cog sci 131 section
week 04/25/22
by yuan meng
agenda
- overview of key concepts
- information and english
- hw10 prompt walkthrough
key concepts
- surprisal of a particular outcome
- information entropy: average surprisal over a set of outcomes
-
conditional entropy
- one specific outcome:
- a set of outcomes:
-
mutual information: reduction in entropy (a.k.a. "information gain")
- one specific outcome:
- a set of outcomes:
\displaystyle{\mathrm{I}(x_i) =-\log_2 {\mathrm{P}(x_i)}}
\displaystyle{\mathrm{H}(X) = \sum_{i}^{n}\mathrm{P}(x_i)\mathrm{I}(x_i) = -\sum_{i}^{n}\mathrm{P}(x_i)\log \mathrm{P}(x_i)}
P(\square) = 1/2
P(\square) = 1/4
P({\Large{\circ}}) = 1/4
\displaystyle{\mathrm{H}(X|y)}
\mathrm{H}(X|Y) = \sum_{j}^{m}P(y_j)\mathrm{H}(X|y_j)
"is it yellow?"
"nope"
P(\mathrm{\square|blue}) = 1
"yup"
P(\mathrm{\square|blue}) = 0
-\log P(\square) = 1
-\log P(\square) =2
\log_2 P({\Large{\circ}}) = 2
\displaystyle{\mathrm{H}(X) = 1/2 \times 1 + 1/4 \times 2 + 1/4 \times 2} = 3/2
-\log_2 P(\mathrm{\square|blue}) = 0
-\log P(\mathrm{\square|blue}) \to \infty
P({\Large{\circ}}|\mathrm{blue}) = 0
-\log P({\Large{\circ}}|\mathrm{blue}) \to \infty
\mathrm{H}(X|\mathrm{blue}) = 1 \times 0 + 0 \times (-\log_2 0) + 0 \times (-\log_2 0) = 0
P(\mathrm{\square|blue}) = 0
P(\mathrm{\square|blue}) = 1/2
-\log_2 P(\mathrm{\square|blue}) \to \infty
-\log P(\mathrm{\square|blue}) = 1
P({\Large{\circ}}|\mathrm{blue}) = 1/2
-\log P({\Large{\circ}}|\mathrm{blue}) = 1
\mathrm{H}(X|\mathrm{yellow}) = 0 \times (-\log_2 0) + 1/2 \times 1 + 1/2 \times 1 =1
\mathrm{H}(X|\mathrm{color}) = 1/2 \times 0 + 1/2 \times 1 = 0.5
\displaystyle{\mathrm{H}(X) - \mathrm{H}(X|y)}
\displaystyle{\mathrm{H}(X) - \mathrm{H}(X|Y)}
to find the answer, is it cleverer to ask about shape or color?
\mathrm{H}(X|\mathrm{shape}) \approx 1/4 \times 0 + 3/4 \times 0.91 \approx 0.68
same for shape (square or circle)
color reduces more entropy!
l'hôpital's rule
insight: clever questions roughly halve the hypothesis space
"thus twenty skillful hypotheses will ascertain what two hundred thousand stupid ones might fail to do." — charles s. pierce (1901)
get "yes" half of time and "no" also half of the time
information and english
20 questions game
- let's play... i'll think of a noun and you can ask me at most 20 yes/no questions to guess what it is
- what are some good questions to ask?
-
analyze theoretical limit
- if you always ask perfect questions, how many do you need at most to get to the answer?
- in principle, when is it impossible for a perfect question asker to find the answer?
information of english
variation: "guess which word i'm thinking about!"
- probability of a word: use entire vocabulary
- "it starts with b" 👉 conditional probability of a word: use filtered vocabulary
- mutual information:
data: 41,460 english words + their frequencies
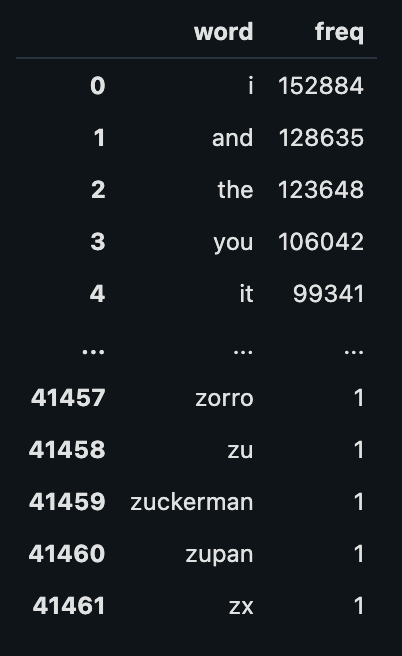
P(\mathrm{word}_i) = \frac{\mathrm{frequency}_i}{\sum_i^{n}\mathrm{frequency}_i}
| word | freq |
|---|---|
| amen | 10 |
| banana | 100 |
| boba | 50 |
toy vobaculary
P(\mathrm{boba|b}) = \frac{P(\mathrm{boba})}{P(\mathrm{boba})+P(\mathrm{banana})} = \frac{\frac{50}{10+100+50}}{\frac{50}{10+100+50}+\frac{100}{10+100+50}} = \frac{50}{50+100}
P(\mathrm{word}_i|\mathrm{condition}) = \frac{\mathrm{frequency'}_i}{\sum_i^{m}\mathrm{frequency'}_i}
\mathrm{H(words)} - \mathrm{H(words|condition)}
cross out impossible row(s)
\displaystyle{\mathrm{H}(\mathrm{words}) = -\sum_{i}^{n}P(\mathrm{word}_i)\log P(\mathrm{word}_i)}
entropy of all words
\displaystyle{\mathrm{H}(\mathrm{words|condition}) = -\sum_{i}^{m} P(\mathrm{word_i|condition})\log P(\mathrm{word_i|condition})}
entropy of remaining words
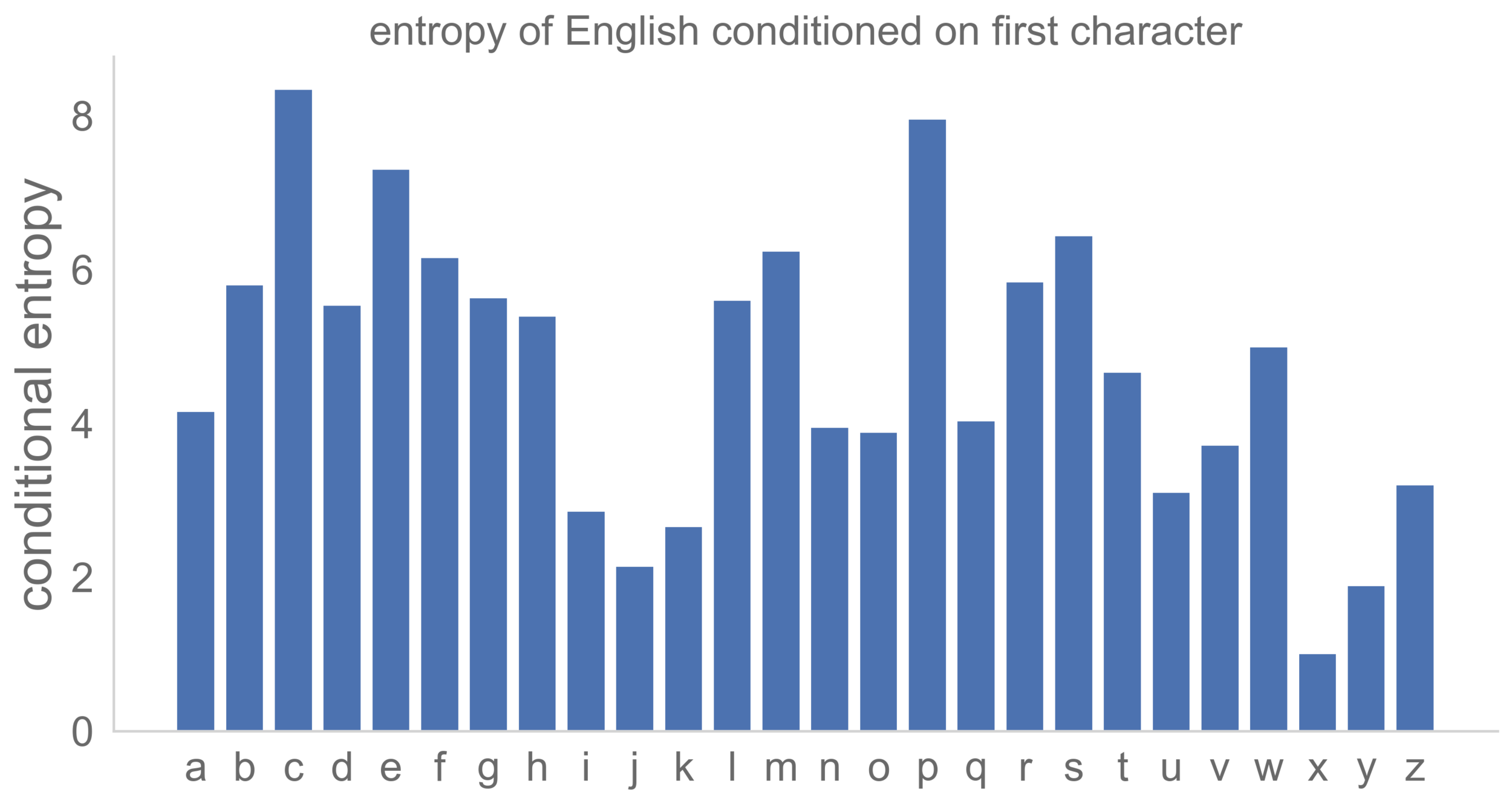
most useful condition: neither too common or rare
hw10 prompts
hints & details
- base of log: use np.log2, not np.log
- missing values: "Assignment10-WordFrequencies.csv" has 2 rows with missing values 👉 can drop them
-
not all words have vowels 👉 how to compute conditional probabilities and conditional entropies?
- create a 'first_vowel' column from 'word'
- filter rows by first_vowel
- useful functions: filter rows by strings in a column
# start with a character (e.g., char = 'b')
df[df["word"].str.startswith(char)]
# end with a character
df[df["word"].str.endswith(char)]
# first vowel (e.g., vowel = 'a')
df[df["first_vowel"] == vowel]entropy conditioned on first character
homework 10, q4
more info on info theory
david mackay's "bible" (website)

- simon dedeo's tutorial: information theory for intelligent people
- statquest: entropy (for data science) clearly explained!
- 3blue1brown: solving wordle using information theory
cogsci131_04_25
By Yuan Meng
cogsci131_04_25
- 162



