Knowledge extraction from text
I'm Alex, Burlacu
Long story short - I use ML to extract knowledge from text @ DevelopmentAid
Before that worked with images, time series and it all started with text and sentiment analysis
So, I guess, I'm back to where it started
Data mining from text?
- Extract entities (NER)
- Extract parts of speech (POS)
- Classification (Sentiment Analysis, etc)
- Natural language understanding (Co-reference resolution, relation extraction)
Classic approach
Use parsers and narrowly specialized algorithms.
Works well with small data.
A more recent way
Just throw it into a big neural network, which was already pre-trained on huge amount of data.
Isn't clear how it works, but it works, better than the classic approach (to my knowledge)
Generic Pipeline Overview
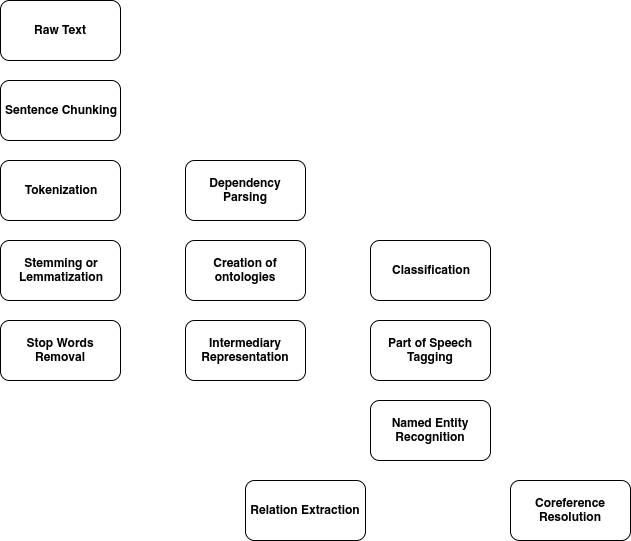
How to use ML to conquer text?
- Use text vectors (TF-IDF -> Word2Vec -> Smth2Vec)
- Or, use a full blown neural network (LSTM and variants)
- Or, use a pre-trained model (BERT, OpenAI's GPT-2, etc)
Need a way to make text understandable for algorithms
TF-IDF
TF-IDF
- Term Frequency - Inverse document frequency
- Reflects the importance of a word in a document corpus
- One of the most used and robust methods in practice
Word2Vec
Skip-gram and CBoW
CBoW - continuous bag of words
- Tries to predict the middle word given a context window
- Uses probabilities of every word in the vocabulary
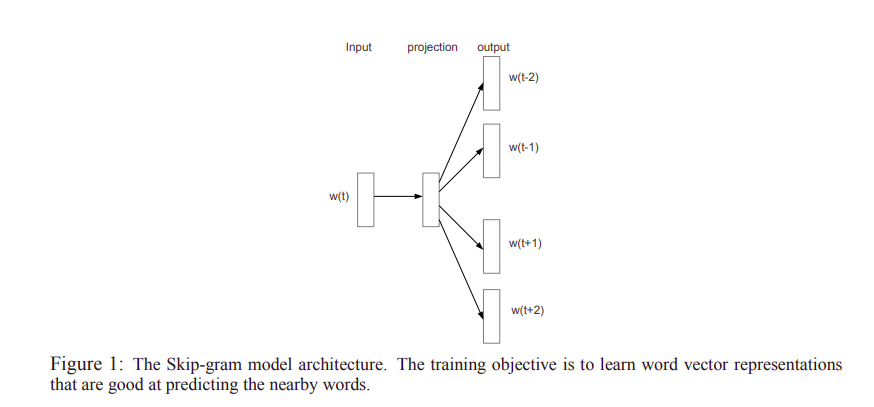
Mikolov et al - Distributed "Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality"
LSTM
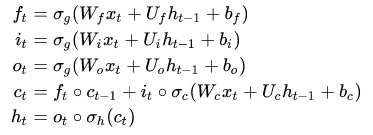
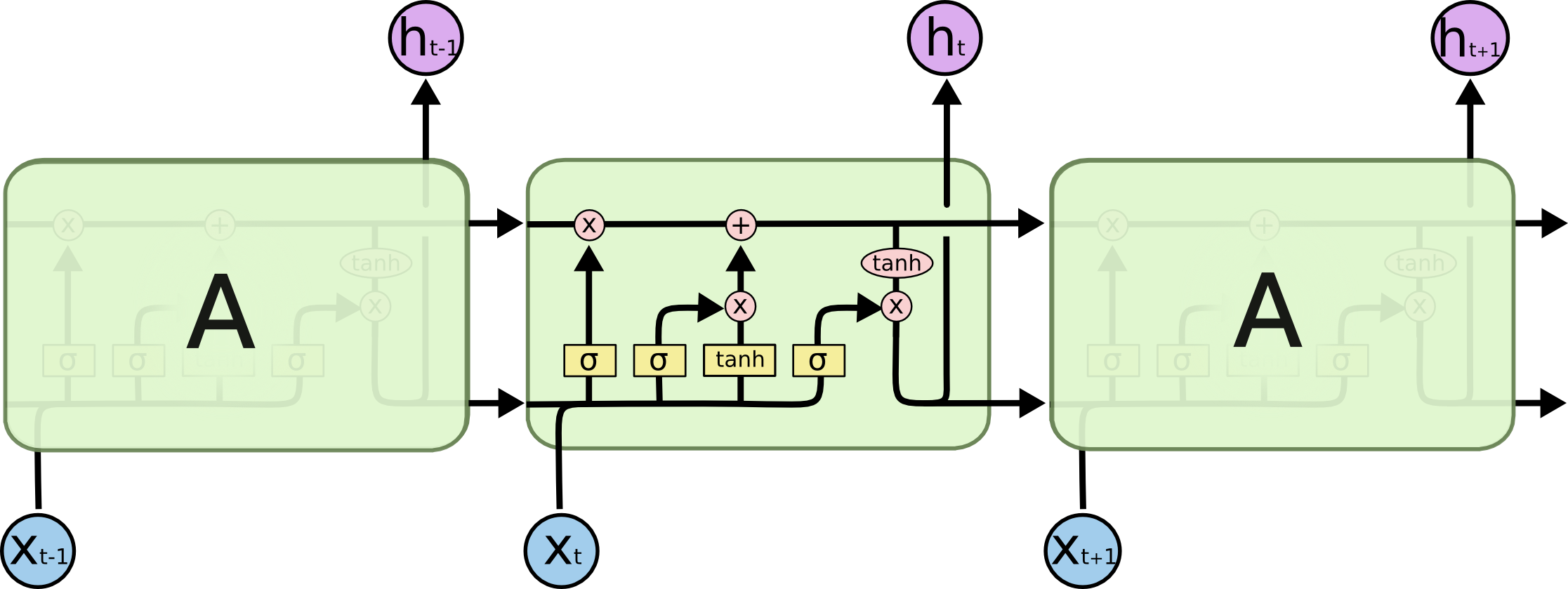
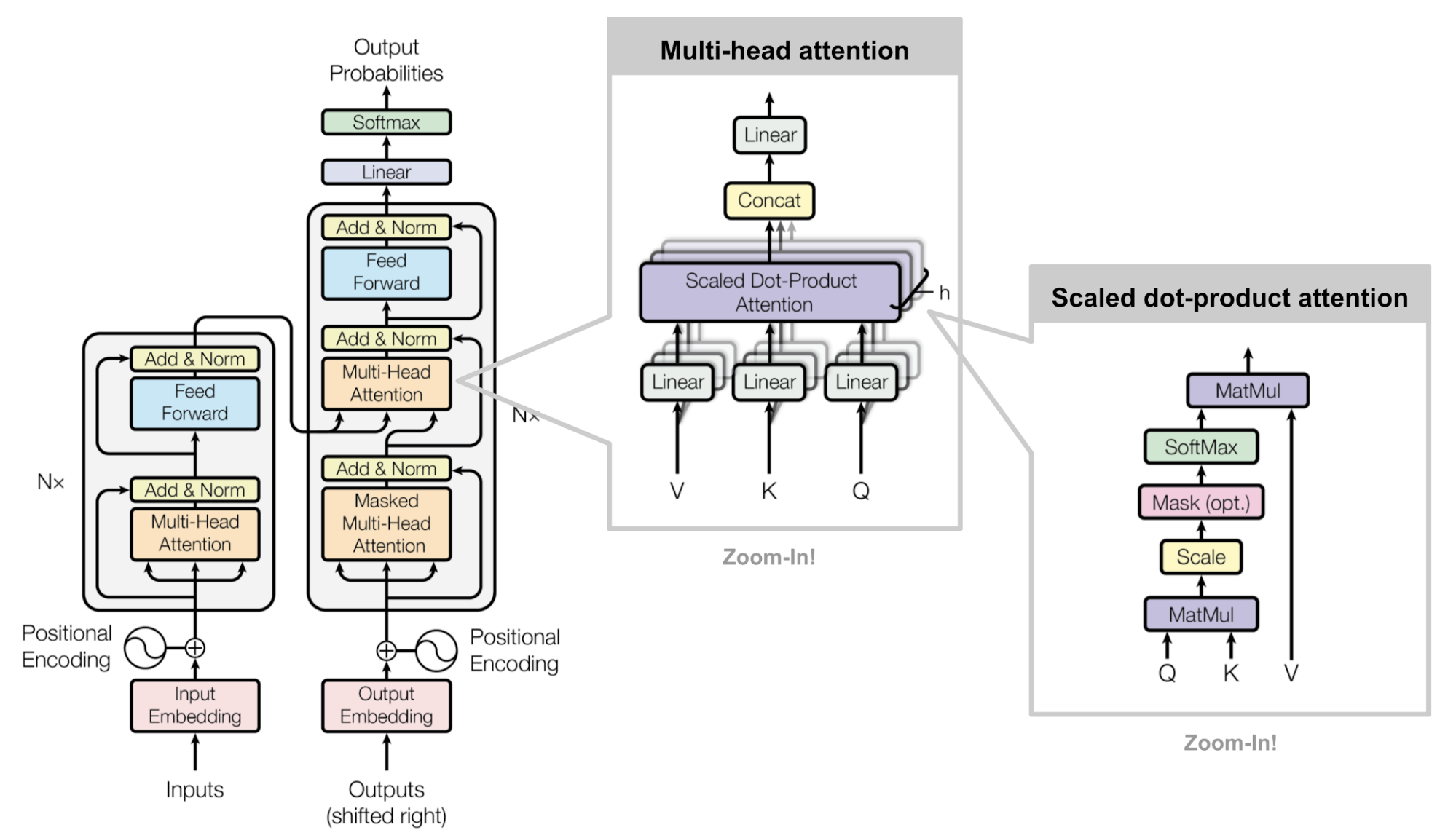
Transformers
(BERT, GPT-2)
Transformers use a mechanism called attention
Attention is a mechanism for creating context vectors that are sum of hidden states weighted by some alignment scores
Initially created for NMT attention helped propagate the important signals further in time and also provide interpretability, in a way
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, k, heads):
super().__init__()
self.attention = SelfAttention(k, heads=heads)
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(k)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(k)
self.ff = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(k, 4 * k),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(4 * k, k))
def forward(self, x):
attended = self.attention(x)
x = self.norm1(attended + x)
fedforward = self.ff(x)
return self.norm2(fedforward + x)class SelfAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, k, heads=8):
super().__init__()
self.k, self.heads = k, heads
self.tokeys = nn.Linear(k, k * heads, bias=False)
self.toqueries = nn.Linear(k, k * heads, bias=False)
self.tovalues = nn.Linear(k, k * heads, bias=False)
self.unifyheads = nn.Linear(heads * k, k)
def forward(self, x):
b, t, k = x.size()
h = self.heads
queries = self.toqueries(x).view(b, t, h, k)
keys = self.tokeys(x) .view(b, t, h, k)
values = self.tovalues(x) .view(b, t, h, k)
keys = (keys.transpose(1, 2)
.contiguous().view(b * h, t, k))
queries = (queries.transpose(1, 2)
.contiguous().view(b * h, t, k))
values = (values.transpose(1, 2)
.contiguous().view(b * h, t, k))
queries = queries / (k ** (1/4))
keys = keys / (k ** (1/4))
dot = torch.bmm(queries, keys.transpose(1, 2))
dot = F.softmax(dot, dim=2)
out = torch.bmm(dot, values).view(b, h, t, k)
out = (out.transpose(1, 2)
.contiguous().view(b, t, h * k))
return self.unifyheads(out)
Think that's it?
Haha!
*entering the cutting edge of the domain*
Multi-task learning
Experiments show that having a single Deep Learning model learn to perform multiple related tasks enhance its performance
For example BERT uses 2 pre-training tasks, missing word insertion (Cloze test) and next sentence prediction
Self-supervision
Self-supervision - extracting a supervision signal from the data itself. Feels like usupervised learning, works like supervised
In case of BERT, it actually uses self-supervision for pre-training.
Language modeling, back-translation, next sentence prediction, Cloze test. These are some self-supervised methods for text
Thank you
Questions?
Reading List
Knowledge extraction
By Alexandru Burlacu
Knowledge extraction
- 330



