ARIMA
ARIMA-Def
- ARIMA stands for Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average. There are seasonal and Non-seasonal ARIMA models that can be used for forecasting
- p,d,q
- P = Periods to lag: P helps adjust the line that is being fitted to forecast the series
- d= D refers to the number of differencing transformations required by the time series to get stationary. The best way to determine whether or not the series is sufficiently differenced is to plot the differenced series and check to see if there is a constant mean and variance.
- Q= The variable denotes the lag of the error component- you get it from the autocorrelation plot. The Autocorrelation function plot will let you know how the given time series is correlated with itself
Results we obtained:
- Resync Data
- RMSE: 209
- Prediction graph
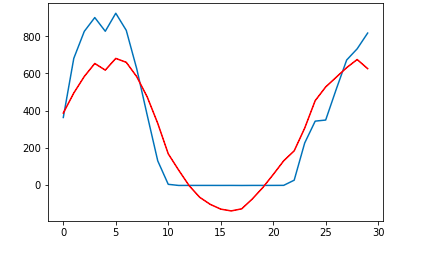
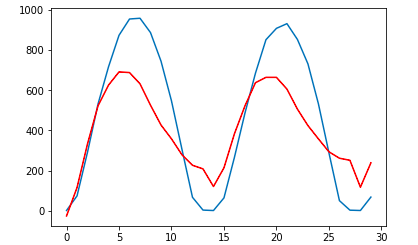
-
Solcast Data
- RMSE:398
- Prediction graph
Why not ARIMA?
- Takes a longer time to run
- Needs parameters -p,q,d- to be calculated-LSTM does not require setting such parameters. However, there are some hyperparameters we need to tune for LSTM.
- ARIMA might be better for smaller datasets- for specific sites
- Might not work with Singapore-since it is difficult to predict for each site, but taking as a whole the prediction has a special averaging effect.
ARIMA
By archana iyer
ARIMA
- 746



