C++ Intro & STL
Presented By Du
Outline
- deque
- set and map
- opeartor overloading
- priority queue
- c++ 基本介紹
- string
- vector
- stack and queue
C++ intro
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
cin >> a;
cout << a << endl;
}std::
- std:: 是個名稱空間標示符
- 使用標準函式庫中的函式或物件(cin, cout)都要使用std來限定。
- 這樣編譯器就會明白我們呼叫的cout是名字空間std中的cout。
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int a;
std :: cin >> a;
std :: cout << a << std::endl;
}namespace
- 一開始,就宣告使用std的命名空間
- 名稱不能跟關鍵字一樣 EX. int, break(會變色的都算)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
namespace first {
int cin = 5;
int break = 10;
// error: expected unqualified-id before 'break'
}
int main()
{
cout << first::cin;
// output : 5;
}library
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
cin >> a;
cout << a ;
}
萬能標頭檔 ! ! !
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
cin >> a;
cout << a ;
}加速器
- ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
- cin和cout要與stdio同步,中間會有一個緩衝,所以導致cin,cout語句輸入輸出緩慢
- cin、cout、endl速度比scanf、printf、\n慢
EOF
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
while(cin >> a){
cout << a ;
}
}String
判斷是否為11的倍數。

string
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
cin >> str;
cout << str << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++){
cout << str[i] << endl;
}
}#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
while(cin >> str){
if(str == "0")
break;
int odd = 0, even = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++){
if(i % 2 != 0){
odd += (str[i] - '0');
}
else even += (str[i] - '0');
}
int ans;
ans = abs(odd - even);
if(ans % 11 != 0)
cout << str << " is" << " not a multiple of 11." << endl;
else
cout << str << " is" << " a multiple of 11." << endl;
}
}Lab 2
第一個"換成‵‵,第二個"換成’'。
UVA - 272

getline
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
getline(cin, str);
cout << str;
}#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str;
int fg = 0;
bool space = false;
while( getline(cin,str) ){
if(space){
cout<<endl;
}
space = true;
for(int i = 0;i < str.size();i++){
if(str[i] == '"'){
if(fg % 2 == 0){
cout << "``";
fg++;
continue;
}
else{
cout << "''";
fg++;
continue;
}
}
else{
cout << str[i];
}
}
}
}UVA - 272
string 加法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1 = "123";
string str2 = "456";
str1 += str2;
cout << str1;
// str1 : 123456
}stringstream
- 型態轉換的橋樑
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
stringstream s1;
double b = 0.5;
string str;
s1 << b;
s1 >> str;
cout << str << endl;
}型態轉換
- int to string : to_string()
- string to int : stoi()
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 25;
string str = to_string(a);
cout << str << endl;
int b;
b = stoi(str);
cout << b << endl;
}Sort

找回文
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a,int b){
return a > b;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {4, 5, 8, 3, 7, 1, 2, 6, 10, 9};
sort(arr, arr+10); //由小到大
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout<<arr[i]<<' ';
}
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
cout<<endl;
vector<int> v;
for(int i=10;i>0;i--){
v.push_back(i);
}
//10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
sort(v.begin(), v.end()); //小到大
for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){
cout<<v[i]<<' ';
}
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
cout<<endl;
string str = "abcd123+-*/";
sort(str.begin(), str.end());
cout<<str<<endl;
//*+-/123abcd
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), cmp);
for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){
cout<<v[i]<<' ';
}
//10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
cout<<endl;
}S
O
R
T
Reverse
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[10] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
reverse(a, a+5); // 轉換0~4
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<' ';
}
//4 3 2 1 0 5 6 7 8 9
cout<<endl;
vector<int> v;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
v.push_back(i);
}
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){
cout<<v[i]<<' ';
}
//9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
cout<<endl;
string str = "123";
reverse(str.begin(), str.end());
cout<<str<<endl;
//321
}
UVA - 10945
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
while(getline(cin,str)){
if(str == "DONE") break;
string str2 = "";
for(int i = 0;i < str.size();i++){
if(isalpha(str[i])){
str2 += tolower(str[i]);
}
}
string str3 = str2;
reverse(str2.begin(), str2.end());
if(str2 == str3)
cout<<"You won't be eaten!"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Uh oh.."<<endl;
}
}
STL
Why STL
- Standard Template Library
- 內建資料結構
- 不用自己手刻
- 可以自己設定想要儲存的資型態
vector
benefit
- 動態陣列,可以隨時改變大小
- 可以做比array多的事
- v.push_back()
- v.pop_back()
- v.size()
- v.insert()
- v.erase()
- v.front()
- v.back()
- v.begin() //回傳iterator
- v.end() //回傳iterator
- v.clear()
- v.empty()
- v.resize(10)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.resize(5);//預留空間給使用者輸入
v[3] = 5;
cout<<v[3];
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
v.push_back(i); //從後放入
}
cout << v.size() << endl; //vector大小
cout<<v.front();//輸出第一個
cout<<v.back();//輸出最後一個
sort(v.begin(), v.end());//由大到小sort
v.insert(v.begin() + 2, 30); // 插入
v.erase(v.begin() + 1); //刪除
v.erase(v.begin() + 1, v.begin() + 3); //刪除某段
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
while(!v.empty()){
v.pop_back(); //從後丟出
}
v.clear(); //清空
if(v.empty()) cout << "It is empty!!\n"; //是否為空
}2D vector
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int>v[10]; // 長度為10的vector array
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
v1[i].resize(5);
v1[i][3] = 3;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < v1[i].size(); j++){
cout << v1[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
// size => 10 x 5
return 0;
}2D vector
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<vector<int>> v2; // 2D vector
v2.resize(5);
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
v2[i].resize(10);
v2[i][5] = 5;
}
for(int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < v2[i].size(); j++){
cout << v2[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
//vector size = 5 x 10
}stack
- FILO: First In Last Out
- LIFO: Last In First Out
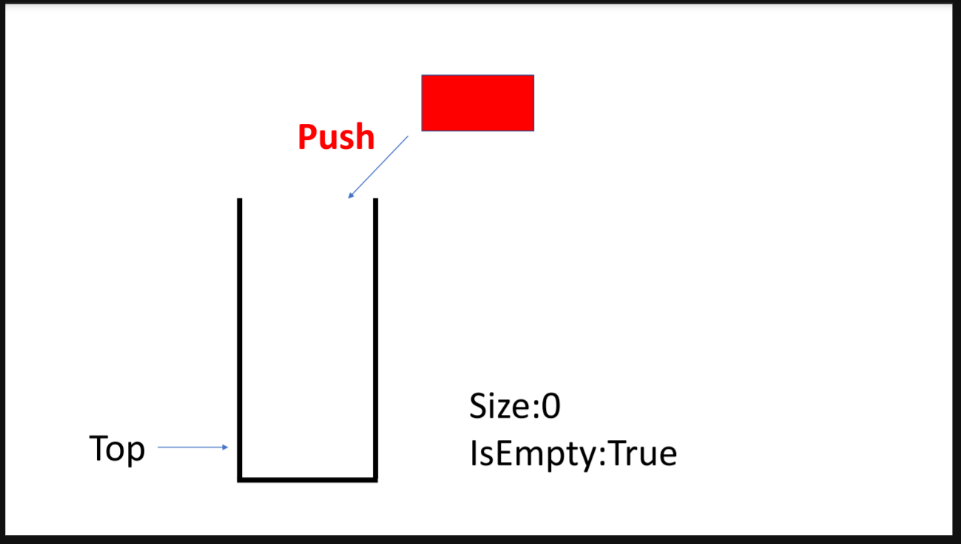
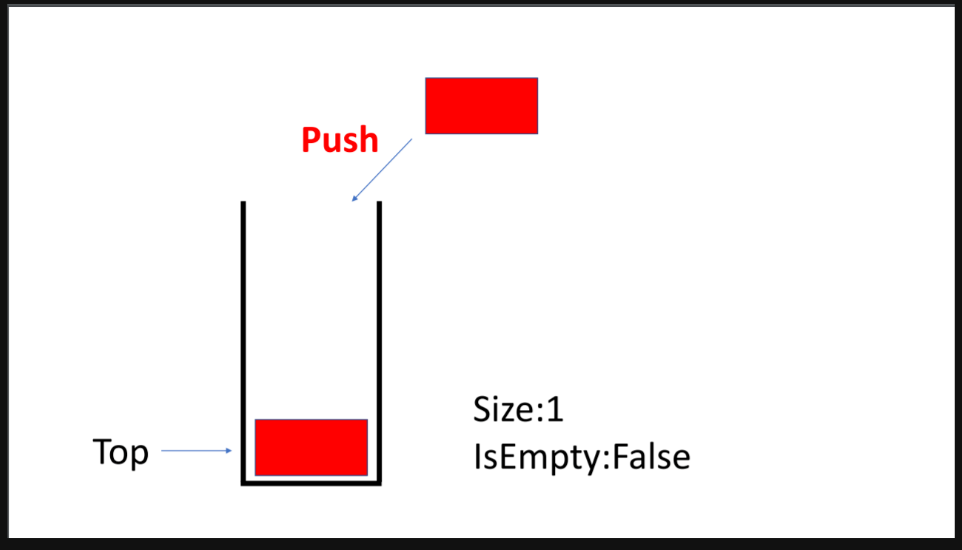
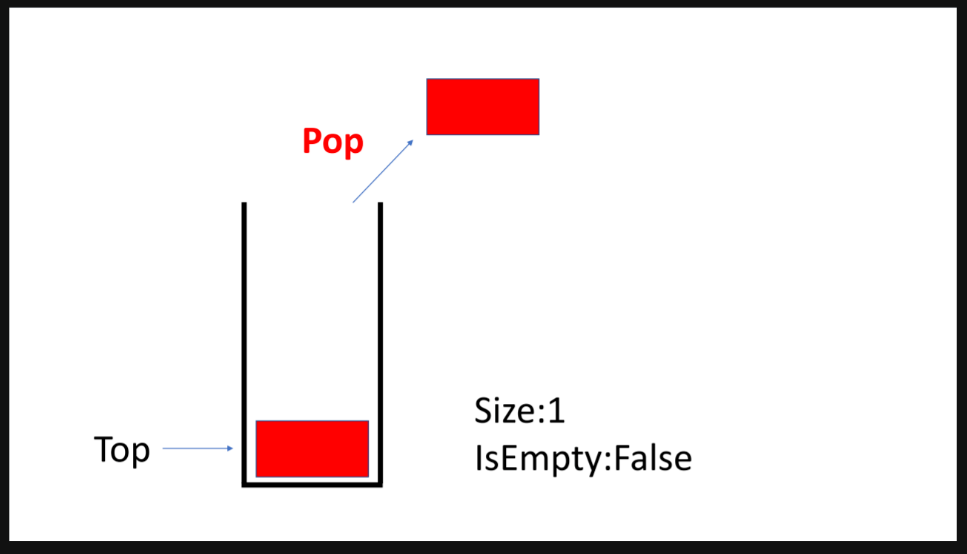
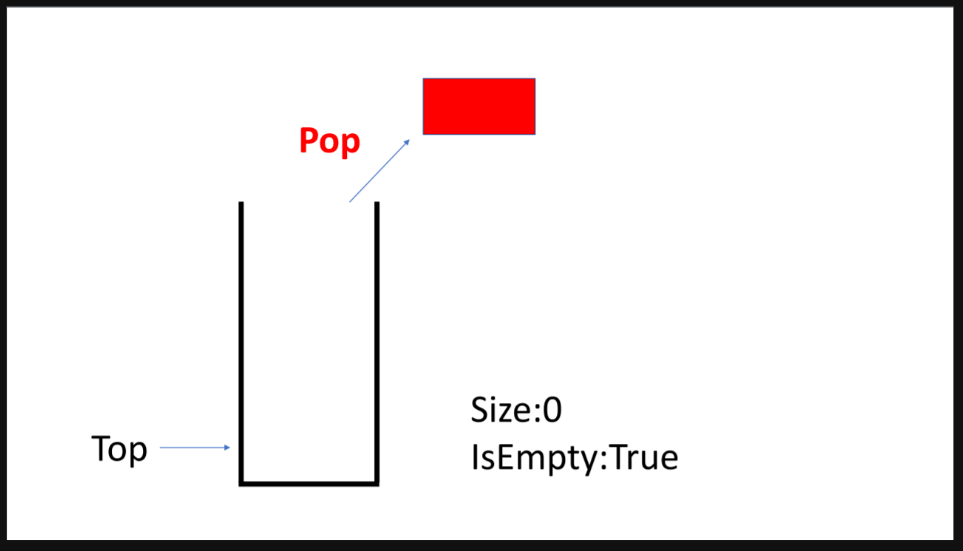

- s.push()
- s.pop()
- s.top()
- s.empty()
- s.size()
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
stack<int>Stack;
Stack.push(1);
//將東西放在stack的最上方
Stack.push(2);
Stack.push(3);
cout << "the top of the stack is " << Stack.top() << '\n';
//3(回傳stack最上方的值)
Stack.pop();
//將stack最上方的值刪除
cout << "the top of the stack is " << Stack.top() << '\n';
//2(回傳stack最上方的值)
cout << "the size of the stack is " << Stack.size() << '\n';
//2(回傳stack現在有幾個元素)
while(!Stack.empty()){
Stack.pop();
}
//清空stack
}Lab1 Stack練習
給定兩種操作
push x : 在 stack 插入 x
pop : 刪除 stack 的頂端元素
對於每個 pop 操作,如果 stack 沒有元素,輸出"The stack is empty.",否則請輸出被刪除的元素。

queue
- FIFO: First In First Out
- LILO: Last In Last Out
理論演示 (我就偷懶不想做簡報
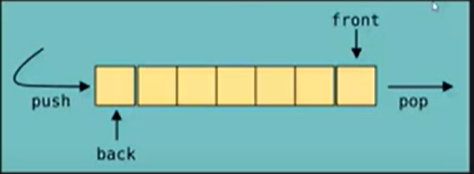
- q.push()
- q.pop()
- q.size()
- q.front()
- q.back()
- q.empty()
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
queue<int>Queue;
Queue.push(1);
//將東西放在queue的最後方
Queue.push(2);
Queue.push(3);
cout << "the front of the Queue is " << Queue.front() << '\n';
// 1(回傳最前方的值)
cout << "the back of the Queue is " << Queue.back() << '\n';
// 3(回傳最後方的值)
Queue.pop();
//將queue最前方的值刪除
cout << "the front of the Queue is " << Queue.front() << '\n';
// 2(回傳最前方的值)
cout << "the size of the queue is " << Queue.size() << '\n';
// 2(回傳現在有幾個元素)
while(!Queue.empty()){
Queue.pop();
}
//清空queue
}queue練習
給定兩種操作
push x : 在 queue 插入 x
pop : 刪除 queue 的頂端元素
對於每個 pop 操作,如果 queue 沒有元素,輸出"The queue is empty.",否則請輸出被刪除的元素。
deque
- d.push_front(x)
- d.push_back(x)
- d.pop_front(x)
- d.pop_back(x)
- d.front()
- d.back()
- d.empty()
- d.size()
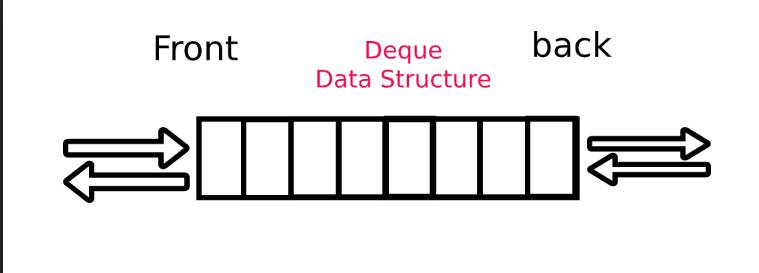
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
deque<int>Deque;
Deque.push_front(2);
Deque.push_front(1);
Deque.push_back(3);
//將東西放在deque的最前方或最後方
cout << "the front of the deque is " << Deque.front() << '\n';
// 1(回傳最前方的值)
cout << "the back of the deque is " << Deque.back() << '\n';
// 3(回傳最後方的值)
Deque.pop_front();
//刪除最前方的值
Deque.pop_back();
//刪除最後方的值
cout << "the front of the deque is " << Deque.front() << '\n';
// 2(回傳最前方的值)
cout << "the back of the deque is " << Deque.back() << '\n';
// 2(回傳最後方的值)
cout << "the size of the deque is " << Deque.size() << '\n';
//1(回傳deque現在有幾個元素)
for(int i = 0; i < Deque.size(); i++){
cout << Deque[i] << " ";
}
cout<<endl;
//隨機存取
while(Deque.empty() == false){
cout << "the deque is not empty !\n";
cout << "the front of the deque now is " << Deque.back() << '\n';
Deque.pop_back();
}
//清空deque
}deque 練習


#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int P, C, cs = 1;
while (cin >> P >> C && P != 0 && C != 0){
deque<int>d;
char command;
int s;
for (int i = 1; i <= min(P,C); i++){
d.push_back(i);
}
cout << "Case " << cs++ << ":"<<"\n";
while (C--){
cin >> command;
if (command == 'N')
{
cout << d.front() << "\n";
d.push_back(d.front());
d.pop_front();
}
else
{
cin >> s;
for (auto it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++){
if (*it == s)
{
d.erase(it);
break;
}
}
d.push_front(s);
}
}
}
}set
-
只存node的紅黑樹(一種二元搜尋樹)
-
儲存的type需要可排序
- 將我們的資料丟進set中
- 判斷我們的資料是否在set中
- 若已存在的值不會被重複儲存
- s.insert(x) //將x插入set中
- s.count(x) //回傳x是否存在於set中
- s.erase(x) //刪除在set中的x
- s.clear() //刪除set中所有元素
- s.begin() //回傳set第一個元素的位置
- s.end() //回傳set最後一個個元素 + 1的位置
- s.empty()
- s.size()
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
set<int>Set;
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(2);
Set.insert(3);
//將東西存入set中
cout << "Set.count(1) = " << Set.count(1) << endl;
// Set.count(1) = 1
cout << "Set.count(10) = " << Set.count(10) << endl;
// Set.count(10) = 0
Set.erase(1);
//刪除set中的1
cout << "Set.count(1) = " << Set.count(1) << endl;
// Set.count(1) = 0
cout << "the size of the set is " << Set.size() << endl;
// 3(回傳set中的元素個數)
Set.clear();
//清空set中元素
cout << "the size of the set is " << Set.size() << endl;
// the size of the set is 0
if(Set.empty()){
cout << "the set is empty now !!"<<endl;
}
// the set is empty now!!
}遍歷所有在set中的元素
- 利用iterator、begin()與end()
- 利用auto來遍歷
利用iterator、begin()與end()
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
set<int>Set;
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(2);
Set.insert(3);
set<int>::iterator iter;
for(iter = Set.begin(); iter != Set.end(); iter++){
cout << *iter << " ";
}
// 1 2 3
}利用auto
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
set<int>Set;
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(1);
Set.insert(2);
Set.insert(3);
for(auto it: Set){
cout << it << " ";
}
// 1 2 3
}map
Title Text
- 紅黑樹(一種二元搜尋樹)
- 有key 與 value
- 將我們的key與value丟進map中
- key不能重複,value可以重複
- 用key就可以得到value
Key
value
001
Key
002
John
Bill
pair
- 一種資料型態,為兩種型態的組合
- 兩個個別的type可以不一樣
- 可利用first與second取值或建立
- 可利用make_pair來建立
pair
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
pair<string, int> p[2];
p[0] = make_pair("Hank", 891008);
p[1].first = "Catherine";
p[1].second = 900131;
cout << p[0].first << " " << p[0].second << '\n';
// Hank 891008
cout << p[1].first << " " << p[1].second << '\n';
// Catherine 900131
}- m.insert(x) //將x插入map中
- m.count(x) //回傳x這個key是否在map中
- m.erase(x) //刪除在map中key為x的
- m.clear() //刪除map中所有元素
- m.begin() //回傳map第一個元素的位置
- m.end() //回傳map最後一個個元素 + 1的位置
- m.empty()
- m.size()
Map
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
map<int,string>Map;
Map.insert(make_pair(0, "Hank"));
//可以利用make_pair
Map[1] = "Catherine";
//也可以用類似陣列儲存的方式來儲存
cout << "Map.count(1) = " << Map.count(1) << '\n';
// Map.count(1) = 1
cout << "Map.count(2) = " << Map.count(2) << '\n';
// Map.count(2) = 0
Map.erase(0);
cout << "Map.count(0) = " << Map.count(0) << '\n';
// Map.count(0) = 0
cout << "the size of map is " << Map.size() << '\n';
// the size of map is 1
Map.clear();
if(Map.empty()){
cout << "the map is empty now !!\n";
}
//清空map
}利用iterator、begin()與end()來遍歷
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
map<int, string>Map;
Map.insert(make_pair(0, "Hank"));
Map[1] = "Catherine";
Map[2] = "Linus";
Map[3] = "Jason";
Map[4] = "Jimmy";
map<int, string>::iterator it;
for(it = Map.begin(); it != Map.end(); it++){
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << " ";
}
// 0 Hank 1 Catherine 2 Linus 3 Jason 4 Jimmy
}使用auto來遍歷
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
map<int, string>Map;
Map.insert(make_pair(0, "Hank"));
Map[1] = "Catherine";
Map[2] = "Linus";
Map[3] = "Jason";
Map[4] = "Jimmy";
for(auto it: Map){
cout << it.first << " " << it.second << " ";
}
// 0 Hank 1 Catherine 2 Linus 3 Jason 4 Jimmy
}opeator overloading
- 因為有些資料結構的儲存要利用到可排序的資料,因此必須自訂排序規則
- 較常使用在sort、priority_queue
- STL中我們介紹的資料結構如set, map等若要自訂資料型態也須使用
struct
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct item{
int x, y;
//constructor
item(int x, int y):x(x), y(y){}
};operator overloading
bool operator < (const item& rhs) const{
// item代表左邊,rhs代表右邊
// return true 如果左右邊不需交換
// return false 如果左右邊要交換
}希望x從大到小,
若x相同則y從大到小
struct item{
int x, y;
//constructor
item(int x, int y):x(x), y(y){}
//operator overloading
bool operator<(const item& rhs)const{
//若左邊的x比右邊的x大,不用交換位置,回傳true
if(x > rhs.x){
return true;
}
//若左邊的x與右邊的x相同,且左邊的y比右邊的y大,不用交換位置,回傳true
else if(x == rhs.x && y > rhs.y){
return true;
}
else{ //交換位置
return false;
}
}
};希望x從大到小,
若x相同則y從大到小
struct item{
int x, y;
//constructor
item(int x, int y):x(x), y(y){}
//operator overloading
bool operator<(const item& rhs)const{
return x > rhs.x || (x == rhs.x && y > rhs.y);
}
};#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct item{
int x, y;
//constructor
item(int x, int y):x(x), y(y){}
//operator overloading
bool operator<(const item& rhs)const{
return x > rhs.x || (x == rhs.x && y > rhs.y);
}
};
int main(){
vector<item>v;
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= 3; j++)
v.push_back(item(i, j));
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for(auto it: v)
cout << it.x << " " << it.y << '\n';
}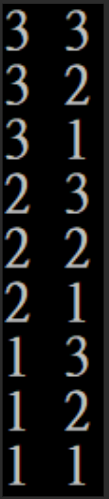
priority queue
- heap
- 資料預設從大到小排序,從優先度高先取出
- 儲存的type需要可排序
- 在O(log(n))時間內維護最大/最小值
- pq.push(x)
- pq.pop() //刪除優先級最高元素
- pq.top() //回傳優先級最高元素
- pq.empty()
- pq.size()
priority queue
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
priority_queue<int>pq;
pq.push(1);
pq.push(2);
pq.push(5);
//將元素加入priority queue
cout << "pq.top() = " << pq.top() << '\n';
// pq.top() = 5
pq.pop();
//刪除priority queue中優先級最高元素
cout << "pq.top() = " << pq.top() << '\n';
// pq.top() = 2
cout << "pq.size() = " << pq.size() << '\n';
// pq.size() = 2
while(!pq.empty()){
pq.pop();
}
//清空priority queue
cout << "pq.size() = " << pq.size() << '\n';
// pq.size() = 0
}讓priority_queue從小到大排
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 從小到大
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>pq;
pq.push(1);
pq.push(3);
pq.push(5);
while(pq.empty() == false){
cout << "pq.top() = " << pq.top() << endl;
pq.pop();
}
// pq.top() = 1
// pq.top() = 3
// pq.top() = 5
}自定義priority queue儲存內容
- 使用struct來定義儲存的內容,必須定義出排序方式,才可以使用priority_queue
- 由於priority_queue預設是「從大到小」,所以我們的operator要寫「相反」(非常重要)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct item{
int x, y;
//constructor
item(int x, int y):x(x), y(y){}
//operator overloading
bool operator<(const item& rhs)const{
return x > rhs.x || (x == rhs.x && y > rhs.y);
}
};
int main(){
priority_queue<item>pq;
pq.push(item(4, 4));
pq.push(item(3, 2));
pq.push(item(4, 3));
pq.push(item(1, 2));
while(!pq.empty()){
cout << pq.top().x << " " << pq.top().y << endl;
pq.pop();
}
}看看code,是看看會執行出什麼結果
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct item{
int x, y;
//constructor
item(int x, int y):x(x), y(y){}
//operator overloading
bool operator<(const item& rhs)const{
return x > rhs.x || (x == rhs.x && y > rhs.y);
}
};
int main(){
priority_queue<item>pq;
pq.push(item(4, 4));
pq.push(item(3, 2));
pq.push(item(4, 3));
pq.push(item(1, 2));
while(!pq.empty()){
cout << pq.top().x << " " << pq.top().y << endl;
pq.pop();
}
}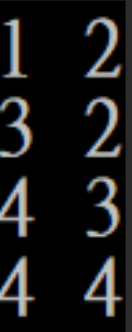
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct item{
int x, y;
//constructor
item(int x, int y):x(x), y(y){}
//operator overloading
bool operator<(const item& rhs)const{
return (x < rhs.x || (x == rhs.x && y < rhs.y));
}
};
int main(){
priority_queue<item>pq;
pq.push(item(4, 4));
pq.push(item(3, 2));
pq.push(item(4, 3));
pq.push(item(1, 2));
while(!pq.empty()){
cout << pq.top().x << " " << pq.top().y << endl;
pq.pop();
}
}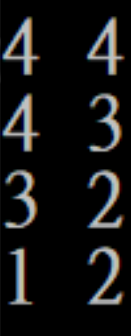
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,num,a,b;
while(cin>>n&&n){
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>pq;
long long ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>num;
pq.push(num);
}
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
a=pq.top();
pq.pop();
b=pq.top();
pq.pop();
ans+=(a+b);
pq.push(a+b);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}感謝
-
Hank 學長110-2課程簡報
-
Mimmy 學姊110-2課程簡報
C++ intro & stl
By zonghao
C++ intro & stl
- 176


