C黑魔法
$whoami
- Du
- 輔大資工三乙
- 輔大資訊安全研究會(NISRA)111屆副會長
- AIS3 2023 學員
- 行政院國家資通安全會 112 年網路攻防演練攻擊手資格
Agenda
- C 的黑魔法
- C 的安全問題

Warning
C 的黑魔法
判斷奇偶
Lab 0x0
寫一個判斷奇偶數的程式
左邊還是右邊
if(n % 2 == 1)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數if(n % 2 != 0)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數測試 -5 這個測資
左邊還是右邊
if(n % 2 == 1)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數if(n % 2 != 0)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數-5 是偶數
-5 是奇數
為什麼
試試看編譯執行下面的程式碼
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("\n");
printf("-5 %% 2 = %d\n" , -5 % 2);
printf(" 5 %% -2 = %d\n" , 5 % -2);
return 0;
}
結果.....
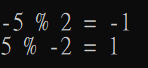

為什麼???
你真的懂 % (取餘數) 嗎 ?
C99 define: a / b

C99 define: a / b
a = (a / b) * b + a % b
=> (a % b) = a - (a / b) * b
(a % b) = a - (a / b) * b
// a=-5, b=2
-5 % 2 = -5 - (-5 / 2) * 2
= -5 - (-2) * 2
= -5 - (-4)
= -5 + 4
= -1
// a= 5, b=-2
5 % -2 = 5 - (5 / -2) * -2
= 5 - (-2) * -2
= 5 - 4
= 1
回來看一開始的問題
左邊還是右邊
if(n % 2 == 1)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數if(n % 2 != 0)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數n = -5
n % 2 = -1
-5 是偶數
n = -5
n % 2 = -1
-5 是奇數
C 的黑魔法
運算子優先順序
輸出結果是 ???
int a = -1, b = 1, c;
c = a+++b;
printf("a, b, c = %d, %d, %d\n", a, b, c);輸出結果是 ???
int a = -1, b = 1, c;
c = a+++b;
printf("a, b, c = %d, %d, %d\n", a, b, c);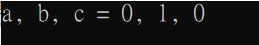
為什麼 ???
Operator Precedence
- 運算子有優先順序
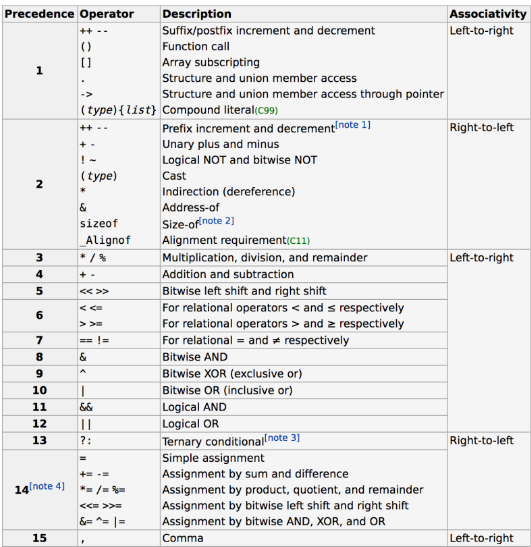
看回來原本的問題
int a = -1, b = 1, c;
c = a+++b;
printf("a, b, c = %d, %d, %d\n", a, b, c);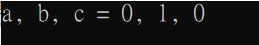
執行的結果是 ??? 好像哪裡怪怪的
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i=1;0<i<10;i++){
printf("NISRA");
}
return 0;
}

結果 - 無窮迴圈
為什麼 ???
Operator Precedence
-
運算子有優先順序
- 遇到同優先級運算子時看Associativity

回來看看
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i=1;0<i<10;i++){
printf("NISRA");
}
return 0;
}
第一次迴圈:i=1 → (0<i)=1 → 1<10
第二次迴圈:i=2 → (0<i)=1 → 1<10
.......

舉個
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 20, c = 30;
if (c > b > a)
printf("True\n");
else
printf("False\n");
}
你覺得會輸出什麼
False ! ! !
c > b > a
(c > b) > a (30>20)>a 1 > a
1 > 30 0
C 的黑魔法
for-loop各種寫法
先來個簡單的lab
使用for-loop印出右圖
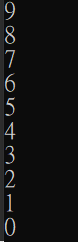
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 9; i >= 0; i--){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}
1
2
4
3
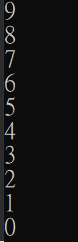
還能怎麼寫???
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 10; 0 <= --i;){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}
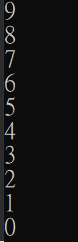
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 10;i-->0;){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}
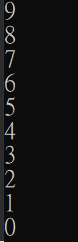
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 10; 0 <= ~~ --i;){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}
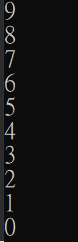
再來一個簡單的lab
再來個簡單的lab
使用for-loop印出右圖
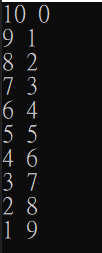
再來個簡單的lab
使用for-loop印出右圖
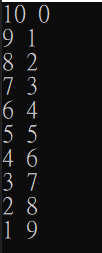
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for (int i = 10, j = 0; i > 0 && j < 10; i--, j++){
printf("%d %d\n",i,j);
}
}
小結論
珍惜生命,不要亂寫噁心別人
C 的黑魔法
Scope
return 的值是???
int x=0;
int getNum(){
int x=1214;
{
return x;
}
}變數的可視範圍
○ 由下而上,由內而外,遇到的第一個
int x=0;
int getNum(){
int x=1214;
{
return x;
}
}如果想要讀取全域變數 ???
int x=0;
int getNum(){
int x=1214;
{
extern int x;
return x;
}
}如果想要讀取全域變數
○ 使用 extern
int x=0;
int getNum(){
int x=1214;
{
extern int x;
return x;
}
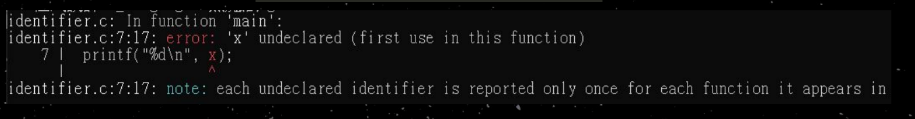
}印出的值是 ???
int main(){
{
int x=0;
}
printf("%d\n",x);
}發生了一些問題
○ 如果不小心在變數沒有定義的區域使用的話...
int main(){
{
int x=0;
}
printf("%d\n",x);
}
C 的黑魔法
Random
輸入 key 印出 You got it
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int random, key = 0;
random = rand();
printf("Give secret number: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
if( (key ^ random) == 0xdeadbeef ){
printf("You got it!!\n");
return 0;
}
printf("No, keep trying.\n");
return 0;
}
輸入 key 印出 You got it
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int random, key = 0;
random = rand();
printf("Give secret number: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
if( (key ^ random) == 0xdeadbeef ){
printf("You got it!!\n");
return 0;
}
printf("No, keep trying.\n");
return 0;
}
提示:
A ^ B = C
A = B ^ C
Random真的有亂數嗎
執行幾遍看看
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
printf("%u\n",rand());
}
}不管執行幾次結果都是.....
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
printf("%u\n",rand());
}
}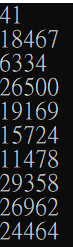
如果真的想做到很亂的亂數的效果
○ 加上srand(time(NULL)); 初始化
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int random, key = 0;
srand(time(NULL));
random = rand();
printf("Give secret number: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
if( (key ^ random) == 0xdeadbeef ){
printf("You got it!!\n");
return 0;
}
printf("No, keep trying.\n");
}
key ^ random = 0xdeadbeef;
key = random ^ 0xdeadbeef;
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int random, key = 0;
random = rand();
printf("key= %d\n",41^ 0xdeadbeef);
printf("Give secret number: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
if( (key ^ random) == 0xdeadbeef ){
printf("You got it!!\n");
return 0;
}
printf("No, keep trying.\n");
return 0;
}
再回來看剛剛的lab
key ^ random = 0xdeadbeef;
key = random ^ 0xdeadbeef;
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int random, key = 0;
random = rand();
printf("key= %d\n",random^ 0xdeadbeef);
printf("Give secret number: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
if( (key ^ random) == 0xdeadbeef ){
printf("You got it!!\n");
return 0;
}
printf("No, keep trying.\n");
return 0;
}
另一個解法
C 的黑魔法
宗教戰爭
while(1){
/* Do something */
}
for(i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++){
/* Do something */
}
while(1)
{
/* Do something */
}
for(i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)
{
/* Do something */
}
左邊還是右邊

C 的安全問題
寫扣得交作業都來不及了誰還會想到安全問題
Lab Time
在不改動程式碼的前提
輸入 input
印出 "Yes you pass it!"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
我沒有要講Lab怎麼解
先來看看下一頁的程式碼有什麼問題
有什麼問題
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char input[10];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
printf("%s\n", input);
return 0;
}有什麼問題
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char input[10];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
printf("%s\n", input);
return 0;
}沒有限制輸入長度
Buffer Overflow
- 緩衝區溢位
- 輸入超過 buffer 的資料
- 可能造成
- 破壞程式執行
- 執行期間竄改程式
- 取得系統控制權
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char input[10];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%9s", input);
printf("%s\n", input);
return 0;
}為什麼是9
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char input[10];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%9s", input);
printf("%s\n", input);
return 0;
}
Memory Layout

系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
高位址
低位址
Memory Layout

系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
- 程式碼區段(codesection)
- 又稱為 text section
Memory Layout

系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
- 存放著程式的全域變數
- 已初始化 / 未初始化
Memory Layout

系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
- 動態分配的空間
- C
- malloc / free
- C++
- new / delete
- C
Memory Layout

系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
- 區域變數
Memory Layout

系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
- 系統保留的空間
Memory Layout

系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
#include <stdio.h>
int global = 87; // data
int main()
{
int a = 10; // stack
}Registers of x86
- EIP
- Instruction Pointer
- 下一個執行的 instruction 之位址
- ESP
- Stack Pointer: 儲存 Stack 頭位址
- EBP
- Base Pointer: 儲存 Stack 基底(base)位址
Registers of x86

EBP
ESP
EIP
高位址
低位址
回來看一開始的Lab
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | ???? |
| EBP-0x4 | ???? |
| EBP-0x8 | ???? |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | ???? |
| EBP-0x8 | ???? |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | 0x 00000041 |
| EBP-0x8 | 0x 5253494E |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00A |
| EBP-0x8 | RSIN |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00A |
| EBP-0x8 | RSIN |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
為什麼反過來
Endian
- 位元組存放順序(byte ordering)
- 資料在記憶體中放的順序
- 最常見的有兩種,分別是 Big-Endian 與 Little-Endian
Endian
- MSB / LSB
- most significant bit / least significant bit
- 最左側 / 最右側的位元組
- Big endian
- MSB 存在最低的位址
- Little endian
- LSB 存在最低的位址
Endian
e.g. 0x12345678
- little-endian \x78 \x56 \x34 \x12
- big-endian \x12 \x34 \x56 \x78
低位址
高位址
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00A |
| EBP-0x8 | RSIN |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00A |
| EBP-0x8 | RSIN |
| EBP-0xC | bbbb |
| EBP-0x10 | aaaa |
EIP
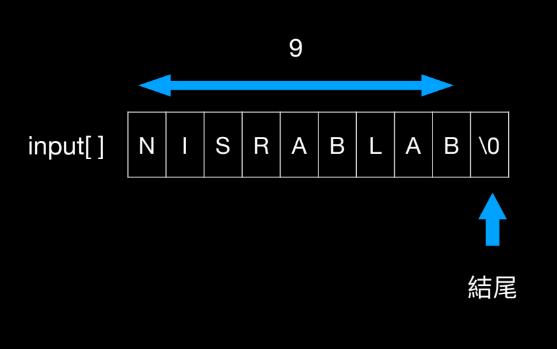
如果輸入aaaabbbb
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00n |
| EBP-0x8 | imda |
| EBP-0xC | bbbb |
| EBP-0x10 | aaaa |
EIP
如果輸入aaaabbbbadmin
覆蓋到pwd[]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}
| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00n |
| EBP-0x8 | imda |
| EBP-0xC | bbbb |
| EBP-0x10 | aaaa |
EIP
如果輸入aaaabbbbadmin
pwd[]
input[]
C黑魔法
By zonghao
C黑魔法
- 148


