Maxim Salnikov
@webmaxru
For Production
In 1-2-3

Part3
Maxim Salnikov
@webmaxru
For Production
In 1-2-3

Part 1
Permanent link:
If you want to code during the session
We need a laptop/desktop with installed (latest stable versions):
- Git
- Node
- NPM
Browsers (latest stable versions):
- Chrome / Firefox / Edge
Quick start
npm install serve -g
git clone https://github.com/webmaxru/pwa-for-production
cd pwa-for-production
git checkout part-1-init
npm install
serve
Recommended to copy code snippets from
Optional
Maxim Salnikov

-
PWA Slack organizer
-
PWA Oslo / PWA Oslo meetups organizer
-
PWA speaker and trainer
Full-Stack Developer, PWAdvocate



Agenda
-
What is a PWA and what advantages does it provide?
-
Browser APIs and specifications we use in PWA and compatibility chart
-
Requirements for our Minimum Viable Product PWA
-
Application shell architecture
-
Service Worker and browser storage foundations
-
Implementing a naive version of the application shell
-
How to test Service Workers
-
Making our app installable
What is PWA at all?
Progressive web apps use modern web APIs along with traditional progressive enhancement strategy to create cross-platform web applications.
These apps work everywhere and provide several features that give them the same user experience advantages as native apps.

UX advantages?
Smart networking + Offline
Proper app experience
Staying notified
Other cool things
}
Service Worker API
Web App Manifest
Predictable caching
Postpone networking while offline
Receiving and showing notifications
Service Worker API
Is there anything REALLY new?
Adding payment methods JIT
Full-scale offline mode
Networking optimizations
install, activate, fetch, backgroundfetchsuccess, backgroundfetchfail, backgroundfetchclick
sync
push, notificationclick
paymentrequest
Cross-platform?
Browser
Desktop
Mobile








Flagged


OS






works everywhere*
* but not everything**

natively
** use progressive enhancement strategy







Platforms / browsers support
Support: detailed

Web API Confluence
APIs actively used in PWAs
-
Service Worker API
-
Cache API
-
IndexedDB
-
Fetch
-
Clients API
-
Broadcast Channel API
-
Push API
-
Notifications API
-
Local Storage
-
Session Storage
-
XMLHttpRequest
-
DOM
Not available in service worker:
Even more capable web
-
Writable Files API
-
WebHID API
-
Scheduled Task / Notification API
-
Web Share Target API
-
Wake Lock API
-
Cookie Store API
-
User Idle Detection API
-
...

Project Fugu
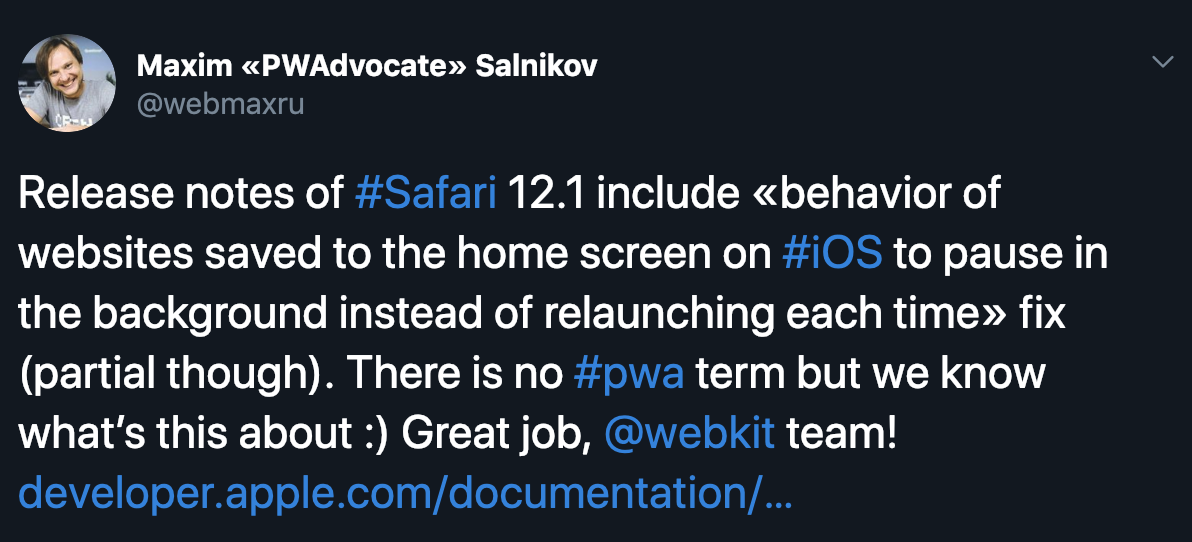
#WSH?
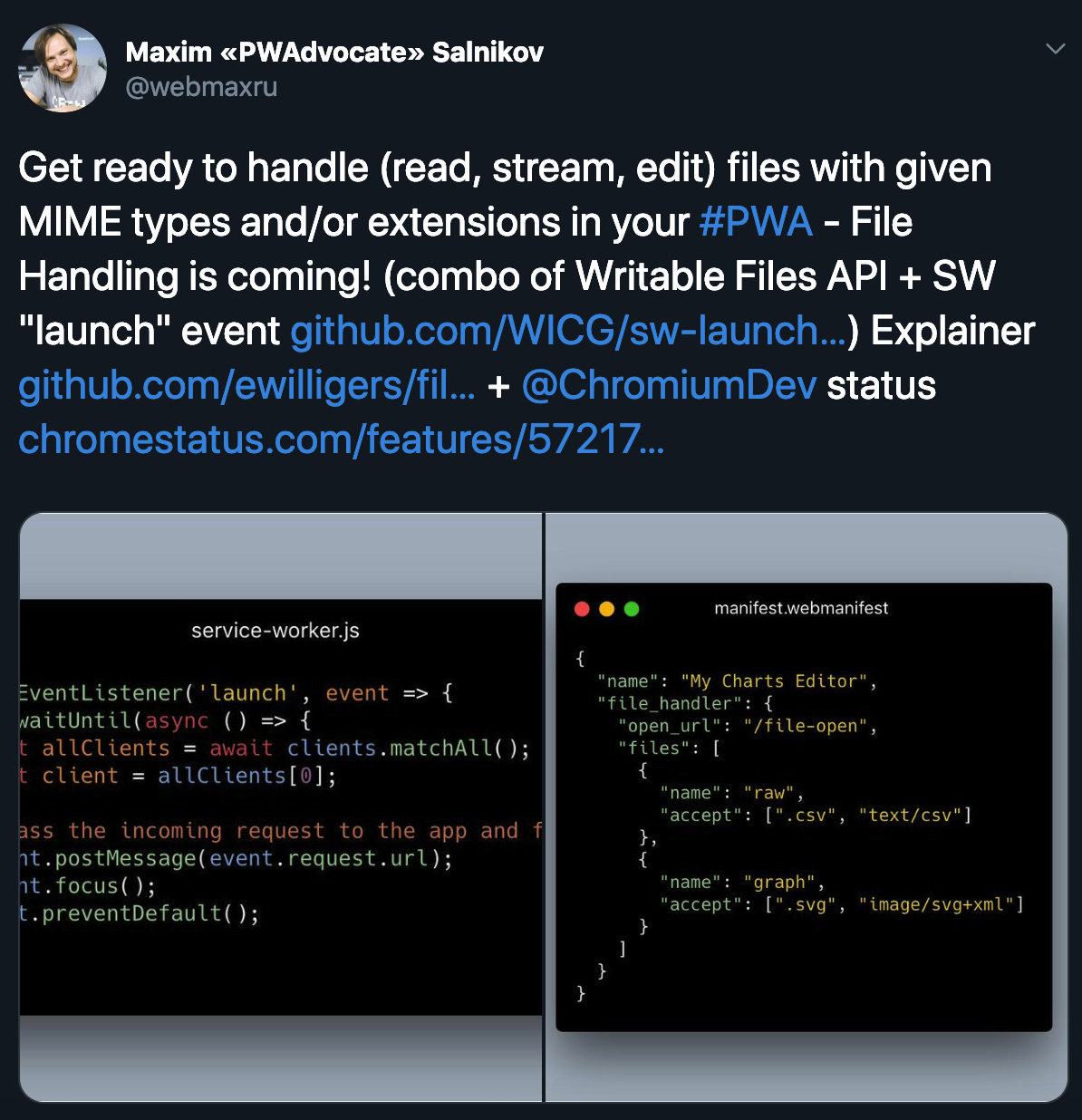
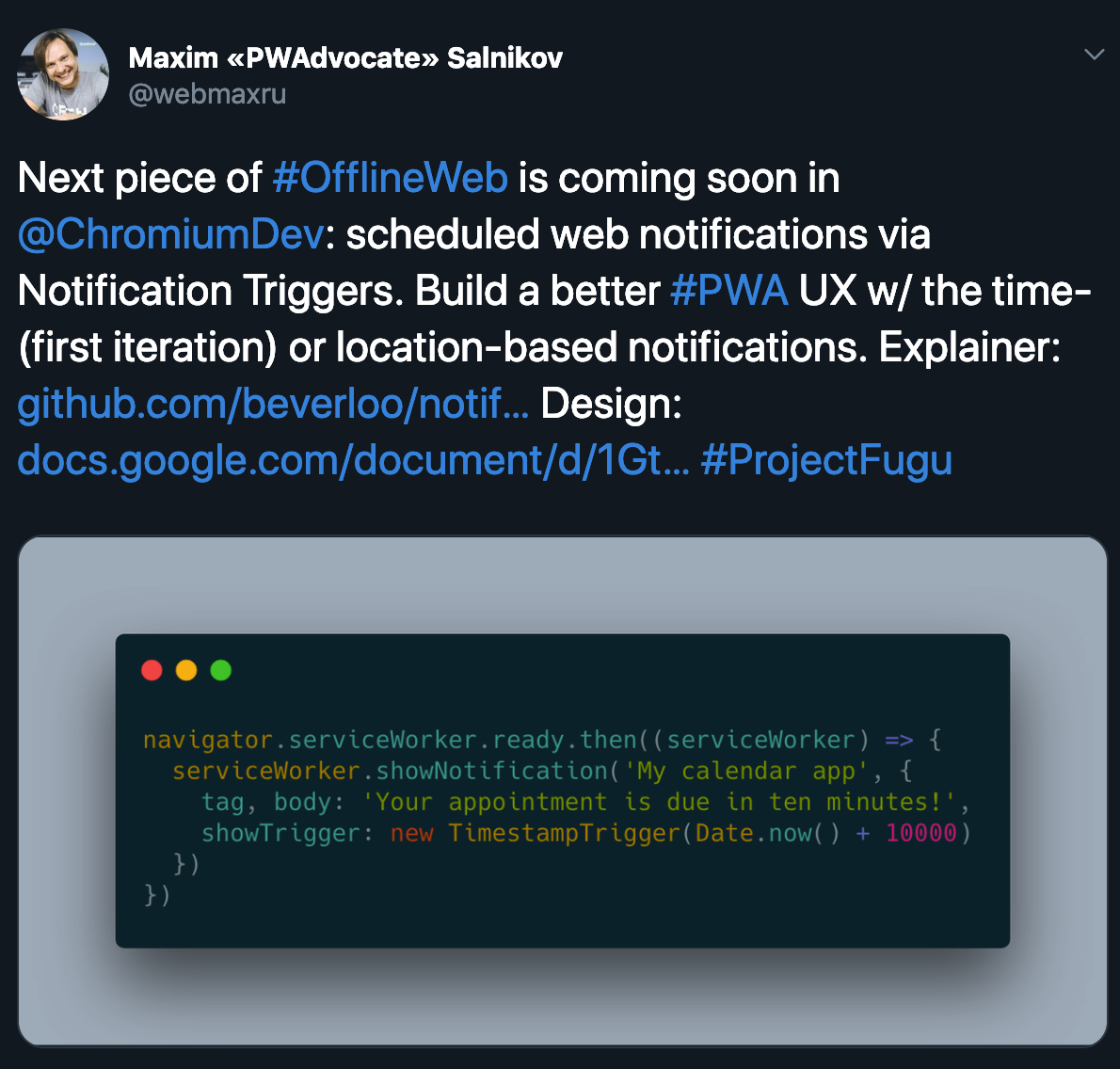
Minimum viable PWA
=
+
Application shell
Web App Manifest
Fast, responsive, mobile-first
Served via HTTPS


Let's build an App Shell
My App
-
Define the set of assets required to show the minimum viable UI
Service worker
-
install: put the assets into Cache Storage
-
activate: clear Cache Storage from the previous app version assets
-
fetch: if the asset is in Cache Storage serve it from there. Otherwise — download and serve it (and cache it)
Build time
-
Register service worker the way it does not affect the app loading performance
Website/webapp
Service Worker


Service Worker 101
Logically
Physically
-file(s)
Website
Service-worker
Browser/OS

Event-driven worker
Lifecycle
'install'
Parsed
Installing
Activating
Redundant
'activate'
Waiting
Active
Coding time
Managing cache
self.addEventListener('install', (event) => {
// Put app's html/js/css to cache
})self.addEventListener('activate', (event) => {
// Wipe previous version of app files from cache
})In the real world
-
Can't add opaque responses directly
-
Redirected requests should be managed
-
Always creating a new version of cache and deleting the old one is not optimal
-
Control over cache size is required
-
Cache invalidation for runtime caching is complex
-
...
Intercepting requests
self.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
if (event.request.url.indexOf('/api') != -1) {
event.respondWith(
// Network-First Strategy
)
} else {
event.respondWith(
// Cache-First Strategy
)
}
})In the real world
-
All kinds of fallbacks needed for the strategies
-
There are more complex strategies like Stale-While-Revalidate
-
Good to have routing
-
Good to have the possibility to provide some extra settings for different resource groups
-
...
Improve
Don't interfere
Don't break

Making an "app" from the website
=
+
Application shell
Web App Manifest
Fast, responsive, mobile-first
Served via HTTPS


For the manual install on Chrome 72 on Mac
-
Not already installed
-
Meets engagement heuristics
-
Proper Web App Manifest
-
Service worker with fetch event
-
Not "prefer related applications"
Installation criteria
-
short_name or name
-
icons must include a 192px and a 512px sized icons
-
start_url
-
display must be one of: fullscreen, standalone, or minimal-ui
MVP Web App Manifest
Test on your [mobile] device
Coding time
On iOS




with PWACompat
}
Resources
Specification
Explainer
Polyfill
Generator
In the next session...
-
Implementing complex algorithms
-
Adopting best practices
-
Focusing on YOUR task
-
Following specifications updates
-
Handling edge cases
Tools help with

Building a proper offline experience using Workbox
1) What are the cons and challenges of the manually written service workers
2) Introducing Workbox
3) Automating application shell lifecycle: from building to serving
4) Organizing a proper UX for the app update
5) Runtime caching: strategies
6) What is background sync and how to implement it using Workbox
7) Proper registration of Workbox in your app
Thank you!
Maxim Salnikov
@webmaxru
Questions?
Maxim Salnikov
@webmaxru

-
Application shell
-
Runtime caching
-
Replaying failed network requests
-
Offline Google Analytics
-
Broadcasting updates
Have our own service worker!
Working modes
-
Workbox CLI
-
Webpack plugin
-
Node module
# Installing the Workbox Node module
$ npm install workbox-build --save-devBuild script
// We will use injectManifest mode
const {injectManifest} = require('workbox-build')
// Sample configuration with the basic options
var workboxConfig = {...}
// Calling the method and output the result
injectManifest(workboxConfig).then(({count, size}) => {
console.log(`Generated ${workboxConfig.swDest},
which will precache ${count} files, ${size} bytes.`)
})workbox-build-inject.js
Workbox manifest
[
{
"url": "index.html",
"revision": "34c45cdf166d266929f6b532a8e3869e"
},
{
"url": "favicon.ico",
"revision": "b9aa7c338693424aae99599bec875b5f"
},
...
]Build script configuration
// Sample configuration with the basic options
var workboxConfig = {
globDirectory: 'dist/angular-pwa/',
globPatterns: [
'**/*.{txt,png,ico,html,js,json,css}'
],
swSrc: 'src/service-worker.js',
swDest: 'dist/angular-pwa/service-worker.js'
}
workbox-build-inject.js
Source service worker
// Importing Workbox itself from Google CDN
importScripts('https://googleapis.com/workbox-sw.js');
// Precaching and setting up the routing
workbox.precaching.precacheAndRoute([])
src/service-worker.js
1
2
Build flow integration
{
"scripts": {
"build-prod": "ng build --prod &&
node workbox-build-inject.js"
}
}package.json
Better app update UX
App version updates
v1
v2
v1
v1
v2
Deployed
Displayed
v2
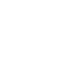
A new version of the app is available. Click to refresh.
const updateChannel = new BroadcastChannel('app-shell');
updateChannel.addEventListener('message', event => {
// Inform about the new version & prompt to reload
});Option #1: BroadcastChannel
updates.component.ts
workbox.precaching.addPlugins([
new workbox.broadcastUpdate.Plugin('app-shell')
]);src/service-worker.js
3
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker
.register('/service-worker.js')
}Option #2: Service worker lifecycle
index.html
Requirements
-
Feature detection
-
Registration after app fully loaded and UI rendered
-
Hook into service worker lifecycle update event
-
Was the service worker updated?
-
Was the app itself updated?
register-service-worker
import { register } from 'register-service-worker'
platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule)
.then( () => {
register('/service-worker.js', {
})
})main.ts
$ npm install register-service-worker updated (registration) {
// Inform & prompt
}3
Runtime caching
Strategies and plugins
workbox.routing.registerRoute(
new RegExp('/app/v2/'),
workbox.strategies.networkFirst()
);src/service-worker.js
workbox.routing.registerRoute(
new RegExp('/images/'),
workbox.strategies.cacheFirst({
plugins: [...]
})
);Push notifications
Notifications handling
self.addEventListener('push', (event) => {
self.registration.showNotification(...)
})src/service-worker.js
self.addEventListener('notificationclick', (event) => {
// React on notification actions
})self.addEventListener('notificationclose', (event) => {
// React on notification closing
})Summary
-
Framework-agnostic
-
Rich functionality
-
Maximum flexible configuration
-
Full power of our own service worker

Setup -> Configure -> Code
Get what you want
-
1900+ developers
-
Major browsers/frameworks/libs reps
PWA For Production In 1-2-3. Part 1
By Maxim Salnikov
PWA For Production In 1-2-3. Part 1
In part one of this three-part hands-on coding series, we’ll look at why the idea of Progressive Web Apps has become so popular, which APIs are in the game, and where (browsers/platforms) PWAs work. We start by answering these questions and then dive directly into coding a minimum viable PWA to understand the foundations of Service Workers and to make sure that it’s cool to have some helper tools there. Feel free to either just watch, or code along too!
- 3,566



