Introduction to HTML & CSS
What is html?
- Stands for Hypertext Markup Language
- Building blocks for web pages
- Like human skeletons
html Code Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Zico's Fancy Portfolio</title>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<nav>
<ul>
<li>About Me</li>
<li>Projects</li>
<li>Contact</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
<main>
<section>About Me</section>
<section>Projects</section>
<section>Contact</section>
</main>
<footer>Created with love by Zico Deng :)</footer>
</body>
</html>html TAGs
- Sometimes people also call them elements
- There are two different types of tags: semantic tag and non-semantic tag
Semantic tags
- A semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer
- Examples: header, footer, article, section...
non-semantic tags
- Tells nothing about its content
- Examples: div, span...
Rule of thumb: prefer semantic tags
SPECIAL TAG: <meta />
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<meta name="description" content="Zico's personal portfolio website" />
<meta name="keywords" content="Zico, Portfolio" />
<meta name="author" content="Zico Deng" />
<title>Zico's Fancy Portfolio</title>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>- Provides metadata about your web page
- Typically used by browsers and web crawlers
- Always inside <head> tag
What is css?
- Stands for Cascading Style sheets
- Like human skins
css Code Example
.container {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 600px;
background-color: orange;
}
.menu {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
flex-direction: row;
justify-content: center;
}
.menu > .item {
color: black;
}
.menu > .item:hover {
color: red;
}
CSS selectors
- Selectors are patterns used to select the element(s) you want to style
- A selector can have a relationship with another selector (a.k.a. combinators)
- Examples
ID selector: #my-container
Class selector: .my-container
All selector: *
Pseudo-element selector: ::before, ::after
Attribute selector: [type="range"]
Descendant selector: div p
Child selector: div > p
Adjacent sibling selector: div + p
General sibling selector: div ~ p
...Key selector
-
Browser reads selector from right to left as opposed to human read it left to right
-
The right-most selector is called key selector because it determines which specific element we will be styling with
Selector specificity
- Specificity determines, which CSS rule is applied by the browsers. If two selectors apply to the same element, the one with higher specificity wins
-
Order (in descending)
-
!important
-
inline style
-
ID
-
Class, attribute, and pseudo-class
-
Type
-
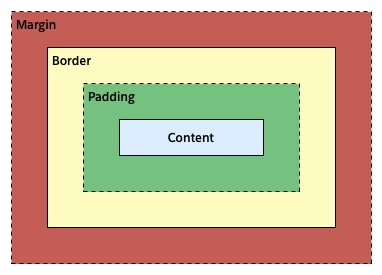
Box model
-
Box model is mainly used to create design and layout of web pages
- Every element in a web page can be thought as a rectangular box
-
Box model CSS properties include:
- Content
- Paddings
- Borders
- Margins
Flexbox
- Relatively new in CSS3
- Best for laying out items in a single dimension, row or column
- Read more: https://css-tricks.com/snippets/css/a-guide-to-flexbox/
CSS is a pain
- Everyone front-end developer hates it but this is currently the only way to style our web pages
- Hard scale and maintain. Code gets nasty as codebase grows
- Too many WTF moments, e.g. why it looks good on my browser, but not yours???
readings
Special top: web browser
Coding Ninjas Bootcamp - Class 1: HTML & CSS
By Zico Deng
Coding Ninjas Bootcamp - Class 1: HTML & CSS
Introduction to HTML and CSS
- 258



