A gentle intro to Machine Learning
UBC Math Grad Seminar
Bernhard Konrad
14 April 2015
Why machine learning?
We live in very exciting times! We have datasets at our hands that we could not conceive of even a few years ago.
"Uber, the world’s largest taxi company, owns no vehicles. Facebook, the world’s most popular media owner, creates no content. Alibaba, the most valuable retailer, has no inventory. And Airbnb, the world’s largest accommodation provider, owns no real estate."
Why machine learning?
-
Uber: How many cab riders and drivers you will have and need at time X?
-
Facebook: Out of all the possible stories, which do you show on a user's timeline?
-
Airbnb: How is growth/update in city A different from city B, why, and what can do about it?
-
LinkedIn: Detect and stop fraud (non-normal behaviour).
-
Khan Academy: Millions of math problems are attempted
online per day. When is someone proficient? -
Netflix: What new show should we make?
-
Enlitic: Let algorithms help doctors make more accurate diagnoses.
-
....
Why machine learning?
- Storage is cheap
- Computer time is cheap
- Machine learning algorithms embarrassingly easy to use (libraries in R, Python, Spark, C++, ...)
- ML mathematically appealing (intuition, at least)
- Surprisingly powerful
- Fun (and you sound like you're fancy)
Types of machine learning
Regression (supervised)
Look for quantitative prediction, given input features. Training set with correct outcome.
- Linear regression
- Random forest
- Neural Networks
- K nearest neighbors
- ...
Classic example: predict housing prices (eg. Opendoor)
Types of machine learning
Linear Regression (supervised)

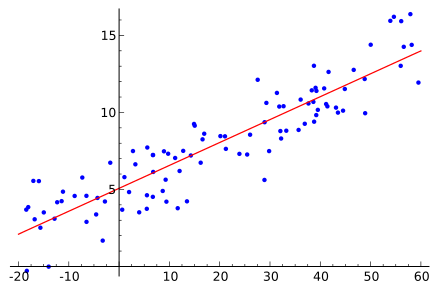
from sklearn import linear_model
X = [[50, 3000],
[60, 2500],
[150, 4200]]
y = [20, 25, 17]
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression().fit(X, y)
regr.predict([70, 3200]) #-> 19.74Types of machine learning
Classification (supervised)
Make a yes-or-no-decision, based on features.
Training set with correct labels.
- Logistic regression
- Support Vector Classifier
- Neural Networks
- Random Forest
- K nearest neighbors
- ...
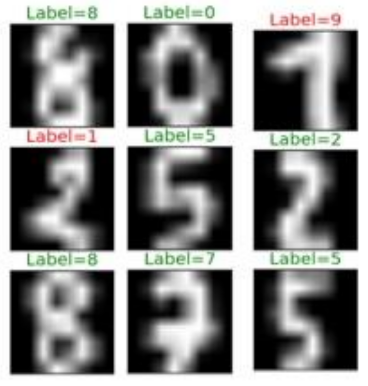
Classic example: hand-written-digit recognition
Types of machine learning
Logistic regression classification (supervised)

from sklearn import linear_model
X = [[50, 3000],
[60, 2500],
[150, 4200]]
y = [0, 1, 1]
regr = linear_model.LogisticRegression().fit(X, y)
print(regr.predict([70, 3200])) # -> 1Types of machine learning
Clustering (unsupervised)
Find similar data points (for exploration and plotting).
No labels available.
- K means
- Hierarchical clustering
- DBSCAN
- Expectation maximization
- ...
Classic example: Social network analysis
Types of machine learning
K-means clustering (unsupervised)
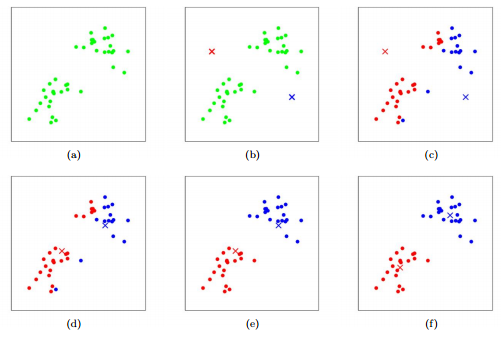
Randomly set K cluster centroids.
Repeat until convergence:
- Assign each point to the closest centroid
- Update centroids as mean of points in cluster
Two practical examples
1. Classification:
Given the statement of a math problem, predict the corresponding topic.
Natural language processing (NLP) and data from Math Education Resources
2. Clustering:
Compress input image by using fewer colours.
K-means algorithm on pixel values of input image


Other things to talk about
- Recommender systems
- Online learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Anomaly detection
- Natural language processing
- Big data
- Deep learning (eg in image recognition)
Machine_Learning
By Bernhard Konrad
Machine_Learning
- 951



