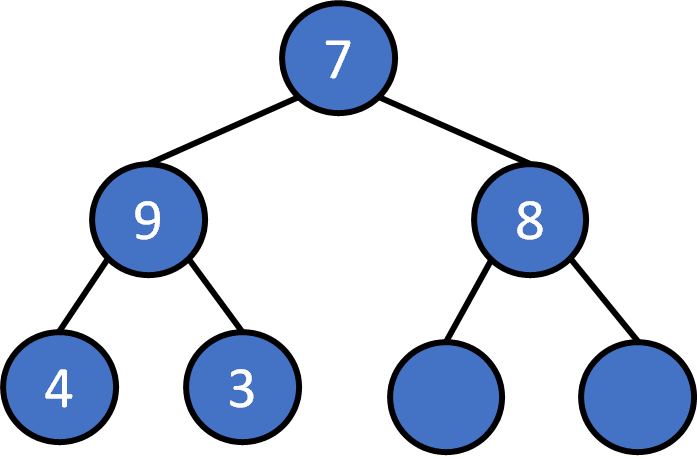
heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it
Put the last element on the root.
Compare with the larger child node. O(1)
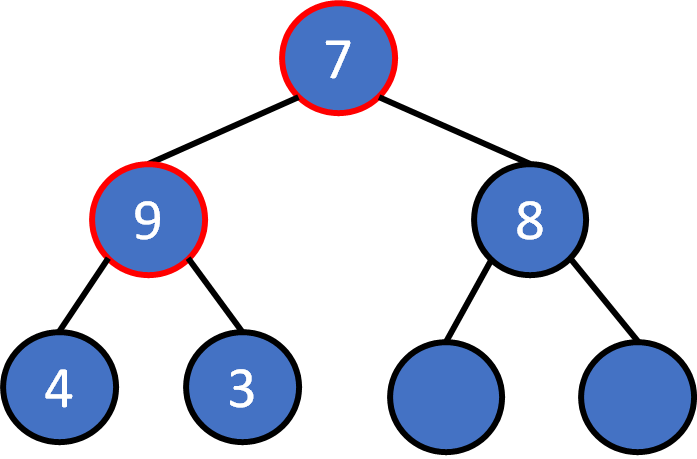
heap pop
Pop
The root must be the largest one. Pop it
Put the last element on the root.
Compare with the larger child node. O(1)

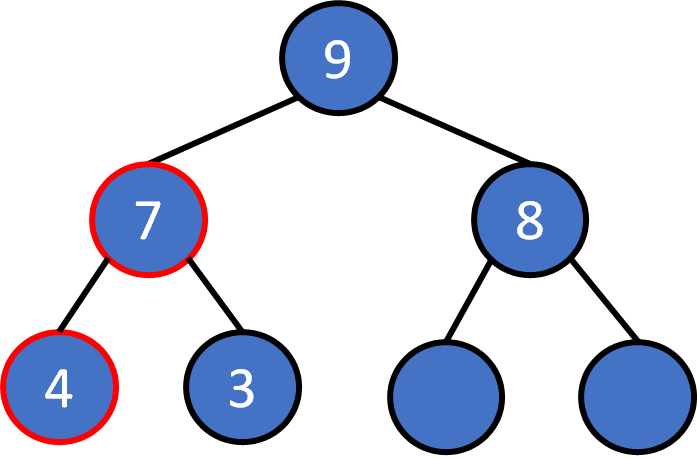
heap pop
Pop
Generally log(N)
The root must be the largest one. Pop it
Put the last element on the root.
Compare with the larger child node. O(1) * O(log(N)
Keep sinking until the value is no less than the value of two child nodes.
At most log(N) times.
heap
Pop : O(log(N))
top: O(1)
push : O(log(N))
standard library
| functions |
|---|
| push(x) |
| pop() |
| top() |
| empty() |
| size() |
heap = priorty queue
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
std::priority_queue<int> pq;
int main(){
pq.push(37);
pq.push(12);
pq.push(23);
pq.push(28);
pq.push(14);
pq.push(64);
pq.push(19);
pq.push(33);
pq.push(9);
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.push(100);
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
while(!pq.empty()){
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
}
}heap is an implementation of priority queue
heap != priority queue
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
std::priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq;
int main(){
pq.push(37);
pq.push(12);
pq.push(23);
pq.push(28);
pq.push(14);
pq.push(64);
pq.push(19);
pq.push(33);
pq.push(9);
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.push(100);
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
while(!pq.empty()){
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
}
}#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
std::priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> pq;
int main(){
pq.push(37);
pq.push(12);
pq.push(23);
pq.push(28);
pq.push(14);
pq.push(64);
pq.push(19);
pq.push(33);
pq.push(9);
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.push(100);
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
while(!pq.empty()){
std::cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
}
}sort()
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(37);
v.push_back(12);
v.push_back(23);
v.push_back(28);
v.push_back(14);
v.push_back(64);
v.push_back(19);
v.push_back(33);
v.push_back(9);
vector<int> v2(v);
vector<int> v3(v);
sort(v2.begin(), v2.end());
sort(v3.begin(), v3.end(), greater<int>());
for(int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++){
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for(auto it: v3){
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}random
random
#include <ctime> // time.h in C, for time(NULL)
#include <cstdlib> // stdlib.h in C, for rand, srand
int generateRangeRand(int L, int R){
return rand() % (R - L + 1) + L;
}
int main(){
srand(time(NULL)); // init random seed, close and see what will happen
int T = 100;
while(T--){
cout << rand() << endl;
}
T=100
while(T--){
cout << generateRangeRand(1, 100) << endl;
}
}random + sort + STL
usually use to test you code valid
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib> // for rand, srand
using namespace std;
struct people{
int age;
int height;
int weight;
string name;
people(){}
people(int age, int height, int weight, string name):
age(age), height(height), weight(weight), name(name){}
bool operator<(people b){
return this->name < b.name;
}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const people &data);
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const people& data){
os << data.age << " " << data.height<< " " << data.weight << " " << data.name;
return os;
}
int getRandNum(int L, int R){
if(L>R)
swap(L, R);
//srand(time(NULL)); // what if we add this line ?
return rand() % (R - L + 1) + L;
}
bool cmp(const people& a, const people& b){
if(a.weight != b.weight)
return (a.weight < b.weight);
else if(a.height != b.height)
return (a.height < b.height);
else if(a.age != b.age)
return (a.age < b.age);
return false;
}
bool cmp2(const people &a, const people &b){
if(a.weight < b.weight)
return true;
else if(a.height < b.height)
return true;
else if(a.age < b.age)
return true;
return false;
}
int main(){
srand(time(NULL));
vector<people> v;
v.push_back(people(getRandNum(1,90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Alice"));
v.emplace_back(getRandNum(1, 90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Bob");
v.emplace_back(getRandNum(1, 90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Cathy");
v.emplace_back(getRandNum(1, 90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Danny");
v.emplace_back(getRandNum(1, 90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Eggo");
v.emplace_back(getRandNum(1, 90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Frank");
v.emplace_back(getRandNum(1, 90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Gilbert");
v.emplace_back(getRandNum(1, 90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Inn");
v.emplace_back(getRandNum(1, 90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Jack");
v.emplace_back(getRandNum(1, 90), getRandNum(160, 200), getRandNum(40, 100), "Ken");
vector<people> v2(v);
vector<people> v3(v);
sort(v2.begin(), v2.end());
sort(v3.begin(), v3.end(), cmp);
for(int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++){
cout << v2[i] << endl;
}
cout << "----------------\n";
for(auto it: v3){
cout << it << endl;
}
cout << "----------------\n";
return 0;
}Heap
By tunchin kao
Heap
- 84



