Machine Learning in Intelligent Transportation
Session 1: Introduction
Ahmad Haj Mosa
PwC Austria & Alpen Adria Universität Klagenfurt
Klagenfurt 2020

Contents

-
Backgrounds
-
History of Artificial Intelligence
-
Definitions
-
Terminologies
-
Machine Learning Tasks
-
Machine Learning Branches
-
Syllabus and Assessments
Objectives of this course

Text
Deep Learning Theory
Natural Language Processing
DL based Machine Vision
Reinforcement Learning
Machine Learning fundamentals
Statistical Machine Learning
Conventional Machine Vision
Course Plan

Text
Linear Regression
Logistics Regression
Shallow/Deep Neural Network
Back propogation algorithms
Convolutional Neural Network
Recurrent Neural Network
Semantic Segmentation
Generative Adversarial Network
Course Plan

-
Day 1:
-
Linear Regression
-
Logistic Regression
-
Shallow Neural Networks
-
Backpropogation Algorithm
-
Variance-Bias Tradeoff
-
-
Day 2:
-
CNN
-
Semantic Segmentation
-
Autoencoders
-
Mask CNN
-
-
Day 3:
-
Recurrent NN
-
LSTMs
-
NLP
-
Transformers
-
-
Day 4:
-
Deep RL
-
AlphaGo Zero
-
GANs
-
History of Artificial Intelligence

History of Artificial Intelligence

AI technologies

Text
Definitions

Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence (AI)
that provides computers with the ability to learn without being explicitly
programmed.
Machine learning is a computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P , if its performance at tasks in T , as measured by P , improves with experience E .
Margaret Rouse
Tom Mitchell
Example 1:

A handwriting recognition learning problem:
- Task T: recognizing and classifying handwritten
words/digits within images
- Performance measure P: percent of words/digits correctly classied
- Training experience E: a database of handwritten words with given classications
Applications

Learning to recognize spoken words:
All of the most successful speech recognition systems employ machine learning in some form.



Alexa
Google Assistant
Zenbo Robot
Applications

Self Driving Cars
Nvidia, Uber, and Tesla all use deep learning as one of the main model in their self driving cars

Applications

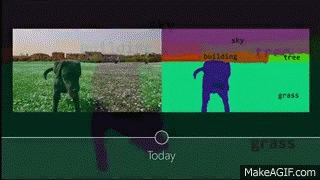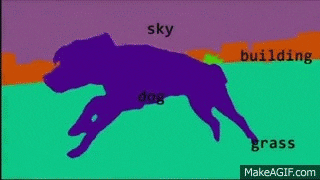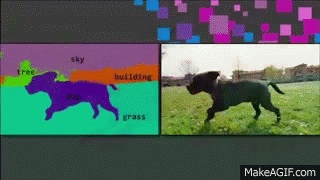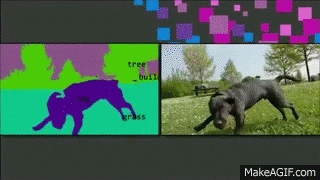
Medical Imaging
Deep Learning is playing a key role in the future of medical imaging dignoses
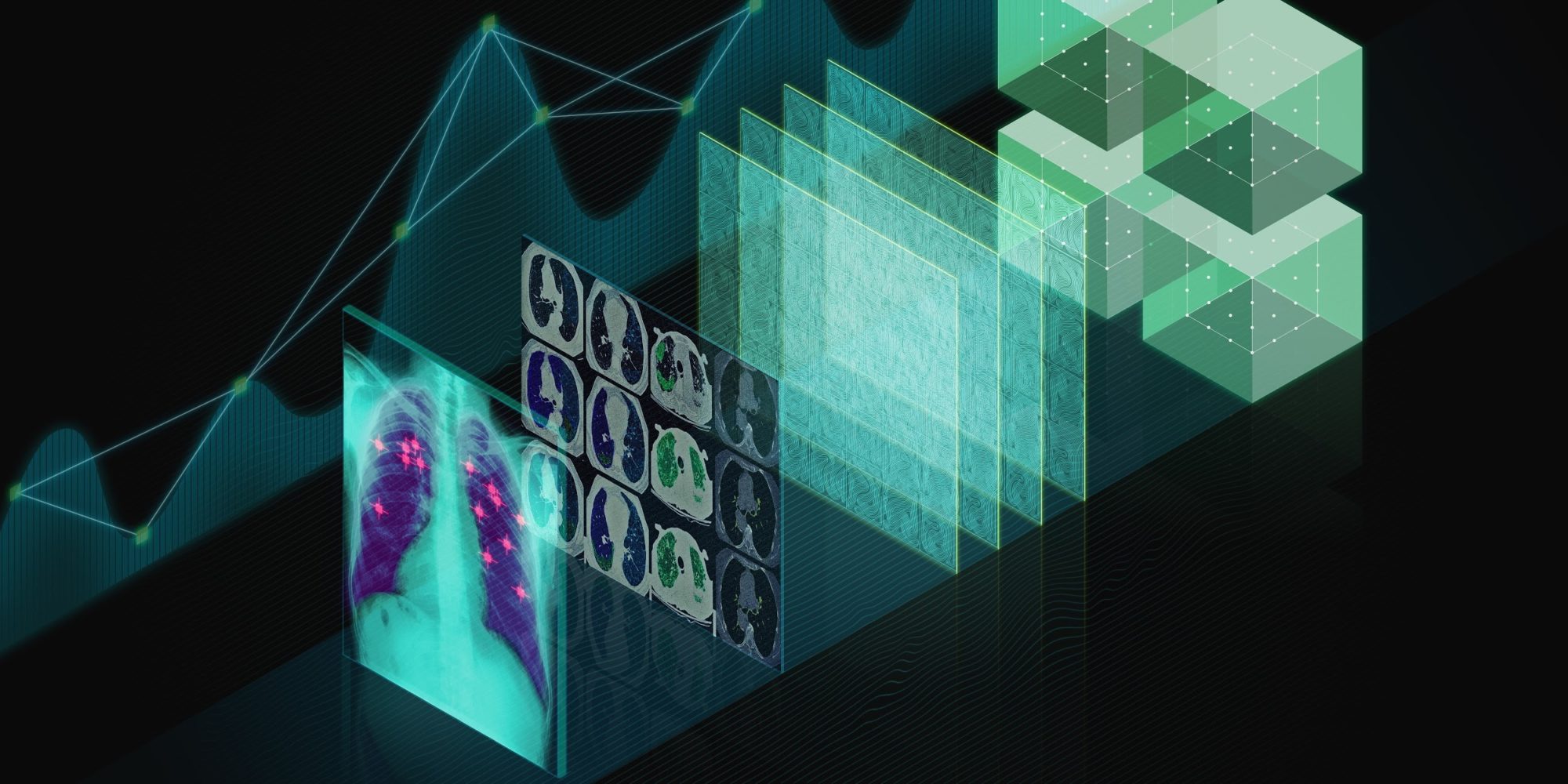
Applications

Terminologies

Data
- Refers to digital (sensor, transactions or text data)
- It could be the output of a device that detects and responds to some type of input from the physical environment .
- It could be a set conversation data collected from a messenger database.
Terminologies

Features / Attributes
- A quantity describing an instance/sample.
- An attribute has a domain defined by the attribute type, which denotes the values that can be taken by an attribute.
- It is a representation that the learning program will use to describe the studied problem.
In case of vision system: colors, edges, motion filed, depth are examples of low level features
In case of acoustic system: frequency, pitch, amplitude are examples of low level features
In case of financial trading: the historical trends, statistical moments (mean, variance)
Example 2:

Features / Attributes
- Considering the house price example let us choose a simple one feature:
| House Size in | House Price in $ |
|---|---|
| 80 | 100k |
| 100 | 120k |
| 120 | 130k |
| 56 | 56k |
| 64 | 70k |
Terminologies

Decision Function/Hypothesis
- A decision function is a function which takes features as input and gives a decision as output
- Decision functions are a mathematical models that maps inputs to targets
In case of self driving cars: the output of the decision function is the steering angle
In case of voice recognition: the output selects a predicted action of a set of actions
Example 3:

- Considering the house price example let us choose a simple linear decision function:
Decision Function/Hypothesis
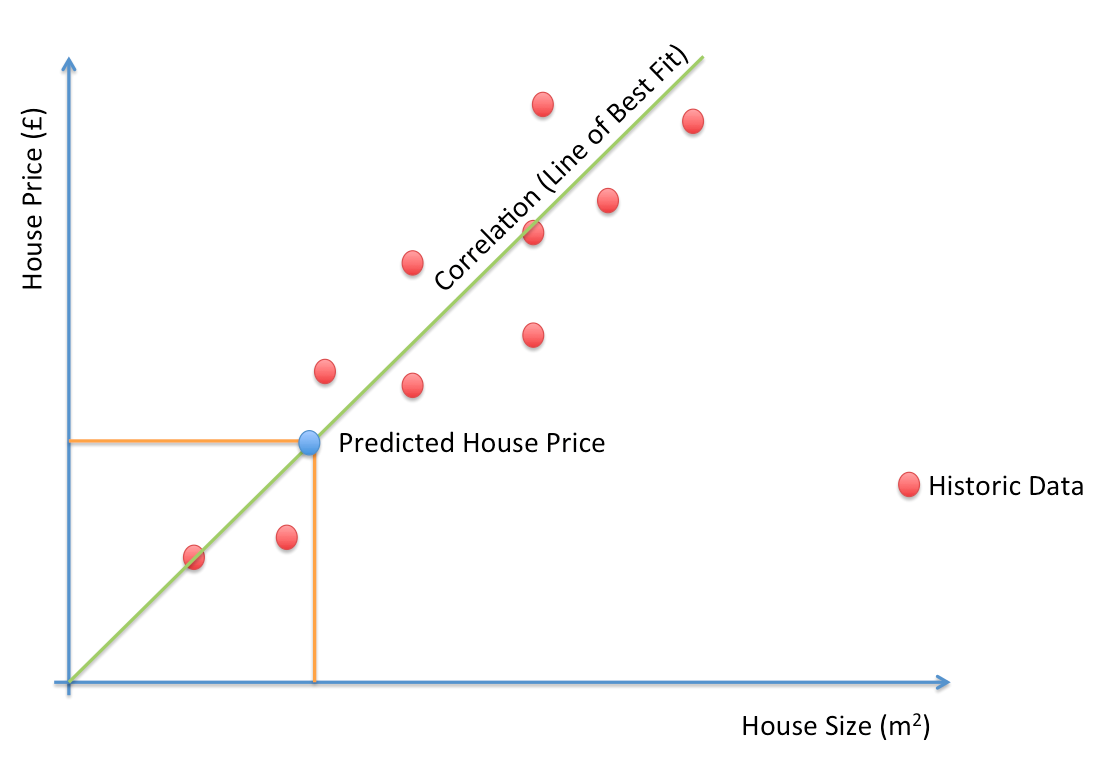
Terminologies

Model Training/Learning
- In order to learn the decision function \(y(x) \) we require a set of training examples, each example \(i\) contains a specific output value (house price) \(y_i\) and the related features value (house size) \(x_i\)
- Then the training process estimates the weights \(\omega \) so that the function \(y_i\) fits the data with the minimum possible error
Terminologies

Performance/Cost/Loss
- A measurement of the cost to the performance task of making a prediction \(y^{\prime}\) when the actual label is \(y\) :
- For example one of the most used cost function is the mean squared error:
where \(e_t = ( y^{\prime}- y_t) \)
Machine Learning Tasks

1. Classification
Machine learning task are categorized by the target of the studies problems as follows:
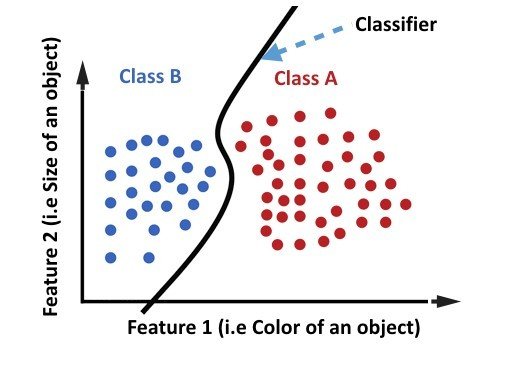
is the problem of identifying to which of a set of categories (sub-populations) a new observation
Machine Learning Tasks

1. Regression
Machine learning task are categorized by the target of the studies problems as follows:
is the problem of identifying the relationship (mathematical model) among different variables

Machine Learning Tasks

3. Clustering
Machine learning task are categorized by the target of the studies problems as follows:
is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters)
Machine Learning Tasks

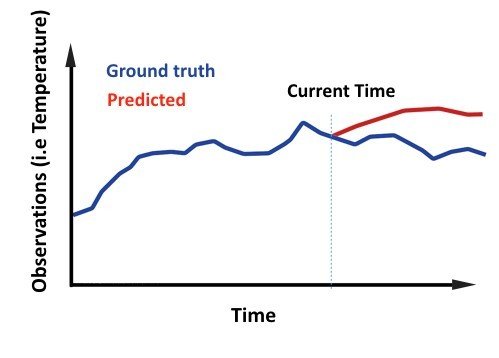
4. Time Series Forecast
Machine learning task are categorized by the target of the studies problems as follows:
Time series forecasting is the use of a model to predict future values based on previously observed values
Machine Learning Branches

The computer is presented with example inputs and their desired outputs, and the goal is to learn a decision function that maps inputs to outputs.
No labels are given to the learning algorithm, leaving it on its own to find structure in its input. Unsupervised learning can be a goal in itself (discovering hidden patterns in data) or a means towards an end (feature learning).
where the teacher gives an incomplete training signal: a training set with some (often many) of the target outputs missing.
Supervised
Unsupervised
Semi Supervised
Machine Learning Branches

A computer program interacts with a dynamic environment in which it must perform a certain goal (such as driving a vehicle or playing a game against an opponent[4]:3). The program is provided feedback in terms of rewards and punishments as it navigates its problem space
is a branch of machine learning that attempt to model high level abstractions. DL can be supervised, Unsupervised, Semi Supervised and Reinforcement learning. The common model used in DL is Neural Networks
Reinforcement
Deep Learning
Copy of Session 1: Introduction
By ahmadadiga
Copy of Session 1: Introduction
- 299




