Content-based recommendation systems try to recommend items similar to those a given user has liked in the past.
Indeed, the basic process performed by a content-based recommender consists in matching up the attributes of a user profile in which preferences and interests are stored, with the attributes of a content object (item), in order to recommend to the user new interesting items.

Advantages
- User Independence
- Transparency
- Can recommend new item
Disadvantages
- Limited Content analysis
- Over Specialization
- Can not recommend to new user
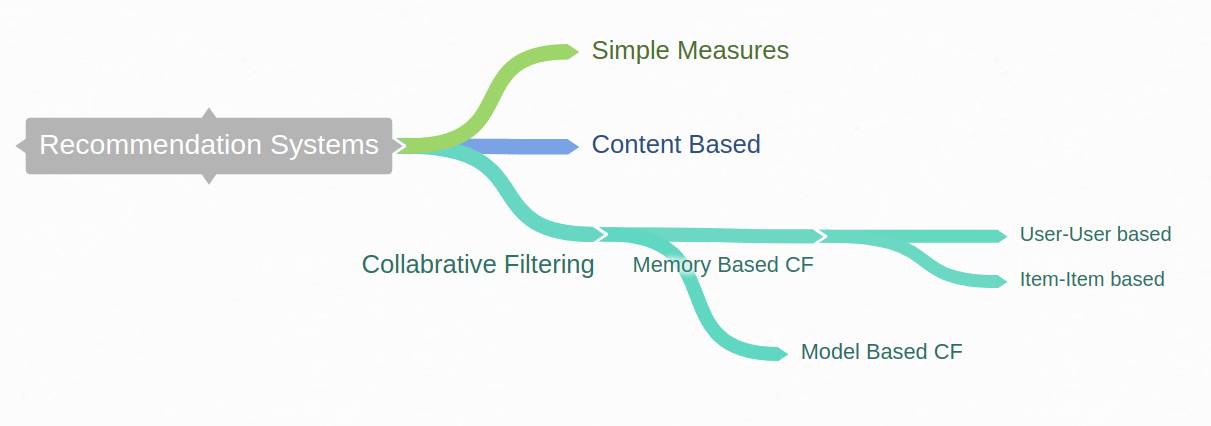
Collaborative Filtering recommendation systems collaborative filtering approaches rely on the ratings of target user as well as those of other users in the system.
Two main Categories:
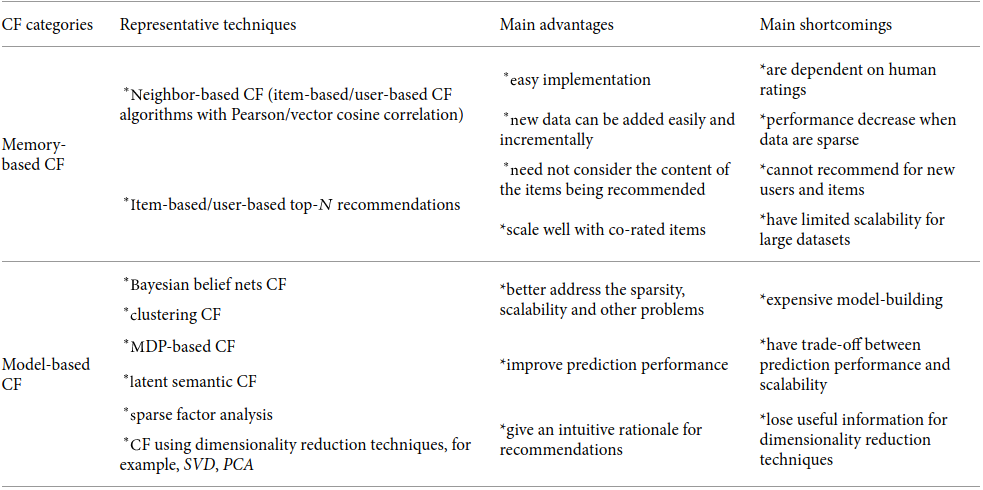
1. Memory Based
2. Model Based
User-based approach, evaluate the interest of a user u for an item i using the ratings for this item by other users, that have similar rating patterns.

Item-based approaches, on the other hand, predict the rating of a user u for an item i based on the ratings of u for items similar to i. In such approaches, two items are similar if several users of the system have rated these items in a similar fashion.
comparisons can be made on Accuracy, Efficiency, Stability, Justifiability, Serendipity.
In contrast to above item/user neighborhood-based systems, which use the stored ratings directly in the prediction, model-based approaches use these ratings to learn a predictive model.
The general idea is to model the user-item interactions with factors representing latent characteristics of the users and items in the system, like the preference class of users and the category class of items. This model is then trained using the available data, and later used to predict ratings of users for new items
Recommendation Systems
By Ashesh Kumar
Recommendation Systems
- 763



