Problem-solving techniques
Sub-systems
- A system can be broken into smaller sub-systems
- Which sub-systems can further breaks down
- Sub-systems is less complex, thus easier to:
- Create and program
- Find mistakes and fix
Test data
Max = 0 FOR i <- 0 to 10 INPUT Number IF Number > Max THEN Max <- Number
END IF Next i PRINT Max
Read the following Python code:
- What is this program doing?
- How can you sure this program is functioning correctly?
Test data
- We need to test a program to see whether it works or not
- We need to prepare sets of test data and feed into the program
- If all the outputs of the program is the same as our expected output then the program is good
Types of test data
| Type | Description | Example* |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | Valid data that the program is expected to accept it | |
| Abnormal/ Erroneous |
Data that the program should reject it. If handled incorrectly sometimes may break the system | |
| Extreme | Valid data, but the data is at the boundary of normal and abnormal |
*Assume we have a program that collects 3 exam scores and calculate the average
Test plan
| Test Data | Type of test data | Expected output | Actual output | Remedial Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50, 30, 40 | Normal | 40 | ||
| Abnormal | ||||
| Extreme | ||||
*Assume we have a program that collects 3 exam scores and calculate the average
Test plan
- A good plan is always important before you do a program
- Include test data from different types
- Fill in the expected output before creating your solution
- After the program is created, fill in the actual outcome and if the actual outcome is different from expected, the Action
- Any changes to the program should re-run the test
Trace table
- A table used to trace the values of variables
- Often use with dry-run
- Helps to determine where are the errors in the code
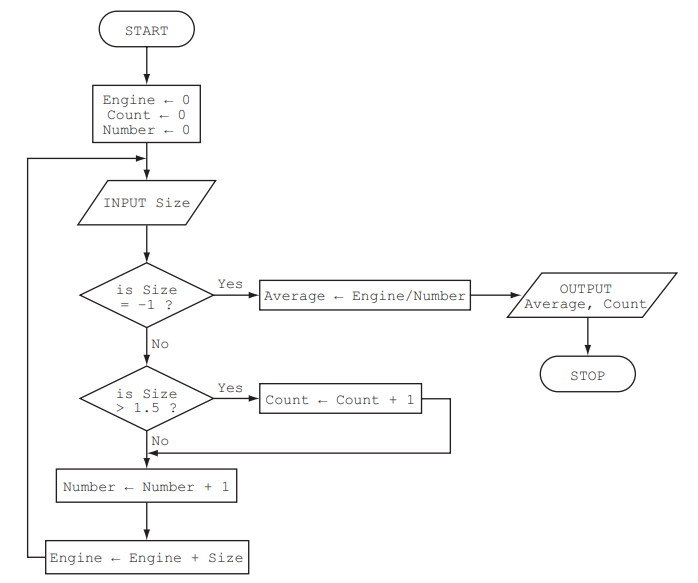
Specimen paper 2015

Always prompt the user about what's happening!
Verification
- Prevent errors when data is copied from one place to another (e.g. typing)
- Data can be totally valid, but it is incorrect
Validation
- Check the data if it satisfies criteria required by system
- Usually done automatically by the software
Think Pair Share
Imagine you are required to input some data in an online application form. Discuss and suggest some verification methods

Verification methods
- Visual check or proof reading
- Double entry

Validation types
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
Please input the score: 120 Input must between 0 and 100 Please input the score: Fifty-one Input must be an integer Please input the score: 85
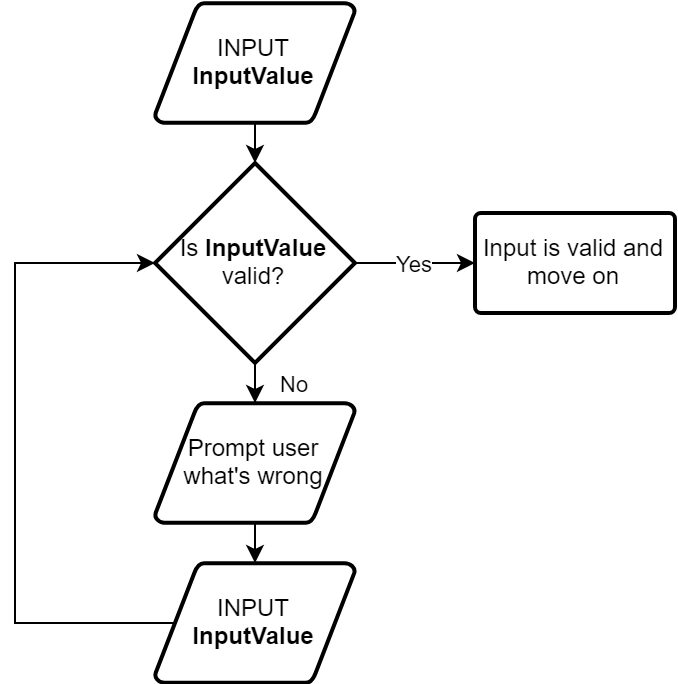
Common validation pattern
- Program should do the validation check, and reject any invalid inputs
- Only accepts when the input is valid
Check digit
- (Usually) final digit included in a code
- Calculated from other digits in the code
- Prevents errors from entering numbers
- From Human entry
- For Input devices (e.g. Barcode scanner)
- Some examples are:
- ISBN number
- Your DESJ Number
- ID Card number
Research
- There are 2 versions in ISBN (What is ISBN?) which are:
- ISBN 10
- ISBN 13
- Research and find the formula for calculating the ISBN-13 check digit (p.123 in textbook)
Class exercise
- Create a program (Validations) to ask user to input:
- Student name
- Student gender ('m' or 'f')
- Student score
- All inputs must be validated
- Must properly prompt user for input and expectations
- Print the entered data
Before you start, what is the proper validations for those data?
[F3CS] Problem solving
By Andy tsui
[F3CS] Problem solving
- 258



