Machine Learning
how to start to teach the machine
ARKADIUSZ KONDAS
Lead Software Architect
@ Proget Sp. z o.o.
Poland
Zend Certified Engineer
Code Craftsman
Blogger
Ultra Runner
@ ArkadiuszKondas

arkadiuszkondas.com


Zend Certified Architect

Agenda:
- Terminology
- Ways of learning
- Types of problems
- Example applications


Why machine learning?
Why Machine Learning?
- Develop systems that can automatically adapt and customize themselves to individual users.
- personalized news or mail filter
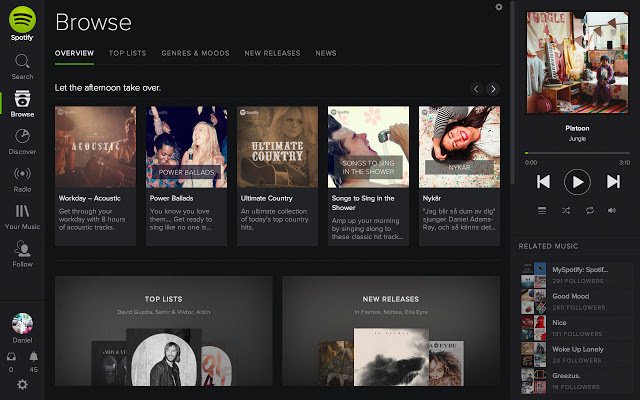
Why Machine Learning?
- Discover new knowledge from large databases (data mining).
- market basket analysis
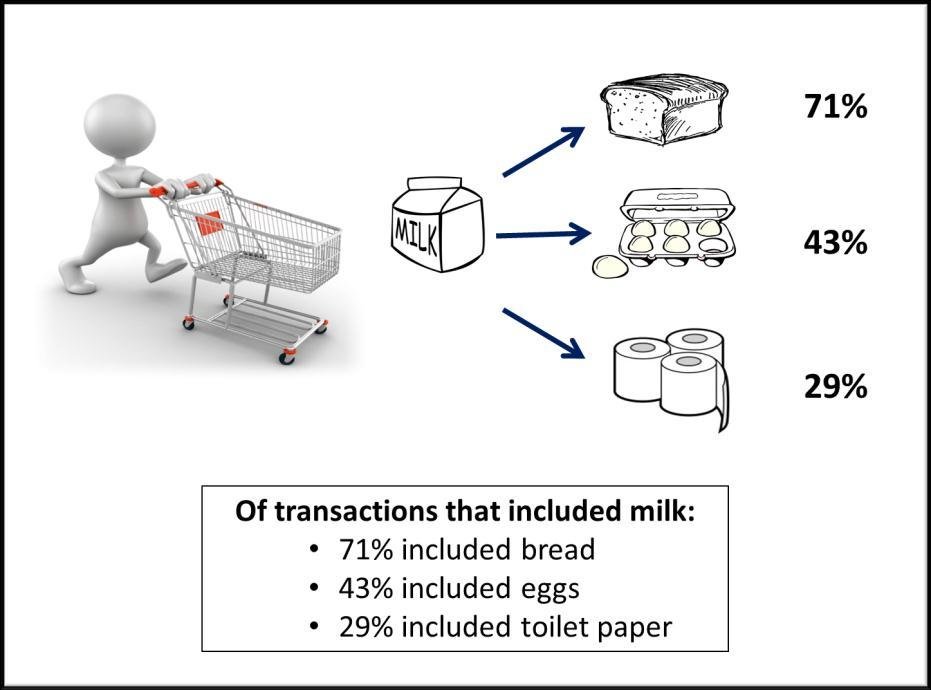
Source: https://blogs.adobe.com/digitalmarketing/analytics/shopping-for-kpis-market-basket-analysis-for-web-analytics-data/
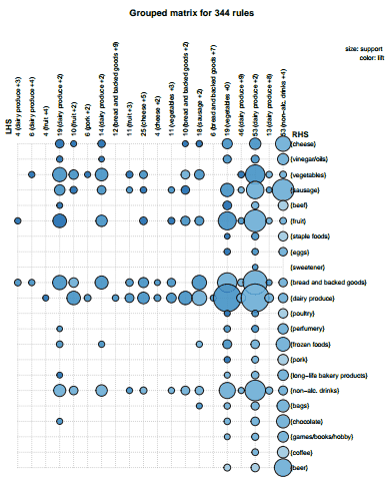
Why Machine Learning?
- Ability to mimic human and replace certain monotonous tasks - which require some intelligence.
- like recognizing handwritten characters

https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/im2txt
Why Machine Learning?
http://articles.concreteinteractive.com/nicole-kidmans-fake-nose/
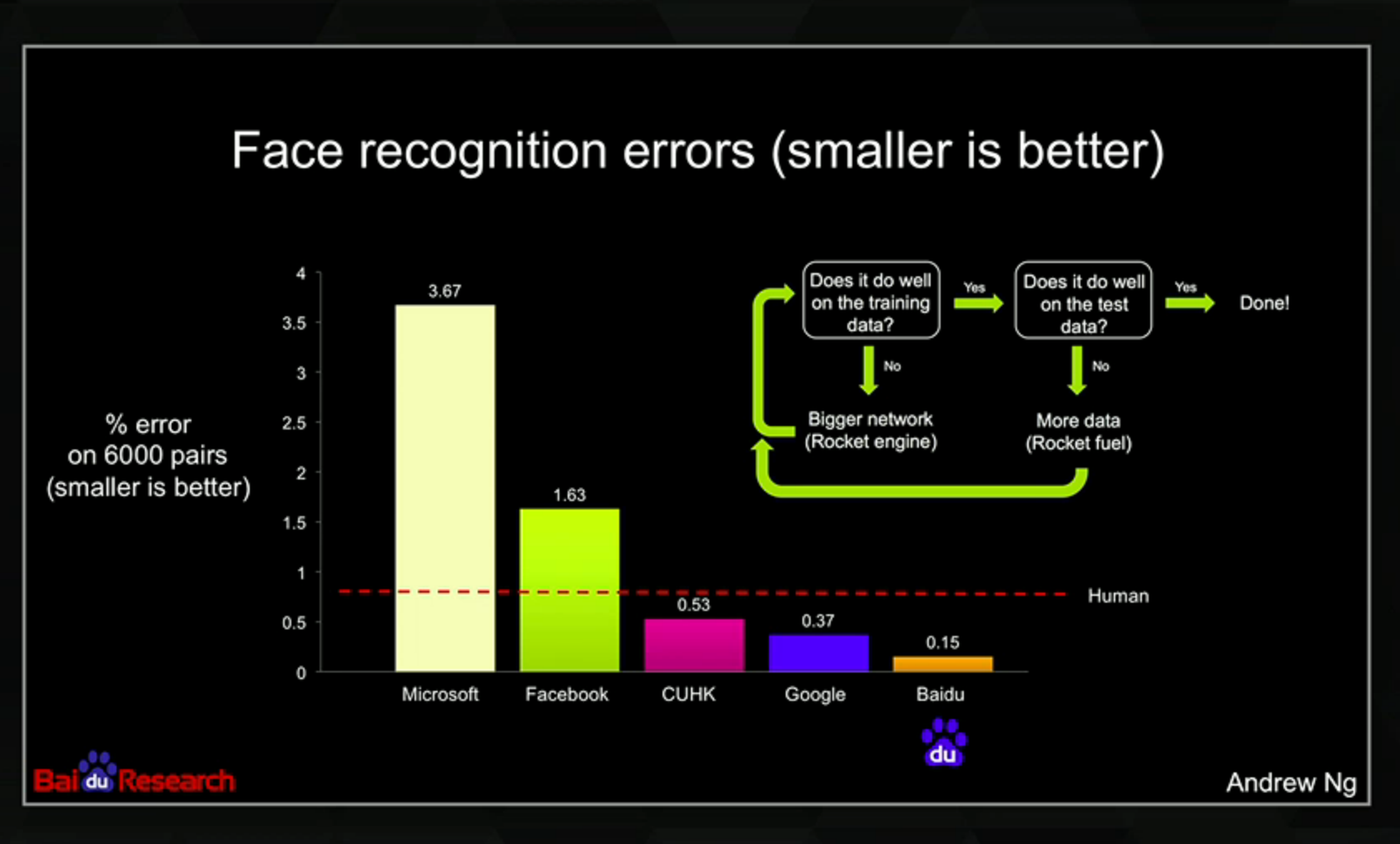
Why Machine Learning?
- Develop systems that are too difficult/expensive to construct manually because they require specific detailed skills or knowledge tuned to a specific task (knowledge engineering bottleneck)


Why now?
The name machine learning was coined in 1959
- Data availability
- Computation power
Terminology
Machine Learning
Learning is any process by which a system improves performance from experience
Samples
a sample is an item to process (e.g. classify). It can be a document, a picture, a sound, a video, a row in database or CSV file, or whatever you can describe with a fixed set of features.







Features
the number of features or distinct traits that can be used to describe each item in a quantitative manner

IBU: 45 (0 - 120) International Bittering Units
ALK: 4,7% (0% - 12%)
EXT: 12,0 (0 - 30) BLG, PLATO
EBC: 9 (0 - 80) European Brewery Convention
Feature vector
is an n-dimensional vector of numerical features that represent some object.

$beer = [45, 4.7, 12.0, 9];Feature extraction
preparation of feature vector – transforms the data in the high-dimensional space to a space of fewer dimensions

$beer = [?, 7.0, 17.5, 9];Training / Evolution set
Set of data to discover potentially predictive relationships.

Ways of learning
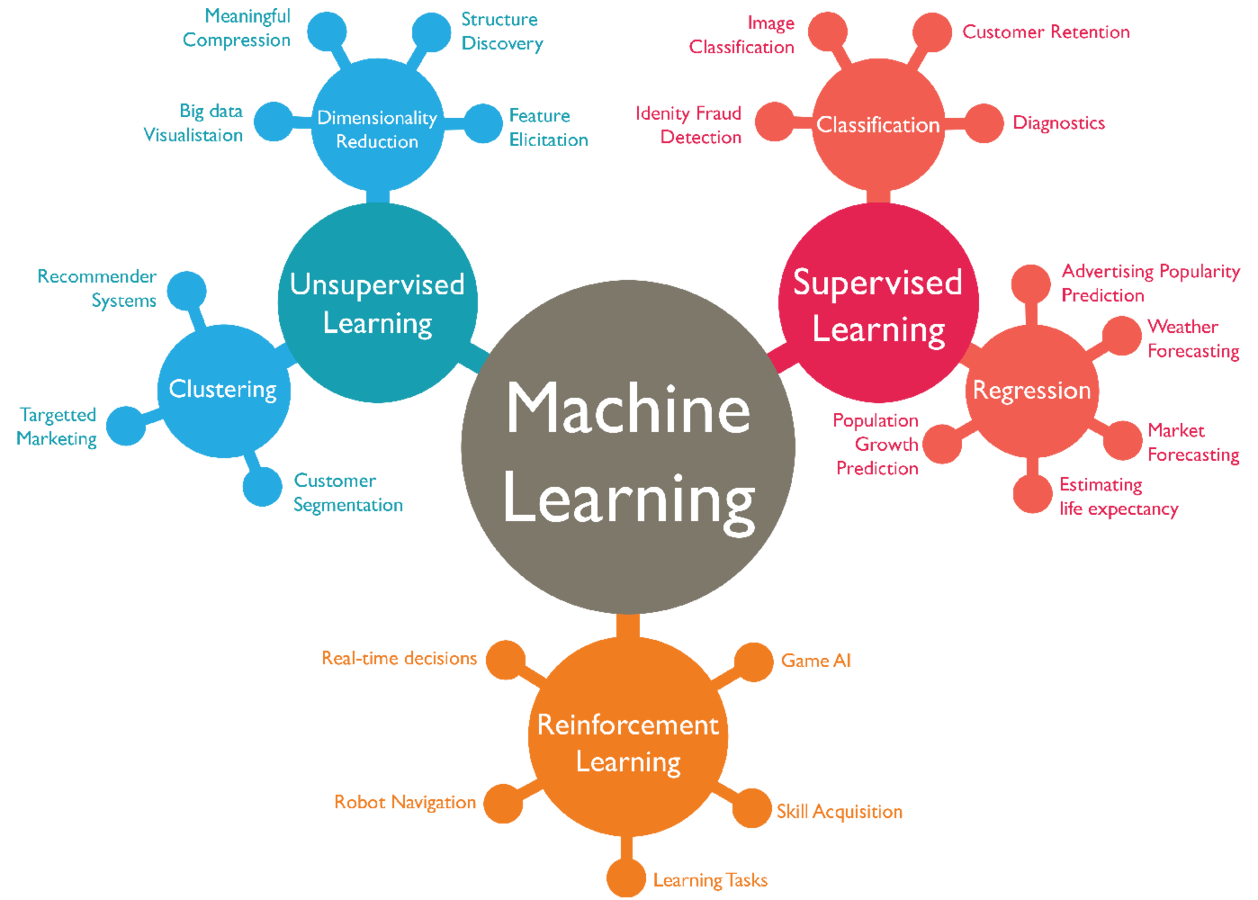
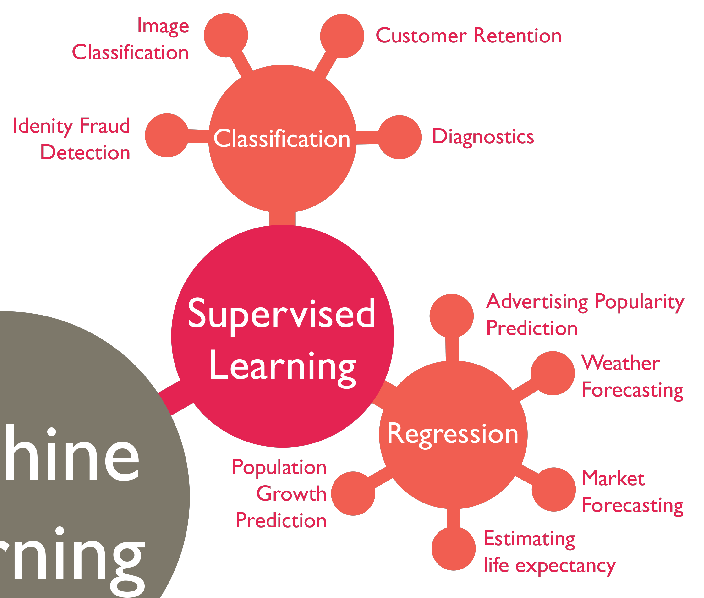
Supervised learning
Source: https://www.slideshare.net/Simplilearn/what-is-machine-learning-machine-learning-basics-machine-learning-algorithms-simplilearn
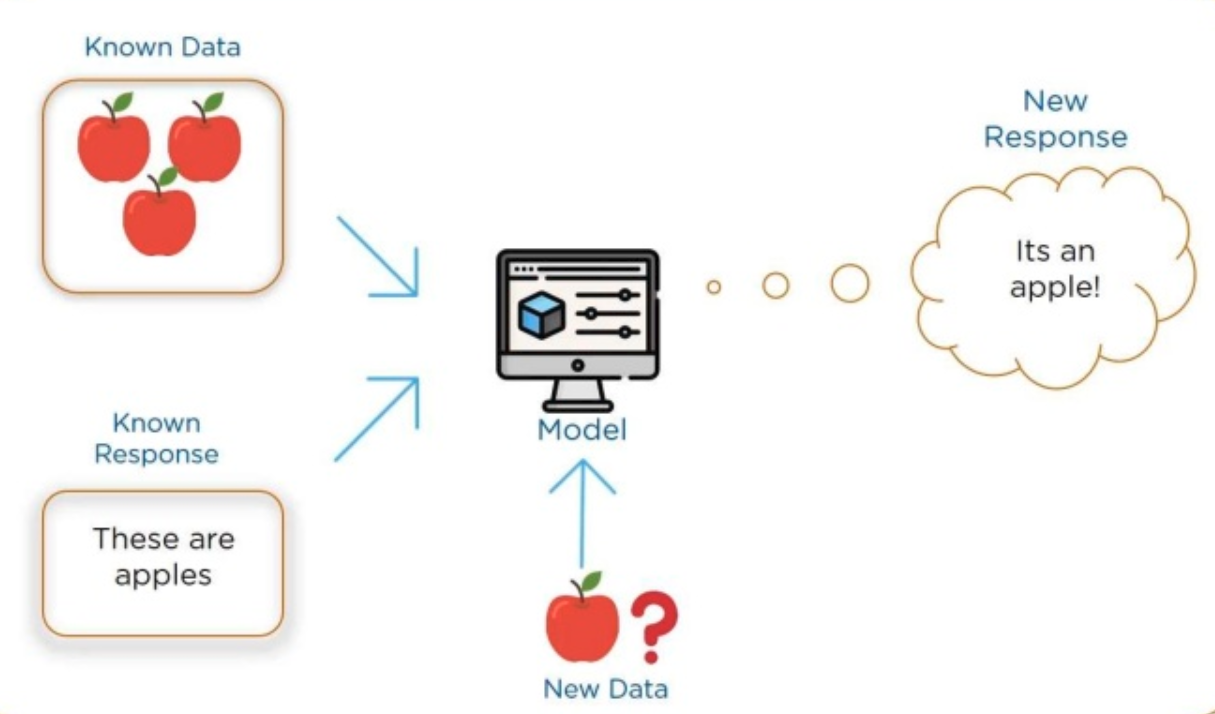
Supervised learning
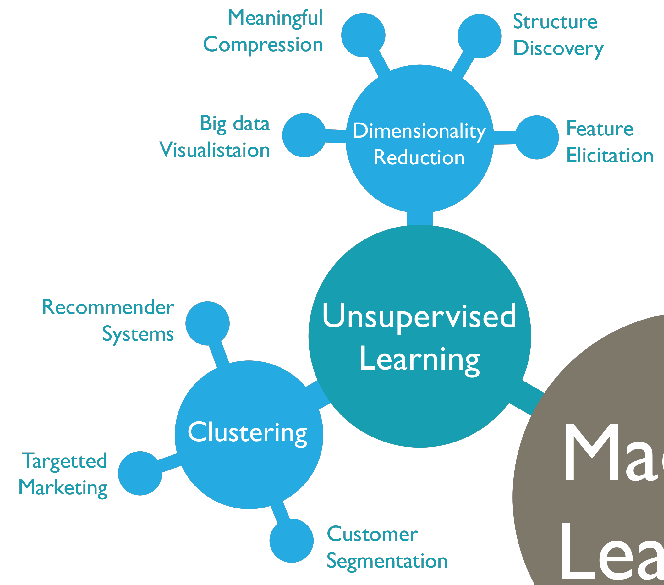
Unsupervised learning
Source: https://www.slideshare.net/Simplilearn/what-is-machine-learning-machine-learning-basics-machine-learning-algorithms-simplilearn
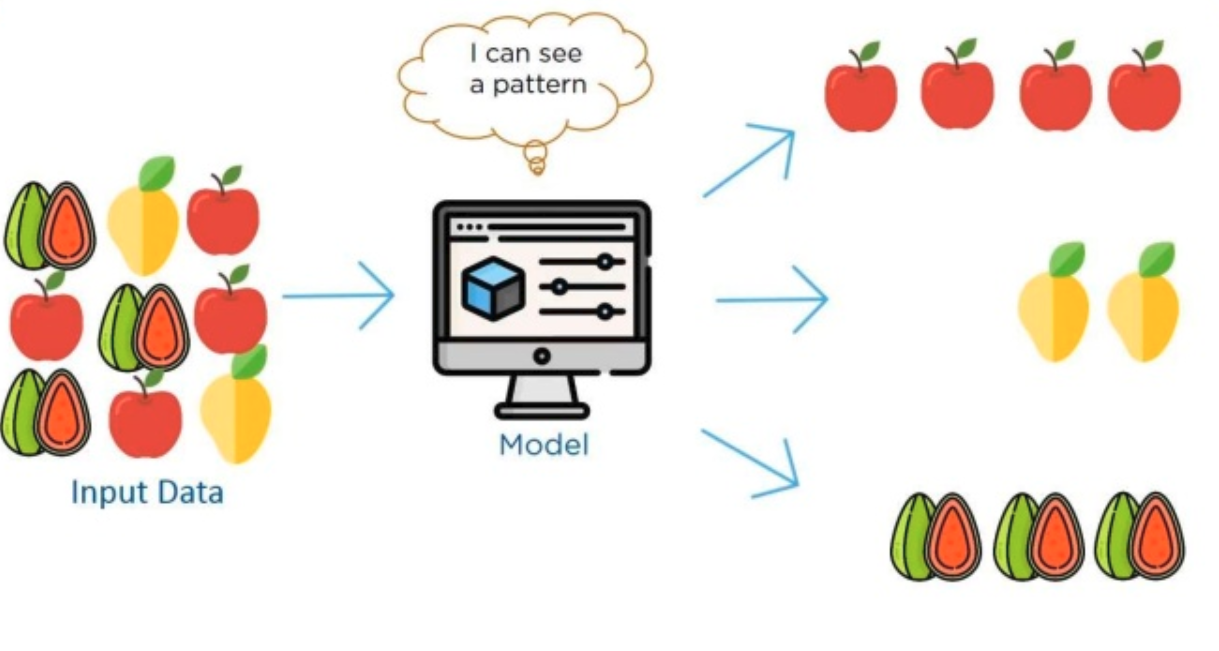
Unsupervised learning
Reinforcement learning
Source: https://www.marutitech.com/businesses-reinforcement-learning/
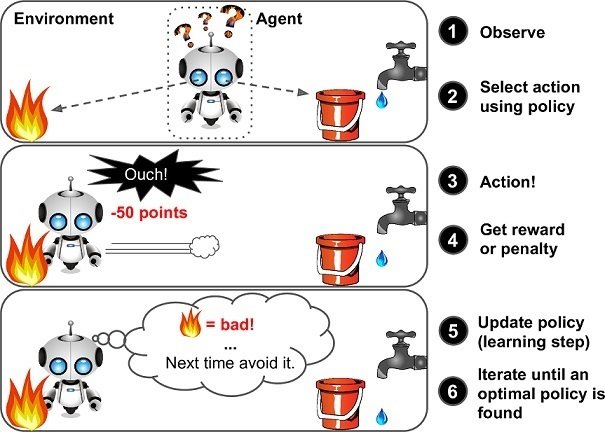
Reinforcement learning
Types of problems
https://github.com/php-ai/php-ml
PHP-ML - Machine Learning library for PHP
Classification



5.1,3.8,1.6,0.2,setosa
4.6,3.2,1.4,0.2,setosa
5.3,3.7,1.5,0.2,setosa
5,3.3,1.4,0.2,setosa
7,3.2,4.7,1.4,versicolor
6.4,3.2,4.5,1.5,versicolor
6.9,3.1,4.9,1.5,versicolor
5.5,2.3,4,1.3,versicolor
5.9,3,5.1,1.8,virginica
5.1,3.5,1.4,0.2,setosa
4.9,3,1.4,0.2,setosa
4.7,3.2,1.3,0.2,setosa
4.6,3.1,1.5,0.2,setosa
5,3.6,1.4,0.2,setosa
5.4,3.9,1.7,0.4,setosa
4.6,3.4,1.4,0.3,setosa
5,3.4,1.5,0.2,setosa
4.4,2.9,1.4,0.2,setosa
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,setosa
5.4,3.7,1.5,0.2,setosa
4.8,3.4,1.6,0.2,setosa
4.8,3,1.4,0.1,setosa
4.3,3,1.1,0.1,setosa
5.8,4,1.2,0.2,setosa
5.7,4.4,1.5,0.4,setosa
5.4,3.9,1.3,0.4,setosa
5.1,3.5,1.4,0.3,setosa
5.7,3.8,1.7,0.3,setosa
5.1,3.8,1.5,0.3,setosa
5.4,3.4,1.7,0.2,setosa
5.1,3.7,1.5,0.4,setosa
4.6,3.6,1,0.2,setosa
5.1,3.3,1.7,0.5,setosa
4.8,3.4,1.9,0.2,setosa
5,3,1.6,0.2,setosa
5,3.4,1.6,0.4,setosa
5.2,3.5,1.5,0.2,setosa
5.2,3.4,1.4,0.2,setosa
4.7,3.2,1.6,0.2,setosa
4.8,3.1,1.6,0.2,setosa
5.4,3.4,1.5,0.4,setosa
5.2,4.1,1.5,0.1,setosa
5.5,4.2,1.4,0.2,setosa
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,setosa
5,3.2,1.2,0.2,setosa
5.5,3.5,1.3,0.2,setosa
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,setosa
4.4,3,1.3,0.2,setosa
5.1,3.4,1.5,0.2,setosa
5,3.5,1.3,0.3,setosa
4.5,2.3,1.3,0.3,setosa
4.4,3.2,1.3,0.2,setosa
5,3.5,1.6,0.6,setosa
5.1,3.8,1.9,0.4,setosa
4.8,3,1.4,0.3,setosa
5.1,3.8,1.6,0.2,setosa
4.6,3.2,1.4,0.2,setosa
5.3,3.7,1.5,0.2,setosa
5,3.3,1.4,0.2,setosa
7,3.2,4.7,1.4,versicolor
6.4,3.2,4.5,1.5,versicolor
6.9,3.1,4.9,1.5,versicolor
5.5,2.3,4,1.3,versicolor
6.5,2.8,4.6,1.5,versicolor
5.7,2.8,4.5,1.3,versicolor
6.3,3.3,4.7,1.6,versicolor
4.9,2.4,3.3,1,versicolor
6.6,2.9,4.6,1.3,versicolor
5.2,2.7,3.9,1.4,versicolor
5,2,3.5,1,versicolor
5.9,3,4.2,1.5,versicolor
6,2.2,4,1,versicolor
6.1,2.9,4.7,1.4,versicolor
5.6,2.9,3.6,1.3,versicolor
6.7,3.1,4.4,1.4,versicolor
5.6,3,4.5,1.5,versicolor
5.8,2.7,4.1,1,versicolor
6.2,2.2,4.5,1.5,versicolor
5.6,2.5,3.9,1.1,versicolor
5.9,3.2,4.8,1.8,versicolor
6.1,2.8,4,1.3,versicolor
6.3,2.5,4.9,1.5,versicolor
6.1,2.8,4.7,1.2,versicolor
6.4,2.9,4.3,1.3,versicolor
6.6,3,4.4,1.4,versicolor
6.8,2.8,4.8,1.4,versicolor
6.7,3,5,1.7,versicolor
6,2.9,4.5,1.5,versicolor
5.7,2.6,3.5,1,versicolor
5.5,2.4,3.8,1.1,versicolor
5.5,2.4,3.7,1,versicolor
5.8,2.7,3.9,1.2,versicolor
6,2.7,5.1,1.6,versicolor
5.4,3,4.5,1.5,versicolor
6,3.4,4.5,1.6,versicolor
6.7,3.1,4.7,1.5,versicolor
6.3,2.3,4.4,1.3,versicolor
5.6,3,4.1,1.3,versicolor
5.5,2.5,4,1.3,versicolor
5.5,2.6,4.4,1.2,versicolor
6.1,3,4.6,1.4,versicolor
5.8,2.6,4,1.2,versicolor
5,2.3,3.3,1,versicolor
5.6,2.7,4.2,1.3,versicolor
5.7,3,4.2,1.2,versicolor
5.7,2.9,4.2,1.3,versicolor
6.2,2.9,4.3,1.3,versicolor
5.1,2.5,3,1.1,versicolor
5.7,2.8,4.1,1.3,versicolor
6.3,3.3,6,2.5,virginica
5.8,2.7,5.1,1.9,virginica
7.1,3,5.9,2.1,virginica
6.3,2.9,5.6,1.8,virginica
6.5,3,5.8,2.2,virginica
7.6,3,6.6,2.1,virginica
4.9,2.5,4.5,1.7,virginica
7.3,2.9,6.3,1.8,virginica
6.7,2.5,5.8,1.8,virginica
7.2,3.6,6.1,2.5,virginica
6.5,3.2,5.1,2,virginica
6.4,2.7,5.3,1.9,virginica
6.8,3,5.5,2.1,virginica
5.7,2.5,5,2,virginica
5.8,2.8,5.1,2.4,virginica
6.4,3.2,5.3,2.3,virginica
6.5,3,5.5,1.8,virginica
7.7,3.8,6.7,2.2,virginica
7.7,2.6,6.9,2.3,virginica
6,2.2,5,1.5,virginica
6.9,3.2,5.7,2.3,virginica
5.6,2.8,4.9,2,virginica
7.7,2.8,6.7,2,virginica
6.3,2.7,4.9,1.8,virginica
6.7,3.3,5.7,2.1,virginica
7.2,3.2,6,1.8,virginica
6.2,2.8,4.8,1.8,virginica
6.1,3,4.9,1.8,virginica
6.4,2.8,5.6,2.1,virginica
7.2,3,5.8,1.6,virginica
7.4,2.8,6.1,1.9,virginica
7.9,3.8,6.4,2,virginica
6.4,2.8,5.6,2.2,virginica
6.3,2.8,5.1,1.5,virginica
6.1,2.6,5.6,1.4,virginica
7.7,3,6.1,2.3,virginica
6.3,3.4,5.6,2.4,virginica
6.4,3.1,5.5,1.8,virginica
6,3,4.8,1.8,virginica
6.9,3.1,5.4,2.1,virginica
6.7,3.1,5.6,2.4,virginica
6.9,3.1,5.1,2.3,virginica
5.8,2.7,5.1,1.9,virginica
6.8,3.2,5.9,2.3,virginica
6.7,3.3,5.7,2.5,virginica
6.7,3,5.2,2.3,virginica
6.3,2.5,5,1.9,virginica
6.5,3,5.2,2,virginica
6.2,3.4,5.4,2.3,virginica
5.9,3,5.1,1.8,virginicaClassification
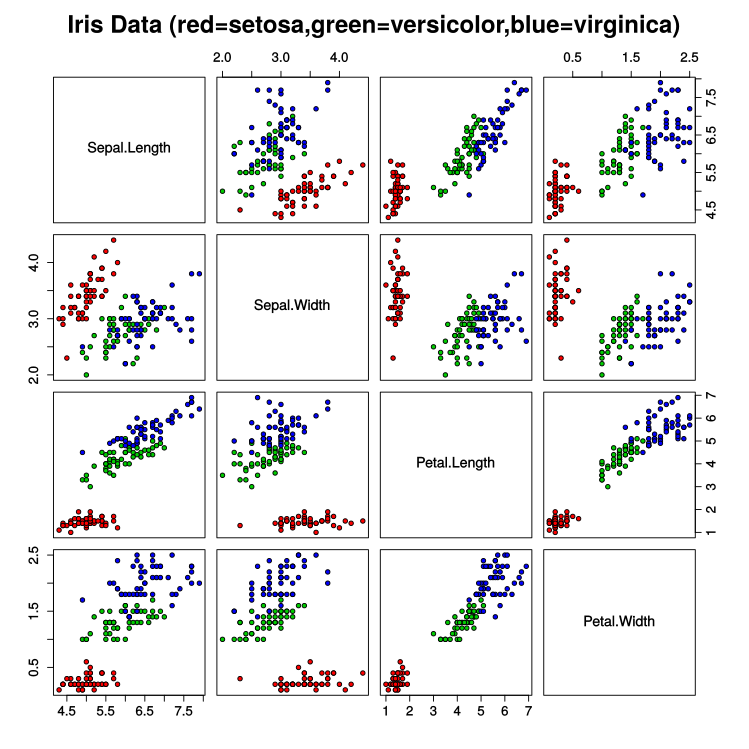
Classification
use Phpml\Classification\KNearestNeighbors;
use Phpml\CrossValidation\RandomSplit;
use Phpml\Dataset\Demo\IrisDataset;
use Phpml\Metric\Accuracy;
$dataset = new IrisDataset();
$split = new RandomSplit($dataset);
$classifier = new KNearestNeighbors();
$classifier->train(
$split->getTrainSamples(),
$split->getTrainLabels()
);
$predicted = $classifier->predict($split->getTestSamples());
echo sprintf("Accuracy: %s",
Accuracy::score($split->getTestLabels(), $predicted)
);
Classification
51.403007;7.208546;good
52.2688736;10.5267696;good
52.235083;5.181552;good
47.5292;9.9267;good
47.9704873;17.7852936;moderate
51.4625;13.526666666667;moderate
48.7344444;19.1128073;good
46.815277777778;9.8558333333333;good
51.1506269;14.968707;good
47.041668;15.433056;good
50.303207830366;6.0017362891249;good
47.178333333333;14.676666666667;good
47.102253726073;9.3375502158063;good
47.5818083;12.1724111;good
50.97;9.8;moderate
47.146155;5.551039;good
51.64265556;15.12780833;good
54.353333333333;18.635277777778;good
50.5425641;12.7792228;good
52.234504;6.919494;moderate
50.467528;13.412696;good
51.233652208391;5.1639788468472;good
52.14325;19.233225;good
45.14254358;10.04384767;unhealthy for sensitive
49.228472;17.675083;unhealthy for sensitive
50.80425833;8.76932778;moderate
48.396866667006;9.9789750003815;moderate
53.4708393;7.4848308;good
47.871158;17.273464;good
48.33472;16.729445;good
47.409443;15.253333;goodVisualization
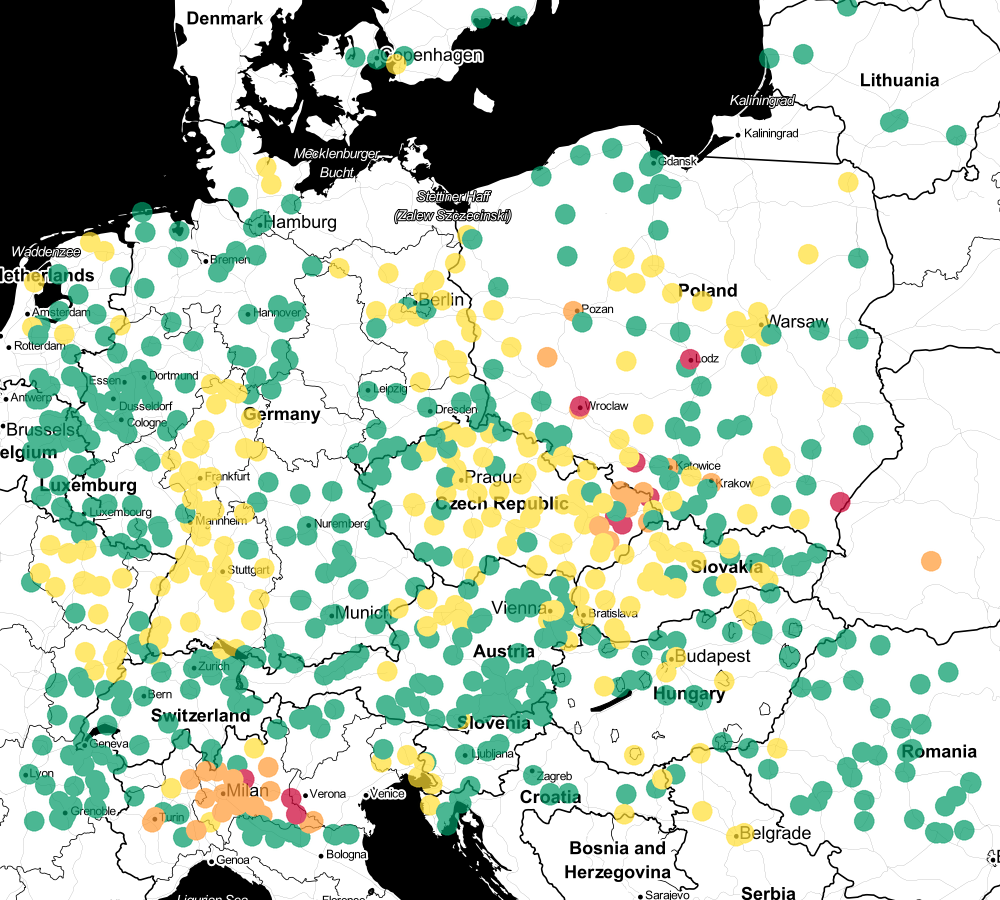
$minLat = 41.34343606848294;
$maxLat = 57.844750992891;
$minLng = -16.040039062500004;
$maxLng = 29.311523437500004;
$step = 0.1;
$k = 3;
$dataset = new CsvDataset(__DIR__.'/../data/air.csv', 2, false, ';');
$estimator = new KNearestNeighbors($k);
$estimator->train($dataset->getSamples(), $dataset->getTargets());
$lines = [];
for ($lat=$minLat; $lat<$maxLat; $lat+=$step) {
for ($lng=$minLng; $lng<$maxLng; $lng+=$step) {
$lines[] = sprintf('%s;%s;%s', $lat, $lng, $estimator->predict([[$lat, $lng]])[0]);
}
}
file_put_contents(__DIR__.'/../data/airVis.csv', implode(PHP_EOL, $lines));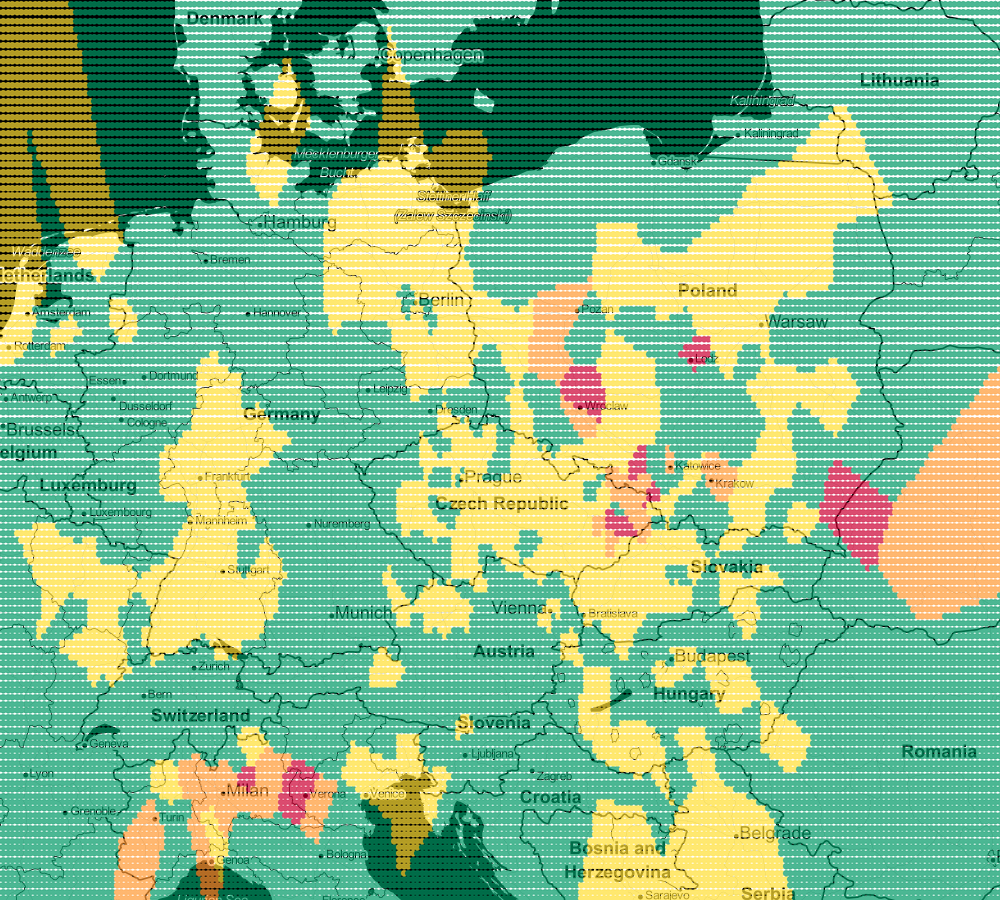
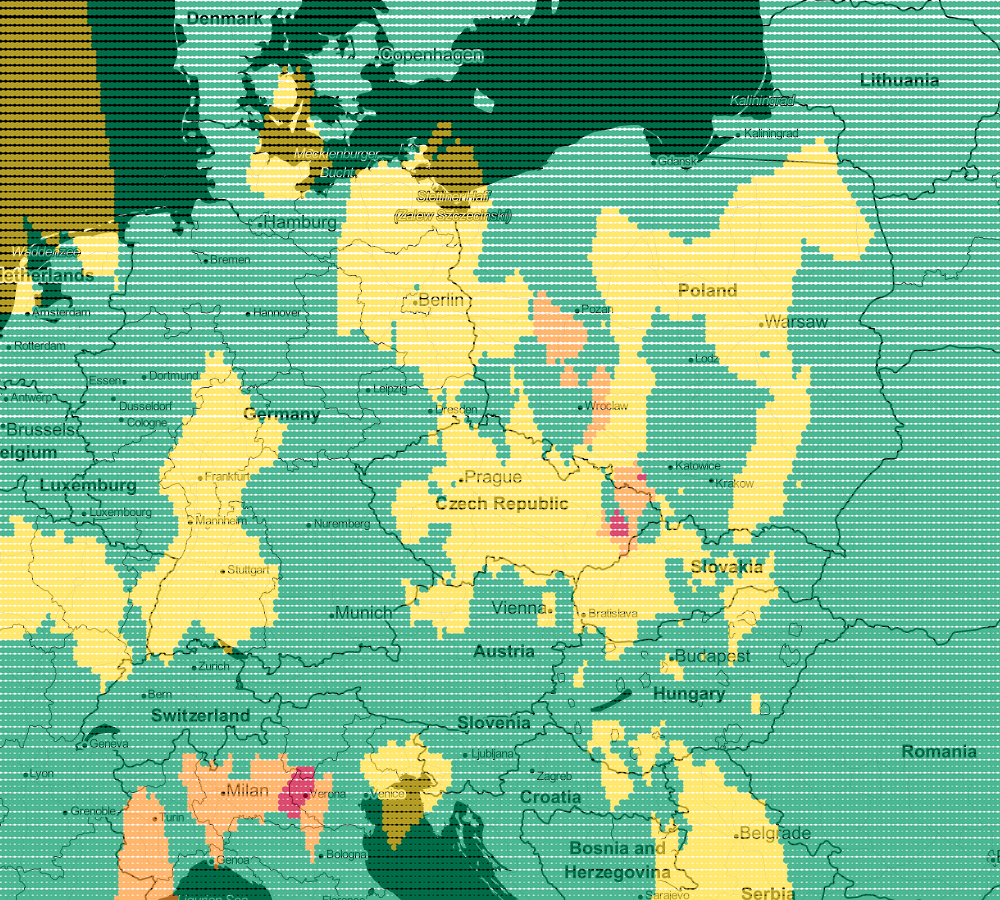
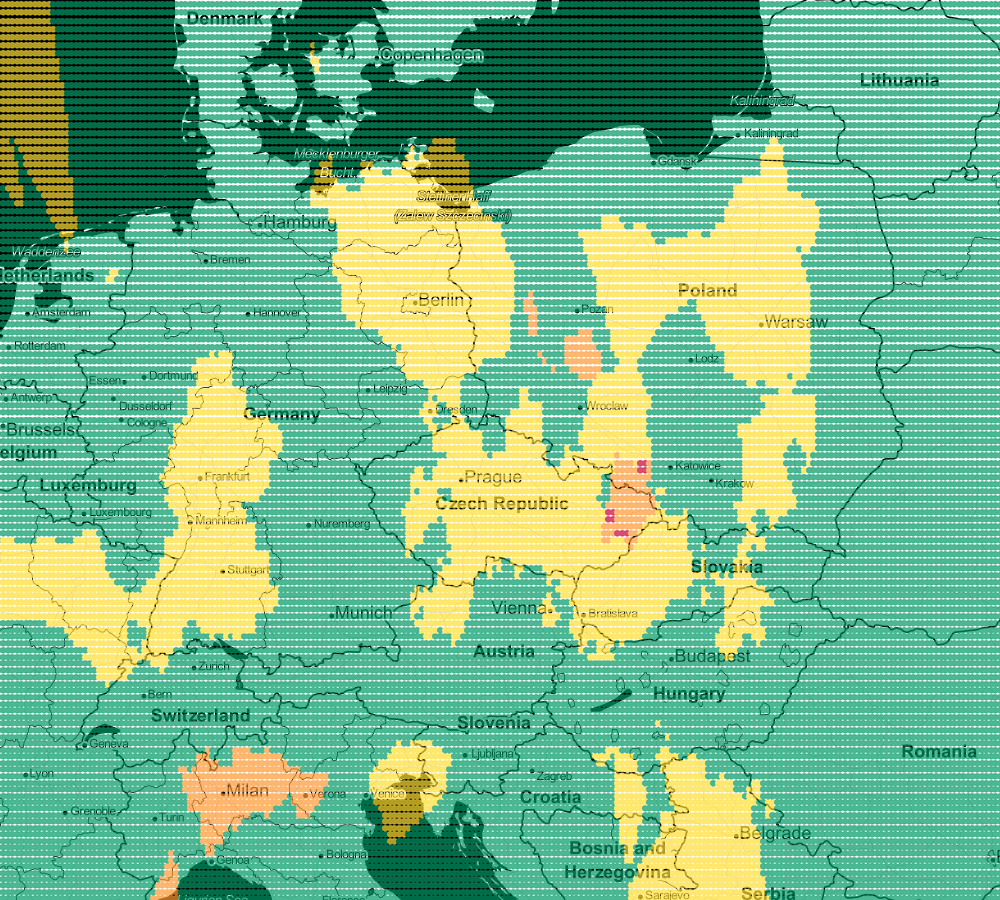
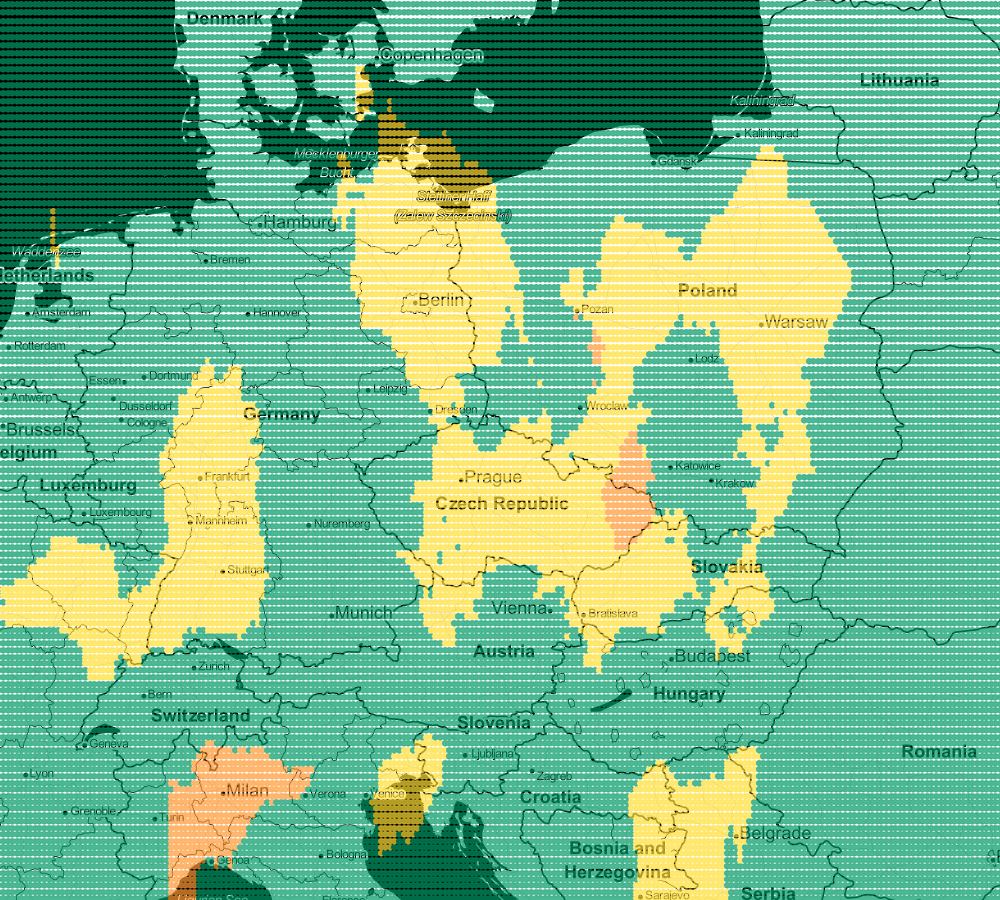
Regression
Miles Price
9300 7100
10565 15500
15000 4400
15000 4400
17764 5900
57000 4600
65940 8800
73676 2000
77006 2750
93739 2550
146088 960
153260 1025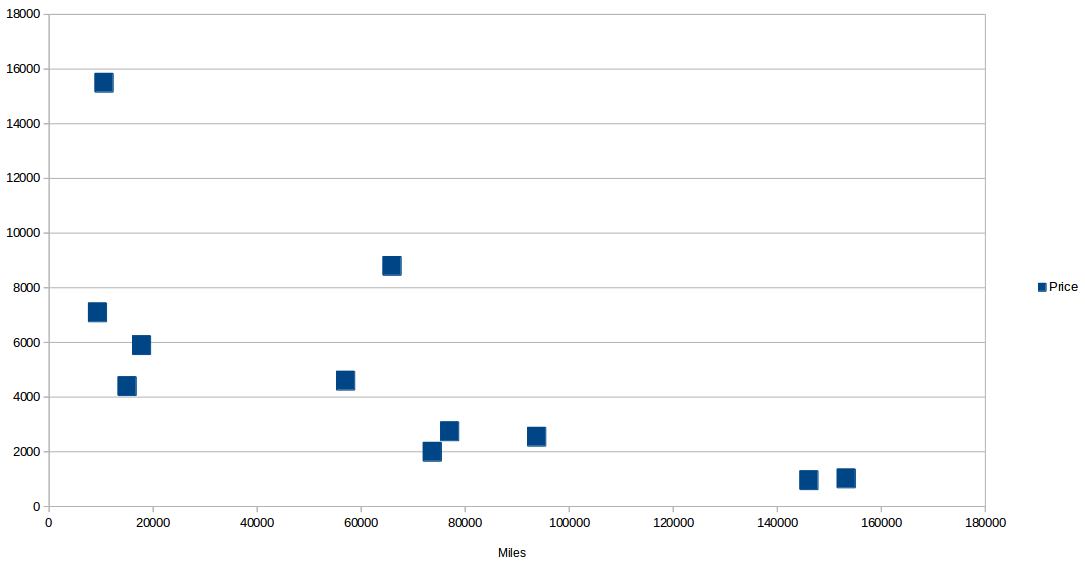
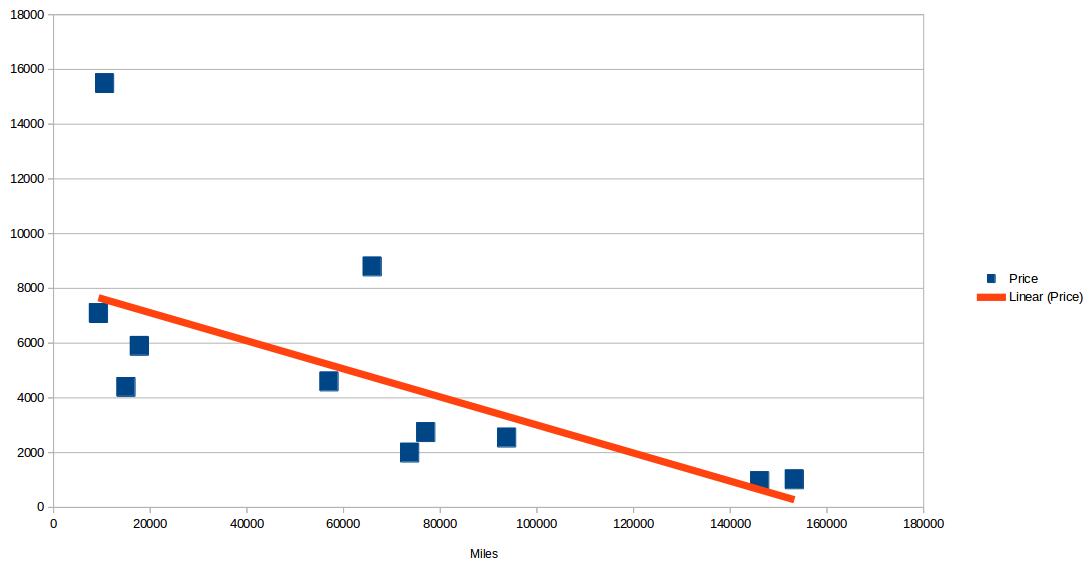
Regression
use Phpml\Regression\LeastSquares;
$samples = [[9300], [10565], [15000], [15000], [17764], [57000], [65940], [73676], [77006], [93739], [146088], [153260]];
$targets = [7100, 15500, 4400, 4400, 5900, 4600, 8800, 2000, 2750, 2550, 960, 1025];
$regression = new LeastSquares();
$regression->train($samples, $targets);
$regression->getCoefficients();
$regression->getIntercept();
$price = $regression->predict([35000]);
Clustering
41.793935909;-87.625680278
41.907274031;-87.722791892
41.851296671;-87.706458801
41.775963639;-87.615517372
41.794879;-87.63179049
41.799461412;-87.596206318
41.989599401;-87.660256868
42.019398729;-87.67543958
42.004487311;-87.679846425
42.009087258;-87.690171862
41.799518433;-87.590997844
41.875039579;-87.743690267
41.875198392;-87.717479393
41.78640901;-87.649813179
41.766229647;-87.577855722
41.900062396;-87.620884259
41.744708666;-87.616371298
41.7737319;-87.651916442
41.692289426;-87.647852131
41.874236291;-87.674657583
41.761450225;-87.623211368
41.831030756;-87.62442424741.974853031;-87.713545123
41.974605662;-87.660819291
41.815419529;-87.702711186
41.750341521;-87.657371388
41.854659562;-87.716303651
41.834650408;-87.62843175
41.793435216;-87.70876482
41.894904052;-87.626344479
41.894993069;-87.746918939
41.90984267;-87.729545576
41.967477901;-87.739224006
41.87522978;-87.728549617
41.765946803;-87.595563723
41.908222431;-87.679234761
41.882757453;-87.709603286
41.876121224;-87.641003973
41.809372853;-87.704024967
41.977043475;-87.76899404
41.943664148;-87.646353396
41.759350571;-87.623168543
41.693840666;-87.613406835
41.964351639;-87.661000678Clustering

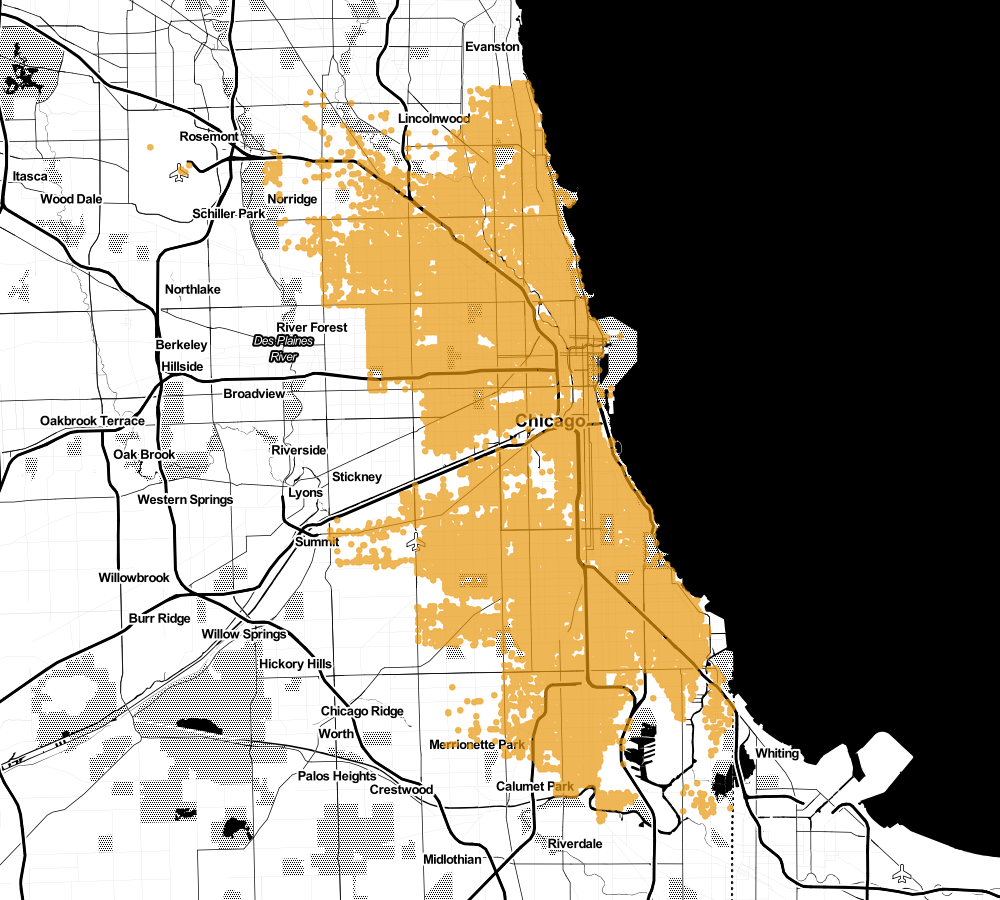
Clustering
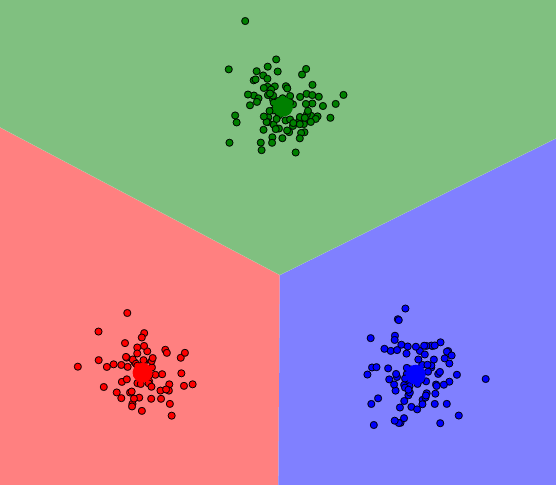
Clustering
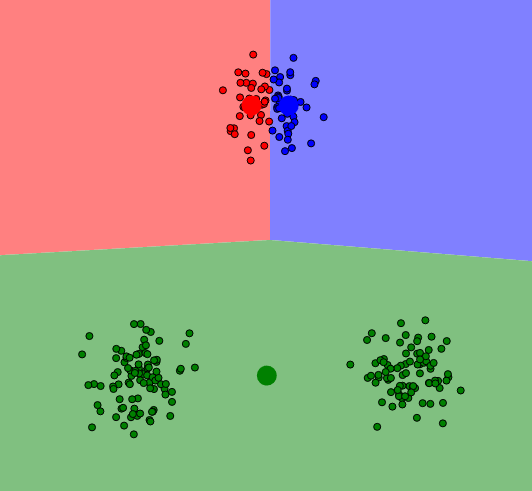
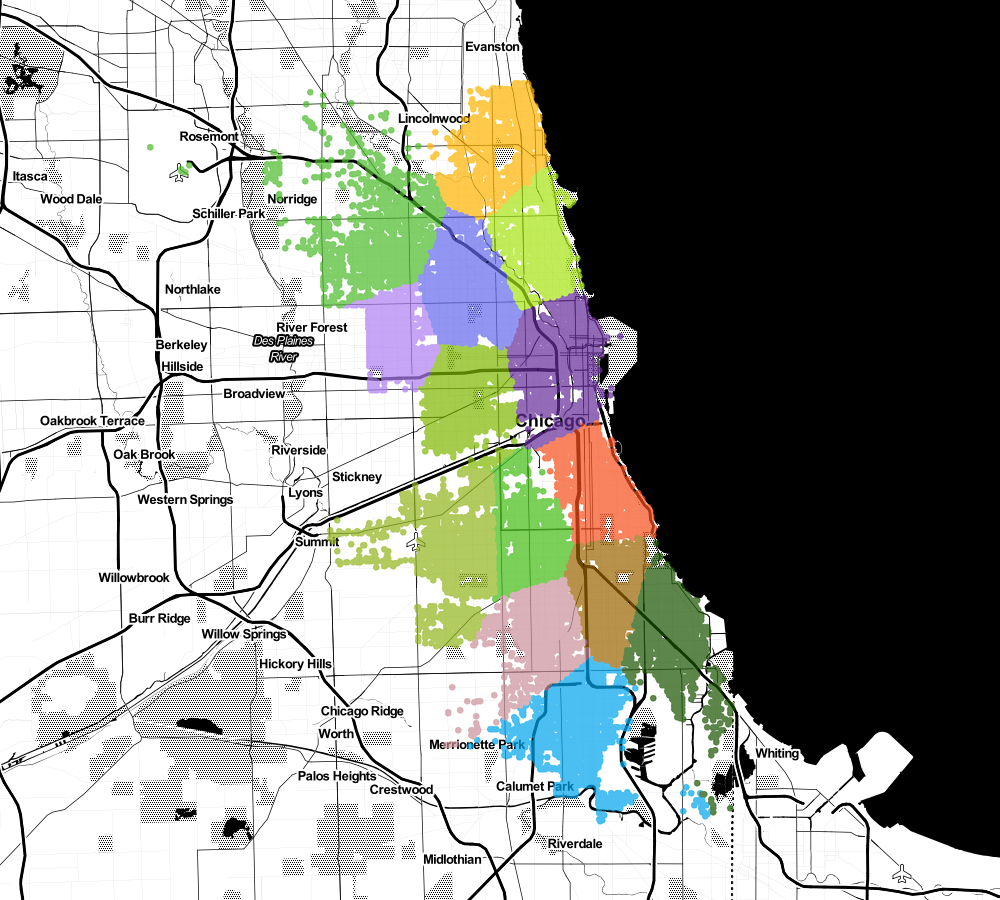
Clustering
Clustering
use Phpml\Clustering\KMeans;
$samples = [
[1, 1], [8, 7], [1, 2],
[7, 8], [2, 1], [8, 9]
];
$kmeans = new KMeans(2);
$clusters = $kmeans->cluster($samples);
$clusters = [
[[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 1]],
[[8, 7], [7, 8], [8, 9]]
];Preprocessing
use Phpml\Preprocessing\Imputer;
use Phpml\Preprocessing\Imputer\Strategy\MeanStrategy;
$data = [
[1, null, 3, 4],
[4, 3, 2, 1],
[null, 6, 7, 8],
[8, 7, null, 5],
];
$imputer = new Imputer(
null, new MeanStrategy(), Imputer::AXIS_COLUMN, $data
);
$imputer->transform($data);
$data = [
[1, 5.33, 3, 4],
[4, 3, 2, 1],
[4.33, 6, 7, 8],
[8, 7, 4, 5],
];Feature Extraction
use Phpml\FeatureExtraction\TokenCountVectorizer;
use Phpml\Tokenization\WhitespaceTokenizer;
$samples = [
'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet dolor',
'Mauris placerat ipsum dolor',
'Mauris diam eros fringilla diam',
];
$vectorizer = new TokenCountVectorizer(new WhitespaceTokenizer());
$vectorizer->fit($samples);
$vectorizer->getVocabulary()
$vectorizer->transform($samples);
$tokensCounts = [
[0 => 1, 1 => 1, 2 => 2, 3 => 1, 4 => 1, 5 => 0, 6 => 0, 7 => 0, 8 => 0, 9 => 0],
[0 => 0, 1 => 1, 2 => 1, 3 => 0, 4 => 0, 5 => 1, 6 => 1, 7 => 0, 8 => 0, 9 => 0],
[0 => 0, 1 => 0, 2 => 0, 3 => 0, 4 => 0, 5 => 1, 6 => 0, 7 => 2, 8 => 1, 9 => 1],
];Model selection
use Phpml\CrossValidation\RandomSplit;
use Phpml\CrossValidation\StratifiedRandomSplit;
use Phpml\Dataset\ArrayDataset;
$dataset = new ArrayDataset(
$samples = [[1], [2], [3], [4]],
$labels = ['a', 'a', 'b', 'b']
);
$randomSplit = new RandomSplit($dataset, 0.5);$dataset = new ArrayDataset(
$samples = [[1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]],
$labels = ['a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'b', 'b']
);
$split = new StratifiedRandomSplit($dataset, 0.5);Workflow
$transformers = [
new Imputer(null, new MostFrequentStrategy()),
new Normalizer(),
];
$estimator = new SVC();
$samples = [
[1, -1, 2],
[2, 0, null],
[null, 1, -1],
];
$targets = [
4,
1,
4,
];
$pipeline = new Pipeline($transformers, $estimator);
$pipeline->train($samples, $targets);
$predicted = $pipeline->predict([[0, 0, 0]]);
// $predicted == 4- Feature Selection
- Dimensionality Reduction
- Datasets
- Models Management
- Neural Network
- Metric
- Association Rule Learning
- Ensemble Algorithms
- Math
https://github.com/php-ai/php-ml
Example applications
Beer Judge
https://github.com/akondas/phpcon-2016-ml/blob/master/examples/beers.php
Beer judge
ibu,alk,ext,score,name
75,6.5,16,7,"Szalony Alchemik"
28,4.2,12.5,6,"Miss Lata"
40,4,10.5,7,"Tajemniczy Jeździec"
42,5.7,14.5,6,"Dziki Samotnik"
20,2.9,7.7,4,"Dębowa Panienka"
36,5.2,12.5,5,"Piękna Nieznajoma"
28,4.8,14.0,3,"Mała Czarna"
35,4.6,12.5,7,"Nieproszony Gość"
20,5.2,12.5,8,"Ostatni sprawiedliwy"
30,4.8,12.5,6,"Dziedzic Pruski"
75,7.5,18.0,9,"Bawidamek"
45,4.7,12.0,8,"Miś Wojtek"
20,5.2,13.0,8,"The Dancer"
30,4.7,12.0,4,"The Dealer"
120,8.9,19.0,3,"The Fighter"
85,6.4,16.0,9,"The Alchemist"
100,10.3,24,4,"The Gravedigger"
40,4.8,12.0,8,"The Teacher"
75,7.0,16.0,7,"The Butcher"
80,6.7,16.0,5,"The Miner"Beer judge
use Phpml\Classification\SVC;
use Phpml\CrossValidation\StratifiedRandomSplit;
use Phpml\Dataset\CsvDataset;
use Phpml\Metric\Accuracy;
use Phpml\SupportVectorMachine\Kernel;
$dataset = new CsvDataset('examples/beers.csv', 3);
$split = new StratifiedRandomSplit($dataset, 0.1);
$classifier = new SVC(Kernel::RBF);
$classifier->train($split->getTrainSamples(), $split->getTrainLabels());
$predicted = $classifier->predict($split->getTestSamples());
echo sprintf("Accuracy: %s\n", Accuracy::score($split->getTestLabels(), $predicted));
$newBeer = [20, 2.5, 7];
echo sprintf("New beer score: %s\n", $classifier->predict($newBeer));
Code Review Estimator
https://github.com/akondas/code-review-estimator
Summary
ML is all about the proccess
- Define a problem
- Gather your data
- Prepare your data for ML
- Select algorithm
- Train model
- Tune parameters
- Select finale model
- Validate finale model
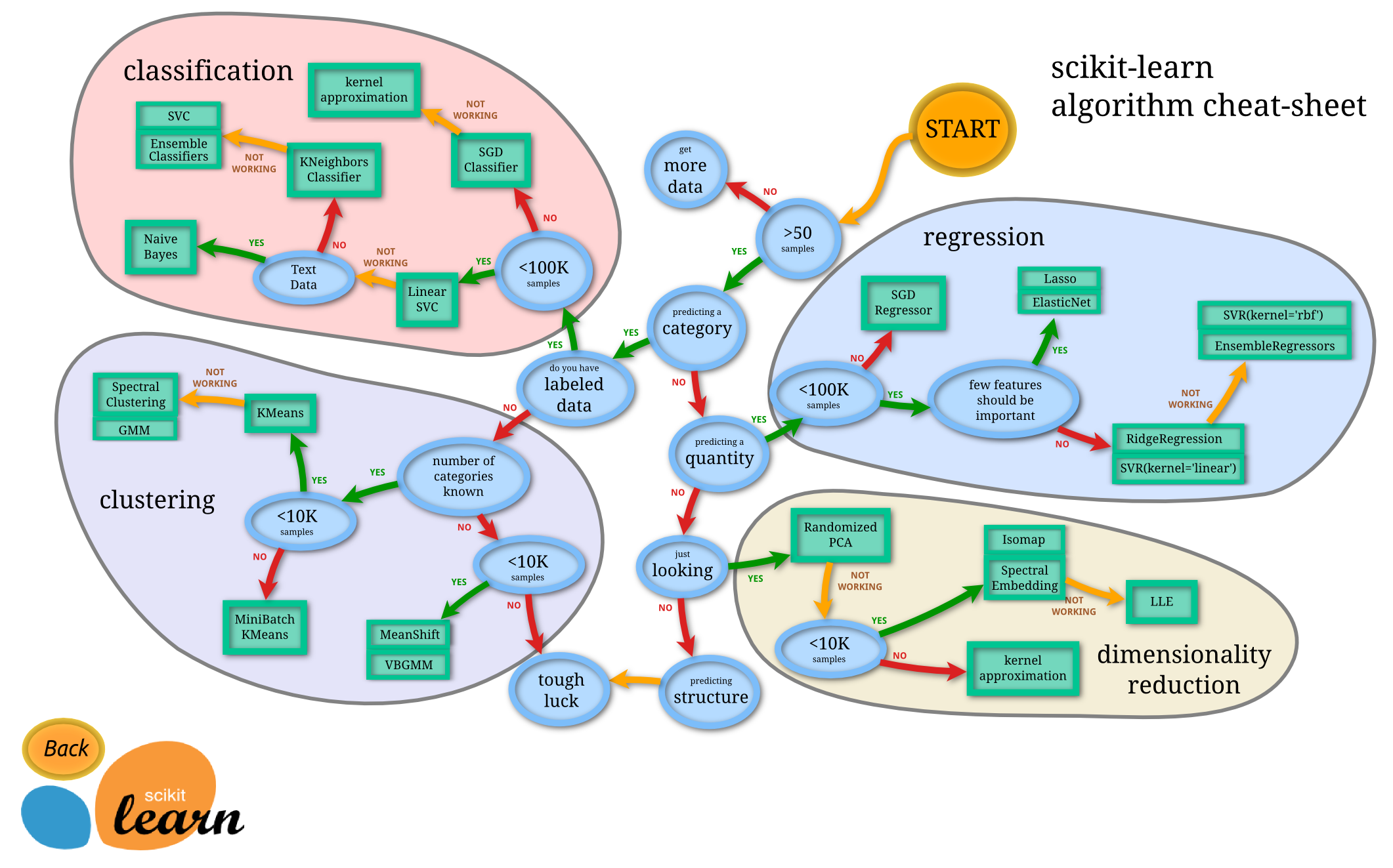
source: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/tutorial/machine_learning_map/index.html
Summary
- the most important is question, data is secondary (but also important)
- many algorithms and techniques
- application can be very simple but also extremely sophiticated
- sometimes difficult to find correct answer
- base math skills are important
Summary
https://twitter.com/JustinMatejka/status/859075295059562498


PHP 7.0
206,128 instances classified in 30 seconds
(6,871 per second)
https://github.com/syntheticminds/php7-ml-comparison
Python 2.7
106,879 instances classified in 30 seconds
(3,562 per second)
NodeJS v5.11.1
245,227 instances classified in 30 seconds
(8,174 per second)
Java 8
16,809,048 instances classified in 30 seconds
(560,301 per second)PHP 7.1
302,931 instances classified in 30 seconds
(10,098 per second)PHP 7.2
365,568 instances classified in 30 seconds
(12,186 per second)PHP 7.3
408,667 instances classified in 30 seconds
(13,622 per second)
Where to begin?
kaggle.com
Where to begin?


Q&A
Thanks for listening
@ ArkadiuszKondas

https://arkadiuszkondas.com
https://github.com/akondas
Machine Learning - how to start to teach the machine
By Arkadiusz Kondas
Machine Learning - how to start to teach the machine
The main goal of Machine Learning is to create intelligent systems that can improve and acquire new knowledge using input data. In practice, this translates into the use of one of hundreds of different available algorithms. This lecture is an introduction to ML from the total basics. We will learn the basic vocabulary and types of problems which the ML allows. I will also present the technique of building the whole pipeline, with the help of which we will go through all stages of ML: data processing (preprocessing), selection of algorithms and evaluation of its effectiveness.
- 2,178



