Activating Angular's
Reactive Core

Ankita Sood
(uh nk - ee t ah s oo d)

SoodAnkita
ankitasood.bsky.social
WebVibesOnlyGuacamoleAnkita


Reactivity
Reactivity
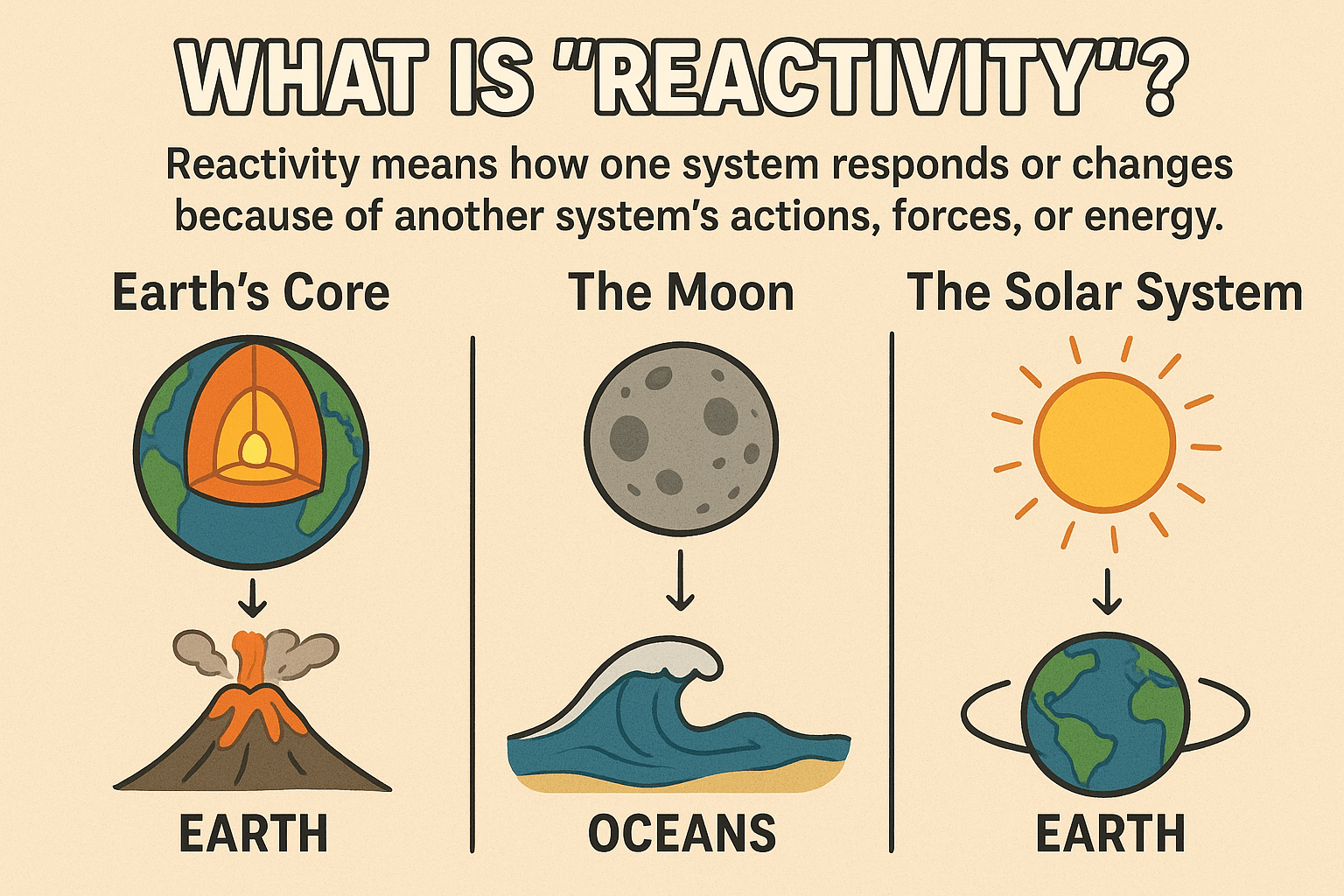
Reactivity
Reactivity can be broadly defined as the automatic update of the UI due to a change in the application's state.
There are as many definitions of reactive programming
as there are
reactive programmers.
〞
Reactivity
in
Angular
Coarse Grained Reactivity
-
Re-runs change detection for entire component tree when any async event occurs.
-
Uses Zone.js to monkey-patch browser APIs and trigger global change detection.
-
Components re-evaluate even if their data hasn't changed.
Fine Grained Reactivity
-
Updates only the specific DOM elements that depend on changed signals.
-
Skips components whose signals haven't changed.
-
Enables zoneless Angular applications.
Reactivity in Angular
Evolved from being primarily
RxJS-based Observables to Signals.
Observables
Used for event handling & asynchronous programming to manage multiple values emitted over time.
Observables
The most common uses:
-
Handling HTTP requests.
-
Routing.
-
Forms modules.
-
Event handling - Dom events, custom component events, web socket events.
Signals
Lightweight wrapper around a value that notifies interested consumers when that value changes.
- Used to watch and react to data changes.
- Value based reactivity - synchronous.
- Built specifically for UI reactivity.
- No manual subscription necessary.
Signals
- Used to watch and react to events over time.
- Stream-based data flow - asynchronous.
- Great for events, HTTP, & complex data flows.
- Needs to be subscribed and unsubscribed.
Observables
Observables Vs Signals
class ItemCount implements OnDestroy {
count = new BehaviorSubject(0);
count$ = this.count.asObservable();
increment():void {
const curr = this.count.value;
this.count.next(curr + 1);
}
ngOnDestroy(): void {
this.count.complete();
}
}class ItemCount {
count = signal(0);
increment(): void {
this.count.update(curr => curr + 1);
}
}Signals
Writable Signals
A Signal with a value that can be mutated.
Read-only Signals
Cannot directly assign values to it.
Signal
const count = signal(0); // Create
count.set(5); // Set directly
count.update(c => c + 1); // Update based on previousComputed Signals
const useDiscount = signal(false);
const price = signal(100);
const discount = signal(0.1);
const finalPrice = computed(() => {
return useDiscount() ? price() * (1 - discount()) : price();
});
Linked Signals
const items = signal(['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']);
// linked signal: always shows the first item
selected = linkedSignal(() => items()[0]);
console.log(selected()); // → 'Apple'
items.set(['Orange', 'Pear']);
console.log(selected()); // → 'Orange'Linked Signals
items = input<string[]>([]);
// linked signal: default to first item, null if no input
selected = linkedSignal({
source: ()=> this.items(),
computation: (source, previous) => {
return source.find(i => previous?.value === i) || null;
}
});
isSelected (item: string) {
return this.selected() === item;
} @for (item of items(); track $index) {
<a (click)="selected.set(item)">{{item}}</a>
}
<span>{{selected() || "No item selected."}}</span>Linked Signals
selectedItem = signal<Item | null>(null);
price = computed(()=> this.selectedItem()?.price ?? 0);
// quantity depends on selected Item
quantity = linkedSignal({
source: this.selectedItem,
computation: () => 1
});
total = computed(()=> this.quantity() * this.price());
onQuantityChanged(q: number) {
this.quantity.set(q);
}- Reset a signal when one or more signals change.
- Access previous value of a signal.
- Writeable result.
COMPUTED
- Derive a value from one or more signals.
-
Re-compute when those signals change.
- Read-only result.
LINKED SIGNALS
Usage Guidelines
Effects
Operations that run when signal values change.
Effects
export class EffectiveCounter {
readonly count = signal(0);
constructor() {
// Register a new effect.
effect(() => {
console.log(`The count is: ${this.count()}`);
});
}
}- Execute at least once.
- Track signal dependencies dynamically.
- Always execute asynchronously.
Effects
Pass an Injector to create outside the constructor.
export class EffectiveCounter {
readonly count = signal(0);
private injector = inject(Injector);
initializeLogging(): void {
effect(() => {
console.log(`The count is: ${this.count()}`);
}, {injector: this.injector});
}
}Automatically destroyed when its enclosing context is destroyed.
-
Performing custom rendering to a canvas, charting library, or other third party UI library.
-
Logging.
-
Syncing data with window.localStorage.
-
Adding custom DOM behavior.
When to Use
When to Avoid
Don't use effects for state propagation!
-
Can result in
ExpressionChangedAfterItHasBeenCheckederrors.
-
Infinite circular updates.
- Unnecessary change detection cycles.
effect(() => {
console.log(`User set to ${currentUser()} and the counter is ${untracked(counter)}`);
});Prevent a signal read from being tracked by calling its getter with untracked.
Effects Decision Tree
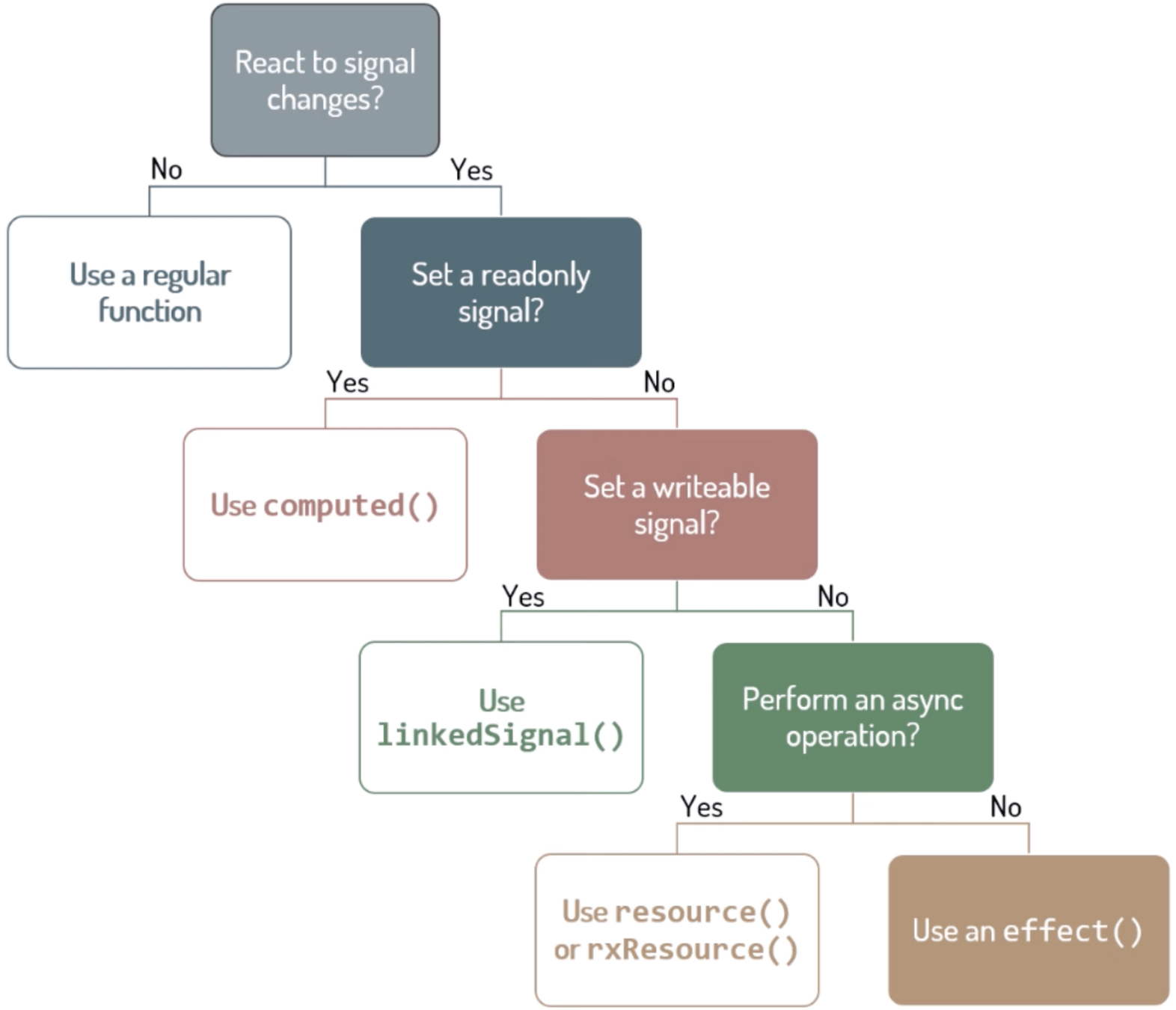
Deborah Kurata's Effects decision tree: https://youtu.be/XWz8pxQWD8c?si=Xrgy7Is9ESCvoZUE
Component Specific Signals
Writable Signals
Model Inputs
Non-Writable Signals
InputSignal
View Queries (viewChild, viewChildren)
Content Queries (contentChild, contentChildren)
Model Inputs
export class DateComponent {
@Input() value = new Date();
@Output() valueChange = new EventEmitter();
value = model(new Date());
}
Model Inputs
@Component({
selector: 'app-settings-page',
template: `<h2>Dark Mode Setting</h2>
<app-toggle-switch [(checked)]="darkModeEnabled" />
<p>Dark Mode is: {{ darkModeEnabled() ? 'ON' : 'OFF' }}</p>`,
})
export class SettingsPage {
darkModeEnabled = signal(false);
}
@Component({
selector: 'app-toggle-switch',
// template: A switch UI that calls this.checked.set(!this.checked()) on click
})
export class ToggleSwitch {
checked = model(false);
toggle(): void {
this.checked.update(isCurrentlyChecked => !isCurrentlyChecked);
}
}Input Signals
export class ListItem {
@Input("required")title: string = “”;
title = input.required<string>();
@Input({transform: (value: string) => value.toUpperCase()}) descr: string = "Default description"
descr = input('Default description',{transform: (value: string) => value.toUpperCase()});
}
View Queries
export class SearchDialog {
isOpen = false;
@ViewChild('search') searchInput: ElementRef<HTMLElement> | undefined;
searchInput = viewChild.required<ElementRef<HTMLElement>>('search');
// some additional logic goes here that updates value of isOpen
ngAfterViewInit(): void {
if (isOpen) {
this.searchInput.nativeElement.focus();
this.searchInput().nativeElement.focus();
}
}
}Content Queries
@Component({
selector: 'custom-toggle',
})
export class CustomToggle {
text: string;
}
@Component({
selector: 'custom-expando',
})
export class CustomExpando {
toggle = contentChild(CustomToggle);
toggleText = computed(() => this.toggle()?.text);
}
@Component({
template: `
<custom-expando>
<custom-toggle>Show</custom-toggle>
</custom-expando>
`
})
export class UserProfile { }@Component({
selector: 'custom-toggle',
})
export class CustomToggle {
text: string;
}
@Component({
selector: 'custom-expando',
})
export class CustomExpando {
@ContentChild(CustomToggle) toggle: CustomToggle;
ngAfterContentInit() {
console.log(this.toggle.text);
}
}
@Component({
template: `
<custom-expando>
<custom-toggle>Show</custom-toggle>
</custom-expando>
`
})
export class UserProfile { }Asynchronous Reactivity
-
resource(): Lower level, works with promises. -
httpResource(): Works with a url string. -
rxResource: Works with Observables.
Experimental APIs
Resource
Streamline asynchronous data fetching with built-in reactivity.
-
Includes built-in status tracking (loading, error, success).
-
Similar behavior to switchMap built-in to handle consecutive requests (AbortSignal).
-
Easy to set default value & trigger reload.
-
Doesn't rely on
zone.js.
Resource
const userId: Signal<string> = getUserId();
const userResource = resource({
params: () => ({id: userId()}),
loader: ({params}) => fetchUser(params),
defaultValue: ''
});
const firstName = computed(() => {
if (userResource.hasValue()) {
return userResource.value().firstName;
}
// fallback in case the resource value is `undefined` or if the resource is in error state
return undefined;
});Resource
const userId: Signal<string> = getUserId();
const userResource = resource({
params: () => ({id: userId()}),
loader: ({params, abortSignal}): Promise<User> => {
// fetch cancels any outstanding HTTP requests when the given `AbortSignal`
// indicates that the request has been aborted.
return fetch(`users/${params.id}`,
{signal: abortSignal});
},
});// programatically trigger a resource's loader
userResource.reload();httpResource
-
Wrapper around
HttpClient. -
Initiates the request eagerly.
-
Exposes the request status and response values as a
WriteableResource. -
Only for retrive operations only i.e.
get().
Facilitates http requests.
httpResource
@if(user.hasValue()) {
<user-details [user]="user.value()">
} @else if (user.error()) {
<div>Could not load user information</div>
} @else if (user.isLoading()) {
<div>Loading user info...</div>
}userId = input.required<string>();
user = httpResource(() => `/api/user/${userId()}`); // A reactive function as argumentThe signals of the httpResource can be used in the template to control which elements should be displayed.
rxResource
-
Source is defined as RxJS Observable.
-
Instead of a
loaderfunction, it accepts astreamfunction that accepts anRxJS Observable. -
Same APIs as
resource.
rxResource
export class UserProfile {
// Relies on a service that exposes data through an RxJS Observable.
private userData = inject(MyUserDataClient);
protected userId = input<string>();
private userResource = rxResource({
params: () => ({ userId: this.userId() }),
stream: ({params}) => this.userData.load(params.userId),
});
}Comparison
| Feature | resource | httpResource() | rxResource |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | General async operations with Promises | Simple HTTP GET requests | Working with existing RxJS Observables |
| Data Source | Any Promise-returning function | Built-in HttpClient (GET only) | RxJS Observable streams |
| Request Initiation | Lazy (when accessed) | Eager (immediate) | Lazy (when accessed) |
| Best For | Custom fetch logic, non-HTTP async operations | Simple data fetching from REST APIs | Integrating with existing RxJS services |
RxJS Interop
@angular/core/rxjs-interopAPIs that help you integrate RxJS & Signals.
-
Create a
signalfrom anRxJsObservablewithtoSignal.
-
Create an
RxJS Observable from asignalwithtoObservable.
-
Create an
outputbased on anRxJs Observable.
-
Creating an
RxJS Observablefrom a component or directive output.
-
Unsubscribing with
takeUntilDestroyed
toSignal
counterObservable = interval(1000);
// Get a Signal representing the counterObservable's value.
counter = toSignal(
this.counterObservable,
{initialValue: 0}
);toObservable
export class SearchResults {
query: Signal<string> = inject(QueryService).query;
query$ = toObservable(this.query);
results$ = this.query$.pipe(
switchMap(query => this.http.get('/search?q=' + query ))
);
}const obs$ = toObservable(mySignal);
obs$.subscribe(value => console.log(value));
mySignal.set(1);
mySignal.set(2);
mySignal.set(3);outputFromObservable
@Directive({/*...*/})
class Draggable {
pointerMoves$: Observable<PointerMovements> = listenToPointerMoves();
// Whenever `pointerMoves$` emits, the `pointerMove` event fires.
pointerMove = outputFromObservable(this.pointerMoves$);
}outputToObservable
@Component(/*...*/)
class CustomSlider {
valueChange = output<number>();
}
// Instance reference to CustomSlider.
const slider: CustomSlider = createSlider();
outputToObservable(slider.valueChange) // Observable<number>
.pipe(...)
.subscribe(...);takeUntilDestroyed
export class UserProfile {
private dispatcher = inject(NotificationDispatcher);
private popup = inject(CustomPopupShower);
constructor() {
// This subscription the 'notifications' Observable is automatically
// unsubscribed when the 'UserProfile' component is destroyed.
const messages: Observable<string> = this.dispatcher.notifications;
messages.pipe(takeUntilDestroyed()).subscribe(message => {
this.popup.show(message);
});
}
}Roadmap
Improving the Angular developer experience

Decision Tree



SoodAnkita
ankitasood.bsky.social
WebVibesOnlyGuacamoleAnkita


Techorama - Activating Angular's Reactive Core
By Ankita Sood
Techorama - Activating Angular's Reactive Core
- 42



