a review
Alvin Chan
AI
Secure
Outline
- Introduction
- Target Domains
- Attacks
- Defenses
- Challenges & Discussion
Adversarial Attacks

stop sign



90 km/h
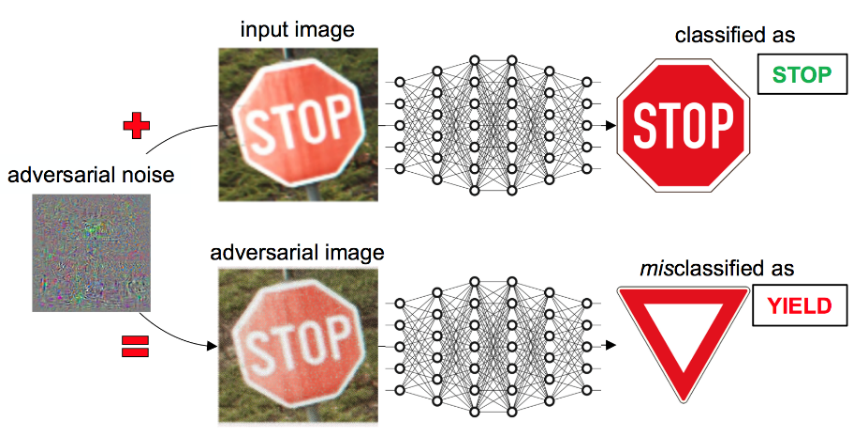
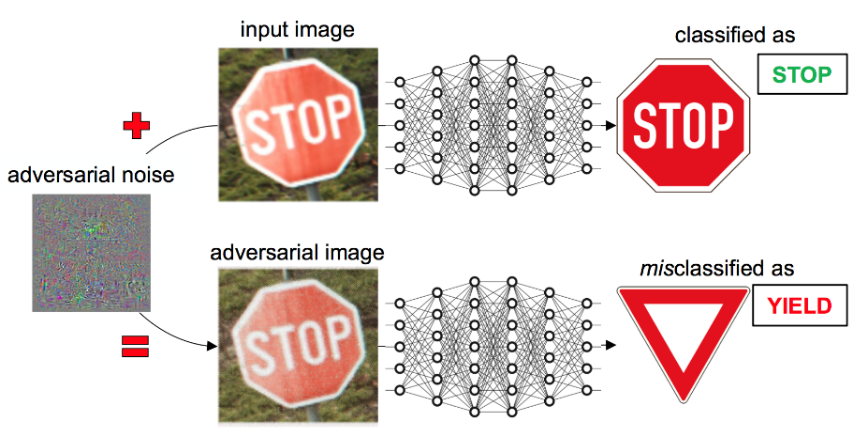
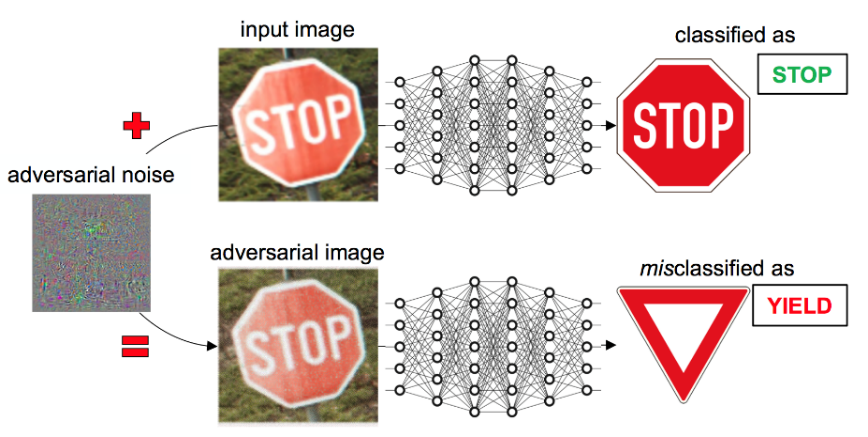
Introduction
- Deep Learning models are still vulnerable to adversarial attacks despite new defenses
- Adversarial attacks can be imperceptible to human
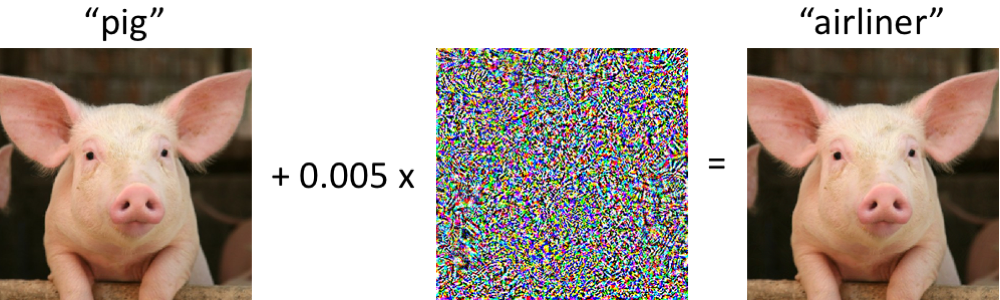
Target Domains
- Computer Vision
- Natural Language Processing
- Malware
Computer Vision
- Mostly studied domain
- Continuous input space
- Compatible with gradient-based attacks

Computer Vision
-
Misclassification of image recognition
-
Face recognition
-
Object detection
-
Image segmentation
-
-
Reinforcement learning

Natural Language Processing
- Discrete input space
- Not directly compatible with gradient-based attacks
- Local search algorithm
- Reinforcement learning

Malware Detection
- Discrete input space
-
Genetic algorithm for evasive malicious PDF files
-
Local search in latent space of MalGan
-
Reinforcement Learning algorithm where evasion is considered as reward
-

Attacks
- Direct gradient-based
- Search-based
Gradient-based Attacks
-
Mostly used in Computer Vision domain
-
Uses gradient of the target models to directly perturb pixel values
Gradient-based Attacks
-
Optimizing two components:
- Distance between the clean and adversarial input
- Label prediction of image
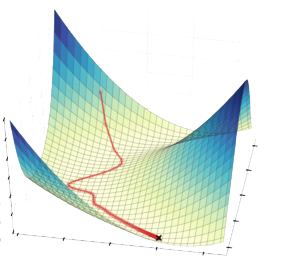
Gradient-based Attacks
-
White-box: Access to architecture & hyperparameters
-
Black-box: Access to target model’s prediction
-
Transfer attacks from single or an ensemble of substitute target models
-
Gradient-based Attacks
-
Trade-off between effectiveness & computational time
Gradient-based Attacks
-
Single-step or iterative
-
Successful gradient based approaches
-
FGSM
-
i-FGSM
-
R+FGSM
-
-
JSMA
-
C&W
-
PGD
-
Search-based Attacks
-
Evolutionary & genetic algorithm
-
PDF-Malware evasion
-
Image misclassification from noisy images
-
-
Local search algorithm
-
Comprehension task using greedy search
-
Malware evasion
-
Defenses
-
Most defenses are in computer vision domain
-
Adversarial retraining
-
Regularization techniques
-
Certification & Guarantees
-
Network distillation
-
Adversarial detection
-
Input reconstruction
-
Ensemble of defenses
-
New model architecture
Adversarial Retraining
- Training on adversarial examples
- Attacks used affects
effectiveness - Ensemble adversarial training

Regularization Techniques
-
Regularize model’s confidence in prediction
-
Adversarial Logit Pairing
Certification & Guarantees
-
Guarantee of adversarial examples within input space
-
Direct methods are computationally intensive and limited in scope
-
Convex approximation as an upper bound
-

Other Techniques
-
Network distillation
-
Another model is trained on the prediction of a model
-
Overcome by stronger attacks
-
-
Adversarial Detection
-
Classifies adversarial images from ‘clean’ images
-
Overcome by including the detector into the attack’s objective function
-
Other Techniques
-
Input reconstruction
-
Scrub adversarial images ‘clean’
-
Overcome by attacks
-
-
Ensemble of defenses
-
Ensemble of models of the above defenses
-
Can be overcome if the underlying defense is weak
-
Uncertainty Modeling
-
Express degree of certainty:
-
“Know when they do not know”
-
-
Gaussian Process Hybrid Deep Neural Networks
-
Expresses latent variable as a Gaussian distribution parameters
-

New Model Architectures
-
“Capsule” network for image
-
New model architecture’s inductive bias
Challenges & Discussion
-
Definition of an adversarial example
-
Studies limited to Lp in images
-
No standard definition for discrete domains like NLP
-
-
Standard of robustness evaluation
-
Benchmarks like Cleverhans
-
Certification & guarantees
-
Challenges & Discussion
-
Ultimate robust model
-
Adversarial examples exist whenever there is classification error
-
-
Adversarial attacks and defenses in other domains
-
NLP
-
Other neural network architecture
-
Cheers!
https://slides.com/alvinchan/resilient-ai-6
Secure AI
By Alvin Chan
Secure AI
- 883


