Get checked online
Mathematical models on Increasing HIV testing in Vancouver
Work in progress, June 9th 2015
Bernhard Konrad, Dan Coombs (UBC)
Warren Michelow, Mark Gilbert (BCCDC)


Get checked online
Mathematical models on Increasing HIV testing in Vancouver
This talk may contain explicit language - please attend at your own discretion.

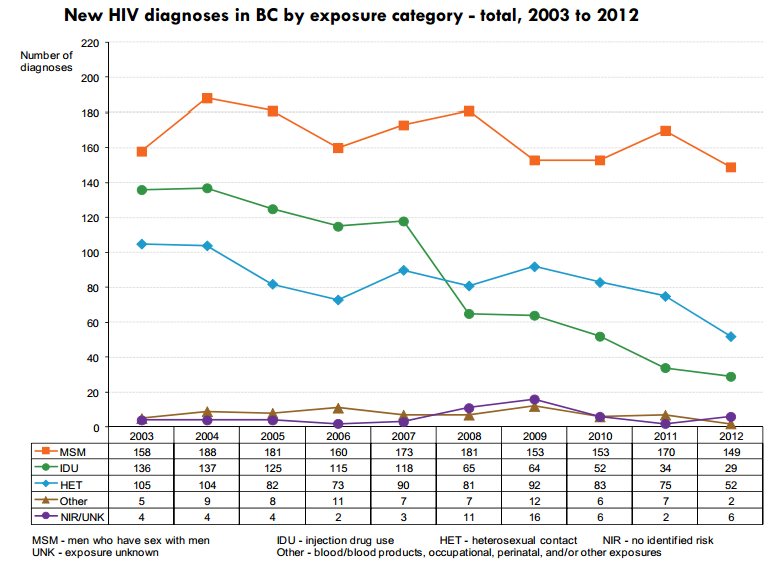
HIV in Canada
Canada
British Columbia
Vancouver
- 71,000 HIV+ (2011)
- 3,200 new diagnosis every year
- one new infection every 2.5h
- 300 new diagnosis every year
- 3,500 unaware of infection (25%!)
- 6,000 HIV+ (1.2%)
- 175 new infections every year
- 150 new diagnosis every year
- ~50% MSM, ~25% IDU, ~25%
Understand! Non-improvement for MSM
GetCheckedOnline (GCO)
BCCDC survey data
- Sex Now (Canada-wide, ongoing since 2000)
- ManCount (Vancouver, 2008)
=> MSM use the internet (you don't say...) to meet sexual partners and to look for health information.
=> 23% of young men under age of 30 never tested for HIV
GCO
- Print lab form, go to LifeLab, get results online/phone
- Check for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, HIV, Syphilis, HCV
- Goal: Start treatment (as prevention), change risk behaviour
Mathematical models - starting simple
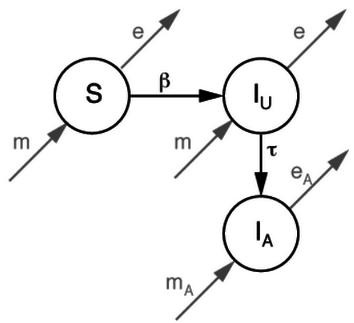
Find total number of new infections as function of testing rate
Change in risk behaviour if aware of infection
Rate of risky events
Sensitivity Analysis
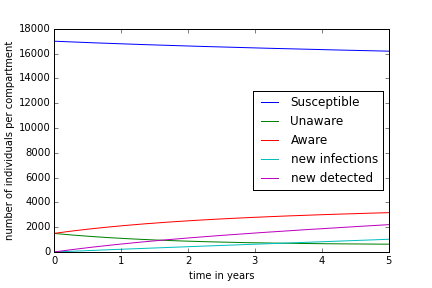
Data: ~175 annual new infections
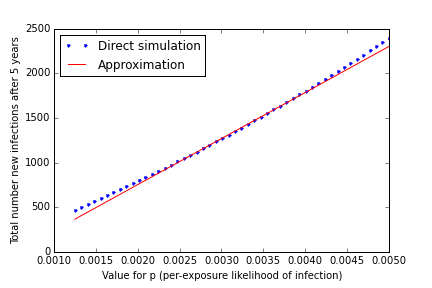
Find total number of new infections as function of testing rate
The Direct Differential Method
Let
ODE with parameters
We want
where J is the Jacobian and
can be found analytically.
The Direct Differential Method
It is more typical to consider the relative change, e.g. in the simple model:
That is, doubling per-exposure risk leads to a relative increase of total new infections of a factor of 1.16.
Effect of change in testing rate:
Susceptibles: 0.01
Infected unaware: -1.03
Infected aware: 0.15
new infections: -0.19
new dections: 0.34
Extracting parameters from surveys

Change in risk behaviour if aware of infection
Rate of risky events
- Sex Now (Canada-wide, ongoing since 2000)
- ManCount (Vancouver, 2008)
- BCCDC Acute study (HIV- cohort)
Survey data
BCCDC Acute study (HIV-)
- 166 MSM recruited at HIV testing clinics in Vancouver between June 2011 - March 2012
- Four questionnaires, four network grids on days 7, 30, 180, 360
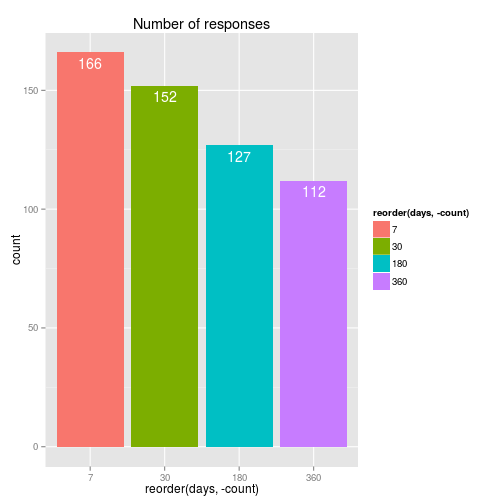
Q: Testing behaviour, general risk behaviour, HIV knowledge
Grids: Detailed interview on partnerships and risk events
BCCDC Acute study (HIV-)
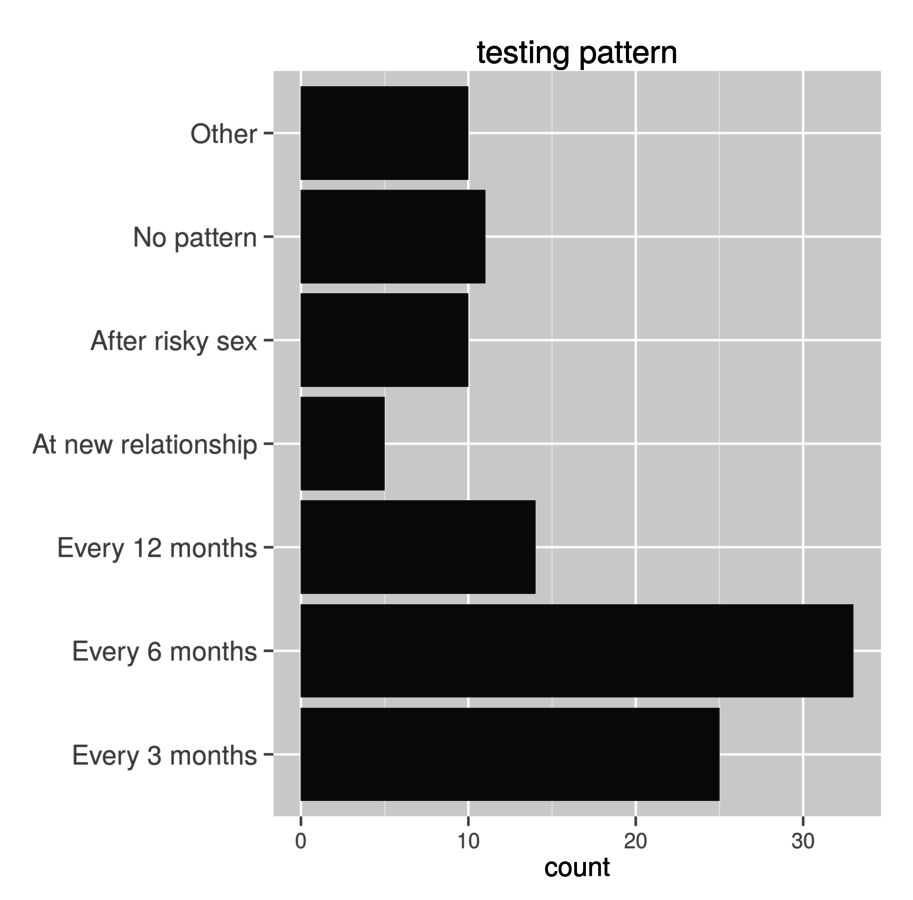
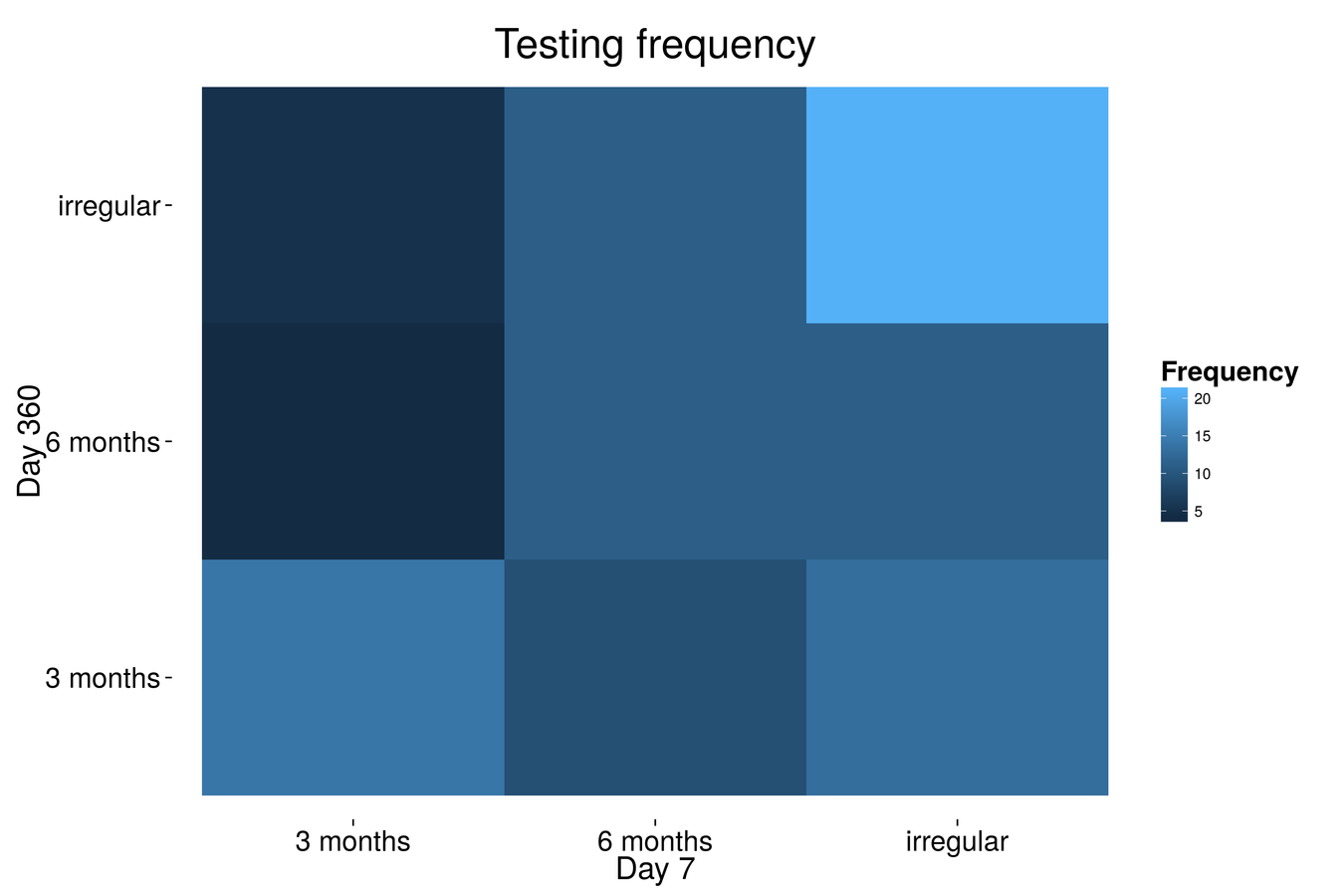
"What best describes your usual testing pattern."
Questionnaires: Testing behaviour
BCCDC Acute study (HIV-)
Questionnaires: general risk behaviour
Number of male partners
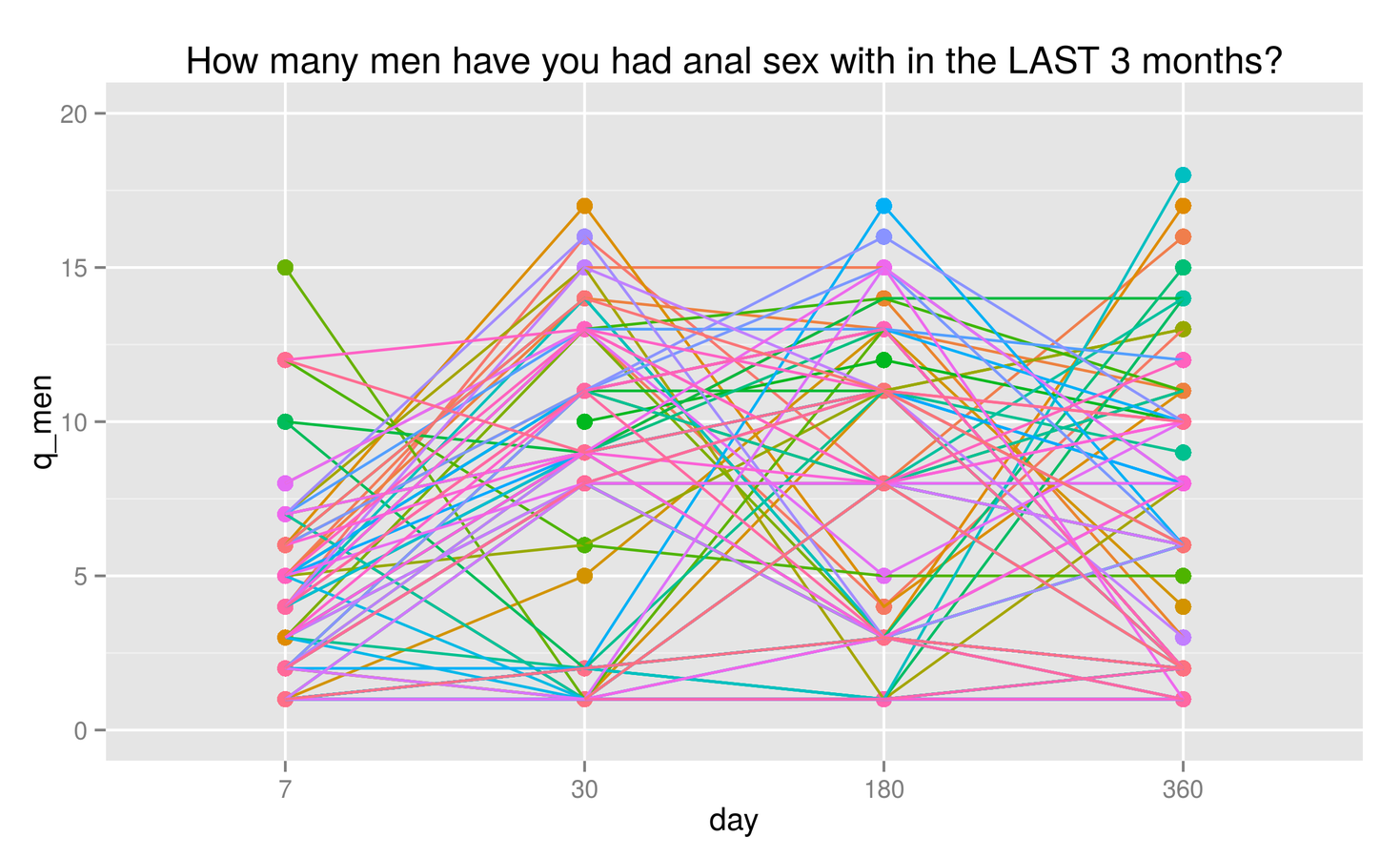
BCCDC Acute study (HIV-)
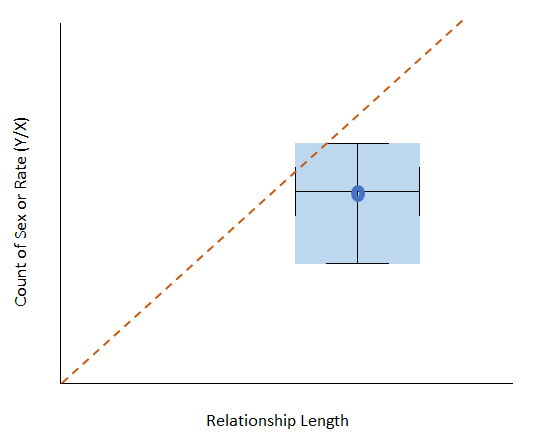
Grid: Relationships and risk events
Length and number of recent relationships
"During the past year, how often did you have sex with this partner."
The role of GCO in a diverse population

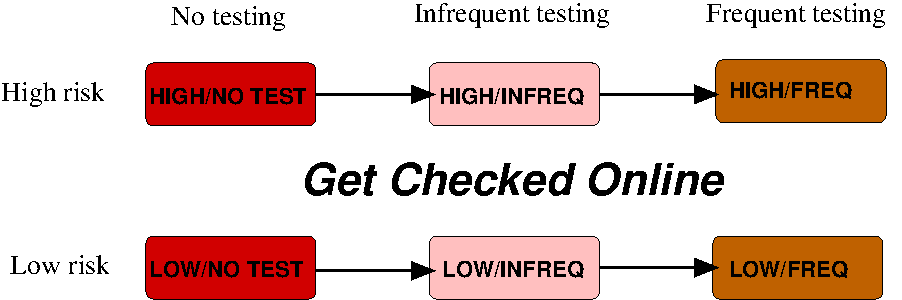





The role of GCO in a diverse population

- Identify/Classify subgroup boundaries (hand-picked or clustering)
- Average relevant parameters to obtain average subgroup risk, testing
- Estimate mixing rates of subgroups
- Report resulting sensitivity of GCO effect
WIP
deck
By Bernhard Konrad
deck
- 485



