Caching with Spring: From Cache theory to cache Implementation

Yegor Bondar
Key Terms
Cache (/ˈkæʃ/ kash) is a component that transparently stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster. The data that is stored within a cache might be values that have been computed earlier or duplicates of original values that are stored elsewhere.
Happy App
more happy App?
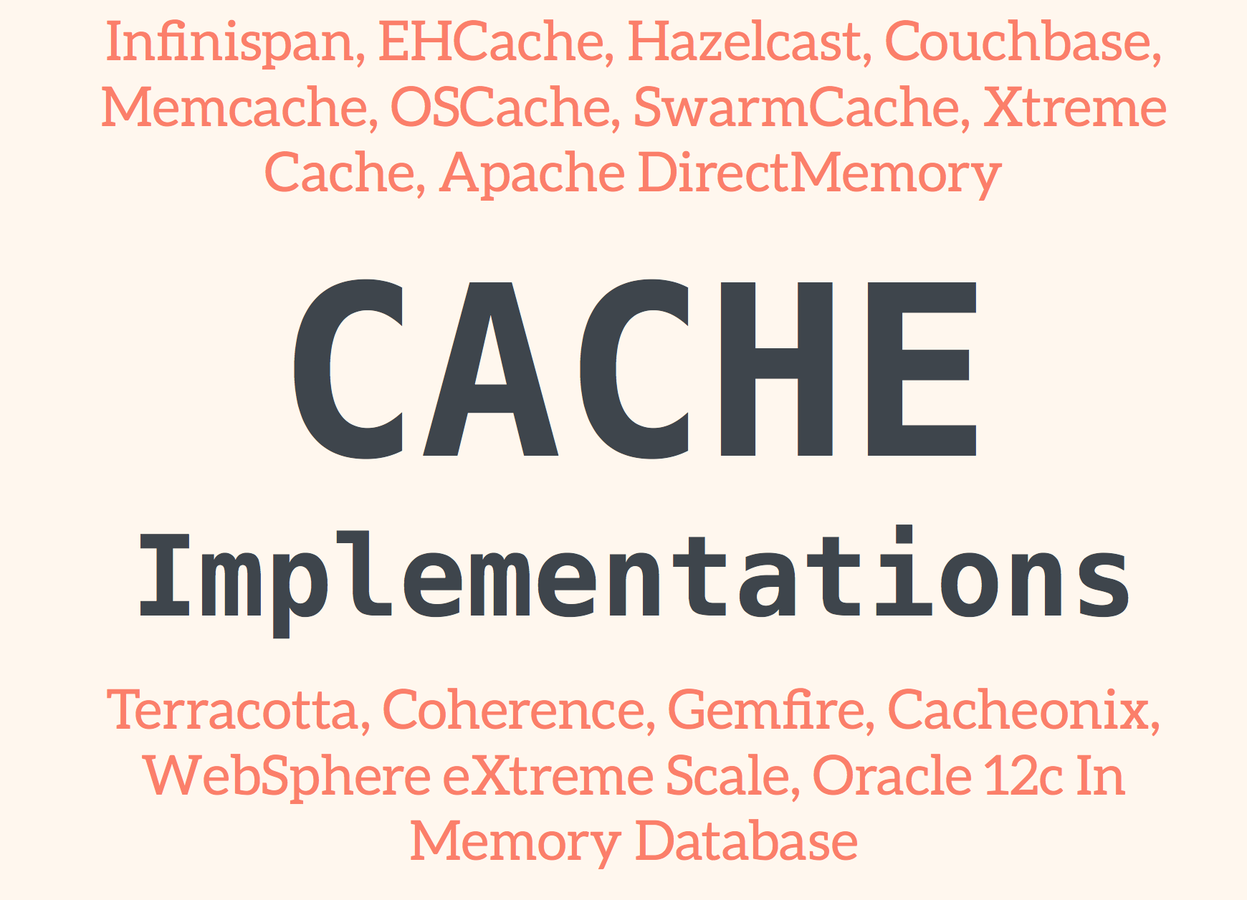
Solution?
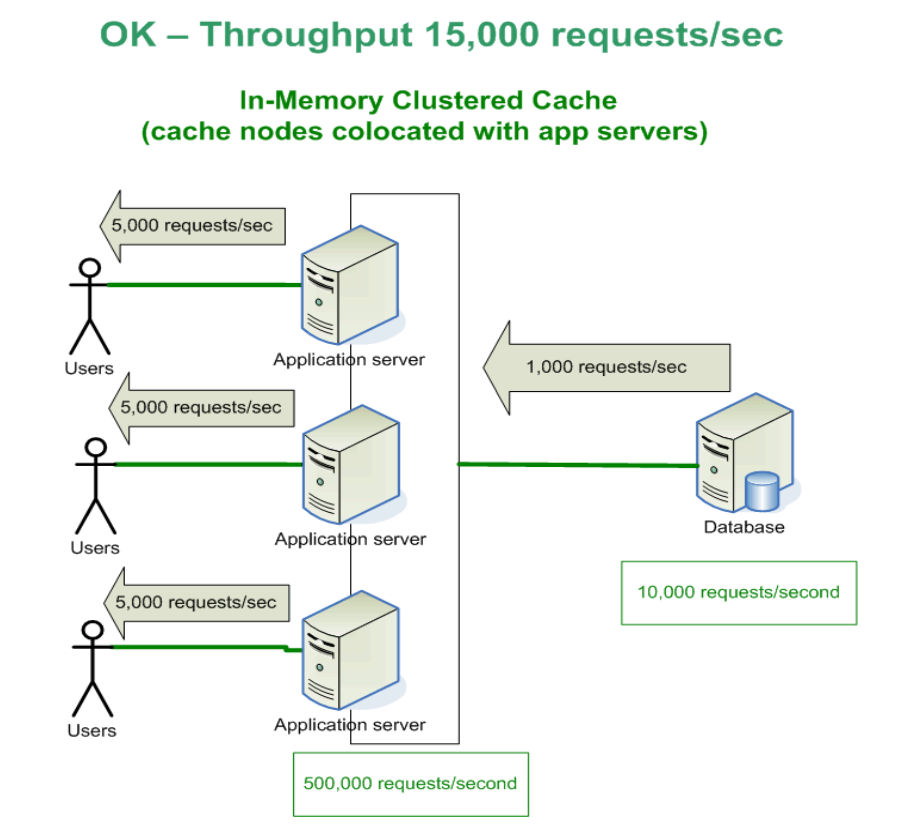
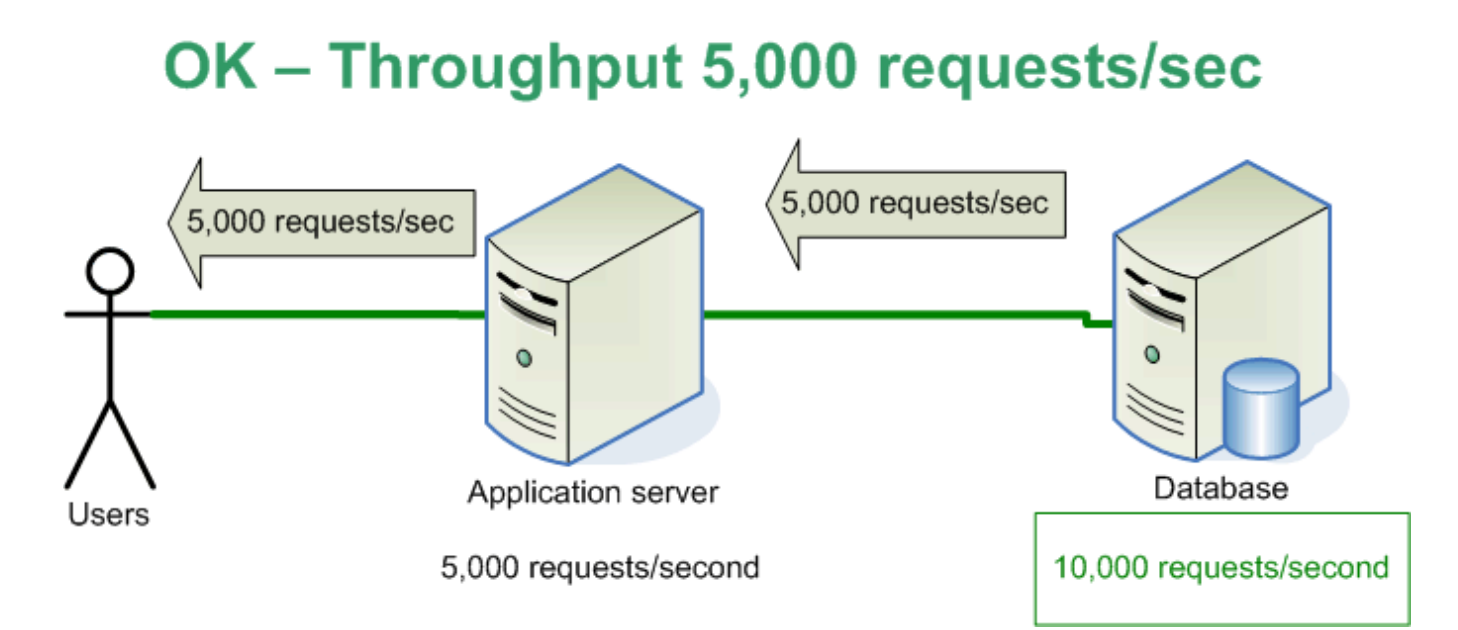
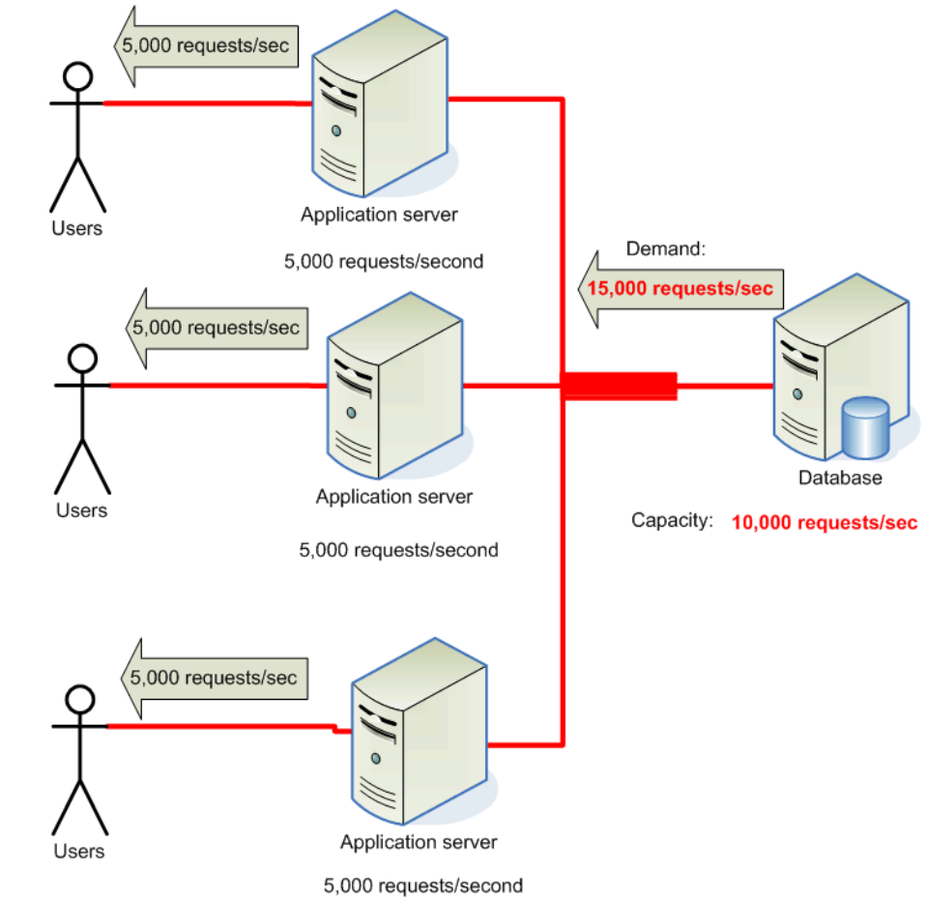
Suitable Areas for caching
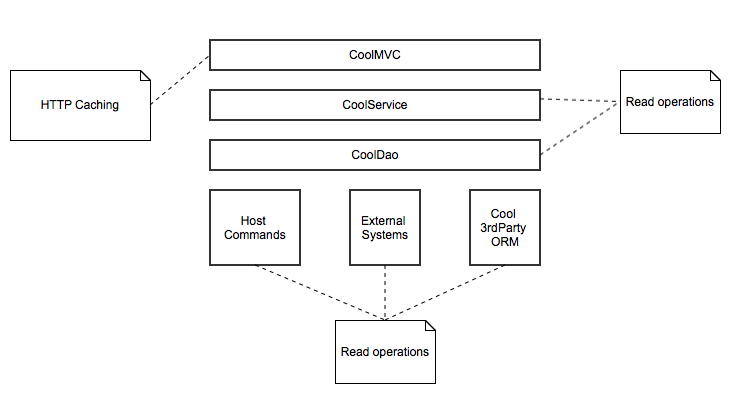
Cache concept
Cache types:
-
Application cache
-
Second level (L2) cache
-
Hybrid cache
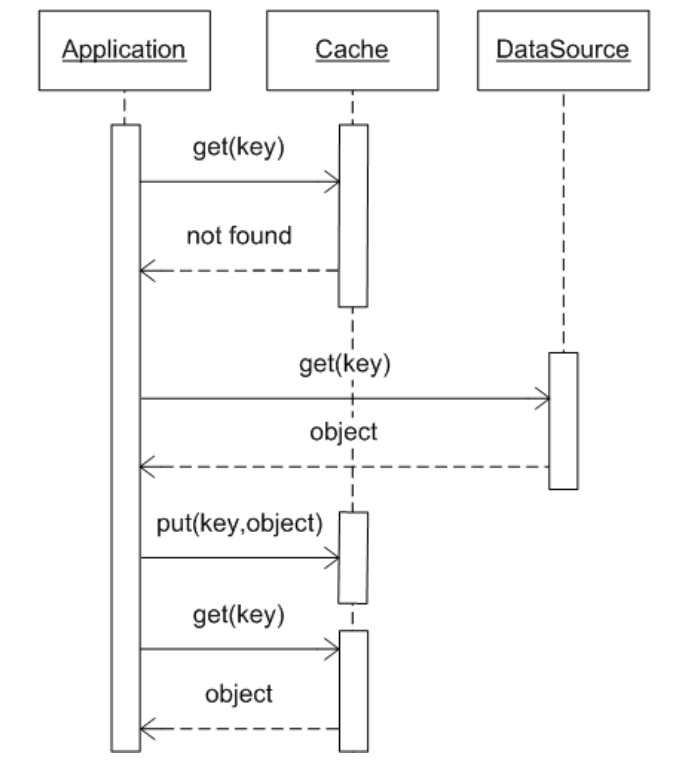
Application cache
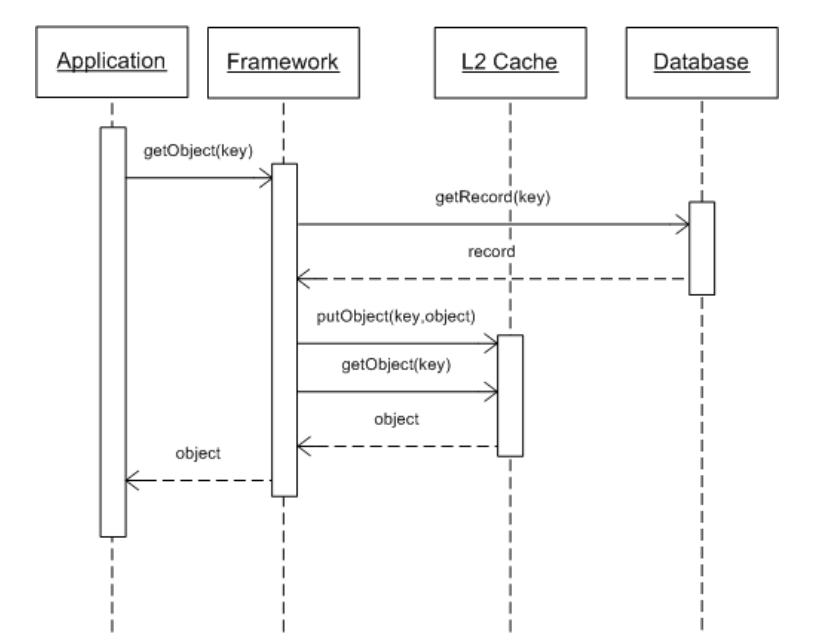
l2 cache
Hybrid cache
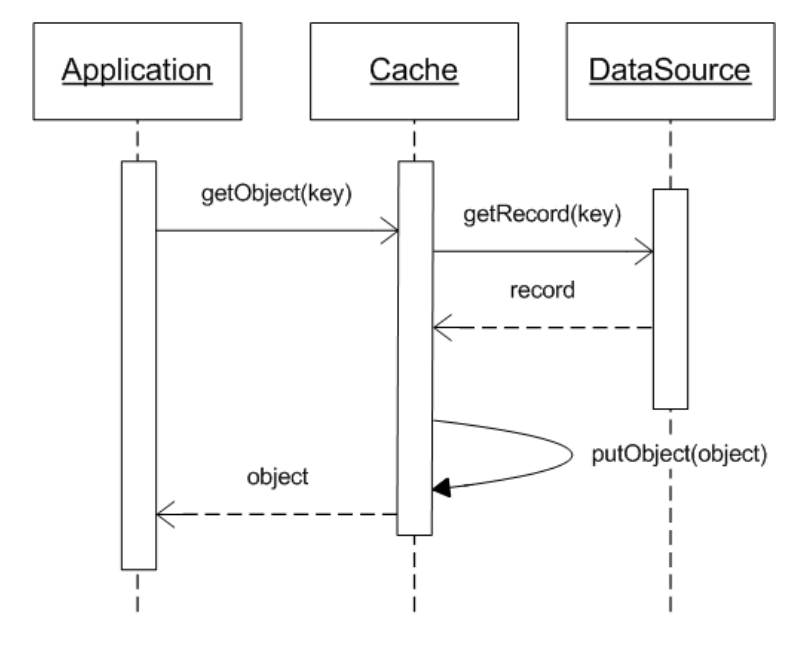
key cache terms
- Cache size - defines how many elements a cache can hold;
- Cache eviction - algorithm defines what to do when the number of elements in cache exceeds the size (LRU, LFU, FIFO) & eviction percentage;
- Time-to-live - defines time after that a cache key should be remove from the cache (expired);
Cache topologies
Local Heap cache
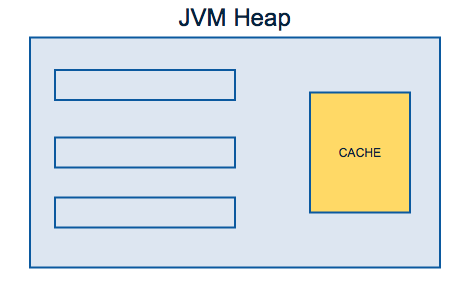
CAche Topologies
Local Off-Heap Cache (Terracotta, Hazelcast Enterprise)
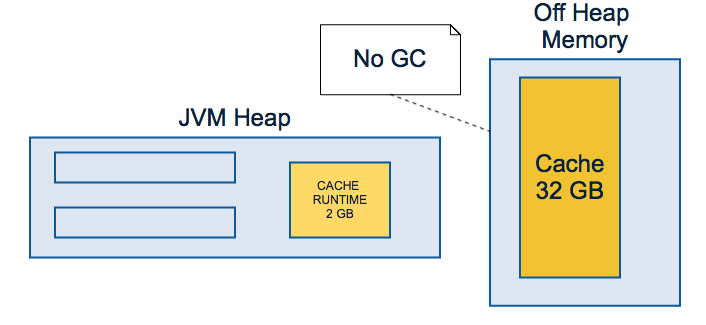
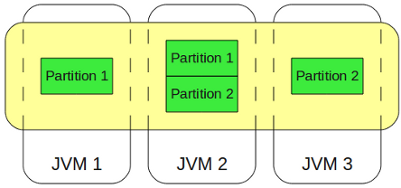
REPLICATED CACHE VS distributed cache
Shared Cache Topologies
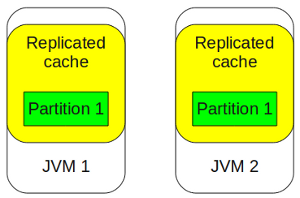
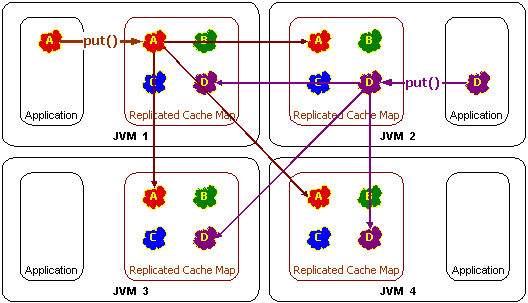
Replicated Get

REplicated put
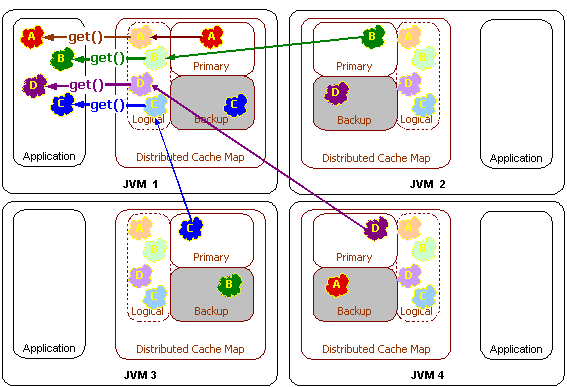
Distributed Get
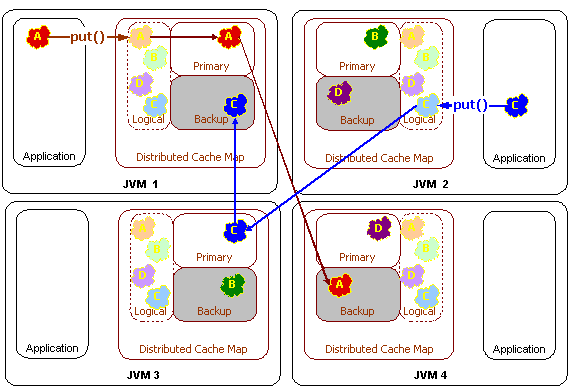
distributed Put
Distributed node failure
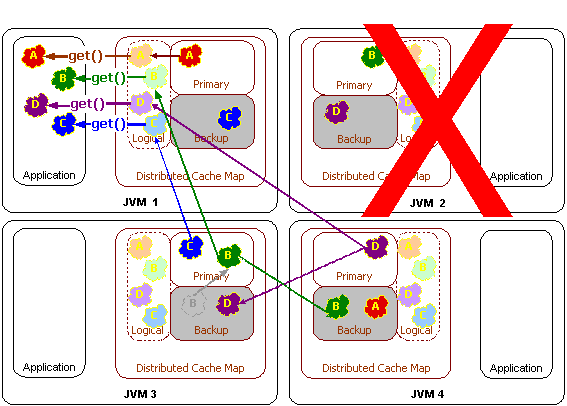
How to work with cache?
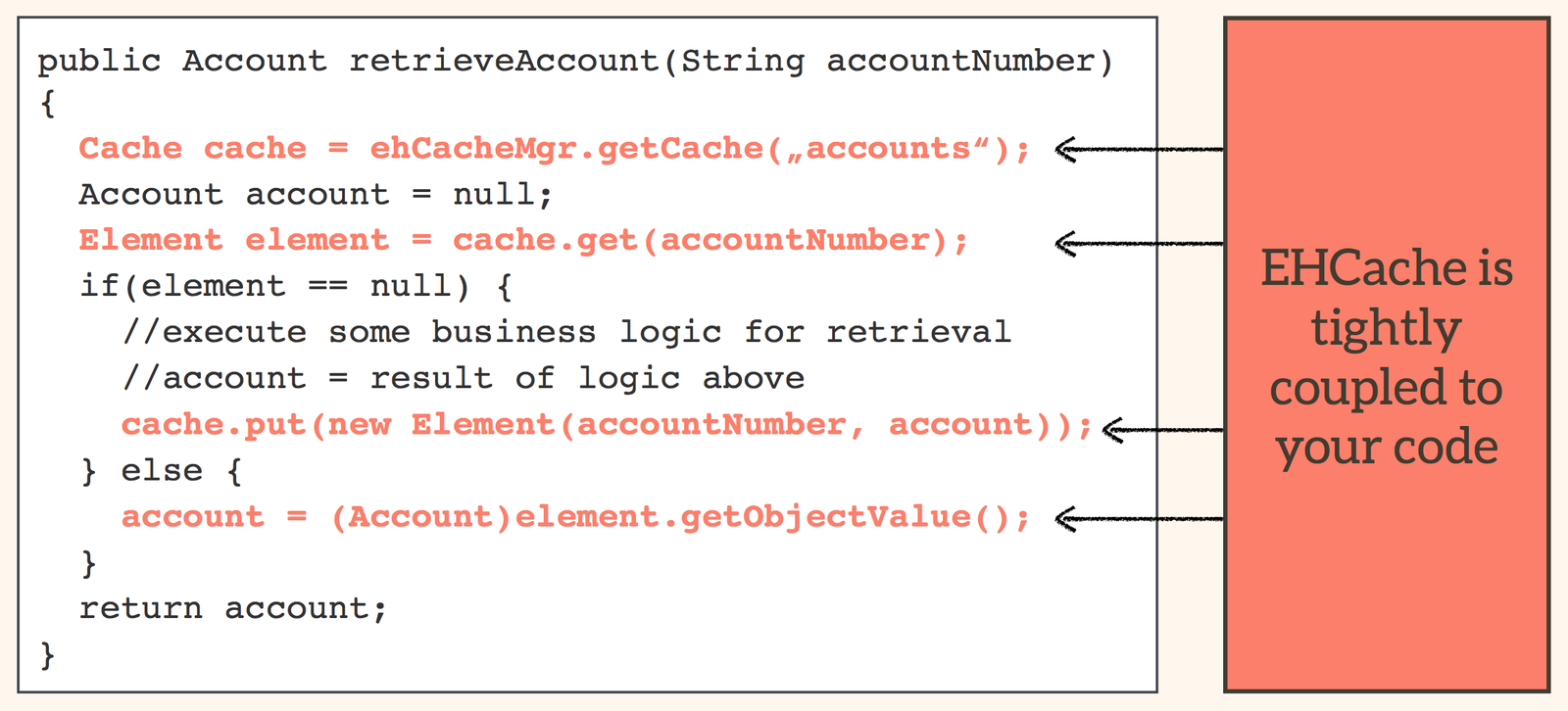
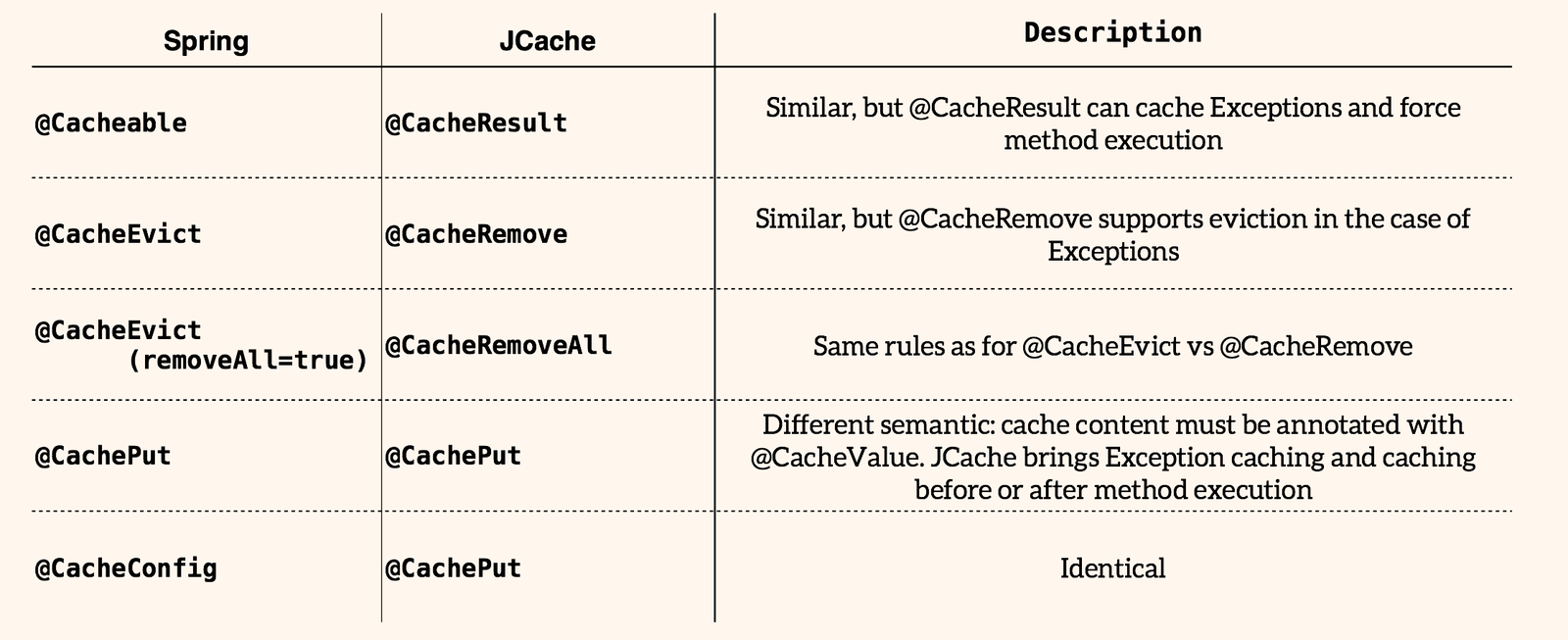
Spring Framework
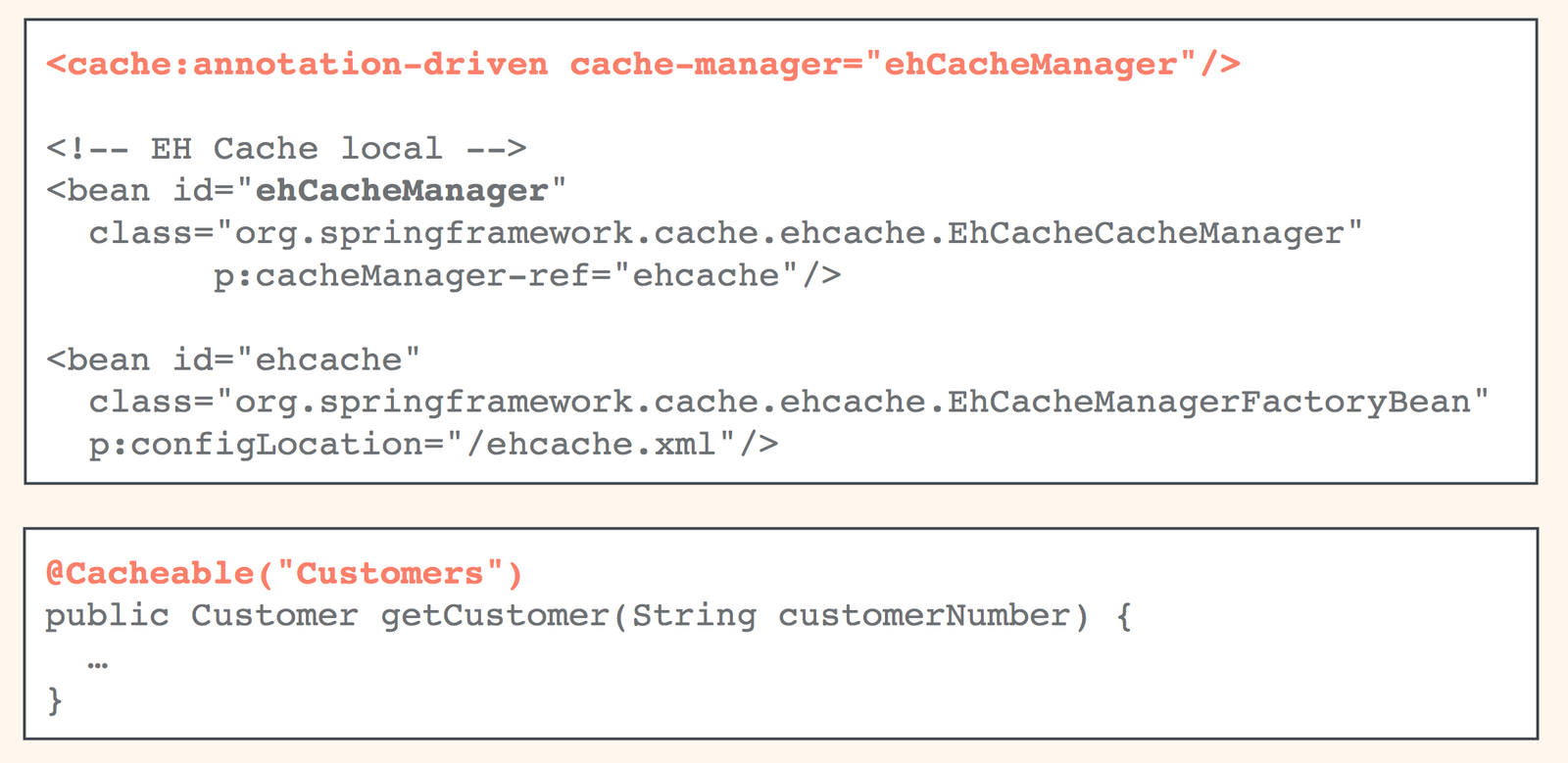
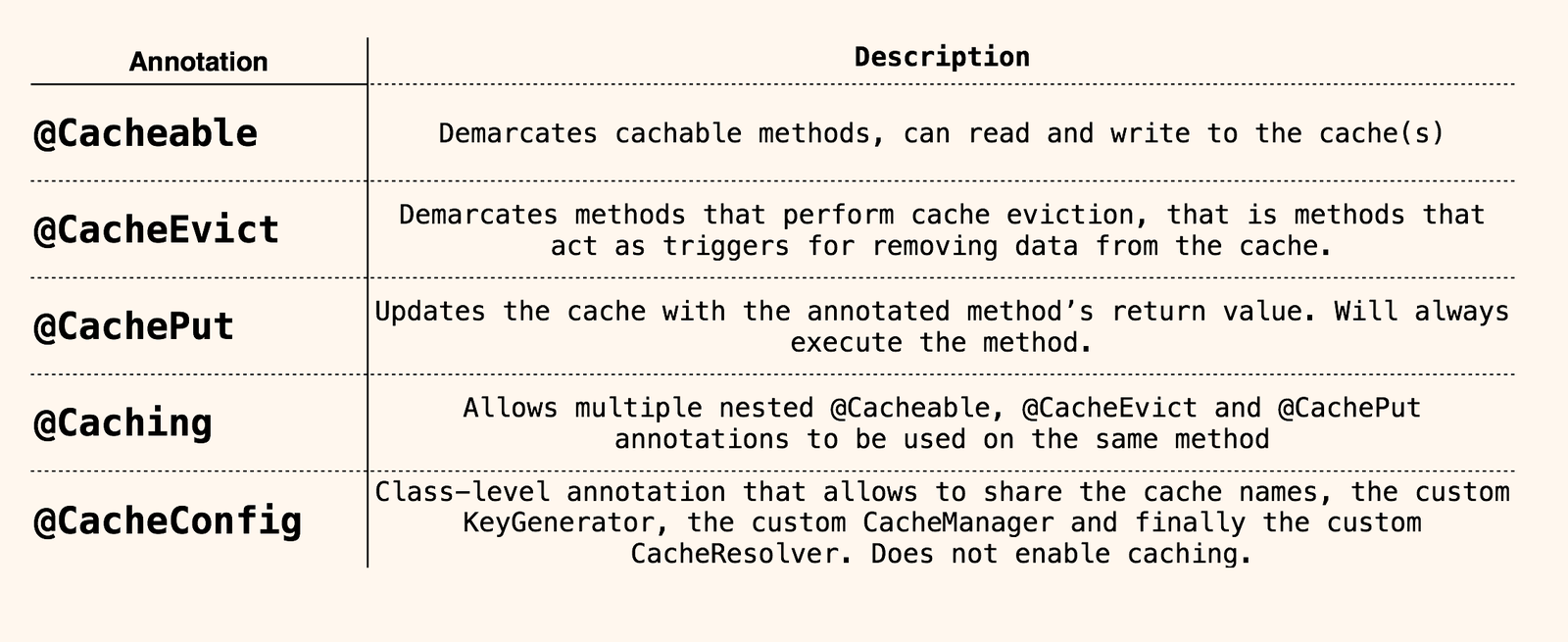
Spring Framework
Jsr-107
Apache license
1 solid Jar file ~3MB + HibernateProvider
Transactional & Secure
IMDG
3-way configuration: XML, Java, Spring
Demo
conclusion
-
Use Cache only if needed
-
Keep it local as much as possible
-
Use Cache Abstractions and don't rely on implementation
REferences
-
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E18686_01/coh.37/e18677/cache_intro.htm
-
http://coherence.oracle.com/display/COH31UG/Read-Through,+Write- Through,+Refresh-Ahead+and+Write-Behind+Caching
-
http://blog.tekmindsolutions.com/oracle-coherence-diffrence-between- replicated-cache-vs-partitioneddistributed-cache/
- Spring Documentation
spring-caching
By Yegor Bondar
spring-caching
Slides about cache concepts and Spring Cache abstraction. Hazelcast inside.
- 1,288