Machine Learning in Intelligent Transportation
Session 3: Bias Variance Trade off
Ahmad Haj Mosa
PwC Austria & Alpen Adria Universität Klagenfurt
Klagenfurt 2020

Model Generalisation

The central challenge in machine learning is that our algorithm must perform well on new, previously unseeninputs—not just those on which our model was trained.
The ability to perform well on previously unobserved inputs is called generalization.
Goodfellow, Ian; Bengio, Yoshua; Courville, Aaron. Deep Learning (Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning series) (Page 107). The MIT Press. Kindle Edition.
Model Generalisation

Optimization problem: is the minimization process to what is called a training error, which an error measure on the training set.
What separates machine learning from optimization is that we want the generalization error, also called the test error, to be low as well.
Goodfellow, Ian; Bengio, Yoshua; Courville, Aaron. Deep Learning (Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning series) (Page 107). The MIT Press. Kindle Edition.
Training vs Testing

In our linear regression example, we trained the model by minimizing the training error \( MSE_{train} \)
Text
What is also important is the test error \( MSE_{test} \)
Training vs Testing

There are two goals of machine learning systems:
Minimizing the training error
Make the gap between training and test error small
These two factors correspond to the two central challenges in machine learning: underfitting and overfitting
1
2
Training vs Testing

Underfitting occurs when the model is not able to obtain a sufficiently low error value on the training set.
Overfitting occurs when the gap between the training error and test error is too large.
capacity is its ability to fit a wide variety of functions.
Models with low capacity may struggle to fit the training set.
Models with high capacity can overfit by memorizing properties of the training set that do not serve them well on the test set.
Bias-Variance Tradeoff

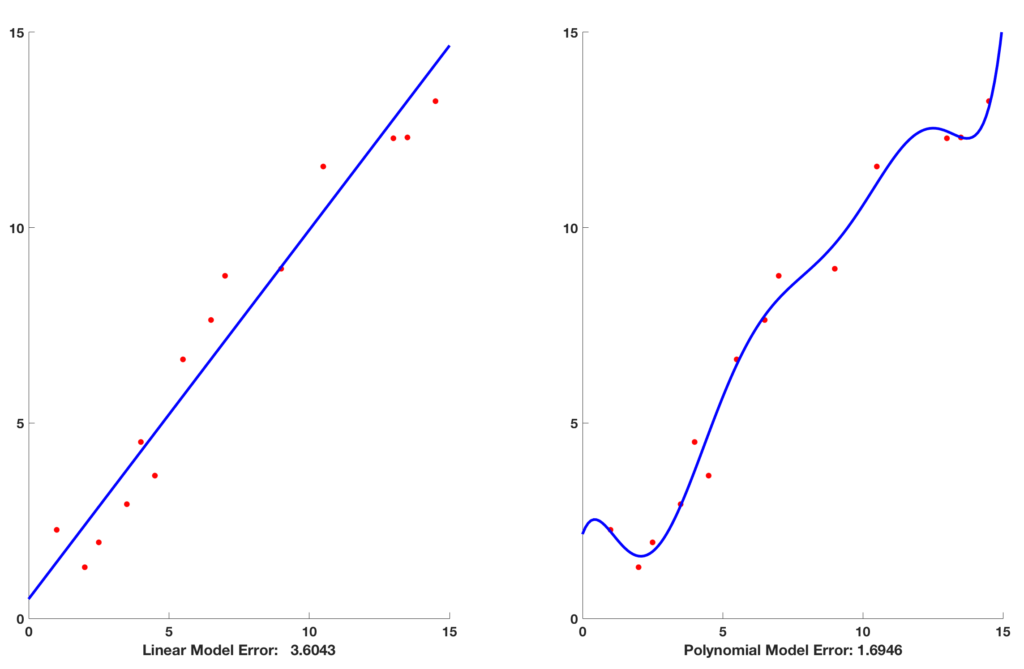
- On the left fit a line to the data points. A line is just a polynomial of degree 1.
- Naturally, the line cannot pass through all the points, and there is an error between data ( red dots ) and the predicted value ( blue line ).
- In this example, the error is approximately 3.6. If this error is too large, we say the model is underfitting the data.
Bias-Variance Tradeoff


- The Linear model does not fit the data very well and is therefore said to have a higher bias than the polynomial model
- With a Polynomial model of degree 8, The error goes down to approximately 1.69.
- The Linear model does not fit the data very well and is therefore said to have a higher bias than the polynomial model
Bias-Variance Tradeoff


- On the left, we see the training error of both linear and polynomial models
- On the right, we the testing errors
-
For the linear model, the error on this test set is very close to the error he had seen on the training set. In such cases, we say the model has generalized well to unseen data.
-
For the polynomial model, the error is very high (929.12)!. This problem, where the model does very well on the training data but does poorly on the test data is called overfitting.
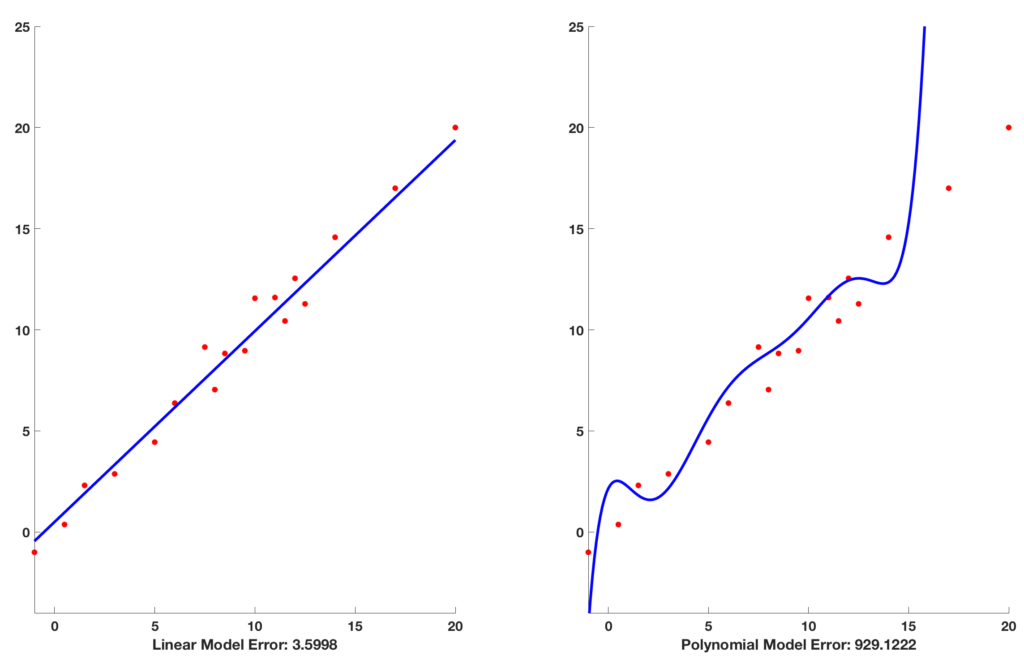
Bias-Variance Tradeoff

the Linear model (low capacity) had a higher bias
The polynomial model, on the other hand, suffers from a different problem. The model depends a lot on the choice of training data. If you change the data slightly, the shape of the curve will look very different, and the error will swing widely. Therefore, the model is said to have high variance.
Machine Learning is not a pursuit of perfection (i.e. zero error), but it is about seeking the best tradeoff.
Common Training Approach

Divide the data into three parts
Training set: The training set is typically 60% of the data. As the name suggests, this is used for training a machine learning model.
Validation set: The validation is also called the the development set. This is typically 20% of the data. This set is not used during training (not including in the training cost function ). It is used to test the quality of the trained model. Errors on the validation set are used to guide the choice of model (e.g. what value of neurons/layers). Even though this set is not used for training, the fact it was used for model selection makes it a bad choice for reporting the final accuracy of the model.
Test set: This set is typically 20% of the data. Its only purpose is to report the accuracy of the final model.
K-Folds Cross Validation

Create a K-fold partition of the the dataset
For each of K experiments, use ( k-1 ) folds (i.e 3) for training and a different fold for testing
Text
Experiment 1
Experiment 2
Experiment 3
Experiment 4
the true error is estimated as the average error rate on test examples
Common Training Approach

In Machine Learning : the errors made by your model is the sum of three kinds of errors
Total Error = Bias + Variance + Irreducible Error
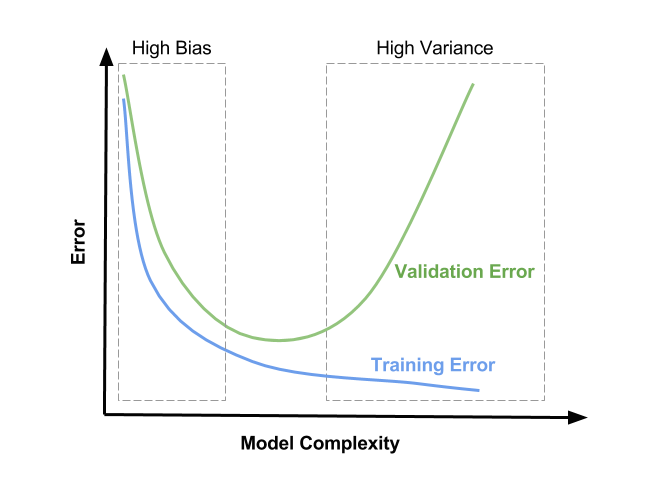
- The region on the left, where both training and validation errors are high, is the region of high bias.
- The region on the right where validation error is high, but training error is low is the region of high variance.
- We want to be in the sweet spot in the middle.
Common Training Approach

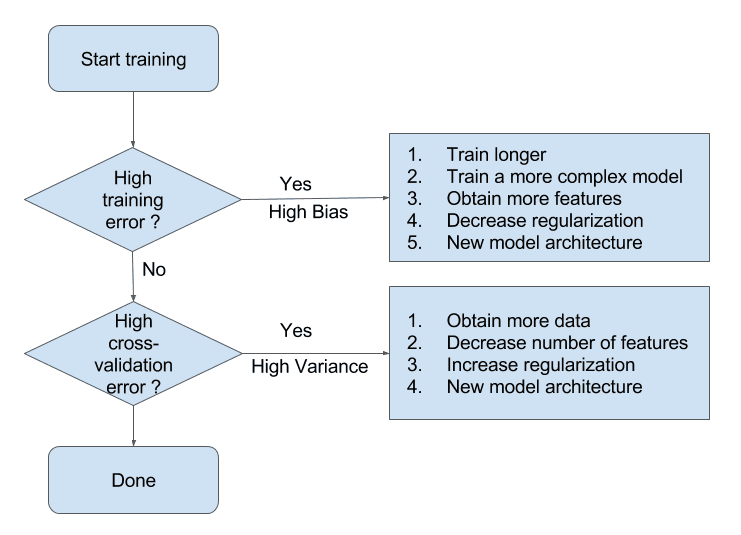
How to detect a high bias problem?
- High training error.
- Validation error is similar in magnitude to the training error
How to detect a high variance problem?
- Low training error.
- Very high validation error



Common Training Approach

Copy of Session 3: Challenges of Learning
By ahmadadiga
Copy of Session 3: Challenges of Learning
- 183



