Security
Asymmetric keys and encryption
- Including the use of public key, private key, plain text,
cipher text, encryption, symmetric key cryptography
and asymmetric key cryptography - How the keys can be used to send a private message
from the public to an individual/organisation - How the keys can be used to send a verified message
to the public - How data is encrypted and decrypted, using symmetric and asymmetric cryptography
- Purpose, benefits and drawbacks of quantum
cryptography

Objectives
Think Pair Share
- Imagine you are required to send a letter with secret information, what do you need to ensure?
- If you are receiving that information, what do you need to ensure?

Plaintext
Plaintext
Ciphertext
Encryption
Decryption
Key
Algorithm
Key
Algorithm
Process of encryption
Symmetric key encryption
- Sender and receiver are using the same algorithm
- A key is created to encrypt the plaintext to ciphertext and send to the receiver
- receiver use the same key and reverse the encryption process to decypher the code
Asymmetric key encryption
- Similar to symmetric key encryption, but sender and receiver has two different keys
Receiver generate private key
Public key generated using private key
Public key sends to Sender
Sender encrypt message with public key
Ciphertext send to receiver
Decrypt message with private key
Digital signatures and digital certificates
- How a digital certificate is acquired
- How a digital certificate is used to produce digital
signatures

Objectives
Digital Signature
- A digital signature is used to validate the authenticity and integrity of a message
- What is authenticity and integrity means?

Discussion Time
With Digital Signature, we can asserted that the data is coming from the particular source. What is the problem with this approach?
Digital Certificate
- A Digital Certificate is an electronic "password" that allows a person, organizaion to exchange data securely over the Internet
- Using the public key infrastructure (PKI)
- A Certification Authority (CA) issue this certificate
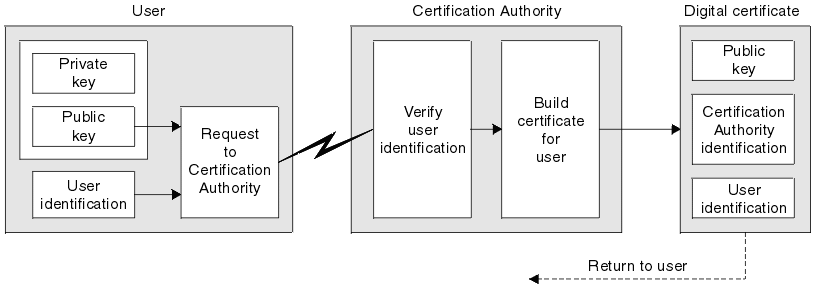
Obtaining a digital Certificate
Security in Transmission of Data
- Followings should be ensure of:
- Confidentiality - Only intended recipient should be able to read the message
- Authenticity - Both sender and receiver are sure who are they communicating with
- Integrity - Data must not be modified during transmission
- Describe how the above 3 measures can be guaranteed using the technology/technique we mentioned before.
SSL/TLS and HTTP/S
- SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and the successor TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- Protocols for Establishing authenticated and encrypted links between computers
- HTTP sends raw data, while HTTP/S incorporate TLS while establishing the connection

Handshake / Establish connection
Notes on SSL
- Checking certificate is done only during handshake
- Asymmetric key encryption is used during handshake
- The further communication became Symmetric Encryption
- Asymmetric key is computation expensive, while symmetric key is much simpler
- Improve performance
HTTP/S Handshake - Note different layer of protocols involved

[CSAL] Security
By Andy tsui
[CSAL] Security
- 369



