Intro to JavaScript
Hours: 18 hrs
Instructor : Andy Tseng
Module 0 背景知識
預備知識
- 基礎的程式識讀 ( Python )
- Chrome
課程大綱
-
Module 1. 測試及除錯工具
-
Module 2. 使用 script 標籤
-
Module 3. 常數和變數宣告
- Module 4. 基本類型
- Module 5. 運算子
- Module 6. String
課程大綱
- Module 7. 取得標籤元素
- Module 8. 流程控制
- Module 9. Object類型
- Module 10. Array類型
- Module 11. JSON
- Module 12. 函式的定義
課程大綱
- Module 13. Scope變數領域
- Module 14. 時間與計時器
- Module 15. 數學物件
- Module 16. window物件
- Module 17. 事件處理
- Module 18. AJAX
Module 1: 測試及除錯工具
Module 1: 測試及除錯工具
1-1: Chrome開發者工具 1-2: Console面板 1-3: Network面板
Javascript 是什麼?
- 原名: LiveScript,因為一開始 Java 很流行,取個相近的名稱
- Chrome 將 Js 效能提高 20幾倍
- 在2008年到2009年的第二次瀏覽器大戰之前,JavaScript引擎僅簡單地被當作能閱讀執行JavaScript原始碼的直譯器。
1-1: Chrome開發者工具
- 在 Chrome 按右鍵 Inspect Element / Inspect
- 在 Chrome 的 Menu 選單 -> View -> Developer -> Developer Tools
1-1: Chrome開發者工具
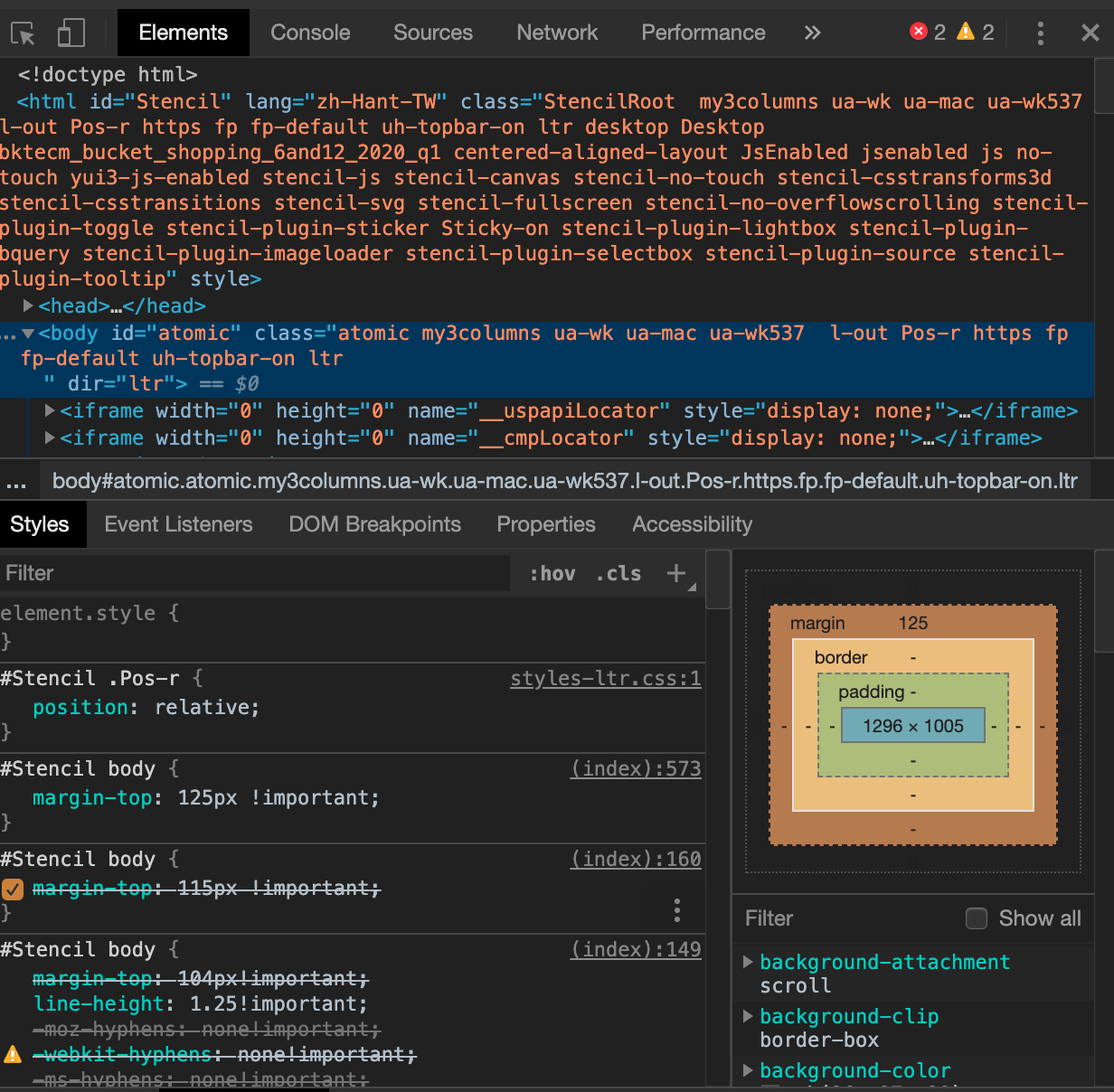
- Elements: 查詢 HTML 網頁原始碼的元素。若手動修改一元素的屬性和樣式,可直觀的看見瀏覽器頁面也相對應改變。
- Console: 顯示開發過程的日誌資訊 ( log ) 與警告。是可與 Js 進行互動的命令列 ( Shell ),Js 除錯時常用。
- Sources: 可見頁面的檔案來處。
-
Network: 自發起頁面請求 ( Request ) 後,分析各個請求資源資訊(包括狀態、資源型別、大小、所用時間等)。可以根據這些資料條件進行網頁效能優化。
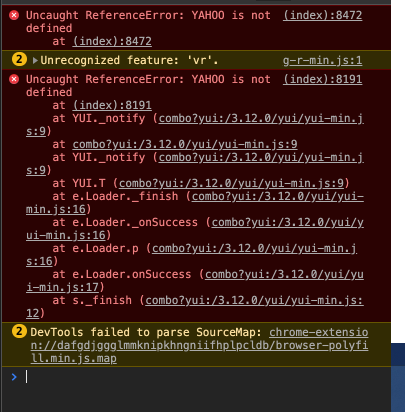
1-2: Console面板
- 能在這邊直接看到 Console.log 的結果
- 與網頁的變數與功能進行互動
- 測試一些 Js Code
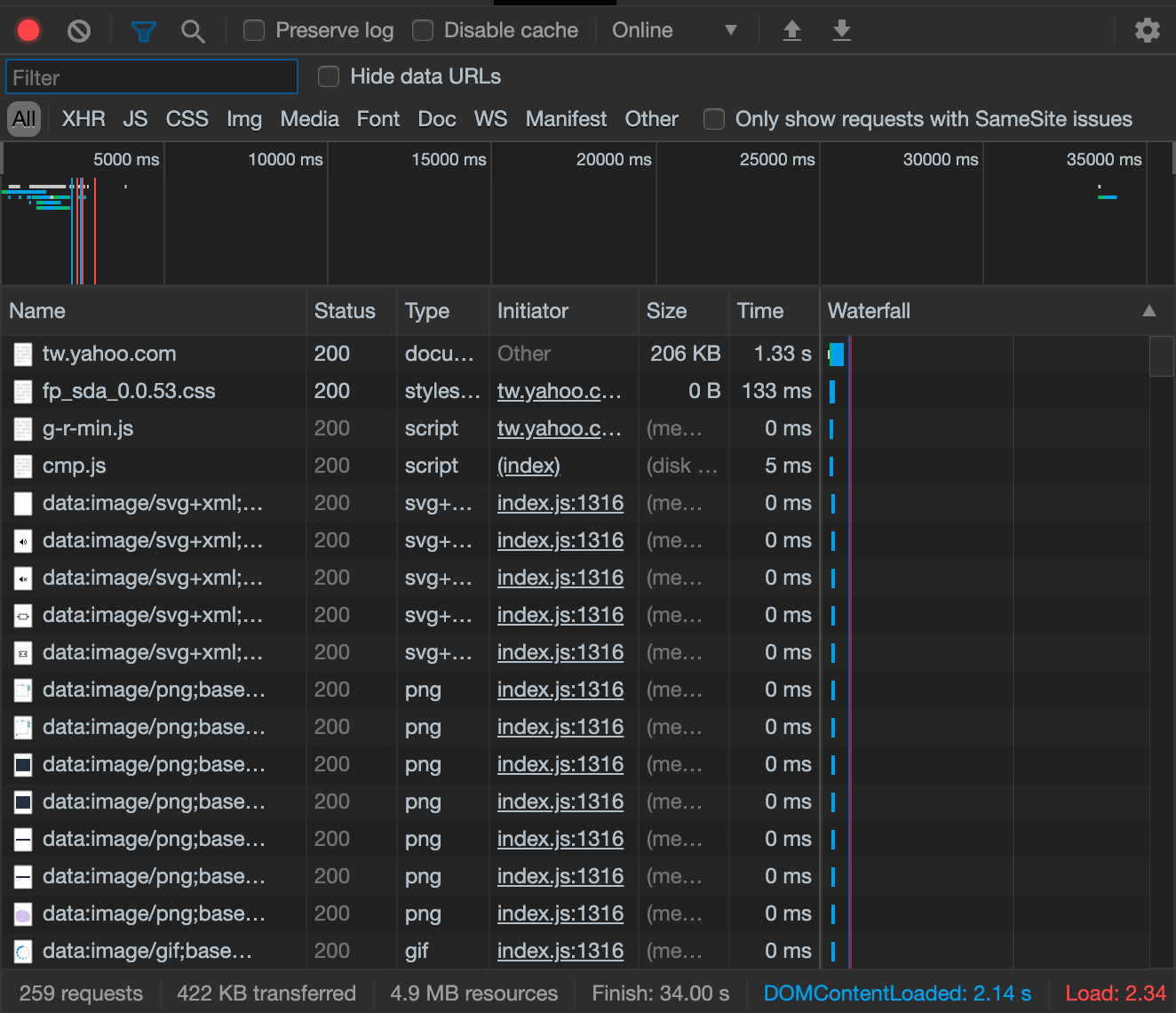
1-3: Network面板
- 使用瀑布流看到檔案載入的結果
- 左上角的紅色鈕可以錄製 request
- Disable cache 可以暫停暫存
- Filter 可以搜索你要的資料關鍵字
- 各型態可以選擇你想關注的檔案類型。
Module 2. 使用 script 標籤
Module 2. 使用 script 標籤
2-1: DOM簡介
2-2: 動態新增頁面標籤內容
2-3: 取得標籤元素
2-1: DOM 簡介

2-1: DOM 簡介
-
document.head
回傳 <head> 元件
-
document.body
回傳 <body> 元件
-
document.scripts
回傳 <scripts> 元件
-
document.title
回傳 <title> 元件
2-2: 動態新增頁面標籤內容
2-3: 取得標籤元素
Coding Style 程式的命名規則
Camel Case 駝峰式 :
-
lower camel case 小駝峰, 首字母小寫
- 例如: firstName, lastName
- 常用在 Javascript 系列語言
- upper camel case 大駝峰, 首字母大寫
- 例如: FirstName, LastName
- 常用在 ReactJs 的元件
Snake Case 蛇式 :
- 字與字之間用下劃線連接
- 例如: first_name, last_name
Module 3. 常數和變數宣告
3-1: var、let 和 const
var: 變數
- ES5
let: 變數
- ES6
const: 常數 -> 不會重新被定義
- ES6
Demo on nb or DevTools
常數表示法
- // console.log(0o23) // 舊的 8 進位用法, 不建議使用 - console.log(0o23) // 8 進位 - console.log(0x23) // 16 進位 - console.log(0b1111) // 2 進位 - console.log(2e5) // 科學表示法
Let's Test on DevTools or Appendix on nb
3-2: 識別字的規則
3-3: var 和 let 的主要差異
1. 域不一樣!
- var的作用域在函數 (function) 裡
- let的作用域則是在區塊 (block) 裡。
2.
- var 會改到原本的 window
- 但,let 不會
- eg. alert() function
Let's test on DevTools
if(true){
//Start of the Block scope
let b = 'Hi I am in the Block';
//End of the Block scope
}
console.log(b);
//ReferenceError
(function(){
var s = 'Hi I am in the Function';
}())
console.log(s)
//ReferenceError Module 4. 基本類型
4-1: Number、Boolean和String
- Boolean // 布林 - Number // 數字 - String // 字串 - null // 空值 - undefined // 空值,也可視為一個型態 - true // 常數,不可作為變數名稱 (Js 開頭為小寫,與 Python 不同) - false // 常數,不可作為變數名稱 (Js 開頭為小寫,與 Python 不同)
4-1: Number、Boolean和String
我們來在 DevTools 測試 - true = 100
- 12 = 33 // 不能使用 因為 12 不是變數
- 0xFF0000 //色碼 RGB 所以這個是紅色
- 2e3
- 2E3 //大小寫皆可
- 2E-3 //後面是負的代表示 10^-3次方 2*0.001
- Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER //Type in DevTools
- Number.MAX_VALUE //Type in DevTools
- Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY //Type in DevTools
4-2: 轉換為Number
Number("123") // 123 Number("12.3") // 12.3 Number("") // 0 Number("0x11") // 17 Number("0b11") // 3 Number("0o11") // 9 Number("foo") // NaN Number("100a") // NaN
parseInt() 函式能將輸入的字串轉成整數。
parseFloat() 函式能將輸入的字串轉成浮點數。
!!n 轉換為 Boolean
4-3: 轉換為String
.toString()可以將所有的的資料都轉換為字串,但是要排除null 和 undefined
toString() 括號中的可以寫一個數字,代表進位制,對應進位制字串
二進位制:.toString(2);
八進位制:.toString(8);
十進位制:.toString(10);
十六進位制:.toString(16);
4-3: 轉換為String
String()可以將null和undefined轉換為字串,但是沒法轉進位制字串
example:
var str = String(null);
console.log(str, typeof str);
var str = String(undefined);
console.log(str, typeof str);Module 5. 運算子
5-1: 算術運算子
| 運算子 | 例子 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|
| + | x + y | x, y 相加 |
| - | x - y | x,y 相減 |
| * | x * y | x, y 相乘 |
| / | x /y | x,y 相除 |
| % | x % y | x,y 取餘數 |
| ** | x **y | x 的 y 次方 |
| & | x &y | x y 做位元 AND 運算 |
| ^ | x ^ y | x y 做位元 XOR 運算 |
| | | x | y | x y 做位元 OR 運算 |
5-2: 關係運算子 relational operators
10 > 5 //true 10 是否大於 5
10 >= 5 //true
10 < 5 //false
10 <= 5 //false
10 == 5 //false 值是否相同
10 != 5 //true
10 === 5 //false 值是否相同, 型態也要相同
10 !== 5 //true 值是否不同, 嚴謹
////陣列
'a' in ['a','b'] //false
0 in ['a','b'] //true
//陣列是看索引位置的
var people = { firstName: 'Andy', lastName: 'Tseng', gender: 'M' };
'firstName' in people; //true5-3: 邏輯運算子
//邏輯 AND -> &&
let fruit = 'Apple' && 'Banana'
//邏輯 OR -> ||
let fruit = 'Apple' || 'Banana'
//邏輯 NOT -> !
let notTrue = !(true && true)Module 6. String
6-1: 字串的標示方式
var str = 'This is string text';
var str = "This is string text";
var str = `This is string text` ;可以使用 單引' 雙引" 與反引號` example:
6-2: 字串的跳脫表示法
這樣會發生錯誤 example:
var str = 'Andy's hat.';
var str = "This is a "cat".";6-2: 字串的跳脫表示法
這樣可以解決 example:
var str = "Andy's hat."; // 雙引內放單引
var str = 'This is a "cat".'; // 單引內放雙引6-2: 字串的跳脫表示法
用跳脫字元 (escape character) 反斜線 (backslash) \
來處理引號
example:
var str = 'Andy \'s hat.';
var str = "This is a \"cat\"."; // 單引內放雙引6-2: 字串的跳脫表示法
跳脫字元 \ 還可以處理以下這些
| 特殊符號 | 表示的符號 |
|---|---|
| \0 | NULL 字元 |
| ' | 單引號 |
| " | 雙引號 |
| \ | 反斜線 |
| \n | 換行符號 |
| \r | return 回車鍵 |
| \t | tab |
| \v | vertical tab |
| \b | backspace |
| \f | form feed |
| \uXXXX | unicode codepoint |
6-3: 字串的常用方法
字串相加
let a = 'hel'+'llo'
//'hello'
let name = 'Andy'
//'Andy'
let greetings = a + ' ' + name
// 'hello Andy'
let greetings += '!'
//'hello Andy!'多行字串
let a = 'hel' +
'llo ' +
'Andy' +
//'hello Andy'
//Or,
let a = 'hel \
llo \
Andy'
//'hello Andy'
6-3: 字串的常用方法
let name = 'Andy'
let greetings = `Hello ${name}, How are you?`
// Length
console.log(greetings.length)
//split
console.log(greetings.split(""))
//(24) ["H", "e", "l", "l", "o", " ", "A", "n", "d", "y", ",", " ", "H", "o", "w", " ", "a", "r", "e", " ", "y", "o", "u", "?"]
console.log(greetings.split(" "))
//(5) ["Hello", "Andy,", "How", "are", "you?"]
console.log(greetings.split(","))
//["Hello Andy", " How are you?"]
var str = "This is an 'ant'";
var index = str.indexOf("an");
console.log(index)
// 8
Module 7. 取得標籤元素
Get script tag
Module 7. 取得標籤元素
7-1: 使用ES3的方法
7-2: querySelector()
7-3: querySelectorAll()
7-1: 使用ES3的方法
- getElementById
- getElementsByTagName
- getElementsByName
- getElementsByClassName
7-1-1 範例
7-2&3: querySelector() & querySelectorAll()
document.querySelector('#my_id') // 抓單一物件 抓 id
document.querySelector('.my_class') // 抓第一物件 抓 class
document.querySelectorAll("p") // 抓所有的 p
document.querySelectorAll("a[target]")// 抓有target屬性的aModule 8. Flow Control
Module 8. Flow Control
8-1: Case selector statement
8-2: Loop
8-3: break & continue
8-1: Case selector statement
if(condition){
//When condition is true
}if: Use "if" statement to run specific block of code when statement is true
if/else: when condition is true run block 1. When false, block 2
8-1: Case selector statement
if( condition1){
//when condition is true to run
}else{
if(condition2{
}else{
if(condition3)
}
}if(condition1){
//When condition is true to run
}else if(condition2){
}
else if(condition3){
}8-1: Case selector statement
8-1: Case selector statement
switch(variable){
case value1:
//When the variable is the same as value1
break
case value2:
//When the variable is the same as value2
break
case value3:
//When the variable is the same as value3
break
default:
// default value
}switch/case
8-1: Case selector statement
switch/case
8-2: Loop
for(initial setup;condition;addition){
//block of code
}
// Example
for(i=0; i<8; i++){
console.log(i)
}for loop
a++
means
a = a+1
which is adding 1 to the existing value
8-2: Loop
8-2: Loop
8-2: Loop
8-2: Loop
8-2: Loop
8-2: Loop
let i = 0
while(condition){
//Block of code
i++
}
// Example
let i = 0
while(i<5){
console.log(i)
i++
}while Loop
8-2: Loop
8-2: Loop
let i = 0
do {
//block of code
i++
}while(condition)
// Example
let i = 0
do {
console.log(i)
i++
}while(i<5)do while loop: Run for a time, then check condition
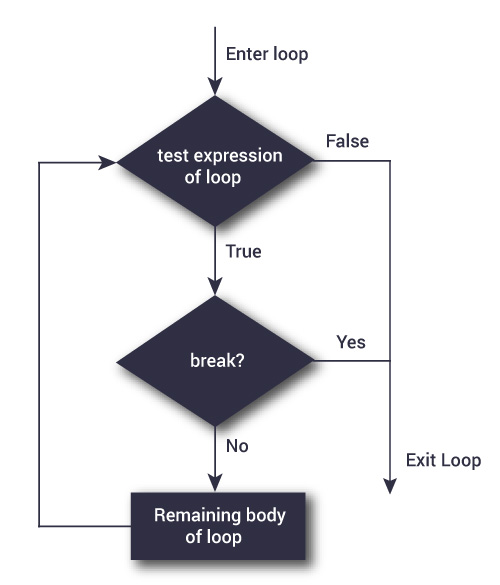
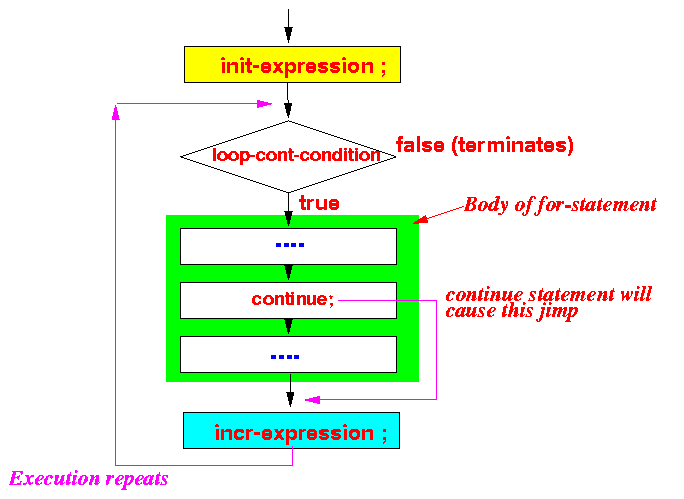
8-3: break & continue
The break statement "jumps out" of a loop.
The continue statement "jumps over" one iteration in the loop.
8-3: break
The break statement "jumps out" of a loop.
8-3: continue
The continue statement "jumps over" one iteration in the loop.
Module 9. Object
Module 9. Object
9-1: What is Object?
9-2: Object Expression
9-3: for/in loop
9-1: What is Object?
var str = {firstName: 'Andy', lastName: 'Tseng'}
var list1 = ['apple', 'banana', 'cat']
str['firstName'] // Andy
str.firstName // Andy
delete str.firstNameObject: Objects are variables too. But objects can contain many values. It uses key and value in {}
Array: a dataset with order
9-2: Object Expression
Object: a key with a value and also called, hash table
key is a non-repeated "String", we also called it Dictionary
value can also be a function
key is without order
let obj = {}
let obj1 = Object()9-3: for/in loop
for/in loop can be use with Object
and also Array
Object to get key
Array to get index
9-3: for/in loop
Module 10. Array
Module 10. Array
10-1: What is Array?
10-2: Array Expressions
10-3: Methods of Array
for/of Syntex
for/of use for iterable object, eg. Array,String
Difference between for in vs for of
Differences:
- for in is ES5 syntax;for of is ES6 syntax。for of fixed for in compatibility
- For object, for in finds all keys;for of finds all values。However, in JavaScript, objectis not iterable, for of would send error message
- for of cannot find through normal object, Mainly for list (iterable type eg. array, arguments ), it would ignore the non-iterable variable
- for of is used for Array、Map、Set、String、TypedArray、arguments
- for in finds properties can be customize, also prototype would be find which is not what we wanted
How to use for of with object
let obj = {
a:'apple',
b:'banana',
c:'cake'
}
for(let key of Object.keys(obj)){
console.log(obj[key]);
}
// 不如直接 for in
for(let id in obj){
console.log(obj[id]);
}10-1&2: Array Type & Expression
var list1 = ['apple', 'banana', 'cat']
for(let i =0; i<list1.length;i++){
console.log(i+':'+ list1[i])
}
list1[2] = "cake"
Array is a combination of data with order. We use [] for expression. The index starts from 0
we use .length to know how long the array is
10-1&2: Array Type & Expression
10-3: Methods of Array
10-3: Methods Array
//Unicode way of sort
const slogan = 'Andy TV Pro Course'
const cutSlogan = slogan.split('')
cutSlogan.sort();
console.log(cutSlogan);
let follower = [ 6, 8, 10, 23, 8]
follower.sort()
console.log(follower);10-3: Methods of Array
// From small to large number
let follower = [ 6, 8, 10, 23, 8]
follower.sort(function(a,b){
return a-b
})
console.log(follower);10-3: Methods of Array
//Splice method
//.splice(index, number of delete items, Add items);
const months = ['Jan', 'March', 'April', 'June'];
months.splice(1, 0, 'Feb');
// inserts at index 1
console.log(months);
// expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "June"]
months.splice(4, 1, 'May');
// replaces 1 element at index 4
console.log(months);
// expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "May"]
10-3: Methods of Array
// forEach method
let man = [
{ name: 'Steve', age: 25, id: 'A006' },
{ name: 'Dave', age: 27, id: 'A009' },
{ name: 'Andy', age: 3, id: 'A088' },
];
man.forEach(function(val, index){
console.log( index +': ' + val.name )
})10-3: Methods of Array
// filter method
let words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant',
'destruction', 'present'];
let result = words.filter(function(word){return word.length > 6})
//let result = words.filter(word => word.length > 6);
console.log(result);
// expected output: Array ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
10-3: Methods of Array
// map method
let array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
// pass a function to map
let map1 = array1.map(function(x){ return x * 2});
console.log(map1);
// expected output: Array [2, 8, 18, 32]
10-3: How to use forEach to replace map method?
// map method
let array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
// pass a function to map
let map1 = array1.map(function(x){ return x * 2});
console.log(map1);
// expected output: Array [2, 8, 18, 32]
let array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
let map1 = []
array1.forEach(function(x){
map1.push(x*2)
})
console.log(map1);Module 11. JSON
Module 11. JSON
11-1: JSON string rules
11-2: Replication of Object and Array
11-3: Edit JSON Files
11-1: JSON Syntax
What is JSON? (JavaScript Object Notation)
JSON is a text based data structure for storing and transmitting data. You can store various types of data, e.g, array, number, string and object. Also, complex syntax like object and array are allowed 。Once JSON is set, it's pretty easy to communicate and exchange data between applications since JSON is stored as plain text.
Advantage for using JSON:
- High compatibility
- Syntax structure is easy to read and edit
- Support various data format ( number, string, booleans, nulls, array, associative array)
- Many libraries support read and write for JSON data
11-1: JSON Syntax Rules
{
"orderID": 54101,
"shopperName": "John Doe",
"shopperEmail": "johndoe@example.com",
"contents": [
{
"productID": 46,
"productName": "Helmet",
"quantity": 1
},
{
"productID": 98,
"productName": "Gas",
"quantity": 3
}
],
"orderCompleted": true
}
11-1: JSON vs XML
<object>
<property>
<key>orderID</key>
<number>54101</number>
</property>
<property>
<key>shopperName</key>
<string>John Doe</string>
</property>
<property>
<key>shopperEmail</key>
<string>johndoe@example.com</string>
</property>
<property>
<key>contents</key>
<array>
<object>
<property>
<key>productID</key>
<number>46</number>
</property>
<property>
<key>productName</key>
<string>Helmet</string>
</property>
<property>
<key>quantity</key>
<number>1</number>
</property>
</object>
<object>
<property>
<key>productID</key>
<number>88</number>
</property>
<property>
<key>productName</key>
<string>iPad</string>
</property>
<property>
<key>quantity</key>
<number>3</number>
</property>
</object>
</array>
</property>
<property>
<key>orderCompleted</key>
<boolean>true</boolean>
</property>
</object>
XML data size is larger than JSON
11-1: JSON String Expression
var jsonString = ' \
{ \
"orderID": 54101, \
"shopperName": "John Doe", \
"shopperEmail": "johndoe@example.com", \
"contents": [ \
{ \
"productID": 64, \
"productName": "Helmet", \
"quantity": 1 \
}, \
{ \
"productID": 88, \
"productName": "iPad", \
"quantity": 3 \
} \
], \
"orderCompleted": true \
} \
';
11-1: JSON String Expression
// JSON String to js Object
let cart = JSON.parse ( jsonString );
console.log( cart.shopperEmail );
console.log( cart.contents[1].productName );
// Turning JS Object to JSON String
let jsonStr = JSON.stringify(cart)
console.log(jsonStr) 11-2: Copy Object, Array in JS
let arrayA = [28, 77, 'abc', ['John', 63, 'male'] ];
let arrayB = arrayA;
let arrayC = arrayA.slice(); // Single layer
arrayA[3][0] = 'Mary';
arrayA[0] = 87;
console.log('arrayA:', arrayA);
console.log('arrayB:', arrayB);
console.log('arrayC:', arrayC);Shallow copy,slice for deep copy
11-2: Copy Object, Array in JS
let arrayA = [28, 77, 'abc', ['John', 63, 'male'] ];
let arrayB = arrayA;
let arrayJSON = JSON.stringify(arrayA)
let arrayC = JSON.parse(arrayJSON)
arrayA[3][0] = 'Mary';
arrayA[0] = 87;
console.log('arrayA:', arrayA);
console.log('arrayB:', arrayB);
console.log('arrayC:', arrayC);11-3: Edit JSON File
Let's try jsoneditoronline.org
Module 12. Definition of Function
Module 12. Definition of Function
12-1: Basic Function
12-2: Anonymous Function
12-3: Arrow Function
12-1: Basic Function
function functionName(params) {
// code in block
return returnValue
}
// Example
function myFunc() {
console.log('hi')
}
myFunc() // call myFunc functionDefinition
12-1: Basic Function
// Use parameters
function myFunc(a, b) {
console.log('a:' + a)
console.log('b:' + b)
console.log('arguments:' + arguments)
console.log(JSON.stringify(arguments))
}
myFunc(5, 8, 7);
// ES6
function myFunc2(a, ...b) {
console.log('a:' + a)
console.log('b:' + b);
}
myFunc2(5, 8, 7);12-1: Basic Function
//The old way
function multiplyJS(a, b) {
b = (typeof b !== 'undefined') ? b : 1;
return a * b;
}
multiplyJS(3, 3); // 9
multiplyJS(4, 6); // 24
multiplyJS(7); // 7
12-1: Basic Function
//ES6
function multiplyES6(a, b = 1) {
return a * b;
}
multiplyES6(3, 3); // 9
multiplyES6(4, 6); // 24
multiplyES6(7); // 712-2: Anonymous Function
var square = function(num) {
return num**2;
};
square(2) //4
square(3) //9
Use function directly without naming it
12-3: Arrow Function (ES6)
let square = (num) => {
return num**2;
}
let square = num => num**2
Module 13. Scope
( Variable Space )
Module 13. Scope
13-1: Global Scope
13-2: Local Scope
13-3: closure
13-1&2: Global and local scope
Definition:
- Global scope is the top level space for variable
- In JS, using "var" to define will become global scope ( window ),let will not
- Local variable can only be viewed inside function. Outside the function, the local variable cannot be access which is secure.
- Parameters ( Augments ) are local variable
- If the variable is not found in the scope , then, it find from the outside
13-1&2: Global Variable and Local Variable
var a='apple'; //Global Variable
function banana(){
var b='banana'; //Local Variable
console.log('aInFunc:'+a)
console.log('bInFunc:'+b)
}
banana()
console.log('aNotInFunc:'+a)
console.log('aNotInFunc:'+b)13-3: closure
Closure allows the inside function run from outside
13-3-1: closure
Take a look!Run function from inside out
Module 14. Time and counter
Module 14. Time and Counter
14-1: Date object
14-2: setTimeout method
14-3: setInterval method
14-1: Date Obect
today = new Date() //No parameter -> Today
Xmas95 = new Date("December 25, 1995 13:30:00") //default as zero
Xmas95 = new Date(1995,11,25,9,30,0) //Multiple parameter
//"set" method: Setting the time value and Date
//"get" method: Getting the time value and Date14-1: Date Object
As we know learn how to use Date object.
Is there a way to program it?
Let's..GO!
14-1-1: Build a function for Date
function JSClock() {
//Save current time
let time = new Date()
//Get the hour from the time
let hour = time.getHours()
//Get the minute from the time
let minute = time.getMinutes()
//Get the second from the time
let second = time.getSeconds()
//Turn 0-24 to 0-12 am/pm
var temp = "" + ((hour > 12) ? hour - 12 : hour)
//if it's 0 then it's 12 o'clock
if (hour == 0)
temp = "12";
//If smaller than zero, you need to add zero to the minute
temp += ((minute < 10) ? ":0" : ":") + minute
//If smaller than zero, you need to add zero to the second
temp += ((second < 10) ? ":0" : ":") + second
//To recognize P.M and A.M
temp += (hour >= 12) ? " P.M." : " A.M."
return temp
}Hold on a second
Can we run the code each second?
Yes we can!
Let's take a look!
14-1-1: Build a function to handle Date
14-2: setTimeout
// Syntax
setTimeout(function ,
milliseconds ,
param1 ,
param2 ,
...);
// Example
setTimeout(function(){
alert("Hello");
}, 3000);Let's take a look!
14-2-1: setTimeout for
setTimeout(function(){ console.log("2 seconds") }, 2000);
setTimeout(function(){ console.log("4 seconds") }, 4000);
setTimeout(function(){ console.log("6 seconds") }, 6000);Multiple times?
14-3: setInterval
// Syntax
setInterval(function,
milliseconds,
param1,
param2,
...);
// Example
let a = setInterval(function(){
console.log("Hello");
}, 3000);
//Clear Interval
setTimeout(function(){
clearInterval(a)
},20000)
Module 15. Math Object
Module 15. Math Object
15-1: Random Numbers
15-2: Trigonometric function
15-3: Circular placement
15-1: Random Number
// 1. This function multiply the 0~0.999999 random value to 0~9.999999
// 2. Then, it floor it to 0-9 integer
// 3. Plus 1 to generate random integer from 1-10
Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 1;
// Math.floor Round down to integer
Math.random() Definition: Generates random number r, 0 ≤ r < 1
Math.floor()
Definition: Run down function, e.g., 5.8 -> 5
Example
15-1-1: Random Number in Specific Range
function getRndInteger(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() *
(max - min) ) + min;
}
// Includes min Not max
.
function getRndInteger(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() *
(max - min + 1) ) + min;
}
// Includes min and max
15-1-2: Placing Random Dots
.
15-2: Trigonometric function
// Use rad for angle.If you use 360 degrees, you need transformation.
// Math.PI * a degree / 180
Math.sin(3); // 0.1411200080598672
Math.sin(-3); // -0.1411200080598672
Math.sin(0); // 0
Math.sin(Math.PI); // 1.2246467991473532e-16
Math.sin(Math.PI / 2); // 1
// cos, tan also.
15-3: Placing objects in round shape
.
Module 16. window object
Module 16. window object
16-1: Methods for window object
16-2: window properties
16-3: document properties
16-1: window Methods
alert() // Alert window
blur() // blur out the window
clearInterval() // Clear the interval function
clearTimeout() // Clear the timeout function.
//Common forgotten
close() // Close window
confirm() // Confirm window
focus() // focus to the window
print() // Print the page for the printer
prompt() // Pop Prompt window
setInterval() // Trigger the function with interval
setTimeout() // Trigger the function after timeout.
16-2: window properties
- navigator : Browser version information
- screen : Display information
- history : history for the current tab
- location : url information
- document : DOM Object
.
16-3: document common properties
//Variable //Type // Information
URL // String // Webpage Address
anchors // HTMLCollection // Web Anchor
characterSet // String // Unicode Character Charset
cookie // String // Cookies
doctype // DocumentType // Doctype
domain // String // Readable Name Dor IP Address
forms // HTMLCollection // Collection for forms
head // HTMLHeadElement // Head Object
images // HTMLCollection // Collection for images
links // HTMLCollection // Connections To Other Page
referrer // String // Where it came from
title // String // Title For The WebpageDocument Common Example at 7-1-1
.
Module 17. Event Handle
Module 17. Even Handling
17-1: Event Handler
17-2: addEventListener
17-3: onclick vs. addEventListener
17-1: Event Handler
onclick // Trigger when single click
ondbclick // Trigger when double click
onmousedown // Trigger when mouse down
onmouseup // Trigger when mouse up
onmousemove // Trigger when mouse moves on top of the element
onmouseover // Trigger when mouse moves into the element
onmouseout // Trigger when mouse moves out of the element
onkeydown // Trigger when keypress down
onkeyup // Trigger when keypress up
onkeypress // Trigger when keypress (can be coninue)
17-1: Event Handler
onload // Trigger when element loads
onresize // Trigger when element resizes
onscroll // Trigger when element scrolls
onblur // Trigger when element move out of focus
onchange // Trigger when element value changes
// for input, select, textarea
onfocus // Trigger when element focus
onreset // Trigger when form reset
onselect // Trigger when element gets selected
// for input, textarea
onsubmit // Trigger when form is submitted
.
17-2: addEventListener
Syntax:
- Element.addEventListener(event, function)
.
17-3: onclick vs. addEventListener
.
Module 18. AJAX
Module 18. AJAX
18-1: 什麼是 AJAX
18-2: XMLHttpRequest
18-3: fetch()方法
18-1: 不刷新頁面更新內容
.
18-2: XMLHttpRequest
說明:
- 要拿資料必須送出一個 HTTP 請求(Request)
- XMLHttpRequest 將會回應一個 Response
.
18-3: fetch()方法
fetch API 讓 http 的處理更加簡單! 發送跟接收資料都可以!
.
Intro to JavaScript
By txshon Tseng
Intro to JavaScript
Hours: 18hr Instructor: Andy Tseng
- 667



