Blockchains and Smart Contracts for the
Internet of Things
IoTx
Blockchain
Structure
- What is IoT?
- Why Blockchain
- Blockchain + IoT
- Conclusion
IoT
Real-time, High-resolution data through:
- Hardware: Sensors & Devices
- Connectivity: Information transfer
- Software: Analysis of data
- User Interface: Window for users to interact with IoT
Gaps & Problems
- High maintenance overhead
- Updates to millions of devices
- Time-consuming workflow
- Not enough transparency
How Can Blockchain Help?
- Decentralized network
- Trustless => Fast reconciliation
- Self-executing scripts
Blockchain
- Every node keeps copy of Blockchain
- Chain of validated transactions
- Ledger of who owns what

Public
- Anyone can participate
- One person can impersonate multiple entities
- Expensive consensus mechanism
Private
- Only whitelisted participants
- Varying degree of role: Mine, transact etc
- Less expensive consensus mechanism
Smart Contracts
"Computerized transaction protocol"
- Scripts on blockchain
- Enable general computation
- Data-driven interactions

Smart Contract: Trade
- Smart contracts have unique address
- Contains 3 functions
- Deposit
- Trade
- Withdraw

15X
1Y 10X
1Y
5X
- Service & Resource Sharing
- Workflow automation
IoTxBlockchain:
Applications
Service Sharing:
Firmware Update
- All IoT devices on Blockchain
- Firmware served by manufacturer's node
- After propagation, stop serving
- Newer nodes get firmware from network





Resource Sharing: Slock.it
- Smart contracts sell tokens to unlock properties

Token


Solar Power Sales
- Smart contracts sell solar energy



Shipping Workflow Automation
- Problem: Each stakeholder maintains own database
- Result: Reduce dispute among stakeholders
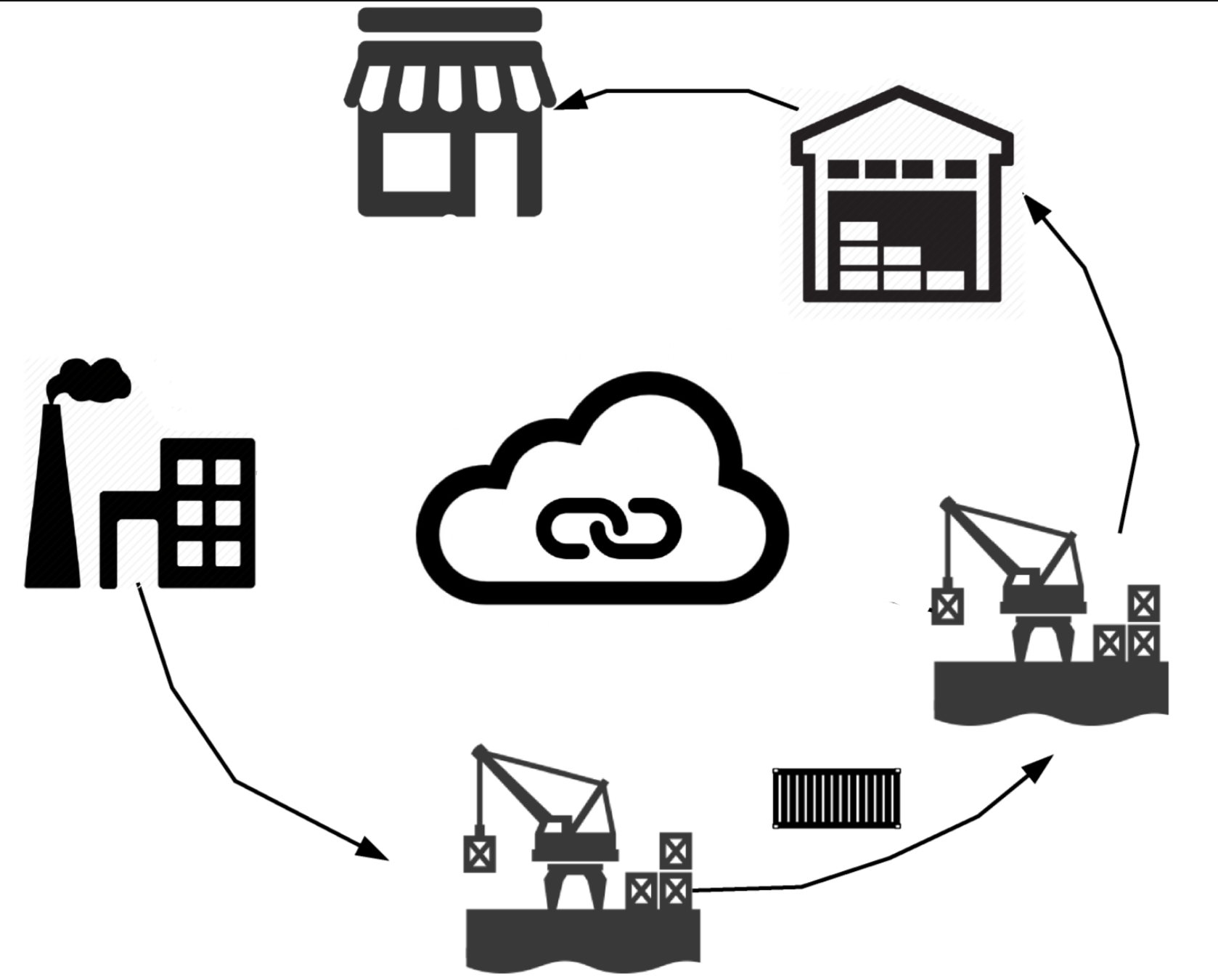
Shipping Workflow Automation
One step further: Automate Blockchain transaction with IoT devices (LTE radio)
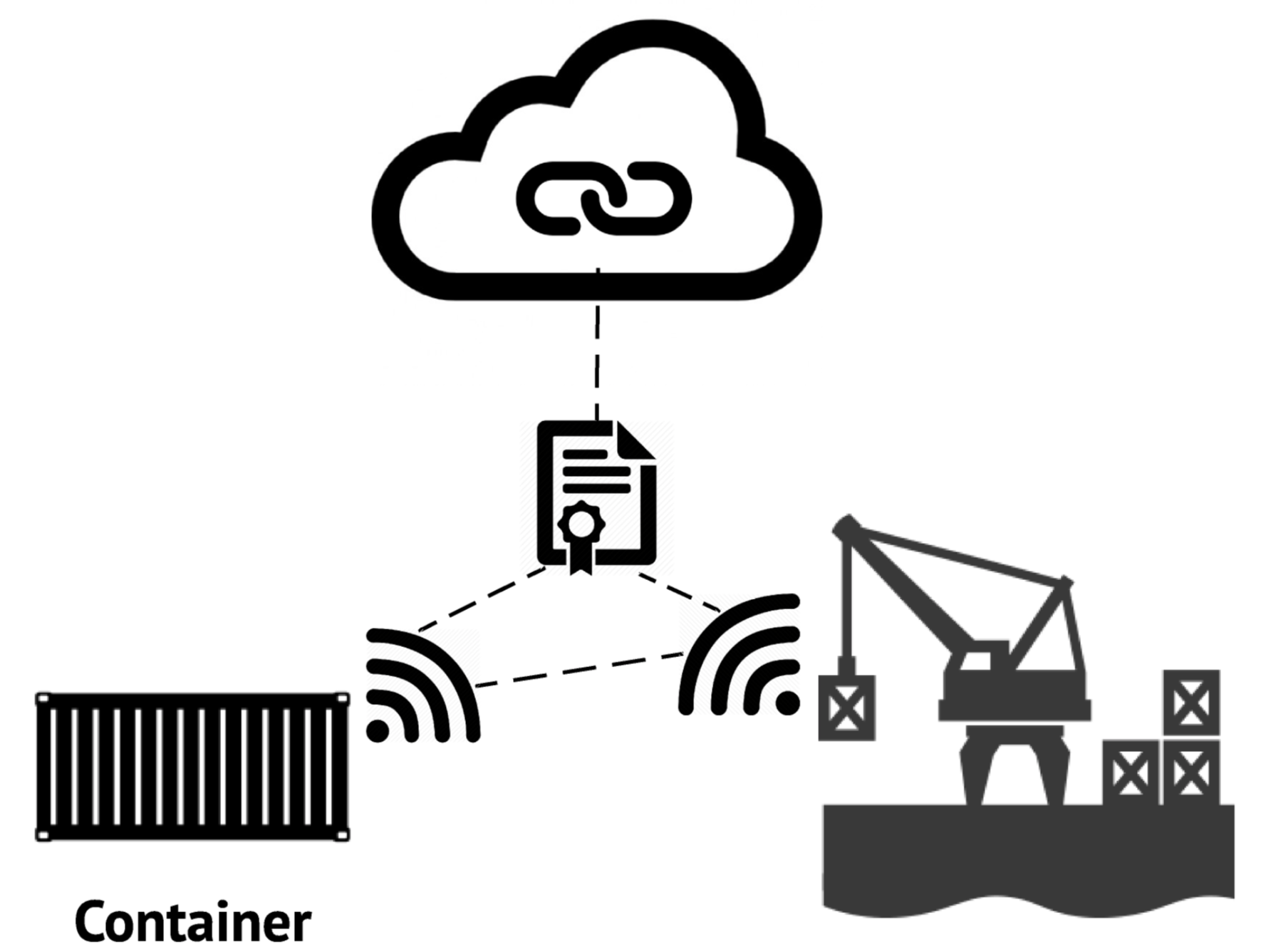
- Performance
- Privacy
- Miner set
- Legal enforceability
- Complete autonomy
IoTxBlockchain:
Issues
Performance:
Throughput & Latency
- High volume: Logistics & Shipping
- Time-sensitive: Manufacturing
- Solution: Reduce blockchain network size and consensus compute

Privacy
- Security through transparency but no security through privacy
-
Solutions:
- Separate blockchain whenever possible
- Content encryption

Miner Set
- Miners may collude to block transactions
- Solution: Separate legal contract to penalize collusion
Legal Enforceability
- Legal enforceability of smart contract is limited
- Solution: Include reference of real-world contract in smart contracts

Complete Autonomy
- Free-running train can become Runaway train
- Solutions:
- Privileged Users to revoke smart contracts
- Smart contracts that change based on inputs

IoTxBlockchain:
- DNS service: pointers to resources
- Secure communication (telehash) & file exchange (IPFS)
Other Parts
- Potential in several domains
- Current applications are limited
- Possible solutions are worth exploring
IoTxBlockchain:
Conclusion
IoTxBlockchain
Q&A
IoTxBlockchain
By Alvin Chan
IoTxBlockchain
- 817


