Redux
wait.
Let's look into Flux, first.
Flux
Architecture, not a framework*
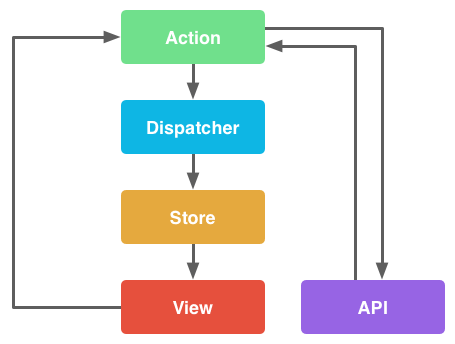
Flux
- Created by Facebook
- Uni-directional data flow
- Half-duplex communication system. Meaning, data flow cannot loop back around.
- Flux applications have three major parts: the dispatcher, the stores, and the views
- Immutable.js backed actions and stores
- Keep the single source of truth in stores
- Views mostly stateless, synchronous
then, what's Redux?
Redux
- Implementation of Flux
- State manager
- There's only one store that holds entire state of app without any logic
- Creates a single source of truth
- Creates a single source of change

Reducer
(redux)
again, wait.
why?
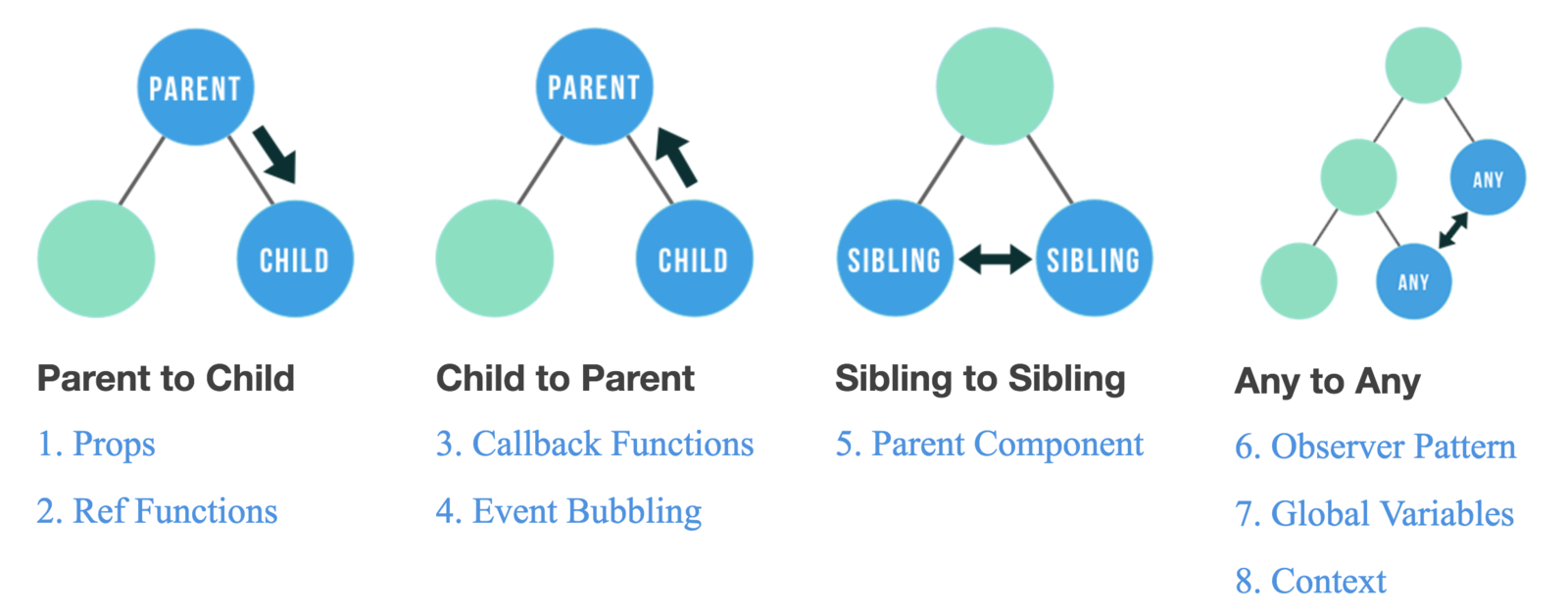
React without Redux
-
Concepts State, Props and Lifecycle Methods
-
Component Communication via parent component and Props
- App State is simple and matches the Component structure
Component Communication
without redux
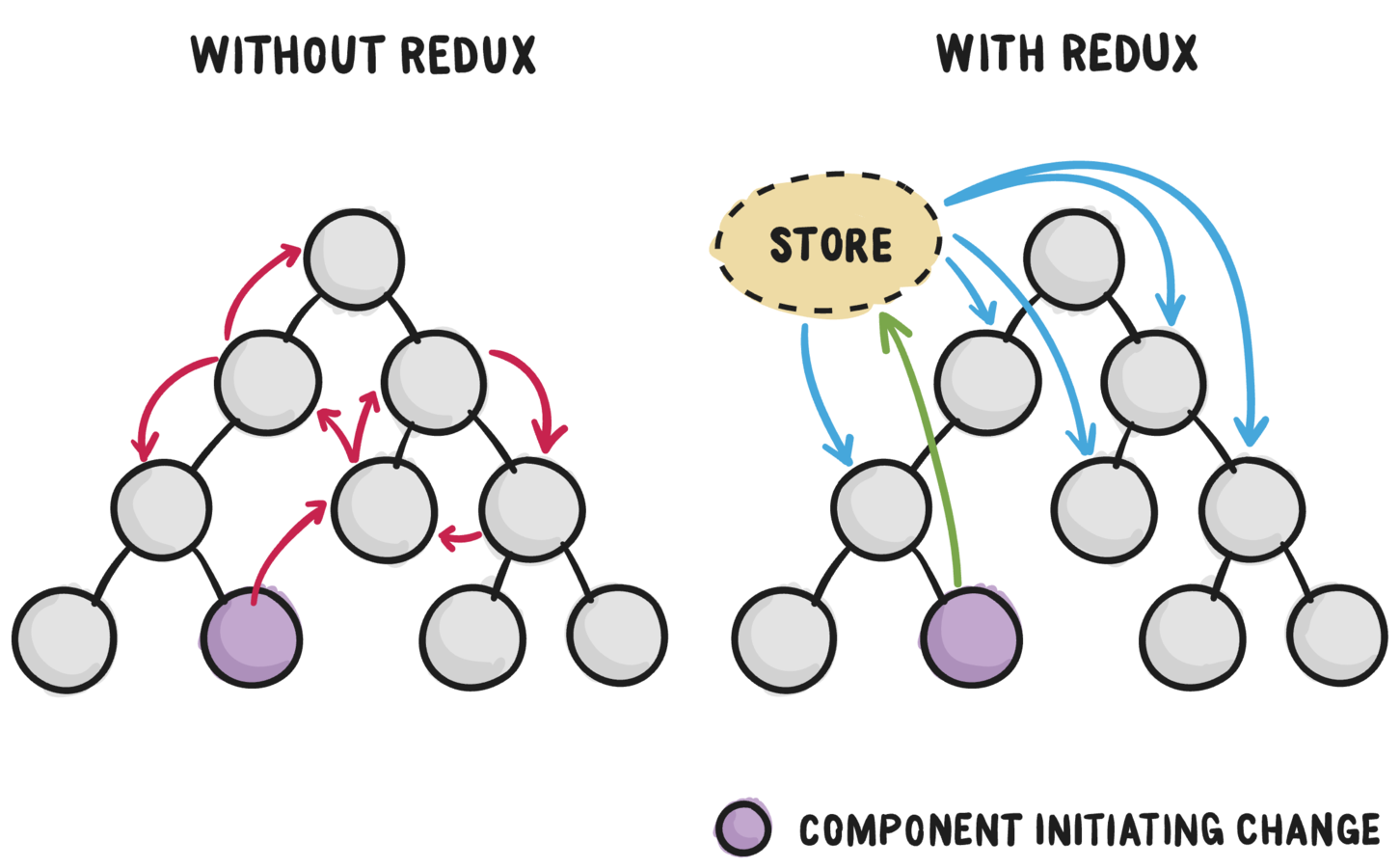
App State Management
without redux
- A lot of the time your app's state tree could be considerably different than the UI tree
-
Leaf components need to access state that their parents don't need
- Many components may need to access the same state and display it in different ways
React vs Redux
Redux Basics
Redux concepts
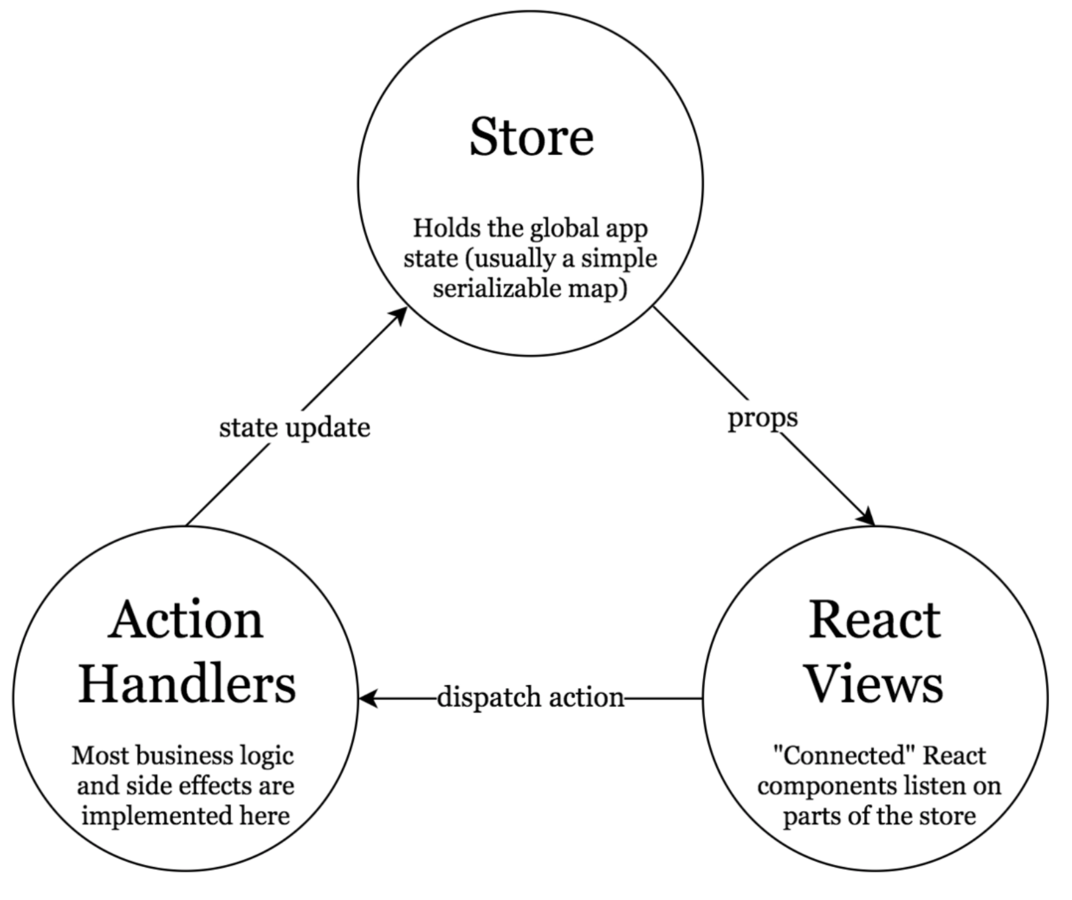
- Store
- Reducers
- Actions
Store
Single source of truth
The state of your whole application is stored in a single object.
import { createStore } from 'redux';
const store = createStore(/* reducers */)
// Allows access to state via:
store.getState()
// Allows state to be updated via:
store.dispatch(action);
// Registers listeners via
store.subscribe(listener);Actions
States are read-only
The only way to change the state in the store is to emit an action, an object describing what happened.
store.dispatch({
type: 'DO_SOMETHING',
value: 'with this',
});
// or
const doSomething = (value) => ({
type: 'DO_SOMETHING',
value,
});
store.dispatch(doSomething('with this'));Reducer
State changer
Actions describe the fact that something happened, but don't specify how the application's state changes in response.
const reducer = (state = {/* set initial state here */}, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
// tell the reducer, how to handle particular actions based on their type
case 'DO_THIS':
// create new state here
// do not mutate previous state
return Object.assign({}, state, {doingThis: true});
default:
// return current state if you don't want to do anything for any action
return state;
}
}Redux
By Umayr Shahid
Redux
- 829



