
Flying drones
using JavaScript
Anca SpAtariu




Core engineer
Event organizer
🤖 + 🌳 = ❤️
What we'll talk about today
- Why are we doing this?
- Demo #1: Establish a communication with the drove via UDP, control and read telemetry in the console
- Demo #2: Establish communication between the drone and browser using WebSockets, control drone via UI
- Demo #3: Get the video stream from the drone and show it in the browser
- Demo #4: Use a pre-trained hand gestures recognition model to control the drone
- - - - - Break - - - - -
- Decreased problem-solving abilities
- Lack of focus and creativity
- Reduced code quality
- No motivation
Burnout is an epidemic
When coding stops being fun
- Our creativity stagnates and the drive to explore diminishes
- We become just button pushers
- We disconnect from passion and kill our joy of problem solving
Setup #1


UDP
what we'll be using



DJI SDK
what we'll be using

DJI Tello Mini
pretty cheap hobby drone
5MP camera
80g weight
15 min flight autonomy
what we'll be using
Node.js
because we need UDP communication
with dgram to handle UDP communication

what we'll be using
DJI Tello SDK
only 6 pages of documentation to learn all commands

DJI SDK
TCP
UDP
vs.
- connection oriented protocol
- reliable
- acknowledges each packet
- we use it day to day for web pages, applications, downloads etc.
- connectionless protocol
- not reliable, but faster
- doesn't care if packages arrive or their order
- used mostly for live video streaming, gaming etc.
TCP looks something like this

While udp resembles this

Why not the browser?
- Browsers use TCP protocols like HTTP/HTTPS
- WebRTC (unlike WebSockets) uses UDP under the hood, but we can't access raw UDP in JavaScript
Let's do it!
Setup #2

UDP

WebSockets
(TCP)

What we'll be using
WebSockets
- a protocol that provides full-duplex communication over a single, long-lived TCP connection.
- unlike HTTP, WebSockets allow for real-time communication between the client (browser) and server.
- once the connection is established, both the server and client can send messages anytime without re-establishing the connection.
how it works
Client connects
Server responds, handshake, connection established
WS chit-chat!
Connection closed


❤
new WebSocket();


Let's do it!
Setup #3

UDP

WebSockets
(TCP)




What we'll be using
TensorFlow.JS
HandPose
- a JavaScript library for machine learning in the browser
- it enables us to run machine learning models using web technologies
- runs 100% on the client, no need for a server
- a pre-trained model for TensorFlow.JS
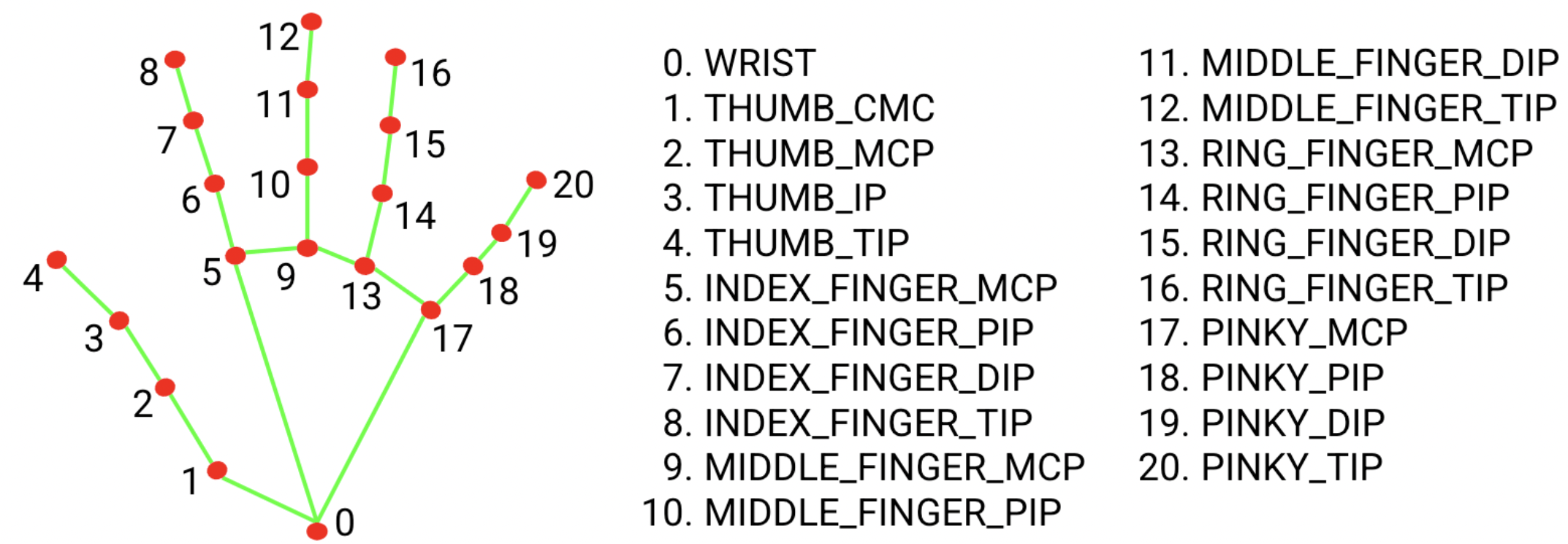
- detects 21 hand key points on a person's hand from an image or video stream.
- Used for hand gesture recognition, tracking finger positions
how the magic happens
Handpose captures video frames from the camera or canvas in the browser
Each frame is processed by the Handpose model to detect hand key points.
TensorFlow.js performs calculations using the browser's WebGL.
Real time interactions




What are we tracking
Let's do it!
Key takeaways
- Resting doesn't help burnout, but doing something fun does
- Controlling a drone is nothing more than just sending messages via UDP. You can even use Scratch!
- If you're easily bored - like me - you can use projects like this to learn new stuff (i.e. working with websockets, machine learning etc.)
Thank you!
Questions?
Flying dronesusing JavaScript
By Anca Spatariu
Flying dronesusing JavaScript
- 186


