Introduction
to
Apache Spark
What is Spark?
"Apache Spark is a fast and general-purpose cluster computing system. It provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python and R, and an optimized engine that supports general execution graphs."
"Apache Spark is an open source big data processing framework built around speed, ease of use, and sophisticated analytics."
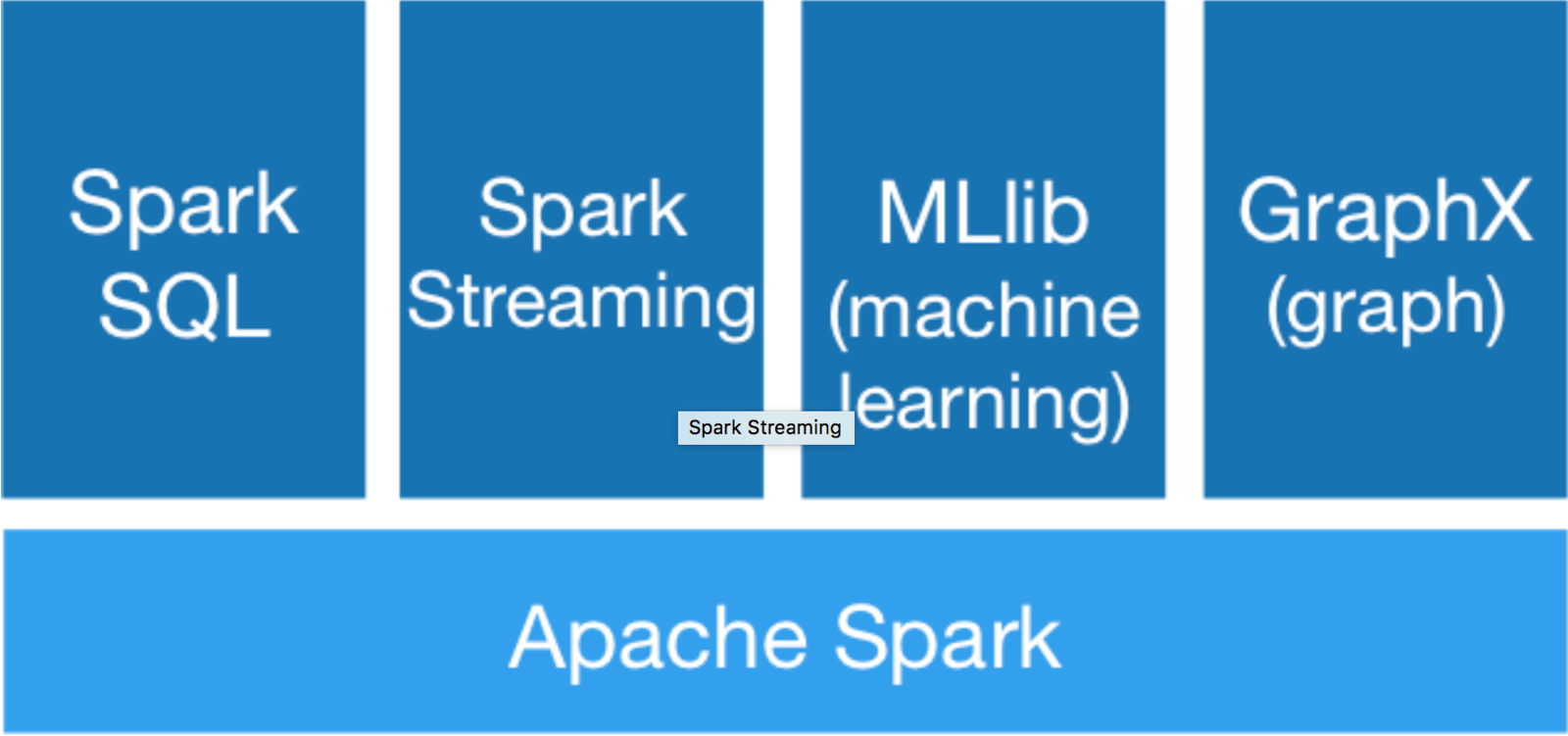
Built-in Libraries
What is Spark comparing to Hadoop?

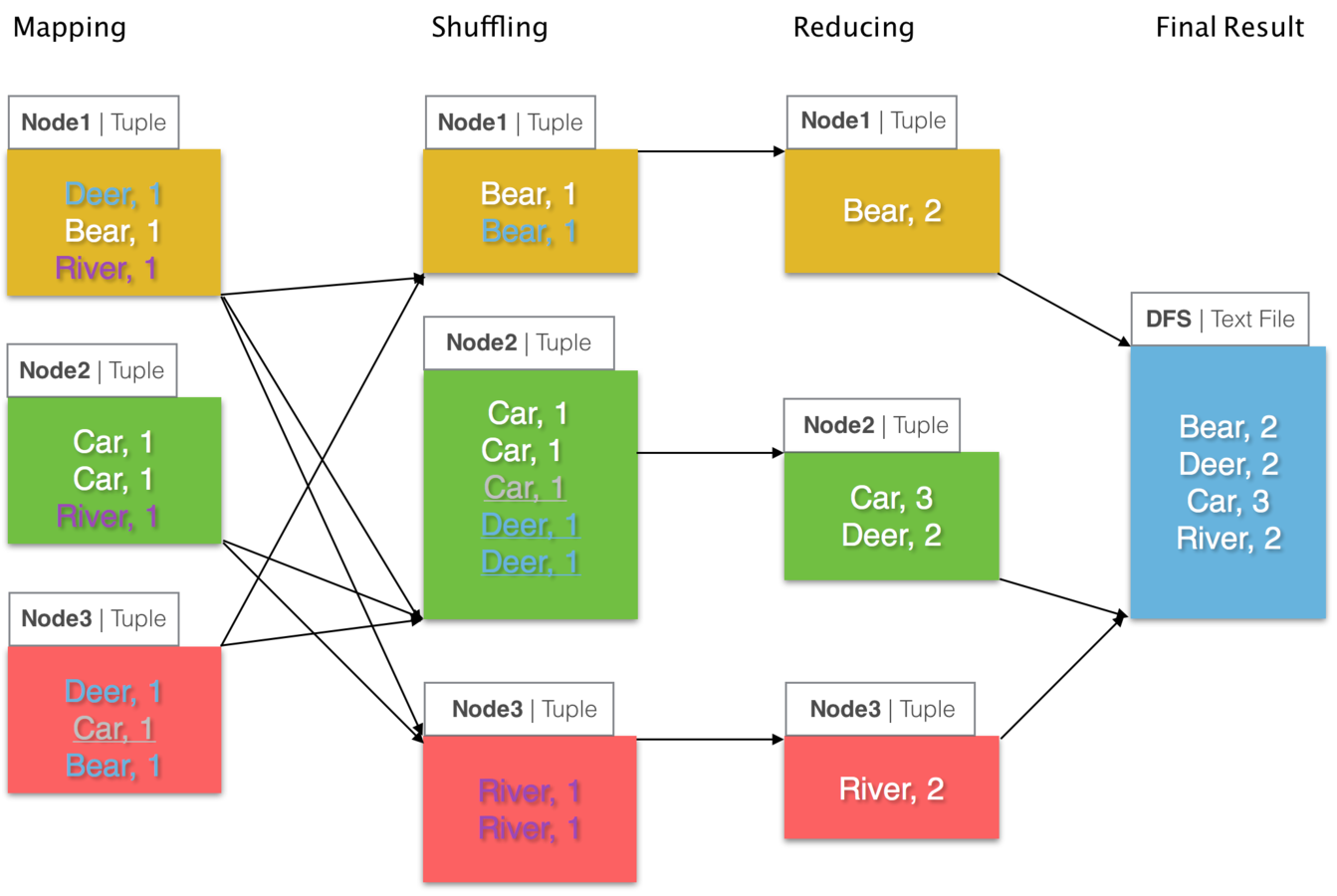
Quick example. Word count
val textFile = sc.textFile("hdfs://...")
val counts = textFile.flatMap(line => line.split(" "))
.map(word => (word, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
counts.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://...")
Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get(URI.create("file:///...")));
Map<String, Long> groups = lines.flatMap(s -> Arrays.stream(s.split(" ")))
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function.identity(),
Collectors.counting()));
groups.forEach((key, count) -> saveAsTextFile(key, count, "file:///..."));using Java Streams:
(red, 2) (fox, 2) (jumps, 2)
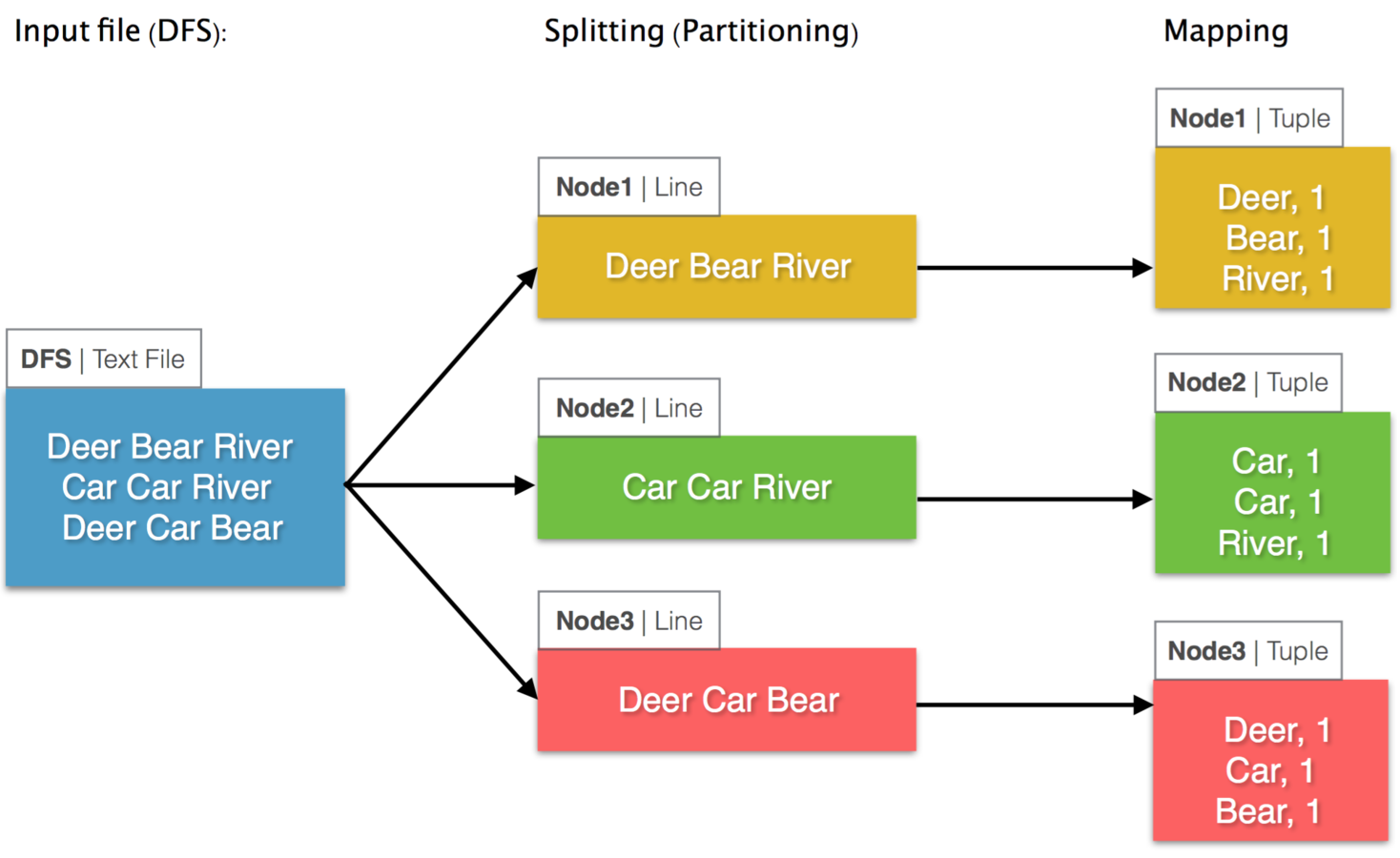
What is happening underneath?
What is happening underneath?
Directed acyclic graph
| map(func) |
| flatMap(func) |
| filter(func) |
| groupByKey() |
| reduceByKey(func) |
| mapValues(func) |
| distinct() |
| sortByKey() |
| ... |
| reduce(func) |
| collect() |
| count() |
| first() |
| take(n) |
| saveAsTextFile(path) |
| countByKey() |
| foreach(func) |
| ... |
Transformations
Actions
Result: another RDD vs primitive and built-in types
Execution: lazy vs immediate
JavaRDD<String> textFile = sc.textFile("hdfs://...");
JavaRDD<String> words = textFile.flatMap(s -> Arrays.asList(s.split(" "));
JavaPairRDD<String, Integer> pairs = words
.mapToPair(s -> new Tuple2<String, Integer>(s, 1));
JavaPairRDD<String, Integer> counts = pairs.reduceByKey((a, b) -> a + b);
counts.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://...");Spark vs Hadoop
public class WordCount {
public static class Map extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(tokenizer.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = new Job(conf, "wordcount");
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}Can be anything calculated by using MapReduce paradigm?
1. calculate sum of all numbers in a file: 1 + 5 + 13 + 27 = 46
2. calculate subtraction: 1 - 5 - 13 - 27 = -44
3. calculate mean: (1 + 5 + 13 + 27)/4 = 11.5
4. sort numbers: [27, 5, 13, 1] = [1, 5, 13, 27]
For example we would like to do the following:
Can be anything calculated by using MapReduce paradigm?
1. calculate sum of all numbers in a file: 1 + 5 + 13 + 27 = 46
plus is associative
2. calculate subtraction: 1 - 5 - 13 - 27 = -44
minus isn't associative (but, 1 - (5 + 13 + 27))
3. calculate mean: (1 + 5 + 13 + 27)/4 = 11.5
break into associative operations
4. sort numbers: [27, 5, 13, 1] = [1, 5, 13, 27]
it can be done OOTB during shuffle step
For example we would like to do the following:
Can RDBMS do computation using SQL?
SELECT ipAddress, COUNT(*) AS total FROM logs GROUP BY ipAddress HAVING total > 10 LIMIT 100
Batch Processing vs Online Processing
Sequential read
Append
- Massive data
- Massive seq read
- Massive append
- Updates & Inserts
- Indexed queries
- Transactions
etc.
Indexed queries
Updates & Inserts
Batch Processing
Online Processing
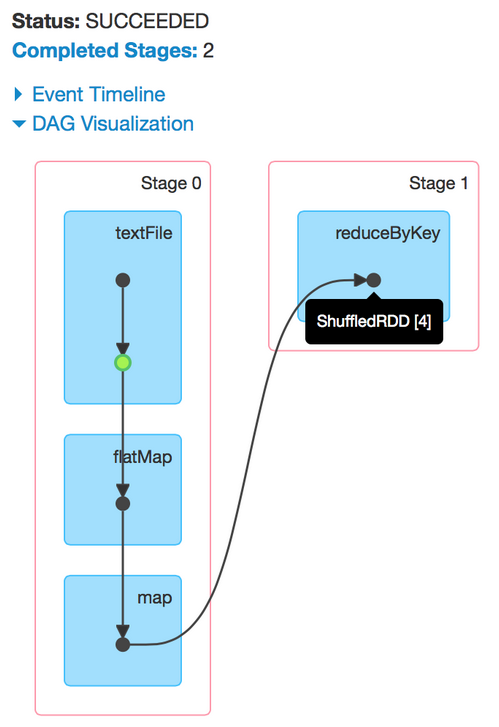
Overview of the flow of a spark job
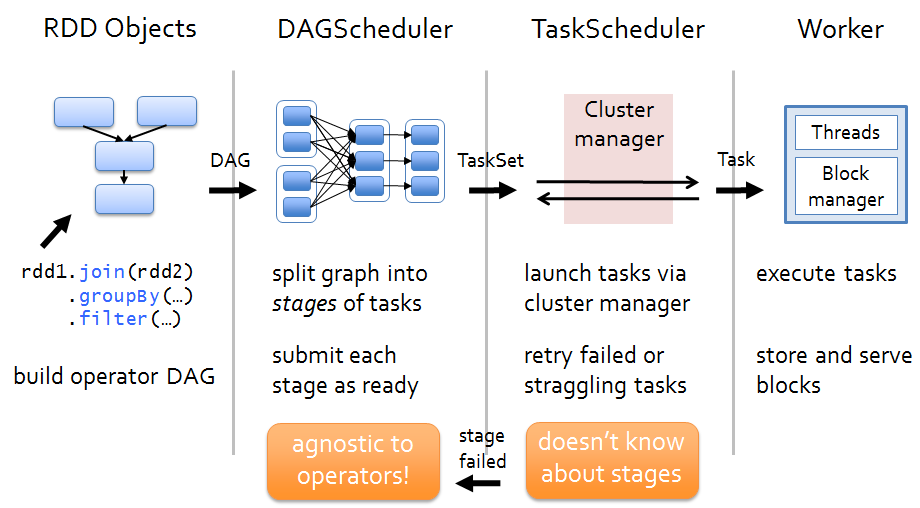

From Driver to Worker
Cluster Manager: Spark standalone, Apache YARN, Apache Mesos
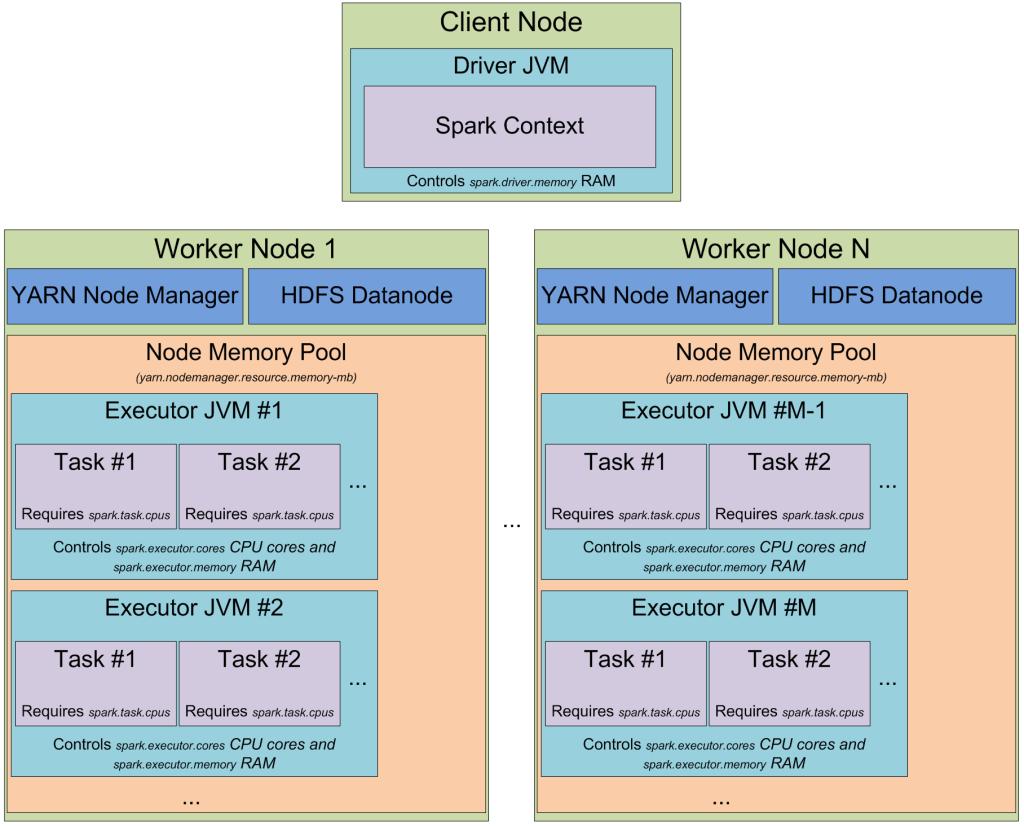
Apache YARN

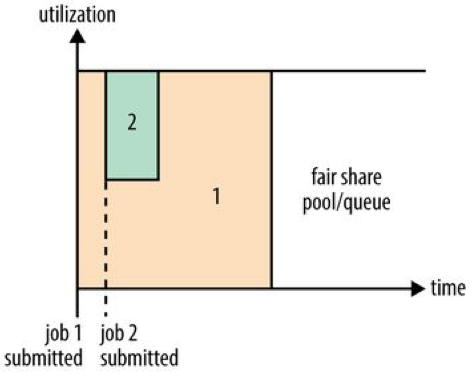
Capacity Scheduler
Fair Scheduler
YARN has following properties: scalability, high availability, good utilization of resources and multitenancy
YARN provides a choice of schedulers and configurable policies
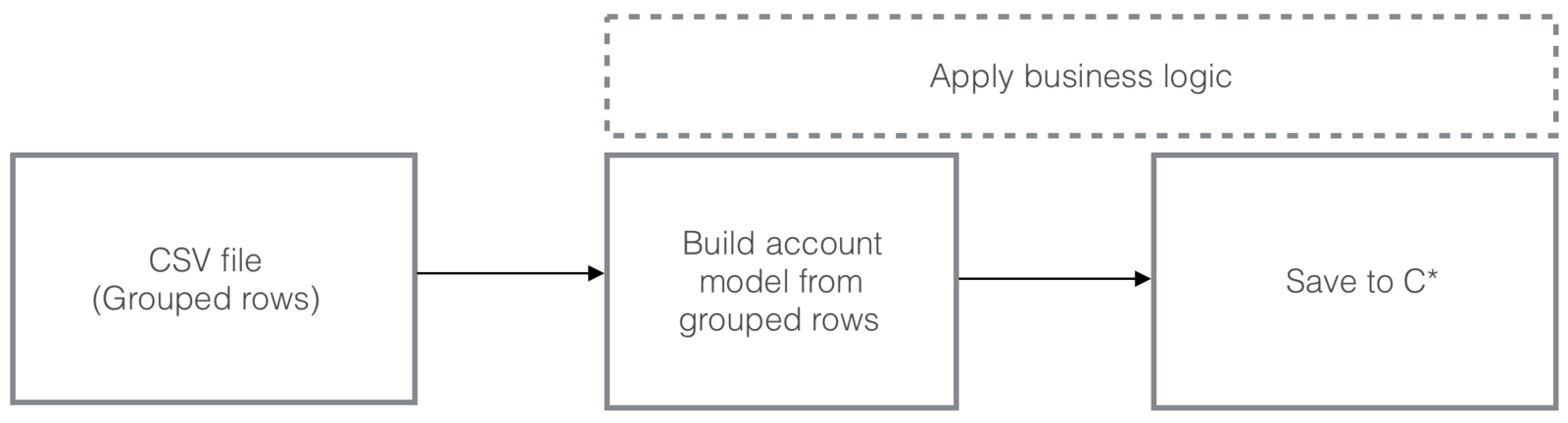
What about our project?
We have one really big csv file and we need to process and import it to C*
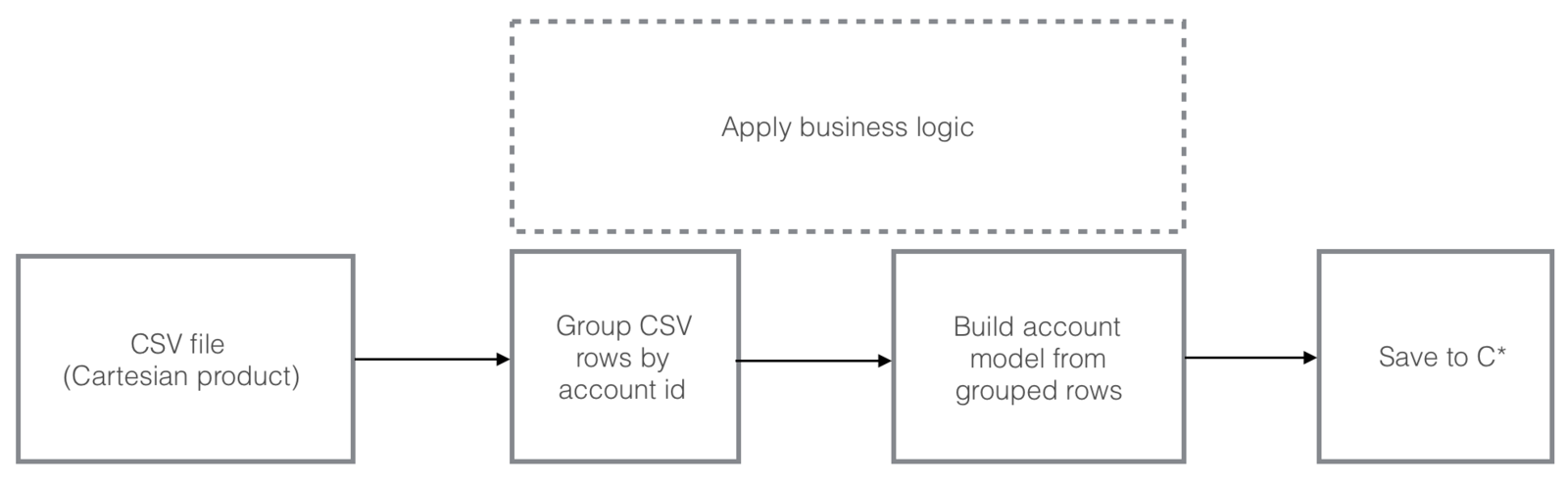
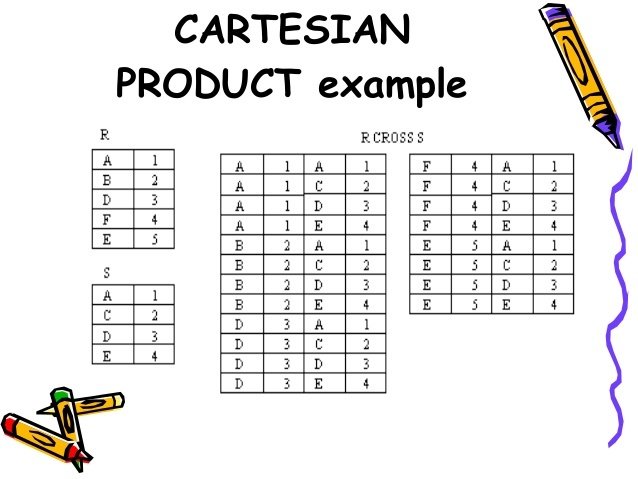
What about our data?
Our DAG
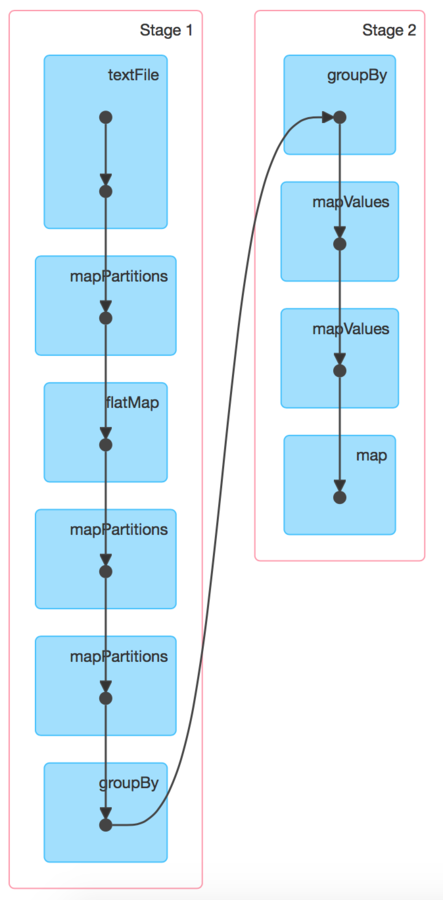
Was it optimal solution?
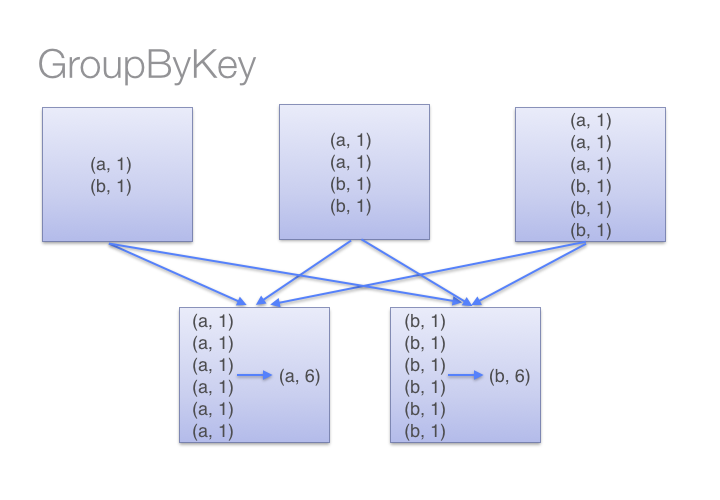
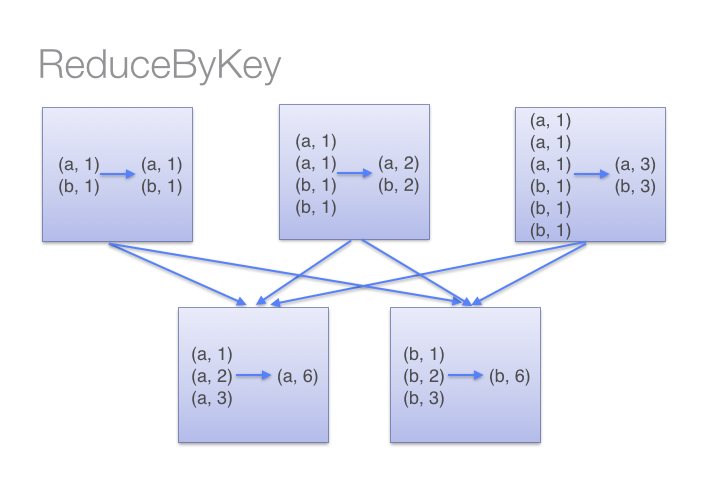
ReduceByKey can apply function locally before shuffle step ~ MapReduce Combiner
Why not Spring Batch?
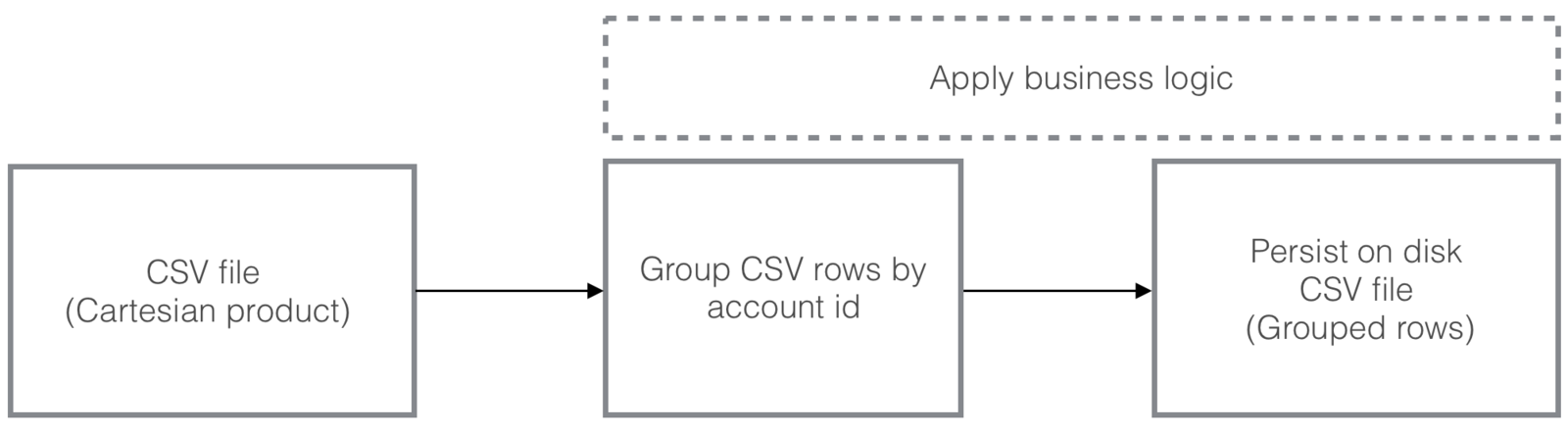
Stage I
Stage II
Spark + Cassandra Data Locality
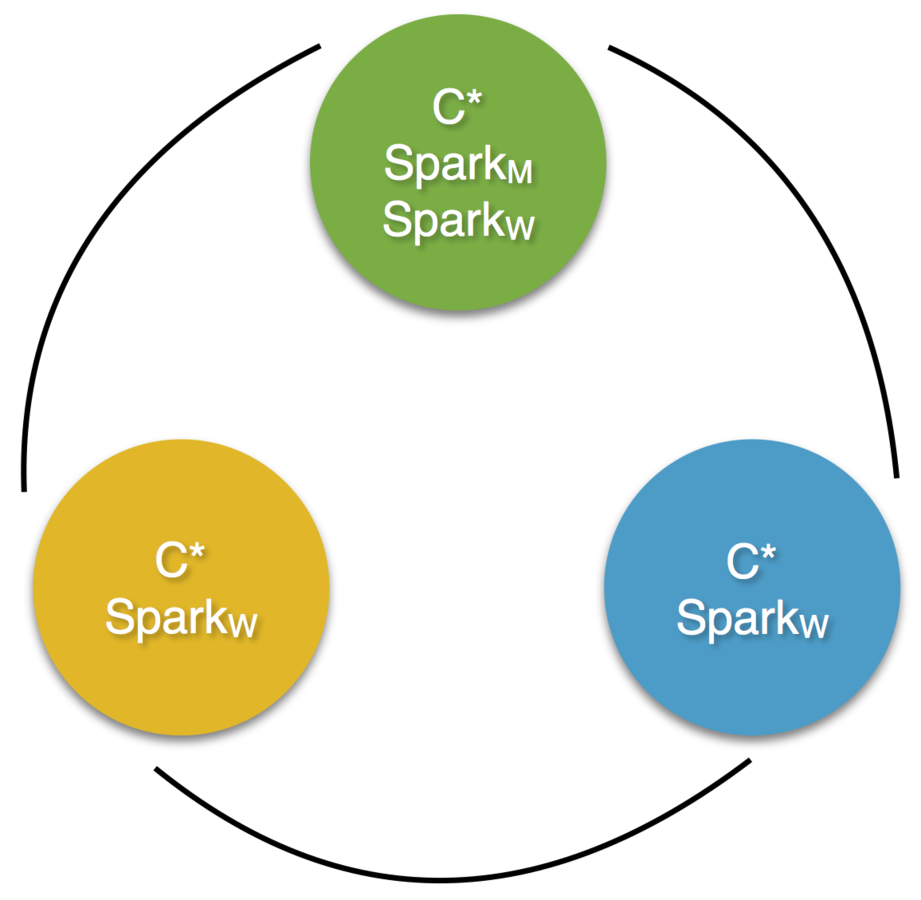
Spark + Cassandra Data Locality
val repartitioned = yourRDD
.repartitionByCassandraReplica("account_schema", "customer_info", 10)
repartitioned.partitions
//... Array(ReplicaPartition(0,Set(/127.0.0.1)), ...)
repartitioned.partitioner
//... com.datastax...ReplicaPartitioner@4484d6c2val localQueryRDD = oddIds
.repartitionByCassandraReplica("account_schema","customer_info")
.joinWithCassandra("account_schema","shopping_history")
repartitionRDD.collect.foreach(println)
//(CustomerID(1),CassandraRow{cust_id: 1,
// address: East Coast, name: Helena})
//(CustomerID(3),CassandraRow{cust_id: 3,
// address: Poland, name: Jacek})repartitionByCassandraReplica:
joinWithCassandra:
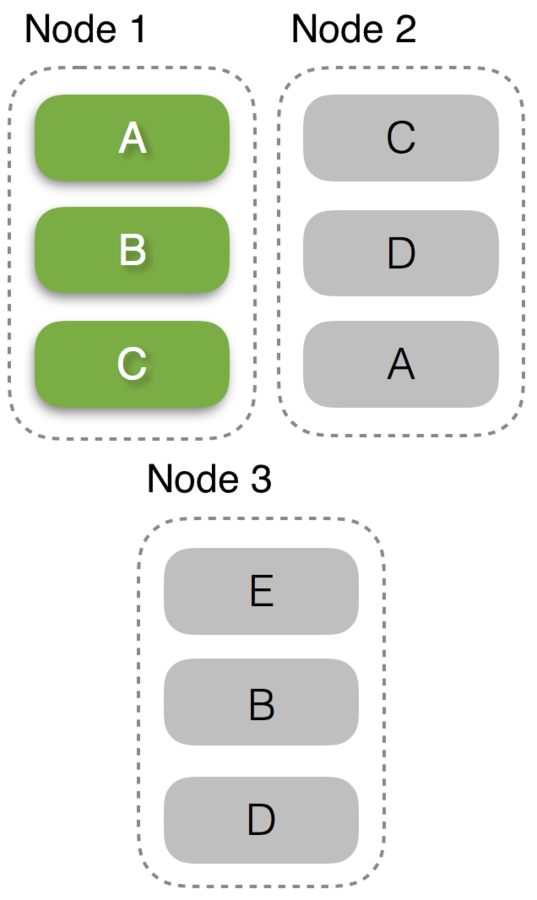
"customer_info" partitions: A,B,C,D,E
How to monitor?
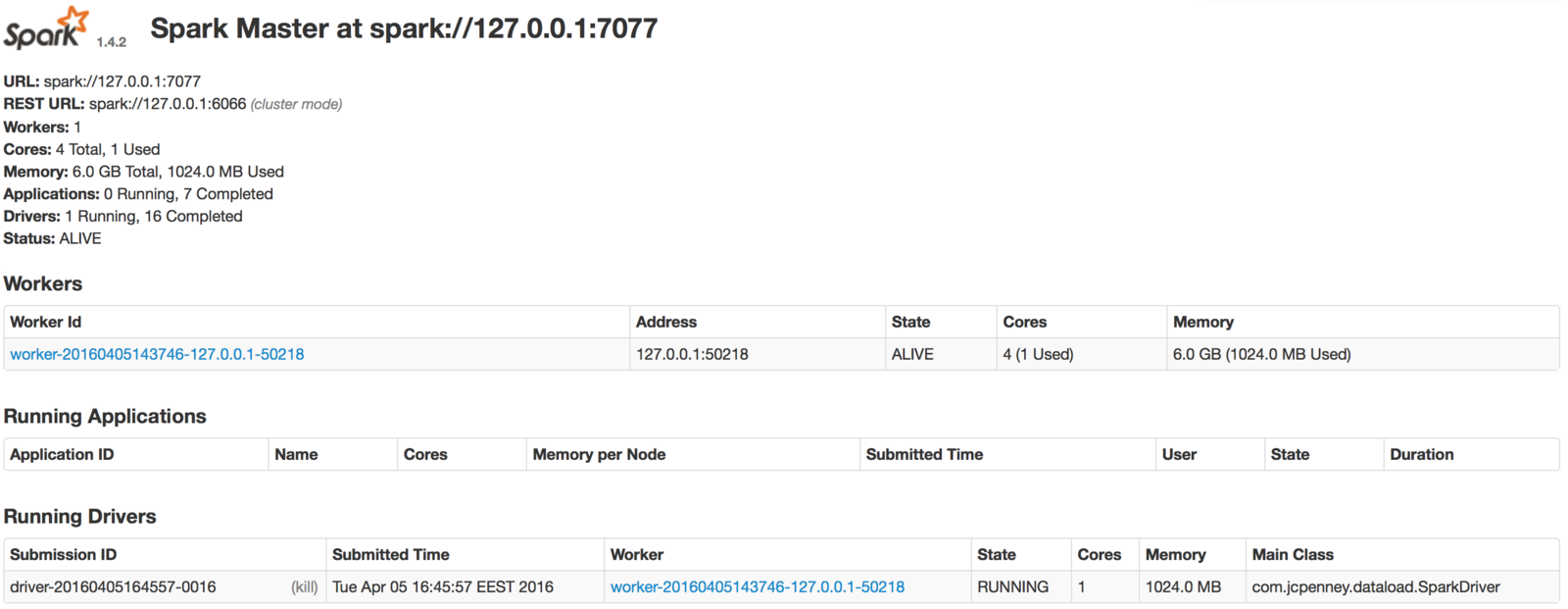
How to monitor?
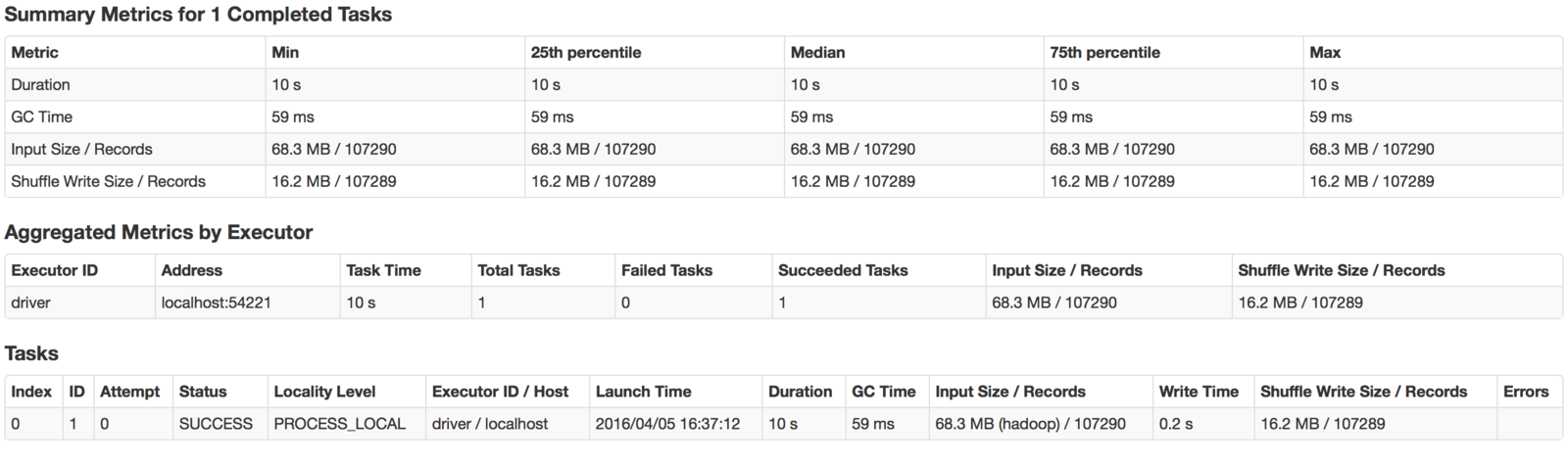
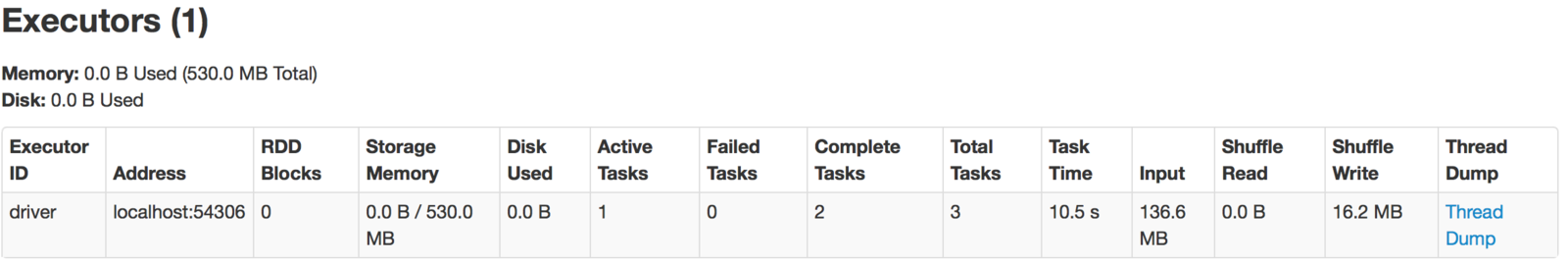
http://localhost:4040
Useful links
http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/
http://www.infoq.com/articles/apache-spark-introduction
http://www.slideshare.net/pumaranikar/spark-presentation-34469395/
https://www.edx.org/course/introduction-spark-uc-berkeleyx-cs105x
Book: Learning Spark: Lightning-Fast Big Data AnalysisFeb 17, 2015 by Holden Karau and Andy Konwinski
https://www.coursera.org/learn/hadoop/
https://www.edx.org/xseries/data-science-engineering-spark
https://trongkhoanguyenblog.wordpress.com/2014/11/27/understand-rdd-operations-transformations-and-actions/
http://www.trongkhoanguyen.com/2014/11/a-gentle-introduction-to-apache-spark.html
https://databricks.com/blog/2015/06/22/understanding-your-spark-application-through-visualization.html
http://0x0fff.com/spark-architecture/
http://0x0fff.com/spark-architecture-shuffle/
http://0x0fff.com/spark-memory-management/
https://bzhangusc.wordpress.com/2014/06/19/optimize-map-performamce-with-mappartitions/
Introduction to Apache Spark
By Alexander Bykovsky
Introduction to Apache Spark
Introduction to Apache Spark. Spark for Bulk Data Load. Processing data using Spark to Cassandra.
- 325



