Node Core #1
Basic cocepts
Plan
- What is node
- When to use node
- Difference between node and other platforms (Java, .net, etc)
- Github code overview
What is ?

Nodejs is a server-side, JavaScript-based runtime environment

open-source high-performance JavaScript and WebAssembly engine, written in C++. It is used in Chrome and in Node.js, among others. It implements ECMAScript and WebAssembly

-
Heap Memory allocation
-
Call stack execution context
-
Orinoco Garbage Collector
-
TurboFan Optimization controller - takes this bytecode and generates machine code from it. (JIT)
-
Ignition JS Interpreter - generates bytecode from this syntax tree using the internal V8 bytecode format.
-
Liftoff WebAssembly
-
Full-featured event loop backed by epoll, kqueue, IOCP, event ports.
-
Asynchronous TCP and UDP sockets
-
Asynchronous DNS resolution
-
Asynchronous file and file system operations
-
File system events
-
ANSI escape code controlled TTY
-
IPC with socket sharing, using Unix domain sockets or named pipes (Windows)
-
Child processes
-
Thread pool
-
Signal handling
-
High resolution clock
-
Threading and synchronization primitives
66.8% of developers rated Nodejs as the most loved tool in Stackoverflow Developer Survey Report 2020
85% of Nodejs developers use it for web app development, and the other 43% use it for enterprise-grade applications
51.4% of developers regarded Nodejs as the most-used tool earlier in the 2020

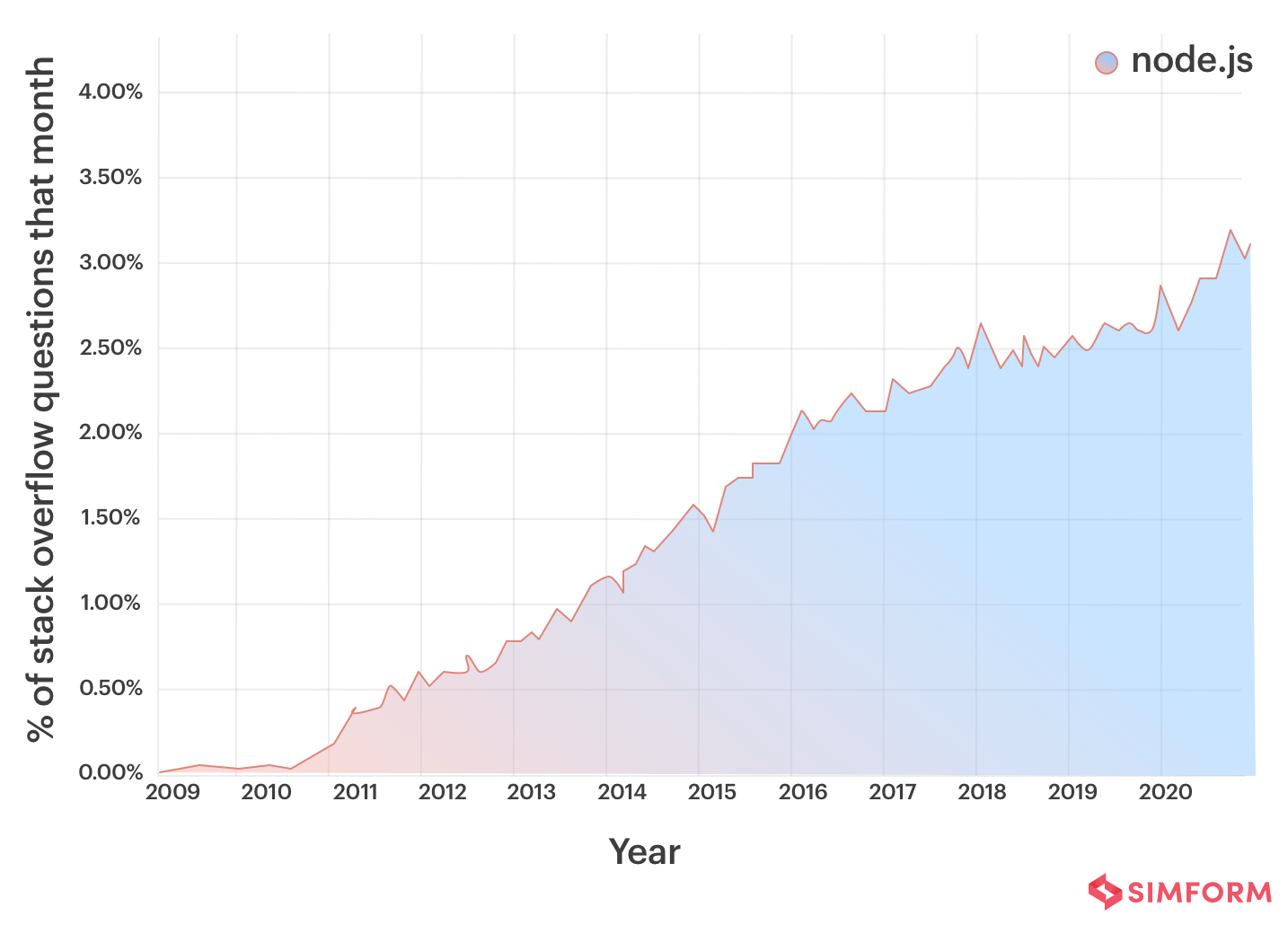
StackOverflow Trends
How does it work?
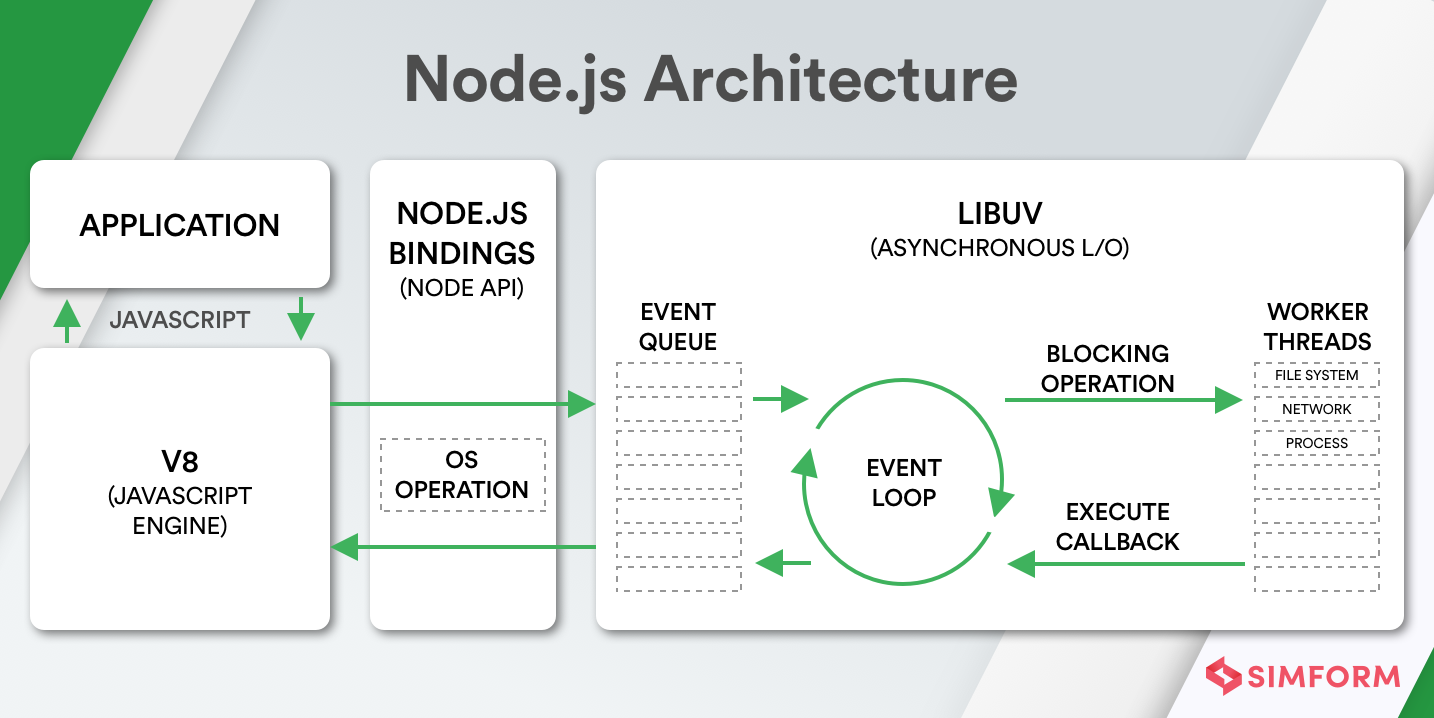
JavaScript is “single-threaded” because JavaScript works on “Event Loop”
NodeJS is NOT “single-threaded” as it has a libuv threadpool in its runtime.
The chefs are the libuv threadpool and OS Async Helpers.
The waiter is the V8 engine and the Event Loop

The JavaScript code you want to be executed is the food
Node.js restorant
Comparison with other platforms
w3techs.com statistic

The following server-side programming languages are used by less than 0.1% of the websites
w3techs.com statistic
The following server-side programming languages are used by less than 0.1% of the websites:
Miva Script
Lasso
C
Lisp
C++
Smalltalk
Tcl
Haskell
Go
Ada



Strong static typing
Dynamic typing / weak static
Event-loop / single threaded
Threads
Mandatory exception handling
Optional exception handling
OOP / Patterns
Proto / FP / Reactive/ NonBlocking
weak static
event loop
tread pool (go routines)
Mandatory exception handling
Dynamic typing / weak static
event loop
sync execution (threads) / reactive libs
Optional exception handling
Used by 79.1% of all websites (w3techs)

Strong static typing
Dynamically typed
Event-loop / single threaded
Threads
Mandatory exception handling
Optional exception handling
OOP / Patterns
OOP / FP / NonBlocking


Advantages of using Node.js
Ability to use the same language on the client and server-side
Speed of work
The lightness of the system allows us to create lightweight applications
The opportunity to use JavaScript syntax
A Node package manager that you can use to install and search for packages
Constant technology development (e.g., TypeScript is being developed now)
Single thread Event loop to process requests
Disadvantages of Node.js
Poor of processing large data volumes
Low CPU-handling capacities
Node.js vs JS problem
- Inconsistent models
- Lack of semantic standardization
- Frequent changes
Messy syntax
When to use Node
Questions to answer
What kind of project are we dealing with?
What kind of product we expect to deliver?
What is the project's reach?
What resources do we currently have?
What is the situation on the market?
What are our main performance criteria?
The main areas, where Node.js is more suitable:
Backend for Front-end
Enterprise web-applications
SSR (Server side rendering)
Message Servers and Event Broadcasting (Chats, Games, Interactive)
Build tools (webpack, babel and etc)
Desktop web-application (Electon: VS Code, Slack)
Microcontrollers
What is Node.js used for?
The environment can support intense traffic of multiple short messages or chatrooms in real-time messaging
Real-time application
Ability to process real-time flows - benefited from its event-driven, non-blocking model
Collaborative tools
The term “streaming” means exactly that – sending large amounts of data in smaller packages instead of a single batch. Node.js is perfectly suited for this task with built-in modules supporting data streaming and allowing to creation of both readable and writable data streams.
Data streaming applications


The superb scalability supported by Node.js answers the “why Node.js” question for apps required to withstand high peak loads.
Applications relying on scalability


LTS vs Current
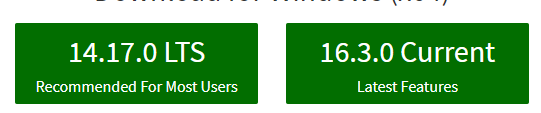
LTS: Releases that receive Long-term Support, with a focus on stability and security.
Current: Under active development. Code for the Current release is in the branch for its major version number
16 vs 14
V8 upgraded to V8 9.0
performance tweaks and improvements
ECMAScript RegExp Match Indices
const matchObj = /(Java)(Script)/d.exec('JavaScript');
undefined
> matchObj.indices
[ [ 0, 10 ], [ 0, 4 ], [ 4, 10 ], groups: undefined ]Stable Timers Promises API
The Timers Promises API provides an alternative set of timer functions that return Promise objects, removing the need to use util.promisify().
import { setTimeout } from 'timers/promises';
async function run() {
await setTimeout(5000);
console.log('Hello, World!');
}Other changes
- Stable AbortController implementation based on the AbortController Web API
- npm 7 (v7.10.0 in Node.js v16.0.0)
- Experimental implementation of the standard Web Crypto API
- Web platform atob (buffer.atob(data)) and btoa (buffer.btoa(data)) implementations for compatibility with legacy web platform APIs
Github source overview
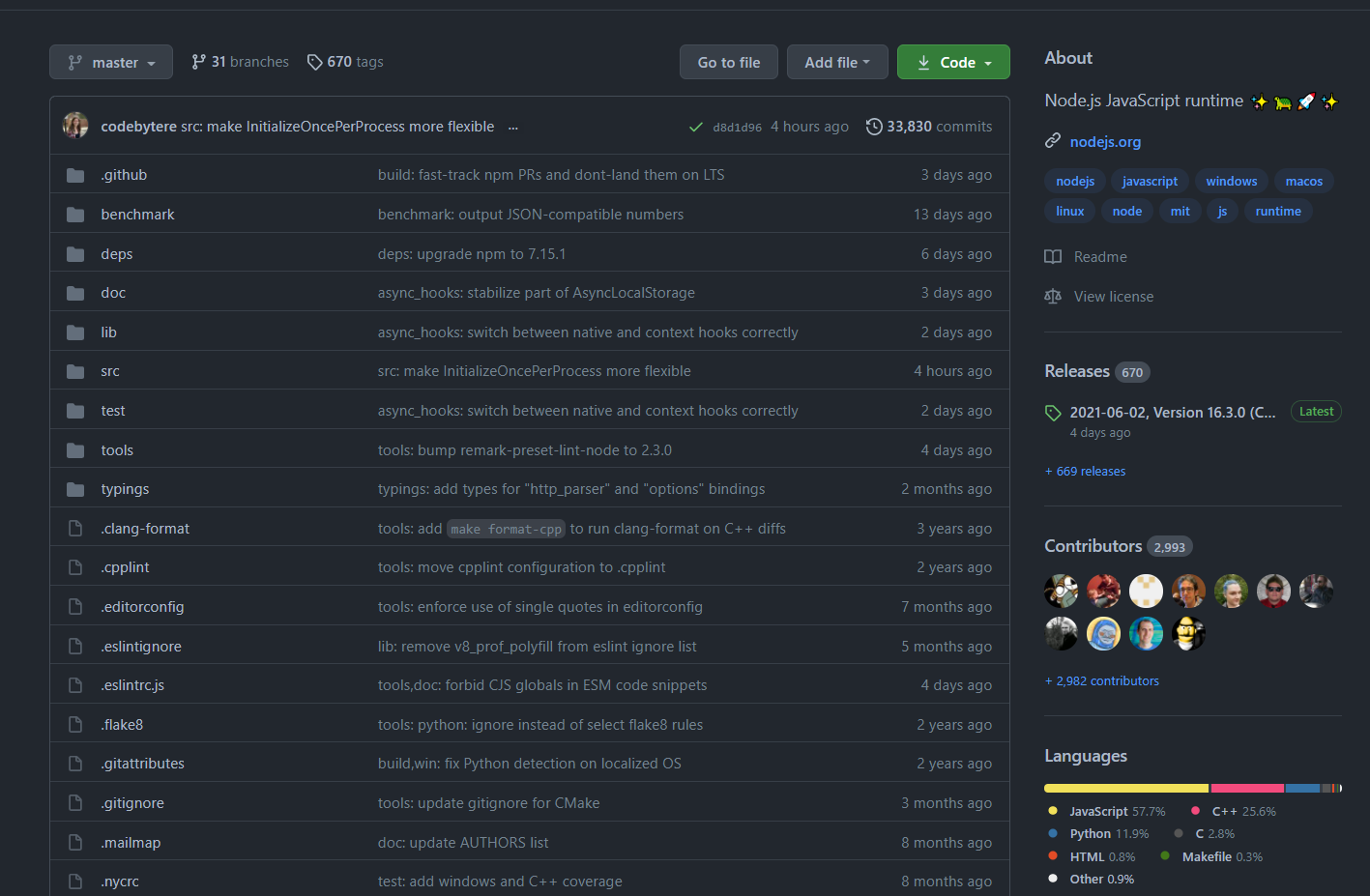
src - contains C++ code
lib - contains JS code
Quiz time!


Thank you!
Node Core #1
By Vladimir Vyshko
Node Core #1
- 882



